Selected images 1
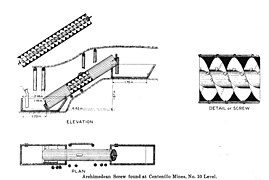
Portal:Physics/Selected images/1 Archimedes' screw, also called the Archimedean screw or screwpump, is a machine historically used for transferring water from a low-lying body of water into irrigation ditches. The screw pump is commonly attributed to Archimedes on the occasion of his visit to Egypt, but this tradition may reflect only that the apparatus was unknown to the Greeks before Hellenistic times and introduced in his lifetime by unknown Greek engineers. Some writers have suggested that the device may have been in use in Assyria some 350 years earlier.
-
Archimedes' screw was operated by hand and could raise water efficiently
-
An Archimedes' screw in Huseby south of Växjö Sweden
-
Archimedes' screw]
-
Roman screw used to dewater mines in Spain
-
Modern Archimedes' screws which have replaced some of the windmills used to drain the polders at Kinderdijk in the Netherlands
-
Archimedes' screw as a form of art by Tony Cragg at 's-Hertogenbosch in the Netherlands
Selected images 2
Portal:Physics/Selected images/2

Astrophysics is a science that employs the methods and principles of physics and chemistry in the study of astronomical objects and phenomena. As one of the founders of the discipline, James Keeler, said, astrophysics "seeks to ascertain the nature of the heavenly bodies, rather than their positions or motions in space–what they are, rather than where they are", which is studied in celestial mechanics. (Full article...)
Selected images 3
Portal:Physics/Selected images/3
Difference between classical and modern physics
edit
While physics aims to discover universal laws, its theories lie in explicit domains of applicability. Loosely speaking, the laws of classical physics accurately describe systems whose important length scales are greater than the atomic scale and whose motions are much slower than the speed of light. Outside of this domain, observations do not match their predictions. Albert Einstein contributed the framework of special relativity, which replaced notions of absolute time and space with spacetime and allowed an accurate description of systems whose components have speeds approaching the speed of light. Max Planck, Erwin Schrödinger, and others introduced quantum mechanics, a probabilistic notion of particles and interactions that allowed an accurate description of atomic and subatomic scales. Later, quantum field theory unified quantum mechanics and special relativity. General relativity allowed for a dynamical, curved spacetime, with which highly massive systems and the large-scale structure of the universe can be well-described. General relativity has not yet been unified with the other fundamental descriptions; several candidate theories of quantum gravity are being developed.
Selected images 4
Portal:Physics/Selected images/4

In modern physics, the double-slit experiment demonstrates that light and matter can exhibit behavior of both classical particles and classical waves. This type of experiment was first performed by Thomas Young in 1801, as a demonstration of the wave behavior of visible light. In 1927, Davisson and Germer and, independently, George Paget Thomson and his research student Alexander Reid demonstrated that electrons show the same behavior, which was later extended to atoms and molecules. Thomas Young's experiment with light was part of classical physics long before the development of quantum mechanics and the concept of wave–particle duality. He believed it demonstrated that the Christiaan Huygens' wave theory of light was correct, and his experiment is sometimes referred to as Young's experiment or Young's slits. (Full article...)
Selected images 5
Portal:Physics/Selected images/5

For simplicity, Mars' period of revolution is depicted as 2 years instead of 1.88, and orbits are depicted as perfectly circular or epitrochoid.
The Copernican Revolution was the paradigm shift from the Ptolemaic model of the heavens, which described the cosmos as having Earth stationary at the center of the universe, to the heliocentric model with the Sun at the center of the Solar System. This revolution consisted of two phases; the first being extremely mathematical in nature and the second phase starting in 1610 with the publication of a pamphlet by Galileo. Beginning with the 1543 publication of Nicolaus Copernicus’s De revolutionibus orbium coelestium, contributions to the “revolution” continued until finally ending with Isaac Newton’s work over a century later. (Full article...)
Selected images 6
Portal:Physics/Selected images/6

Selected images 7
Portal:Physics/Selected images/7

(Paranal Observatory) In mid-August 2010 a group of astronomers were observing the centre of the Milky Way using the laser guide star facility at Yepun, one of the four Unit Telescopes of the Very Large Telescope (VLT).
Yepun’s laser beam crosses the majestic southern sky and creates an artificial star at an altitude of 90 km high in the Earth's mesosphere. More background information can be found at "A Laser Beam Towards the Milky Way's Centre." from the European Southern Observatory web site.
Selected images 8
Portal:Physics/Selected images/8 The Hubble Deep Field (HDF) is an image of a small region in the constellation Ursa Major, constructed from a series of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope. It covers an area 2.5 arcminutes across, two parts in a million of the whole sky
-
The Hubble Deep Field
-
Details from the Hubble Deep Field illustrate the wide variety of galaxy shapes, sizes and colours found in the distant universe.
Selected images 9
Portal:Physics/Selected images/9

The Feynman Lectures on Physics is a 1964 physics textbook by Richard P. Feynman, Robert B. Leighton and Matthew Sands, based upon the lectures given by Feynman to undergraduate students at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) in 1961–63.
It includes lectures on mathematics, electromagnetism, Newtonian physics, quantum physics, and the relation of physics to other sciences. Six readily accessible chapters were later compiled into a book entitled Six Easy Pieces: Essentials of Physics Explained by Its Most Brilliant Teacher, and six more in Six Not So Easy Pieces: Einstein's Relativity, Symmetry and Space-Time.
Selected images 10
Portal:Physics/Selected images/10

Selected images 11
Portal:Physics/Selected images/11
 Engraving of André-Marie Ampère | |
| Born | 20 January 1775 |
| Died | 10 June 1836 (aged 61) Marseille, France |
| Nationality | French |
| Known for | Ampère's circuital law, Ampère's force law |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Physics |
| Institutions | École Polytechnique |
| Signature | |
André-Marie Ampère (20 January 1775 – 10 June 1836) was a French physicist and mathematician who is generally regarded as one of the main founders of the science of classical electromagnetism, which he referred to as "electrodynamics". The electric current unit of measurement known as the ampere is named after him.
Selected images 12
Portal:Physics/Selected images/12 An arc lamp or arc light is a lamp that produces light by an electric arc (also called a voltaic arc). The carbon arc light, which consists of an arc between carbon electrodes in air, invented by Humphry Davy in the early 1800s, was the first practical electric light. It was widely used starting in the 1870s for street and large building lighting until it was superseded by the incandescent light in the early 20th century. It continued in use in more specialized applications where a high intensity point light source was needed, such as searchlights and movie projectors until after World War II.
-
The 15 kW xenon short-arc lamp used in the IMAX projection system
-
A mercury arc lamp from a fluorescence microscope
-
A krypton long arc lamp (top) is shown above a xenon flashtube. The two lamps, used for laser pumping, are very different in the shape of the electrodes, in particular, the cathode, (on the left).
-
A krypton arc lamp during operation.
-
An electric arc, demonstrating the “arch” effect
Selected images 13
Portal:Physics/Selected images/13 Johannes Kepler (December 27, 1571 – November 15, 1630) was a German mathematician, astronomer and astrologer. A key figure in the 17th century scientific revolution, he is best known for his eponymous laws of planetary motion, codified by later astronomers, based on his works Astronomia nova, Harmonices Mundi, and Epitome of Copernican Astronomy. These works also provided one of the foundations for Isaac Newton's theory of universal gravitation. During his career, Kepler was a mathematics teacher at a seminary school in Graz, Austria. Later he became an assistant to astronomer Tycho Brahe, and eventually the imperial mathematician to Emperor Rudolf II and his two successors Matthias and Ferdinand II. He was also a mathematics teacher in Linz, Austria, and an adviser to General Wallenstein. Additionally, he did fundamental work in the field of optics, invented an improved version of the refracting telescope (the Keplerian Telescope), and mentioned the telescopic discoveries of his contemporary Galileo Galilei.
-
A 1610 portrait of Johannes Kepler by an unknown artist
-
Kepler's Platonic solid model of the Solar System from Mysterium Cosmographicum (1600)
-
Close-up of inner section of the model (to the right)
Selected images 14
Portal:Physics/Selected images/14

Hubble Space Telescope discovery of Styx, Pluto's fifth moon.[a] (also informally known as P5) is a small natural satellite of Pluto whose discovery was announced on 11 July 2012. It is the fifth confirmed satellite of Pluto, and was found approximately one year after S/2011 (134340) 1 (or "P4"), Pluto's fourth discovered satellite. The moon is estimated to have a diameter of between 10 and 25 kilometers (6 and 16 mi), and orbital period of 20.2 ± 0.1 days.
Selected images 15
Portal:Physics/Selected images/15
 |
 |
 |
 |
Selected images 16
Portal:Physics/Selected images/16

James Clerk Maxwell FRS FRSE (13 June 1831 – 5 November 1879) was a Scottish[2] theoretical physicist.[3] His most prominent achievement was formulating classical electromagnetic theory. This unites all previously unrelated observations, experiments, and equations of electricity, magnetism, and optics into a consistent theory.[4] Maxwell's equations demonstrate that electricity, magnetism and light are all manifestations of the same phenomenon, namely the electromagnetic field. Subsequently, all other classic laws or equations of these disciplines became simplified cases of Maxwell's equations. Maxwell's achievements concerning electromagnetism have been called the "second great unification in physics",[5] after the first one realised by Isaac Newton.
Selected images 17
Portal:Physics/Selected images/17

Newton's cradle, named after Sir Isaac Newton, is a device that demonstrates conservation of momentum and energy via a series of swinging spheres. When one on the end is lifted and released, the resulting force travels through the line and pushes the last one upward.
Selected images 18
Portal:Physics/Selected images/18

Selected images 19
Portal:Physics/Selected images/19

A ferrofluid is a liquid which becomes strongly polarised in the presence of a magnetic field. Ferrofluids are composed of nanoscale ferromagnetic particles suspended in a carrier fluid, usually an organic solvent or water. The ferromagnetic nano-particles are coated with a surfactant to prevent their agglomeration (due to van der Waals and magnetic forces). Although the name may suggest otherwise, ferrofluids do not display ferromagnetism, since they do not retain magnetisation in the absence of an externally applied field. In fact, ferrofluids display paramagnetism, and are often referred as being "superparamagnetic" due to their large magnetic susceptibility. True ferromagnetic fluids are difficult to create at present.
Selected images 20
Portal:Physics/Selected images/20

Selected images 21
Selected images 22
Portal:Physics/Selected images/22
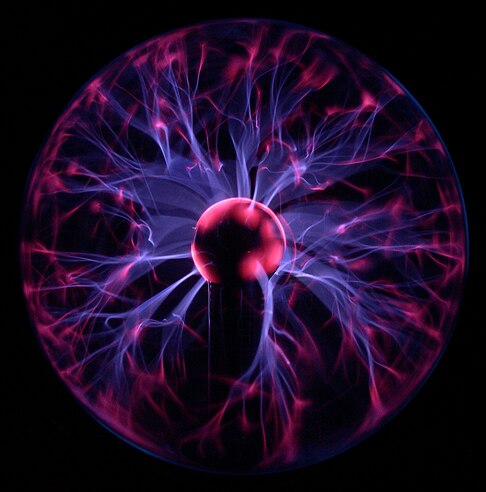
Plasma lamps are a type of electrodeless gas-discharge lamp energized by radio frequency (RF) power. They are distinct from the novelty plasma lamps that were popular in the 1980s.
The internal-electrodeless lamp was invented by Nikola Tesla after his experimentation with high-frequency currents in evacuated glass tubes for the purposes of lighting and the study of high voltage phenomena. The first practical plasma lamps were the sulfur lamps manufactured by Fusion Lighting. This lamp suffered several practical problems and did not prosper commercially. Plasma lamps with an internal phosphor coating are called external electrode fluorescent lamps (EEFL); these external electrodes or terminal conductors provide the radio frequency electric field. (Full article...)
Selected images 23
Portal:Physics/Selected images/23

Selected images 24
Portal:Physics/Selected images/24

Selected images 25
Selected images 26
Portal:Physics/Selected images/26
- ^ 134340 is Pluto's Minor Planet Center number, assigned following its demotion from full planetary status in 2006.[1] "S/2012 P 1" is the format that would have been used without the demotion.
- ^ "Pluto is Now Just a Number: 134340". Purch. September 11, 2006. Retrieved August 19, 2014.
- ^ "James Clerk Maxwell". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 24 February 2010.
Scottish physicist best known for his formulation of electromagnetic theory
- ^ James Clerk Maxwell
- ^ "James Clerk Maxwell". IEEE Global History Network. 2011. Retrieved 2011-06-21.
- ^ Nahin, P.J. (1992). "Maxwell's grand unification". IEEE Spectrum. 29 (3): 45. doi:10.1109/6.123329.