Chromosome 6: Difference between revisions
m Task 18 (cosmetic): eval 18 templates: hyphenate params (9×); |
BombCraft8 (talk | contribs) THE |
||
| (30 intermediate revisions by 20 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Human chromosome}} |
|||
{{Infobox chromosome |
{{Infobox chromosome |
||
| image = Human male karyotpe high resolution - Chromosome 6 cropped.png |
| image = Human male karyotpe high resolution - Chromosome 6 cropped.png |
||
| Line 4: | Line 5: | ||
| image2 = Human male karyotpe high resolution - Chromosome 6.png |
| image2 = Human male karyotpe high resolution - Chromosome 6.png |
||
| caption2 = Chromosome 6 pair<br/> in human male [[karyogram]]. |
| caption2 = Chromosome 6 pair<br/> in human male [[karyogram]]. |
||
| length_bp = 172,126,628 bp<br/>(CHM13) |
|||
| length_bp = 170,805,979 bp<br/>([[GRCh38]])<ref name="National Center for Biotechnology Information 2017">{{cite web | title=Human Genome Assembly GRCh38 - Genome Reference Consortium | website=National Center for Biotechnology Information | date=2013-12-24 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/grc/human/data?asm=GRCh38 | language=en | access-date=2017-03-04}}</ref> |
|||
| genes = 996 ([[Consensus CDS Project|CCDS]])<ref name="CCDS"/> |
| genes = 996 ([[Consensus CDS Project|CCDS]])<ref name="CCDS"/> |
||
| type = [[Autosome]] |
| type = [[Autosome]] |
||
| centromere_position = [[Centromere#Submetacentric|Submetacentric]]<ref name="StrachanRead2010">{{cite book|author1=Tom Strachan|author2=Andrew Read|title=Human Molecular Genetics|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=dSwWBAAAQBAJ&pg=PA45|date=2 April 2010|publisher=Garland Science|isbn=978-1-136-84407-2|page=45}}</ref><br/>(59.8 Mbp<ref name="850bphs">Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. [ |
| centromere_position = [[Centromere#Submetacentric|Submetacentric]]<ref name="StrachanRead2010">{{cite book|author1=Tom Strachan|author2=Andrew Read|title=Human Molecular Genetics|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=dSwWBAAAQBAJ&pg=PA45|date=2 April 2010|publisher=Garland Science|isbn=978-1-136-84407-2|page=45}}</ref><br/>(59.8 Mbp<ref name="850bphs">Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. [http://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/gdp/ideogram_9606_GCF_000001305.14_850_V1 Ideogram data for Homo sapience (850 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3)]. Last update 2014-06-03. Retrieved 2017-04-26.</ref>) |
||
| chr = 6 |
| chr = 6 |
||
| ensembl_id = 6 |
| ensembl_id = 6 |
||
| Line 16: | Line 17: | ||
| genbank_id = CM000668 |
| genbank_id = CM000668 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Chromosome 6 ''' is one of the 23 pairs of [[chromosome]]s in [[human]]s. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 6 spans |
'''Chromosome 6 ''' is one of the 23 pairs of [[chromosome]]s in [[human]]s. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 6 spans nearly 171 million [[base pair]]s (the building material of [[DNA]]) and represents between 5.5 and 6% of the total DNA in [[cell (biology)|cells]]. It contains the [[major histocompatibility complex]], which contains over 100 genes related to the [[immune response]], and plays a vital role in [[organ transplantation]]. |
||
== The evolution of human centromere 6 == |
|||
The [[centromere]] of chromosome 6 illustrates an interesting example of centromere evolution. It was known{{explain|date=February 2024}} that in a [[Catarrhini]] ancestor the chromosome 6 centromere was situated near position 26 Mb of the modern human chromosome. In ''Macaca mulatta'', this old centromere went defunct and repositioned to a different chromosomal location{{relevance|date=February 2024}}. In the case of humans, the old centromere went defunct and a more recent form emerged near the modern position of human cen6 (size of 60 Mb). Such cases are known as Evolutionary New Centromeres (ENC). This assembly phenomenon of the human chromosome 6 gives researchers an opportunity to investigate the origin of the ENC on chromosome 6. <ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Altemose |first1=Nicolas |last2=Logsdon |first2=Glennis A. |last3=Bzikadze |first3=Andrey V. |last4=Sidhwani |first4=Pragya |last5=Langley |first5=Sasha A. |last6=Caldas |first6=Gina V. |last7=Hoyt |first7=Savannah J. |last8=Uralsky |first8=Lev |last9=Ryabov |first9=Fedor D. |last10=Shew |first10=Colin J. |last11=Sauria |first11=Michael E. G. |last12=Borchers |first12=Matthew |last13=Gershman |first13=Ariel |last14=Mikheenko |first14=Alla |last15=Shepelev |first15=Valery A. |date=April 2022 |title=Complete genomic and epigenetic maps of human centromeres |journal=Science |language=en |volume=376 |issue=6588 |pages=eabl4178 |doi=10.1126/science.abl4178 |issn=0036-8075 |pmc=9233505 |pmid=35357911}}</ref> |
|||
==Genes== |
==Genes== |
||
| Line 24: | Line 28: | ||
In 2003, the entirety of chromosome 6 was manually annotated for proteins, resulting in the identification of 1,557 genes, and 633 pseudogenes.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors = Mungall AJ, Palmer SA, Sims SK, Edwards CA, Ashurst JL, Wilming L, Jones MC, Horton R, Hunt SE, Scott CE, Gilbert JG, Clamp ME, Bethel G, Milne S, Ainscough R, Almeida JP, Ambrose KD, Andrews TD, Ashwell RI, Babbage AK, Bagguley CL, Bailey J, Banerjee R, Barker DJ, Barlow KF, Bates K, Beare DM, Beasley H, Beasley O, Bird CP, Blakey S, Bray-Allen S, Brook J, Brown AJ, Brown JY, Burford DC, Burrill W, Burton J, Carder C, Carter NP, Chapman JC, Clark SY, Clark G, Clee CM, Clegg S, Cobley V, Collier RE, Collins JE, Colman LK, Corby NR, Coville GJ, Culley KM, Dhami P, Davies J, Dunn M, Earthrowl ME, Ellington AE, Evans KA, Faulkner L, Francis MD, Frankish A, Frankland J, French L, Garner P, Garnett J, Ghori MJ, Gilby LM, Gillson CJ, Glithero RJ, Grafham DV, Grant M, Gribble S, Griffiths C, Griffiths M, Hall R, Halls KS, Hammond S, Harley JL, Hart EA, Heath PD, Heathcott R, Holmes SJ, Howden PJ, Howe KL, Howell GR, Huckle E, Humphray SJ, Humphries MD, Hunt AR, Johnson CM, Joy AA, Kay M, Keenan SJ, Kimberley AM, King A, Laird GK, Langford C, Lawlor S, Leongamornlert DA, Leversha M, Lloyd CR, Lloyd DM, Loveland JE, Lovell J, Martin S, Mashreghi-Mohammadi M, Maslen GL, Matthews L, McCann OT, McLaren SJ, McLay K, McMurray A, Moore MJ, Mullikin JC, Niblett D, Nickerson T, Novik KL, Oliver K, Overton-Larty EK, Parker A, Patel R, Pearce AV, Peck AI, Phillimore B, Phillips S, Plumb RW, Porter KM, Ramsey Y, Ranby SA, Rice CM, Ross MT, Searle SM, Sehra HK, Sheridan E, Skuce CD, Smith S, Smith M, Spraggon L, Squares SL, Steward CA, Sycamore N, Tamlyn-Hall G, Tester J, Theaker AJ, Thomas DW, Thorpe A, Tracey A, Tromans A, Tubby B, Wall M, Wallis JM, West AP, White SS, Whitehead SL, Whittaker H, Wild A, Willey DJ, Wilmer TE, Wood JM, Wray PW, Wyatt JC, Young L, Younger RM, Bentley DR, Coulson A, Durbin R, Hubbard T, Sulston JE, Dunham I, Rogers J, Beck S|display-authors = 6 |title=The DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 6 |journal=Nature |volume=425 |issue=6960 |pages=805–11 |date=October 2003 |pmid=14574404 |doi=10.1038/nature02055 |doi-access=free |bibcode=2003Natur.425..805M }}</ref> |
In 2003, the entirety of chromosome 6 was manually annotated for proteins, resulting in the identification of 1,557 genes, and 633 pseudogenes.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors = Mungall AJ, Palmer SA, Sims SK, Edwards CA, Ashurst JL, Wilming L, Jones MC, Horton R, Hunt SE, Scott CE, Gilbert JG, Clamp ME, Bethel G, Milne S, Ainscough R, Almeida JP, Ambrose KD, Andrews TD, Ashwell RI, Babbage AK, Bagguley CL, Bailey J, Banerjee R, Barker DJ, Barlow KF, Bates K, Beare DM, Beasley H, Beasley O, Bird CP, Blakey S, Bray-Allen S, Brook J, Brown AJ, Brown JY, Burford DC, Burrill W, Burton J, Carder C, Carter NP, Chapman JC, Clark SY, Clark G, Clee CM, Clegg S, Cobley V, Collier RE, Collins JE, Colman LK, Corby NR, Coville GJ, Culley KM, Dhami P, Davies J, Dunn M, Earthrowl ME, Ellington AE, Evans KA, Faulkner L, Francis MD, Frankish A, Frankland J, French L, Garner P, Garnett J, Ghori MJ, Gilby LM, Gillson CJ, Glithero RJ, Grafham DV, Grant M, Gribble S, Griffiths C, Griffiths M, Hall R, Halls KS, Hammond S, Harley JL, Hart EA, Heath PD, Heathcott R, Holmes SJ, Howden PJ, Howe KL, Howell GR, Huckle E, Humphray SJ, Humphries MD, Hunt AR, Johnson CM, Joy AA, Kay M, Keenan SJ, Kimberley AM, King A, Laird GK, Langford C, Lawlor S, Leongamornlert DA, Leversha M, Lloyd CR, Lloyd DM, Loveland JE, Lovell J, Martin S, Mashreghi-Mohammadi M, Maslen GL, Matthews L, McCann OT, McLaren SJ, McLay K, McMurray A, Moore MJ, Mullikin JC, Niblett D, Nickerson T, Novik KL, Oliver K, Overton-Larty EK, Parker A, Patel R, Pearce AV, Peck AI, Phillimore B, Phillips S, Plumb RW, Porter KM, Ramsey Y, Ranby SA, Rice CM, Ross MT, Searle SM, Sehra HK, Sheridan E, Skuce CD, Smith S, Smith M, Spraggon L, Squares SL, Steward CA, Sycamore N, Tamlyn-Hall G, Tester J, Theaker AJ, Thomas DW, Thorpe A, Tracey A, Tromans A, Tubby B, Wall M, Wallis JM, West AP, White SS, Whitehead SL, Whittaker H, Wild A, Willey DJ, Wilmer TE, Wood JM, Wray PW, Wyatt JC, Young L, Younger RM, Bentley DR, Coulson A, Durbin R, Hubbard T, Sulston JE, Dunham I, Rogers J, Beck S|display-authors = 6 |title=The DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 6 |journal=Nature |volume=425 |issue=6960 |pages=805–11 |date=October 2003 |pmid=14574404 |doi=10.1038/nature02055 |doi-access=free |bibcode=2003Natur.425..805M }}</ref> |
||
The following are some of the newer gene count estimates. Because researchers use different approaches to [[genome annotation]] their predictions of the [[number of genes]] on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see [[gene prediction]]). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project ([[Consensus CDS Project|CCDS]]) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes.<ref name="pmid20441615">{{cite journal |
The following are some of the newer gene count estimates. Because researchers use different approaches to [[genome annotation]] their predictions of the [[number of genes]] on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see [[gene prediction]]). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project ([[Consensus CDS Project|CCDS]]) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes.<ref name="pmid20441615">{{cite journal |author=Pertea M, Salzberg SL |title=Between a chicken and a grape: estimating the number of human genes. |journal=Genome Biol |year=2010 |volume=11 |issue=5 |pages=206 |pmid=20441615 |doi=10.1186/gb-2010-11-5-206 |pmc=2898077 |doi-access=free }}</ref> |
||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:right" |
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:right" |
||
| Line 41: | Line 45: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee|HGNC]]|| 1,007 || 422 || 736 |
| [[HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee|HGNC]]|| 1,007 || 422 || 736 |
||
|style="text-align:center"| <ref name="HGNC20170512">{{cite web | title=Statistics & Downloads for chromosome 6 | website=HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee | url=https://www.genenames.org/cgi-bin/statistics?c=6 |
|style="text-align:center"| <ref name="HGNC20170512">{{cite web | title=Statistics & Downloads for chromosome 6 | website=HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee | url=https://www.genenames.org/cgi-bin/statistics?c=6 | date=2017-05-12 | access-date=2017-05-19 | archive-date=2017-08-18 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170818175240/http://www.genenames.org/cgi-bin/statistics?c=6 | url-status=dead }}</ref> |
||
| 2017-05-12 |
| 2017-05-12 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Line 66: | Line 70: | ||
* [[Androgen-dependent tfpi-regulating protein|ADTRP]]: encoding [[protein]] Androgen-dependent TFPI-regulating protein |
* [[Androgen-dependent tfpi-regulating protein|ADTRP]]: encoding [[protein]] Androgen-dependent TFPI-regulating protein |
||
* [[APOM]]: encoding [[protein]] Apolipoprotein M (6p21.33) |
* [[APOM]]: encoding [[protein]] Apolipoprotein M (6p21.33) |
||
* [[Armadillo repeat containing 12|ARMC12]]: encoding protein Armadillo repeat containing 12 |
|||
* [[Ataxin 1|ATXN1]]: encoding [[protein]] Ataxin 1 (6p16.3-p16.76) |
|||
* [[TSBP1]]: encoding [[protein]] TSBP1 (6p21.32) |
* [[TSBP1]]: encoding [[protein]] TSBP1 (6p21.32) |
||
* [[C6orf62]]: chromosome 6 open reading frame 62 (6p22.3) |
* [[C6orf62]]: chromosome 6 open reading frame 62 (6p22.3) |
||
| Line 71: | Line 77: | ||
* [[CDKAL1]]: CDK5 regulatory subunit associated protein 1 like 1 (6p22.3) |
* [[CDKAL1]]: CDK5 regulatory subunit associated protein 1 like 1 (6p22.3) |
||
* [[COL11A2]]: collagen, type XI, alpha 2(6p21.3) |
* [[COL11A2]]: collagen, type XI, alpha 2(6p21.3) |
||
* [[Cysteine rich protein 3|CRIP3]]: encoding protein Cysteine rich protein 3 |
|||
* [[CYP21A2]]: cytochrome P450, family 21, subfamily A, polypeptide 2 (6p21.33) |
* [[CYP21A2]]: cytochrome P450, family 21, subfamily A, polypeptide 2 (6p21.33) |
||
* [[DHX16]]: DEAH-box helicase 16 (6p21.33) |
* [[DHX16]]: DEAH-box helicase 16 (6p21.33) |
||
| Line 77: | Line 84: | ||
* [[ELOVL5]]: ELOVL fatty acid elongase 5 (6p12.1) |
* [[ELOVL5]]: ELOVL fatty acid elongase 5 (6p12.1) |
||
* [[FBXO9]]: F-box protein 9 (6p12.1) |
* [[FBXO9]]: F-box protein 9 (6p12.1) |
||
* [[FOXP4-AS1]]: encoding protein FOXP4 antisense RNA 1 |
|||
* [[FTH1P5]]: encoding protein Ferritin, heavy polypeptide 1 pseudogene 5 |
|||
* [[G6B]]: Protein G6b (6p21.33) |
* [[G6B]]: Protein G6b (6p21.33) |
||
* [[GCNT2]]: N-acetyllactosaminide beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyl-transferase (6p24.3) |
* [[GCNT2]]: N-acetyllactosaminide beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyl-transferase (6p24.3) |
||
* [[Gametogenetin binding protein 1 (pseudogene)|GGNBP1]]: encoding protein Gametogenetin binding protein 1 (pseudogene) |
|||
* [[GMDS (gene)|GMDS]]: GDP-mannose 4,6-dehydratase (6p25.3) |
* [[GMDS (gene)|GMDS]]: GDP-mannose 4,6-dehydratase (6p25.3) |
||
* [[Gtp binding protein 2|GTPBP2]]: encoding protein Gtp binding protein 2 |
|||
* [[HCG4P11]]: HLA complex group 4 pseudogene 11 |
* [[HCG4P11]]: HLA complex group 4 pseudogene 11 |
||
* [[HFE (gene)|HFE]]: hemochromatosis (6p22.2) |
* [[HFE (gene)|HFE]]: hemochromatosis (6p22.2) |
||
| Line 85: | Line 96: | ||
* [[HLA-A]], [[HLA-B]], [[HLA-C]]: major histocompatibility complex (MHC), class I, A, B, and C loci. (6p21.3) |
* [[HLA-A]], [[HLA-B]], [[HLA-C]]: major histocompatibility complex (MHC), class I, A, B, and C loci. (6p21.3) |
||
* [[HLA-DQA1]] and [[HLA-DQB1]] form [[HLA-DQ]] heterodimer MHC class II, DQ: Celiac1, IDDM (6p21.3) |
* [[HLA-DQA1]] and [[HLA-DQB1]] form [[HLA-DQ]] heterodimer MHC class II, DQ: Celiac1, IDDM (6p21.3) |
||
* [[HLA-DRA]], [[HLA-DRB1]], [[HLA-DRB3]], [[HLA-DRB4]], [[HLA-DRB5]] forms [[HLA-DR]], heterodimer MHC class II, DR (6p21.3) |
* [[HLA-DRA]], [[HLA-DRB1]], [[HLA-DRB3]], [[HLA-DRB4]], [[HLA-DRB5]] forms [[HLA-DR]], heterodimer MHC class II, DR (6p21.3) Mold / Biotoxin Susceptibility |
||
* [[HLA-DPA1]] and [[HLA-DPB1]] forms [[HLA-DP]], MHC class II, DP (6p21.3) |
* [[HLA-DPA1]] and [[HLA-DPB1]] forms [[HLA-DP]], MHC class II, DP (6p21.3) |
||
* [[HLA-C|HLA-Cw*06:02]]: gene variation related to psoriasis (6p21.3) |
* [[HLA-C|HLA-Cw*06:02]]: gene variation related to psoriasis (6p21.3) |
||
* [[ |
* [[KAAG1]]: encoding protein Kidney associated antigen 1 |
||
* [[LOC100533655]]: encoding protein Aryl hydrocarbon receptor pseudogene |
|||
* [[LST1]]: leukocyte specific transcript 1 (6p21.33) |
* [[LST1]]: leukocyte specific transcript 1 (6p21.33) |
||
* [[LY6G6E]] encoding [[protein]] Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex, locus G6E (pseudogene) (6p21.33) |
|||
* [[MIR4640]]: microRNA 4640 (6p21.33) |
* [[MIR4640]]: microRNA 4640 (6p21.33) |
||
* [[MLIP (gene)|MLIP]]: muscular LMNA interaction protein (6p12.1) |
* [[MLIP (gene)|MLIP]]: muscular LMNA interaction protein (6p12.1) |
||
| Line 105: | Line 118: | ||
* [[PRSS16]]: protease, serine 16 (6p22.1) |
* [[PRSS16]]: protease, serine 16 (6p22.1) |
||
* [[Psmb8 antisense rna 1 (head to head)|PSMB8-AS1]]: PSMB8 antisense RNA 1 (head to head) (6p21.32) |
* [[Psmb8 antisense rna 1 (head to head)|PSMB8-AS1]]: PSMB8 antisense RNA 1 (head to head) (6p21.32) |
||
* [[RAB44]]: encoding protein Rab44, member ras oncogene family |
|||
* [[RIPOR2]]: RHO family interacting cell polarization regulator 2 (6p22.3) |
* [[RIPOR2]]: RHO family interacting cell polarization regulator 2 (6p22.3) |
||
* [[60S ribosomal protein L10a|RPL10A]]: encoding [[protein]] 60S ribosomal protein L10a (6p21.31) |
* [[60S ribosomal protein L10a|RPL10A]]: encoding [[protein]] 60S ribosomal protein L10a (6p21.31) |
||
| Line 116: | Line 130: | ||
* [[TNXB]]: tenascin XB (6p21.3) |
* [[TNXB]]: tenascin XB (6p21.3) |
||
* [[TRAM2]]: translocation associated membrane protein 2 (6p12.2) |
* [[TRAM2]]: translocation associated membrane protein 2 (6p12.2) |
||
* [[TRIM38]]: encoding protein Tripartite motif containing 38 |
|||
* [[TTBK1]]: encoding protein Tau tubulin kinase 1 |
|||
* [[UBR2]]: ubiquitin protein ligase E3 component n-recognin 2 (6p21.2) |
* [[UBR2]]: ubiquitin protein ligase E3 component n-recognin 2 (6p21.2) |
||
* [[UNC5CL]]: encoding [[protein]] Unc-5 homolog C (C. elegans)-like |
* [[UNC5CL]]: encoding [[protein]] Unc-5 homolog C (C. elegans)-like |
||
* [[USP8P1]]: encoding protein Ubiquitin specific peptidase 8 pseudogene 1 |
|||
* [[Vascular endothelial growth factor|VEGF]]: vascular endothelial growth factor A (angiogenic growth factor) (6p21.1) |
* [[Vascular endothelial growth factor|VEGF]]: vascular endothelial growth factor A (angiogenic growth factor) (6p21.1) |
||
* [[VPS52]]: GARP complex subunit |
* [[VPS52]]: GARP complex subunit |
||
* [[Von willebrand factor a domain containing 7|VWA7]]: encoding protein Von willebrand factor a domain containing 7 |
|||
* [[ZKSCAN4]]: encoding protein zinc finger with KRAB and SCAN domains 4 |
|||
* [[ZNF76]]: zinc finger protein 76 (6p21.31) |
* [[ZNF76]]: zinc finger protein 76 (6p21.31) |
||
* [[ZNF193]]: zinc finger protein 193 (6p22.1) |
* [[ZNF193]]: zinc finger protein 193 (6p22.1) |
||
| Line 126: | Line 145: | ||
====q-arm==== |
====q-arm==== |
||
The following are some of the genes located on q-arm (long arm) of human chromosome 6: |
The following are some of the genes located on [[q-arm]] (long arm) of human chromosome 6: |
||
{{columns-list| |
{{columns-list| |
||
* [[AIM1]]: encoding [[protein]] Absent in melanoma 1 protein (6q21) |
* [[AIM1]]: encoding [[protein]] Absent in melanoma 1 protein (6q21) |
||
| Line 135: | Line 154: | ||
* [[BMIQ3]]: body mass index QTL 3 |
* [[BMIQ3]]: body mass index QTL 3 |
||
* [[TMEM242]] encoding transmembrane protein TMEM242 |
* [[TMEM242]] encoding transmembrane protein TMEM242 |
||
* [[Chromosome 6 open reading frame 203|C6orf203]]: encoding protein Chromosome 6 open reading frame 203 |
|||
* [[C6orf58]]: chromosome 6 open reading frame 58 (6q22.33) |
* [[C6orf58]]: chromosome 6 open reading frame 58 (6q22.33) |
||
* [[CFAP206]]: encoding [[protein]] Cilia And Flagella Associated Protein 206 |
* [[CFAP206]]: encoding [[protein]] Cilia And Flagella Associated Protein 206 |
||
| Line 140: | Line 160: | ||
* [[CMD1K]]: cardiomyopathy, dilated 1K |
* [[CMD1K]]: cardiomyopathy, dilated 1K |
||
* [[CNR1]]: cannabinoid 1 receptor (6q14-q15)<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors = Matsuda LA, Lolait SJ, Brownstein MJ, Young AC, Bonner TI |title = Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA |journal = Nature |volume = 346 |issue = 6284 |pages = 561–4 |date = August 1990 |pmid = 2165569 |doi = 10.1038/346561a0 |bibcode = 1990Natur.346..561M |s2cid = 4356509 }}</ref> |
* [[CNR1]]: cannabinoid 1 receptor (6q14-q15)<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors = Matsuda LA, Lolait SJ, Brownstein MJ, Young AC, Bonner TI |title = Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA |journal = Nature |volume = 346 |issue = 6284 |pages = 561–4 |date = August 1990 |pmid = 2165569 |doi = 10.1038/346561a0 |bibcode = 1990Natur.346..561M |s2cid = 4356509 }}</ref> |
||
* [[Dishevelled binding antagonist of beta catenin 2|DACT2]]: encoding protein Dishevelled binding antagonist of beta catenin 2 |
|||
* [[DFNB38]]: deafness, autosomal recessive 38 |
* [[DFNB38]]: deafness, autosomal recessive 38 |
||
* [[DYX4]]: dyslexia susceptibility 4 |
* [[DYX4]]: dyslexia susceptibility 4 |
||
| Line 154: | Line 175: | ||
* [[IGF2R]]: insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor (6q25.3) |
* [[IGF2R]]: insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor (6q25.3) |
||
* [[IMPG1]]: interphotoreceptor matrix proteoglylcan 1 (6q14.1) |
* [[IMPG1]]: interphotoreceptor matrix proteoglylcan 1 (6q14.1) |
||
* [[KIAA0408]] |
|||
* [[LGSN]]: encoding protein lengsin |
|||
* [[LIN28B (gene)|LIN28B]]: lin-28 homolog B (6q16.3-q21) |
* [[LIN28B (gene)|LIN28B]]: lin-28 homolog B (6q16.3-q21) |
||
* [[MAN1A1]]: mannosidase alpha class 1A member 1 (6q22.31) |
* [[MAN1A1]]: mannosidase alpha class 1A member 1 (6q22.31) |
||
| Line 165: | Line 188: | ||
* [[MTRF1L]]: mitochondrial translational release factor 1 like (6q25.2) |
* [[MTRF1L]]: mitochondrial translational release factor 1 like (6q25.2) |
||
* [[MYO6]]: myosin VI (6q14.1) |
* [[MYO6]]: myosin VI (6q14.1) |
||
* [[Neuroblastoma highly expressed 1|NHEG1]]: encoding protein Neuroblastoma highly expressed 1 |
|||
* [[OA3]]: ocular albinism 3 |
* [[OA3]]: ocular albinism 3 |
||
* [[OPRM1]]: μ-opioid receptors (6q24-q25) |
* [[OPRM1]]: μ-opioid receptors (6q24-q25) |
||
| Line 175: | Line 199: | ||
* [[PKIB]]: cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor beta (6p22.31) |
* [[PKIB]]: cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor beta (6p22.31) |
||
* [[PLAGL1]]: (6q24.2) |
* [[PLAGL1]]: (6q24.2) |
||
* [[Glutaminyl-trna synthase (glutamine-hydrolyzing)-like 1|QRSL1]]: encoding protein Glutaminyl-trna synthase (glutamine-hydrolyzing)-like 1 |
|||
* [[RCD1]]: retinal cone dystrophy 1 |
* [[RCD1]]: retinal cone dystrophy 1 |
||
* [[RFPL4B]]: Ret finger protein like 4B |
|||
* [[RP63]]: retinitis pigmentosa 63 |
* [[RP63]]: retinitis pigmentosa 63 |
||
* [[SASH1]]: SAM and SH3 domain containing 1 (6q24.3-q25.1) |
* [[SASH1]]: SAM and SH3 domain containing 1 (6q24.3-q25.1) |
||
| Line 187: | Line 213: | ||
* [[Sobp|SOBP]]: sine oculis binding protein homolog (6q21) |
* [[Sobp|SOBP]]: sine oculis binding protein homolog (6q21) |
||
* [[SPG25]]: spastic paraplegia 25 |
* [[SPG25]]: spastic paraplegia 25 |
||
* [[ST8]]:suppression of tumorigenicity 8 |
* [[Suppression of tumorigenicity 8 (ovarian)|ST8]]: suppression of tumorigenicity 8 |
||
* [[SYNJ2]]: synaptojanin 2 (6q25.3) |
* [[SYNJ2]]: synaptojanin 2 (6q25.3) |
||
* [[T (gene)|T]]: T [[brachyury]] [[transcription factor]] (more commonly known as the T gene) linked to [[Hepatocellular carcinoma]] and [[Chordoma]] (6q27)<ref>{{cite web|url=http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/gene/T|website=T - T brachyury transcription factor - Genetics Home Reference|title=T brachyury transcription factor}}</ref> |
* [[T (gene)|T]]: T [[brachyury]] [[transcription factor]] (more commonly known as the T gene) linked to [[Hepatocellular carcinoma]] and [[Chordoma]] (6q27)<ref>{{cite web|url=http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/gene/T|website=T - T brachyury transcription factor - Genetics Home Reference|title=T brachyury transcription factor}}</ref> |
||
| Line 216: | Line 242: | ||
* [[methylmalonic acidemia]] |
* [[methylmalonic acidemia]] |
||
* Autosomal [[nonsyndromic deafness]] |
* Autosomal [[nonsyndromic deafness]] |
||
* [[North Carolina macular dystrophy]] |
|||
* [[otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia]] |
* [[otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia]] |
||
* [[Parkinson disease]] |
* [[Parkinson disease]] |
||
| Line 222: | Line 249: | ||
* [[porphyria cutanea tarda]] |
* [[porphyria cutanea tarda]] |
||
* [[Rheumatoid arthritis]], HLA-DR |
* [[Rheumatoid arthritis]], HLA-DR |
||
* CIRS (Chronic Inflammatory Response Syndrome ), Sick Building Syndrome, Mold Toxin Susceptibility / Poisoning, HLA-DR/DQ |
|||
* [[Spinocerebellar ataxia type 1]], ATXN1 |
|||
* [[Stickler syndrome]], COL11A2 |
* [[Stickler syndrome]], COL11A2 |
||
* [[Systemic lupus erythematosus]] |
* [[Systemic lupus erythematosus]] |
||
| Line 244: | Line 273: | ||
| width2 = 1003 |
| width2 = 1003 |
||
| height2= 2801 |
| height2= 2801 |
||
| caption2 = G-banding patterns of human chromosome 6 in three different resolutions (400,<ref name="400bphs">Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. [ |
| caption2 = G-banding patterns of human chromosome 6 in three different resolutions (400,<ref name="400bphs">Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. [http://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/gdp/ideogram_9606_GCF_000001305.14_400_V1 Ideogram data for Homo sapience (400 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3)]. Last update 2014-03-04. Retrieved 2017-04-26.</ref> 550<ref name="550bphs">Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. [http://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/gdp/ideogram_9606_GCF_000001305.14_550_V1 Ideogram data for Homo sapience (550 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3)]. Last update 2015-08-11. Retrieved 2017-04-26.</ref> and 850<ref name="850bphs">Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. [http://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/gdp/ideogram_9606_GCF_000001305.14_850_V1 Ideogram data for Homo sapience (850 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3)]. Last update 2014-06-03. Retrieved 2017-04-26.</ref>). Band length in this diagram is based on the ideograms from ISCN (2013).<ref name="Nomenclature2013">{{cite book|author=International Standing Committee on Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature|title=ISCN 2013: An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013)|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lGCLrh0DIwEC|year=2013|publisher=Karger Medical and Scientific Publishers|isbn=978-3-318-02253-7}}</ref> This type of ideogram represents actual relative band length observed under a microscope at the different moments during the [[Mitosis|mitotic process]].<ref name="SethakulvichaiManitpornsut2012">{{cite book |last1=Sethakulvichai |first1=W. |last2=Manitpornsut |first2=S. |last3=Wiboonrat |first3=M. |last4=Lilakiatsakun |first4=W. |last5=Assawamakin |first5=A. |last6=Tongsima |first6=S. |title=2012 Ninth International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering (JCSSE) |chapter=Estimation of band level resolutions of human chromosome images |year=2012 |pages=276–282 |doi=10.1109/JCSSE.2012.6261965 |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261304470 |isbn=978-1-4673-1921-8 |s2cid=16666470}}</ref> |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:right" |
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:right" |
||
|+ [[G banding|G-band]]s of human chromosome 6 in resolution 850 bphs<ref>Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. [ |
|+ [[G banding|G-band]]s of human chromosome 6 in resolution 850 bphs<ref>Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. [http://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/gdp/ideogram_9606_GCF_000001305.14_850_V1 Ideogram data for Homo sapience (850 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3)]. Last update 2014-06-03. Retrieved 2017-04-26.</ref> |
||
! Chr. |
! Chr. |
||
! Arm<ref>"'''p'''": Short arm; "'''q'''": Long arm.</ref> |
! Arm<ref>"'''p'''": Short arm; "'''q'''": Long arm.</ref> |
||
| Line 454: | Line 483: | ||
{{reflist}} |
{{reflist}} |
||
;Notes |
;Notes |
||
*''Some text in this article was taken from http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/chromosome=6 (public domain)'' |
*''Some text in this article was taken from http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/chromosome=6 {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070812034128/http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/chromosome=6 |date=2007-08-12 }} (public domain)'' |
||
==Further reading== |
==Further reading== |
||
{{refbegin}} |
{{refbegin}} |
||
| Line 462: | Line 491: | ||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
{{Commons category|Human chromosome 6}} |
{{Commons category|Human chromosome 6}} |
||
* {{cite web | author= National Institutes of Health |
* {{cite web | author= National Institutes of Health | title= Chromosome 6 | work= Genetics Home Reference | url= http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/chromosome=6 | access-date= 2017-05-06 | archive-date= 2007-08-12 | archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20070812034128/http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/chromosome=6 | url-status= dead }} |
||
* {{Cite web|url=http://web.ornl.gov/sci/techresources/Human_Genome/posters/chromosome/chromo06.shtml|title=Chromosome 6|website=Human Genome Project Information Archive 1990–2003|access-date=2017-05-06}} |
* {{Cite web|url=http://web.ornl.gov/sci/techresources/Human_Genome/posters/chromosome/chromo06.shtml|title=Chromosome 6|website=Human Genome Project Information Archive 1990–2003|access-date=2017-05-06}} |
||
* "[http://www.chromosome6.org Chromosome 6 Research Project"]. ''Parent-driven research for genotype-phenotype studies on chromosome 6 disorders.'' Retrieved 2017-06-17 |
* "[http://www.chromosome6.org Chromosome 6 Research Project"]. ''Parent-driven research for genotype-phenotype studies on chromosome 6 disorders.'' Retrieved 2017-06-17 |
||
Latest revision as of 20:57, 24 August 2024
| Chromosome 6 | |
|---|---|
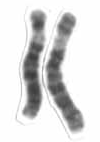 Human chromosome 6 pair after G-banding. One is from mother, one is from father. | |
 Chromosome 6 pair in human male karyogram. | |
| Features | |
| Length (bp) | 172,126,628 bp (CHM13) |
| No. of genes | 996 (CCDS)[1] |
| Type | Autosome |
| Centromere position | Submetacentric[2] (59.8 Mbp[3]) |
| Complete gene lists | |
| CCDS | Gene list |
| HGNC | Gene list |
| UniProt | Gene list |
| NCBI | Gene list |
| External map viewers | |
| Ensembl | Chromosome 6 |
| Entrez | Chromosome 6 |
| NCBI | Chromosome 6 |
| UCSC | Chromosome 6 |
| Full DNA sequences | |
| RefSeq | NC_000006 (FASTA) |
| GenBank | CM000668 (FASTA) |
Chromosome 6 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 6 spans nearly 171 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 5.5 and 6% of the total DNA in cells. It contains the major histocompatibility complex, which contains over 100 genes related to the immune response, and plays a vital role in organ transplantation.
The evolution of human centromere 6
[edit]The centromere of chromosome 6 illustrates an interesting example of centromere evolution. It was known[further explanation needed] that in a Catarrhini ancestor the chromosome 6 centromere was situated near position 26 Mb of the modern human chromosome. In Macaca mulatta, this old centromere went defunct and repositioned to a different chromosomal location[relevant?]. In the case of humans, the old centromere went defunct and a more recent form emerged near the modern position of human cen6 (size of 60 Mb). Such cases are known as Evolutionary New Centromeres (ENC). This assembly phenomenon of the human chromosome 6 gives researchers an opportunity to investigate the origin of the ENC on chromosome 6. [4]
Genes
[edit]The human leukocyte antigen lies on chromosome 6, with the exception of the gene for β2-microglobulin (which is located on chromosome 15), and encodes cell-surface antigen-presenting proteins among other functions.
Number of genes
[edit]In 2003, the entirety of chromosome 6 was manually annotated for proteins, resulting in the identification of 1,557 genes, and 633 pseudogenes.[5]
The following are some of the newer gene count estimates. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project (CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes.[6]
| Estimated by | Protein-coding genes | Non-coding RNA genes | Pseudogenes | Source | Release date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCDS | 996 | — | — | [1] | 2016-09-08 |
| HGNC | 1,007 | 422 | 736 | [7] | 2017-05-12 |
| Ensembl | 1,038 | 985 | 800 | [8] | 2017-03-29 |
| UniProt | 1,111 | — | — | [9] | 2018-02-28 |
| NCBI | 1,053 | 1,188 | 911 | [10][11][12] | 2017-05-19 |
Gene list
[edit]The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 6. For complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right.
p-arm
[edit]The following are some of the genes located on p-arm (short arm) of human chromosome 6:
- ADTRP: encoding protein Androgen-dependent TFPI-regulating protein
- APOM: encoding protein Apolipoprotein M (6p21.33)
- ARMC12: encoding protein Armadillo repeat containing 12
- ATXN1: encoding protein Ataxin 1 (6p16.3-p16.76)
- TSBP1: encoding protein TSBP1 (6p21.32)
- C6orf62: chromosome 6 open reading frame 62 (6p22.3)
- C6orf89: chromosome 6 open reading frame 89 (6p21.2)
- CDKAL1: CDK5 regulatory subunit associated protein 1 like 1 (6p22.3)
- COL11A2: collagen, type XI, alpha 2(6p21.3)
- CRIP3: encoding protein Cysteine rich protein 3
- CYP21A2: cytochrome P450, family 21, subfamily A, polypeptide 2 (6p21.33)
- DHX16: DEAH-box helicase 16 (6p21.33)
- DOM3Z: Decapping exoribonuclease (6p21.33)
- DSP: Desmoplakin gene linked to cardiomyopathy (6p24.3)
- ELOVL5: ELOVL fatty acid elongase 5 (6p12.1)
- FBXO9: F-box protein 9 (6p12.1)
- FOXP4-AS1: encoding protein FOXP4 antisense RNA 1
- FTH1P5: encoding protein Ferritin, heavy polypeptide 1 pseudogene 5
- G6B: Protein G6b (6p21.33)
- GCNT2: N-acetyllactosaminide beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyl-transferase (6p24.3)
- GGNBP1: encoding protein Gametogenetin binding protein 1 (pseudogene)
- GMDS: GDP-mannose 4,6-dehydratase (6p25.3)
- GTPBP2: encoding protein Gtp binding protein 2
- HCG4P11: HLA complex group 4 pseudogene 11
- HFE: hemochromatosis (6p22.2)
- HIST1H2AH: histone cluster 1 H2A family member h (6p22.1)
- HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C: major histocompatibility complex (MHC), class I, A, B, and C loci. (6p21.3)
- HLA-DQA1 and HLA-DQB1 form HLA-DQ heterodimer MHC class II, DQ: Celiac1, IDDM (6p21.3)
- HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, HLA-DRB3, HLA-DRB4, HLA-DRB5 forms HLA-DR, heterodimer MHC class II, DR (6p21.3) Mold / Biotoxin Susceptibility
- HLA-DPA1 and HLA-DPB1 forms HLA-DP, MHC class II, DP (6p21.3)
- HLA-Cw*06:02: gene variation related to psoriasis (6p21.3)
- KAAG1: encoding protein Kidney associated antigen 1
- LOC100533655: encoding protein Aryl hydrocarbon receptor pseudogene
- LST1: leukocyte specific transcript 1 (6p21.33)
- LY6G6E encoding protein Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex, locus G6E (pseudogene) (6p21.33)
- MIR4640: microRNA 4640 (6p21.33)
- MLIP: muscular LMNA interaction protein (6p12.1)
- MRPS18B: mitochondrial ribosomal protein S18B (6p21.33)
- MUT: methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase (6p12.3)
- NHLRC1: NHL repeat containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (6p22.3)
- NOL7: nucleolar protein 7 (6p23)
- NQO2: N-ribosyldihydronicotinamide:quinone reductase 2 (6p25.2)
- NRSN1: neurensin 1 (6p22.3)
- NUDT3: nudix hydrolase 3 (6p21.31)
- PFDN6: prefoldin subunit 6 (6p21.32)
- PHACTR1: phosphatase and actin regulator 1 (6p24.1)
- PKHD1: polycystic kidney and hepatic disease 1 (autosomal recessive) (6p21.2-p12)
- PRICKLE4: prickle planar cell polarity protein 4 (6p21.1)
- PRSS16: protease, serine 16 (6p22.1)
- PSMB8-AS1: PSMB8 antisense RNA 1 (head to head) (6p21.32)
- RAB44: encoding protein Rab44, member ras oncogene family
- RIPOR2: RHO family interacting cell polarization regulator 2 (6p22.3)
- RPL10A: encoding protein 60S ribosomal protein L10a (6p21.31)
- SKIV2L: Ski2 like RNA helicase (6p21.33)
- SSR1: signal sequence receptor subunit 1 (6p24.3)
- TCF19: transcription factor 19 (6p21.33)
- TCP11: t-complex 11 (6p21.31)
- TJAP1: tight junction associated protein 1 (6p21.1)
- TP53COR1 encoding protein Tumor protein p53 pathway corepressor 1 (non-protein coding)
- TMEM151B: encoding protein Transmembrane protein 151B
- TNXB: tenascin XB (6p21.3)
- TRAM2: translocation associated membrane protein 2 (6p12.2)
- TRIM38: encoding protein Tripartite motif containing 38
- TTBK1: encoding protein Tau tubulin kinase 1
- UBR2: ubiquitin protein ligase E3 component n-recognin 2 (6p21.2)
- UNC5CL: encoding protein Unc-5 homolog C (C. elegans)-like
- USP8P1: encoding protein Ubiquitin specific peptidase 8 pseudogene 1
- VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor A (angiogenic growth factor) (6p21.1)
- VPS52: GARP complex subunit
- VWA7: encoding protein Von willebrand factor a domain containing 7
- ZKSCAN4: encoding protein zinc finger with KRAB and SCAN domains 4
- ZNF76: zinc finger protein 76 (6p21.31)
- ZNF193: zinc finger protein 193 (6p22.1)
- ZNRD1: zinc ribbon domain containing 1 (6p22.1)
q-arm
[edit]The following are some of the genes located on q-arm (long arm) of human chromosome 6:
- AIM1: encoding protein Absent in melanoma 1 protein (6q21)
- AIG1: encoding protein Androgen-induced protein 1 (6q24.2)
- AKIRIN2: akirin 2 (6q15)
- ARG1: arginase 1 (6q23.2)
- BCKDHB: branched-chain keto acid dehydrogenase E1, beta polypeptide (maple syrup urine disease) (6q14.1)
- BMIQ3: body mass index QTL 3
- TMEM242 encoding transmembrane protein TMEM242
- C6orf203: encoding protein Chromosome 6 open reading frame 203
- C6orf58: chromosome 6 open reading frame 58 (6q22.33)
- CFAP206: encoding protein Cilia And Flagella Associated Protein 206
- CMD1F: cardiomyopathy, dilated 1F
- CMD1K: cardiomyopathy, dilated 1K
- CNR1: cannabinoid 1 receptor (6q14-q15)[13]
- DACT2: encoding protein Dishevelled binding antagonist of beta catenin 2
- DFNB38: deafness, autosomal recessive 38
- DYX4: dyslexia susceptibility 4
- ECT2L: encoding protein Epithelial cell transforming sequence 2 oncogene-like
- ESR1: Estrogen receptor 1 (6q25)
- EYA4: eyes absent homolog 4 (Drosophila)(6q23.2)
- FBXL4: F-box and leucine rich repeat protein 4 (6q16.1-q16.2)
- FEB5: febrile convulsions 5
- HACE1: HECT domain and Ankyrin repeat containing, E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (6q21)
- HEBP2: heme binding protein 2 (6q24.1)
- IDDM8: insulin dependent diabetes mellitus 8
- IDDM15: insulin dependent diabetes mellitus 15
- IFNGR: interferon-γ receptor gene (6q23-q24)
- IGF2R: insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor (6q25.3)
- IMPG1: interphotoreceptor matrix proteoglylcan 1 (6q14.1)
- KIAA0408
- LGSN: encoding protein lengsin
- LIN28B: lin-28 homolog B (6q16.3-q21)
- MAN1A1: mannosidase alpha class 1A member 1 (6q22.31)
- MB21D1: encoding protein Mab-21 domain containing 1
- MCDR1: macular dystrophy, retinal, 1
- MDN1: midasin AAA ATPase 1 (6q15)
- MOXD1: monooxygenase DBH like 1 (6q23.2)
- MTO1: mitochondrial tRNA translation optimization 1 (6q13)
- MRT18: mental retardation, non-syndromic, autosomal recessive
- MRT28: mental retardation, non-syndromic, autosomal recessive
- MTRF1L: mitochondrial translational release factor 1 like (6q25.2)
- MYO6: myosin VI (6q14.1)
- NHEG1: encoding protein Neuroblastoma highly expressed 1
- OA3: ocular albinism 3
- OPRM1: μ-opioid receptors (6q24-q25)
- OTSC7: otosclerosis 7
- PLG: plasminogen (6q26)
- PBCRA1
- PARK2: Parkinson disease (autosomal recessive, juvenile) 2, parkin (6q26)
- PCMT1: protein-L-isoaspartate (D-aspartate) O-methyltransferase (6q25.1)
- PERP: p53 apoptosis effector related to PMP-22 (6q23.3)
- PKIB: cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor beta (6p22.31)
- PLAGL1: (6q24.2)
- QRSL1: encoding protein Glutaminyl-trna synthase (glutamine-hydrolyzing)-like 1
- RCD1: retinal cone dystrophy 1
- RFPL4B: Ret finger protein like 4B
- RP63: retinitis pigmentosa 63
- SASH1: SAM and SH3 domain containing 1 (6q24.3-q25.1)
- SCZD5: schizophrenia disorder 5
- SEN6: senescence (cellular)-related 6
- SENP6: SUMO1/sentrin specific peptidase 6 (6q14.1)
- SERAC1: serine active site containing 1 (6q25.3)
- SERINC1: serine incorporator 1 (6q22.31)
- SF3B5: splicing factor 3b subunit 5 (6q24.2)
- SMAP1: small ArfGAP 1 (6q13)
- SOBP: sine oculis binding protein homolog (6q21)
- SPG25: spastic paraplegia 25
- ST8: suppression of tumorigenicity 8
- SYNJ2: synaptojanin 2 (6q25.3)
- T: T brachyury transcription factor (more commonly known as the T gene) linked to Hepatocellular carcinoma and Chordoma (6q27)[14]
- TAAR1: trace amine associated receptor 1 (6q23.1)
- TAAR2: trace amine associated receptor 2 (6q24)
- TMEM200A: encoding protein Transmembrane protein 200A
- TSPYL1: TSPY like 1 (6q22.1)
- UNC93A: encoding protein Unc-93 homolog A (C. elegans)
- VNN1: vanin 1 (6q23.2)
- VNN2: vanin 2 (6q23.2)
- VTA1: Vesicle trafficking 1 (6q24.1-2)
- ZC2HC1: encoding protein Zinc finger C2HC-type containing 1B
- ZDHHC14: encoding protein Zinc finger, DHHC-type containing 14
Diseases and disorders
[edit]The following diseases are some of those related to genes on chromosome 6:
- ankylosing spondylitis, HLA-B
- collagenopathy, types II and XI
- Coeliac disease HLA-DQA1 & DQB1
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, classical, hypermobility, and Tenascin-X types
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis
- hemochromatosis
- Hemochromatosis type 1
- 21-hydroxylase deficiency
- maple syrup urine disease
- methylmalonic acidemia
- Autosomal nonsyndromic deafness
- North Carolina macular dystrophy
- otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia
- Parkinson disease
- polycystic kidney disease
- porphyria
- porphyria cutanea tarda
- Rheumatoid arthritis, HLA-DR
- CIRS (Chronic Inflammatory Response Syndrome ), Sick Building Syndrome, Mold Toxin Susceptibility / Poisoning, HLA-DR/DQ
- Spinocerebellar ataxia type 1, ATXN1
- Stickler syndrome, COL11A2
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Diabetes mellitus type 1, HLA-DR, DQA1 & DQB1
- X-linked sideroblastic anemia
- Epilepsy
- Guillain Barre Syndrome
- Chordoma
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Schizophrenia
Cytogenetic band
[edit]| Chr. | Arm[20] | Band[21] | ISCN start[22] |
ISCN stop[22] |
Basepair start |
Basepair stop |
Stain[23] | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | p | 25.3 | 0 | 118 | 1 | 2,300,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | p | 25.2 | 118 | 207 | 2,300,001 | 4,200,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 6 | p | 25.1 | 207 | 355 | 4,200,001 | 7,100,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | p | 24.3 | 355 | 548 | 7,100,001 | 10,600,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 6 | p | 24.2 | 548 | 592 | 10,600,001 | 11,600,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | p | 24.1 | 592 | 740 | 11,600,001 | 13,400,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 6 | p | 23 | 740 | 844 | 13,400,001 | 15,200,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | p | 22.3 | 844 | 1185 | 15,200,001 | 25,200,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 6 | p | 22.2 | 1185 | 1348 | 25,200,001 | 27,100,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | p | 22.1 | 1348 | 1585 | 27,100,001 | 30,500,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 6 | p | 21.33 | 1585 | 1718 | 30,500,001 | 32,100,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | p | 21.32 | 1718 | 1836 | 32,100,001 | 33,500,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 6 | p | 21.31 | 1836 | 2162 | 33,500,001 | 36,600,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | p | 21.2 | 2162 | 2310 | 36,600,001 | 40,500,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 6 | p | 21.1 | 2310 | 2755 | 40,500,001 | 46,200,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | p | 12.3 | 2755 | 3080 | 46,200,001 | 51,800,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 6 | p | 12.2 | 3080 | 3140 | 51,800,001 | 53,000,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | p | 12.1 | 3140 | 3377 | 5,300,0001 | 57,200,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 6 | p | 11.2 | 3377 | 3421 | 57,200,001 | 58,500,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | p | 11.1 | 3421 | 3554 | 58,500,001 | 59,800,000 | acen | |
| 6 | q | 11.1 | 3554 | 3658 | 59,800,001 | 62,600,000 | acen | |
| 6 | q | 11.2 | 3658 | 3732 | 62,600,001 | 62,700,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 12 | 3732 | 4147 | 62,700,001 | 69,200,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 6 | q | 13 | 4147 | 4324 | 69,200,001 | 75,200,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 14.1 | 4324 | 4621 | 75,200,001 | 83,200,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 6 | q | 14.2 | 4621 | 4709 | 83,200,001 | 84,200,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 14.3 | 4709 | 4917 | 84,200,001 | 87,300,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 6 | q | 15 | 4917 | 5228 | 87,300,001 | 92,500,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 16.1 | 5228 | 5613 | 92,500,001 | 98,900,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 6 | q | 16.2 | 5613 | 5687 | 98,900,001 | 100,000,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 16.3 | 5687 | 5983 | 10,000,0001 | 105,000,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 6 | q | 21 | 5983 | 6531 | 10,500,0001 | 114,200,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 22.1 | 6531 | 6753 | 114,200,001 | 117,900,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 6 | q | 22.2 | 6753 | 6872 | 117,900,001 | 118,100,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 22.31 | 6872 | 7168 | 118,100,001 | 125,800,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 6 | q | 22.32 | 7168 | 7345 | 125,800,001 | 126,800,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 22.33 | 7345 | 7642 | 126,800,001 | 130,000,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 6 | q | 23.1 | 7642 | 7923 | 13,000,0001 | 130,900,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 23.2 | 7923 | 8145 | 130,900,001 | 134,700,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 6 | q | 23.3 | 8145 | 8352 | 134,700,001 | 138,300,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 24.1 | 8352 | 8560 | 138,300,001 | 142,200,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 6 | q | 24.2 | 8560 | 8708 | 142,200,001 | 145,100,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 24.3 | 8708 | 8886 | 145,100,001 | 148,500,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 6 | q | 25.1 | 8886 | 9078 | 148,500,001 | 152,100,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 25.2 | 9078 | 9241 | 152,100,001 | 155,200,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 6 | q | 25.3 | 9241 | 9596 | 155,200,001 | 160,600,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 26 | 9596 | 9774 | 160,600,001 | 164,100,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 6 | q | 27 | 9774 | 10100 | 164,100,001 | 170,805,979 | gneg |
References
[edit]- ^ a b "Search results - 6[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("has ccds"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". NCBI. CCDS Release 20 for Homo sapiens. 2016-09-08. Retrieved 2017-05-28.
- ^ Tom Strachan; Andrew Read (2 April 2010). Human Molecular Genetics. Garland Science. p. 45. ISBN 978-1-136-84407-2.
- ^ a b Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (850 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-06-03. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ^ Altemose, Nicolas; Logsdon, Glennis A.; Bzikadze, Andrey V.; Sidhwani, Pragya; Langley, Sasha A.; Caldas, Gina V.; Hoyt, Savannah J.; Uralsky, Lev; Ryabov, Fedor D.; Shew, Colin J.; Sauria, Michael E. G.; Borchers, Matthew; Gershman, Ariel; Mikheenko, Alla; Shepelev, Valery A. (April 2022). "Complete genomic and epigenetic maps of human centromeres". Science. 376 (6588): eabl4178. doi:10.1126/science.abl4178. ISSN 0036-8075. PMC 9233505. PMID 35357911.
- ^ Mungall AJ, Palmer SA, Sims SK, Edwards CA, Ashurst JL, Wilming L, et al. (October 2003). "The DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 6". Nature. 425 (6960): 805–11. Bibcode:2003Natur.425..805M. doi:10.1038/nature02055. PMID 14574404.
- ^ Pertea M, Salzberg SL (2010). "Between a chicken and a grape: estimating the number of human genes". Genome Biol. 11 (5): 206. doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-5-206. PMC 2898077. PMID 20441615.
- ^ "Statistics & Downloads for chromosome 6". HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee. 2017-05-12. Archived from the original on 2017-08-18. Retrieved 2017-05-19.
- ^ "Chromosome 6: Chromosome summary - Homo sapiens". Ensembl Release 88. 2017-03-29. Retrieved 2017-05-19.
- ^ "Human chromosome 6: entries, gene names and cross-references to MIM". UniProt. 2018-02-28. Retrieved 2018-03-16.
- ^ "Search results - 6[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("genetype protein coding"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". NCBI. 2017-05-19. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- ^ "Search results - 6[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ( ("genetype miscrna"[Properties] OR "genetype ncrna"[Properties] OR "genetype rrna"[Properties] OR "genetype trna"[Properties] OR "genetype scrna"[Properties] OR "genetype snrna"[Properties] OR "genetype snorna"[Properties]) NOT "genetype protein coding"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". NCBI. 2017-05-19. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- ^ "Search results - 6[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("genetype pseudo"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". NCBI. 2017-05-19. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- ^ Matsuda LA, Lolait SJ, Brownstein MJ, Young AC, Bonner TI (August 1990). "Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA". Nature. 346 (6284): 561–4. Bibcode:1990Natur.346..561M. doi:10.1038/346561a0. PMID 2165569. S2CID 4356509.
- ^ "T brachyury transcription factor". T - T brachyury transcription factor - Genetics Home Reference.
- ^ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (400 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-03-04. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ^ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (550 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2015-08-11. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ^ International Standing Committee on Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). ISCN 2013: An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Karger Medical and Scientific Publishers. ISBN 978-3-318-02253-7.
- ^ Sethakulvichai, W.; Manitpornsut, S.; Wiboonrat, M.; Lilakiatsakun, W.; Assawamakin, A.; Tongsima, S. (2012). "Estimation of band level resolutions of human chromosome images". 2012 Ninth International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering (JCSSE). pp. 276–282. doi:10.1109/JCSSE.2012.6261965. ISBN 978-1-4673-1921-8. S2CID 16666470.
- ^ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (850 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-06-03. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ^ "p": Short arm; "q": Long arm.
- ^ For cytogenetic banding nomenclature, see article locus.
- ^ a b These values (ISCN start/stop) are based on the length of bands/ideograms from the ISCN book, An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Arbitrary unit.
- ^ gpos: Region which is positively stained by G banding, generally AT-rich and gene poor; gneg: Region which is negatively stained by G banding, generally CG-rich and gene rich; acen Centromere. var: Variable region; stalk: Stalk.
- Notes
- Some text in this article was taken from http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/chromosome=6 Archived 2007-08-12 at the Wayback Machine (public domain)
Further reading
[edit]- Gilbert F (2002). "Chromosome 6". Genet Test. 6 (4): 341–58. doi:10.1089/10906570260471912. PMID 12537662.
External links
[edit]- National Institutes of Health. "Chromosome 6". Genetics Home Reference. Archived from the original on 2007-08-12. Retrieved 2017-05-06.
- "Chromosome 6". Human Genome Project Information Archive 1990–2003. Retrieved 2017-05-06.
- "Chromosome 6 Research Project". Parent-driven research for genotype-phenotype studies on chromosome 6 disorders. Retrieved 2017-06-17

