|
| 1 | +# AWS Fully Serverless Architecture with CI/CD |
| 2 | + |
| 3 | +## **Introduction:** |
| 4 | + |
| 5 | +Enter the world of serverless computing, where developers are freed from server management. Deploying code becomes a breeze, with a focus on deploying functions rather than wrestling with servers. Originally synonymous with FaaS, serverless technology began with **AWS Lambda** from **Amazon Web Services**. It has now evolved to cover various managed services like databases and storage, expanding its scope beyond its initial function-centric approach. |
| 6 | + |
| 7 | +Despite its name, serverless doesn’t mean a server-free existence. Instead, it signals a shift in responsibility — developers no longer need to manage, provision, or see the underlying servers. This allows them to concentrate on crafting efficient code without the distractions of server intricacies. |
| 8 | + |
| 9 | +In this article, we’ll explore a practical example of a Fully Serverless Architecture implemented using Terraform — a popular IaC tool and CI/CD implemented using GitHub Actions. The code repository we’ll be examining is hosted on GitHub: [GitHub Repository](https://github.com/NotHarshhaa/DevOps-Projects/tree/master/DevOps-Project-22) |
| 10 | + |
| 11 | +I have a NodeJS Cloud Native API which I have used to deploy in this architecture. This API is specifically designed to make use of AWS serverless services. |
| 12 | + |
| 13 | +**Architecture:** |
| 14 | + |
| 15 | + |
| 16 | + |
| 17 | +The aim of this project is to deploy API to AWS Public cloud using only serverless components. |
| 18 | + |
| 19 | +### API code is available [here](https://github.com/NotHarshhaa/DevOps-Projects/tree/master/DevOps-Project-22/serverless-api). |
| 20 | + |
| 21 | +Following are the serverless services used in this project: |
| 22 | +- API Gateway |
| 23 | +- Lambda |
| 24 | +- Aurora Serverless (MySql) |
| 25 | +- AWS Simple Storage Service (S3) |
| 26 | +- AWS Secrets Manager |
| 27 | +- AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) |
| 28 | +- Cloudwatch Logs and Metrics |
| 29 | +- Route53 |
| 30 | + |
| 31 | +Secrets Manager stores the database credentials securely and the credentials are rotated every 7 days. |
| 32 | +Lambda is launched in the VPC private subnet. The access to secrets manager from within the VPC is through VPC Interface endpoint and access to S3 is through VPC Gateway Endpoint. |
| 33 | + |
| 34 | +## Terraform |
| 35 | +Terraform is an open-source infrastructure as code software tool that enables you to safely and predictably create, change, and improve infrastructure. |
| 36 | + |
| 37 | +## Setting up Infrastructure using Terraform |
| 38 | + |
| 39 | +The terraform init command initializes a working directory containing Terraform configuration files: |
| 40 | +``` |
| 41 | +terraform init |
| 42 | +``` |
| 43 | + |
| 44 | +The terraform plan command creates an execution plan, which lets you preview the changes that Terraform plans to make to your infrastructure: |
| 45 | +``` |
| 46 | +terraform plan |
| 47 | +``` |
| 48 | + |
| 49 | +The terraform apply command executes the actions proposed in a Terraform plan to create, update, or destroy infrastructure: |
| 50 | +``` |
| 51 | +terraform apply |
| 52 | +``` |
| 53 | + |
| 54 | +The terraform destroy command is a convenient way to destroy all remote objects managed by a particular Terraform configuration: |
| 55 | +``` |
| 56 | +terraform destroy |
| 57 | +``` |
| 58 | + |
| 59 | +## **Key Services and Features:** |
| 60 | + |
| 61 | +Let’s explore the key services and features of this AWS Architecture: |
| 62 | + |
| 63 | +1. **AWS Lambda:** |
| 64 | + AWS Lambda, the pioneer in serverless computing, introduces virtual functions that eliminate the need for manual server management. With a focus on short executions, Lambda operates on-demand, ensuring efficient resource utilization. Its automated scaling feature adapts seamlessly to varying workloads, guaranteeing optimal performance. Lambda is Integrated with many programming languages and a whole AWS suite of services and can easily be monitored through AWS CloudWatch. **AWS Lambda** serves as an ideal solution for executing our Cloud Native API code efficiently, all while maintaining minimal costs. |
| 65 | + |
| 66 | +2. **Aurora Serverless:** |
| 67 | + Aurora, a powerhouse in the realm of cloud databases, seamlessly supports both Postgres and MySQL. Positioned as “AWS cloud optimized,” Aurora boasts a remarkable 5x performance improvement over MySQL on RDS and over 3x the performance over Postgres on RDS. Offering up to 15 replicas with a replication process faster than MySQL. With instantaneous failover, it is inherently designed for High Availability (HA), although it comes at a slightly higher cost than RDS (20% more), its efficiency and performance make it a compelling choice to store our API’s structured data. |
| 68 | + |
| 69 | +3. **Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3):** |
| 70 | + S3 is one of the very popular offerings from AWS. S3 is highly available and durable object based storage service. S3 allows storing objects (files) in buckets with globally unique name. In this case, we are using S3 to store API’s binary image data (JPEG, JPG, PNG). |
| 71 | + |
| 72 | +4. **API Gateway: AWS Lambda** coupled with **API Gateway** presents a hassle-free solution with zero infrastructure management. API Gateway not only supports HTTP, REST Protocols but also the WebSocket Protocol and also adeptly handles API versioning (such as v1, v2) and diverse environments (dev, test, prod). API Gateway also covers authentication and authorization, along with the ability to create API keys and manage request throttling. Additionally, it excels in transforming and validating requests and responses, allowing for the generation of SDKs and API specifications. With the added capability to cache API responses, API Gateway offer a comprehensive and efficient ecosystem for developing and managing APIs. |
| 73 | + |
| 74 | +Some of the managed services used in this Architecture are: |
| 75 | + |
| 76 | +1. **AWS CloudWatch:** |
| 77 | + Amazon CloudWatch is a robust monitoring and observability service provided by AWS, enabling users to collect and track metrics, collect and monitor log files, and set alarms. Logs and Metrics from Lambda functions are sent to CloudWatch for troubleshooting and observability purposes. |
| 78 | + |
| 79 | +2. **VPC:** The foundation of AWS Infrastructure is the VPC, which isolates resources and provides a private network for the application. VPC can be divided into multiple public (With Internet connectivity) and private subnets. |
| 80 | + |
| 81 | +3. **Amazon Route53:** A highly available, scalable, fully managed and *Authoritative* DNS. The only AWS service which provides 100% availability SLA. It is also a Domain Registrar. Route 53 translates human friendly hostnames into machine IP addresses. |
| 82 | + |
| 83 | +# **Security Considerations:** |
| 84 | + |
| 85 | +1. **AWS Certificate Manager (ACM):** |
| 86 | + Responsible for Managing, Provisioning and deploying TLS certificates. SSL/TLS certificates provides security in transit for HTTP websites (HTTPS). Supports both public and private TLS certificates. Free of charge. ACM is used to load/associate TLS certificates on Application load balancer, API Gateway, CloudFront, etc. |
| 87 | + |
| 88 | +2. **AWS Secrets Manager:** AWS Secrets Manager is meant for storing secrets. It has the capability to rotate secrets every X days (automates the generation of new secrets on rotation by making use of Lambda in the background). It is tightly Integrated with Amazon RDS (MySQL, PostgreSQL, Aurora), so it can securely store the database credentials. Secrets that are stored in Secrets Manager are encrypted using Key Management Service (KMS). |
| 89 | + |
| 90 | +3. **Security Groups:** Security groups act as firewall for all the instances like EC2, Lambda (through ENI), Interface Endpoints (through ENI), Databases, within the VPC. In the above architecture, Security groups were used to restrict access to database. Further, we can use security groups to restrict access to Interface endpoint that is responsible for accessing Secrets Manager. |
| 91 | + |
| 92 | +4. **VPC Endpoints:** Utilizing VPC Endpoints, enables the establishment of connections to AWS services through a **private network** rather than relying on the public Internet. These endpoints are designed to be both redundant and horizontally scalable. **IGW** and **NATGW** can be avoided to access the AWS services. In our case, we used VPC Interface endpoint (deploys ENI within the subnet) to access secrets manager privately from within the VPC and VPC Gateway endpoint (deploys a Gateway, must be used as a target in the route tables) to access S3 privately from within the VPC. |
| 93 | + |
| 94 | +5. **IAM ROLES:** Lambda functions in the private subnets are assigned an IAM role with necessary permissions to send Logs and Metrics to CloudWatch, access S3 bucket, access Aurora database and also to create, describe and delete Elastic Network Interface (ENI) for lambda within the VPC. |
| 95 | + |
| 96 | +# **CI/CD:** |
| 97 | +CI and CD stand for continuous integration and continuous delivery/ deployment. In very simple terms, **Continuous Integration** is a modern software development practice in which incremental code changes are made frequently and reliably to a central code repository like GitHub, Bit Bucket, etc. and **Continuous Delivery** is a software development practice that works in conjunction with CI, CD takes over during the final stages to ensure it’s packaged with everything it needs to deploy to any environment at any time (where as, **Continuous deployment** deploys the applications automatically, eliminating the need for human intervention). The CI/CD pipeline for the above architecture consists of the following: |
| 98 | + |
| 99 | +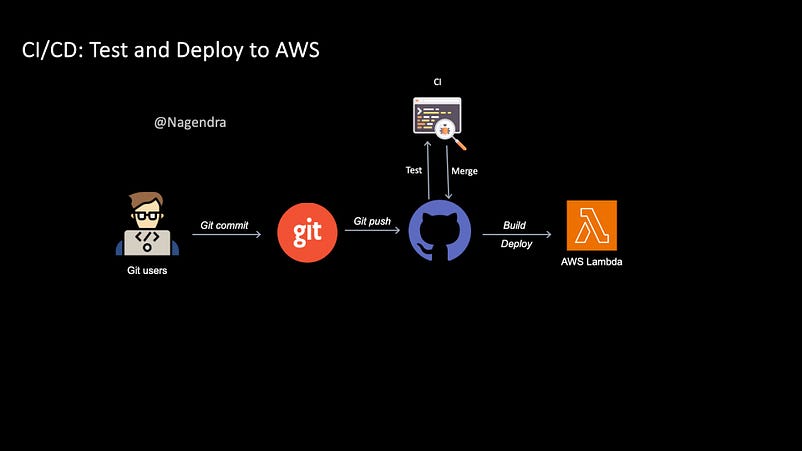 |
| 100 | + |
| 101 | +1. **Git:** Git is a distributed version control system that tracks the changes in your application code. Application code can be committed and pushed to a remote cloud version control service like **Github**. |
| 102 | + |
| 103 | +2. **Github Actions:** Github Actions is a feature of Github that Automates the building, testing and deployment of your application code. When a developer raises a Pull Request, a Github Actions workflow can be triggered to run a series of tests before merging the latest code to the main repository. In the above pipeline, after merging the latest code, another Github Actions Workflow can be triggered to build or package the latest code and deploy to Lambda using **AWS CLI** commands. |
| 104 | + |
| 105 | +A **dedicated IAM user** with relevant permissions can be created for Github Actions for deployment. **Access keys** and **secret keys** can be passed through Github Actions Secrets in the workflow configuration. |
| 106 | + |
| 107 | +# Serverless-api |
| 108 | +This Cloud Native API is designed to run on AWS Infrastructure while making use of AWS serverless services like Secrets Manager, Lambda functions, API Gateway, etc. |
| 109 | + |
| 110 | +## Prerequisites for running the application locally: |
| 111 | +```javascript |
| 112 | +// install dependencies |
| 113 | +npm install |
| 114 | +// start the server script |
| 115 | +npm start |
| 116 | +// run test cases |
| 117 | +npm test |
| 118 | +``` |
| 119 | +## Endpoint URLs |
| 120 | +```javascript |
| 121 | +// 1. Route to check if the server is healthy |
| 122 | +GET /healthz |
| 123 | +// 2. GET route to retrieve user details |
| 124 | +GET /v1/user/{userId} |
| 125 | +// 3. POST route to add a new user to the database |
| 126 | +POST /v1/user |
| 127 | +// 4. PUT route to update user details |
| 128 | +PUT /v1/user/{userId} |
| 129 | +``` |
| 130 | +### Sample JSON Response for GET |
| 131 | +```json |
| 132 | +{ |
| 133 | + "id": 1, |
| 134 | + "first_name": "Jane", |
| 135 | + "last_name": "Doe", |
| 136 | + "username": "jane.doe@example.com", |
| 137 | + "account_created": "2016-08-29T09:12:33.001Z", |
| 138 | + "account_updated": "2016-08-29T09:12:33.001Z" |
| 139 | +} |
| 140 | +``` |
| 141 | + |
| 142 | +### Sample JSON Request for POST |
| 143 | +```json |
| 144 | +{ |
| 145 | + "username": "jane.doe@example.com", |
| 146 | + "password": "password", |
| 147 | + "first_name": "Jane", |
| 148 | + "last_name": "Doe", |
| 149 | +} |
| 150 | +``` |
| 151 | + |
| 152 | +### Sample JSON Request for PUT |
| 153 | +```json |
| 154 | +{ |
| 155 | + "password": "password", |
| 156 | + "first_name": "Jane", |
| 157 | + "last_name": "Doe", |
| 158 | +} |
| 159 | +``` |
| 160 | + |
| 161 | +## Endpoint URLs |
| 162 | +```javascript |
| 163 | +// 1. GET route to retrieve product details |
| 164 | +GET /v1/product/{productId} |
| 165 | +// 2. POST route to add a new product to the database |
| 166 | +POST /v1/product |
| 167 | +// 3. PUT route to update product details |
| 168 | +PUT /v1/product/{productId} |
| 169 | +// 4. PATCH route to update product details partially |
| 170 | +PUT /v1/product/{productId} |
| 171 | +// 5. DELETE route to delete product details |
| 172 | +PUT /v1/product/{productId} |
| 173 | +``` |
| 174 | + |
| 175 | +### Sample JSON Response for GET |
| 176 | +```json |
| 177 | +{ |
| 178 | + "id": 1, |
| 179 | + "name": null, |
| 180 | + "description": null, |
| 181 | + "sku": null, |
| 182 | + "manufacturer": null, |
| 183 | + "quantity": 1, |
| 184 | + "date_added": "2016-08-29T09:12:33.001Z", |
| 185 | + "date_last_updated": "2016-09-29T09:12:33.001Z", |
| 186 | + "owner_user_id": 1 |
| 187 | +} |
| 188 | +``` |
| 189 | + |
| 190 | +### Sample JSON Request for POST |
| 191 | +```json |
| 192 | +{ |
| 193 | + "name": null, |
| 194 | + "description": null, |
| 195 | + "sku": null, |
| 196 | + "manufacturer": null, |
| 197 | + "quantity": 1 |
| 198 | +} |
| 199 | +``` |
| 200 | + |
| 201 | +### Sample JSON Request for PUT |
| 202 | +```json |
| 203 | +{ |
| 204 | + "name": null, |
| 205 | + "description": null, |
| 206 | + "sku": null, |
| 207 | + "manufacturer": null, |
| 208 | + "quantity": 1 |
| 209 | +} |
| 210 | +``` |
| 211 | + |
| 212 | +### Sample JSON Request for PATCH |
| 213 | +```json |
| 214 | +{ |
| 215 | + "name": null, |
| 216 | + "description": null, |
| 217 | + "sku": null, |
| 218 | + "manufacturer": null, |
| 219 | + "quantity": 1 |
| 220 | +} |
| 221 | +``` |
| 222 | +--- |
| 223 | +# Thank you |
| 224 | +Thank you for taking the time to work on this tutorial/labs. Let me know what you thought! |
| 225 | + |
| 226 | +#### Author by [Harshhaa Reddy](https://github.com/NotHarshhaa) |
| 227 | + |
| 228 | +### Ensure to follow me on GitHub. Please star/share this repository! |
0 commit comments