Iota Aquarii: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
Setting DEFAULTSORT key to Iota Aquarii using Hot Default Sort |
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Add: page, volume, journal, issue, s2cid. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Kline | Category:B-type main-sequence stars | via #UCB_Category 77/409 |
||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
{{reflist|refs= |
{{reflist|refs= |
||
<ref name=aaa474_2_653>{{citation | first=F. | last=van Leeuwen |date=November 2007 | title=Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction | journal=Astronomy and Astrophysics | volume=474 | issue=2 | pages=653–664 | bibcode=2007A&A...474..653V | doi=10.1051/0004-6361:20078357 | postscript=. |arxiv = 0708.1752 }}</ref> |
<ref name=aaa474_2_653>{{citation | first=F. | last=van Leeuwen |date=November 2007 | title=Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction | journal=Astronomy and Astrophysics | volume=474 | issue=2 | pages=653–664 | bibcode=2007A&A...474..653V | doi=10.1051/0004-6361:20078357 | postscript=. |arxiv = 0708.1752 | s2cid=18759600 }}</ref> |
||
<ref name=Anderson2012>{{citation |
<ref name=Anderson2012>{{citation |
||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
| volume=38 | issue=5 | pages=331 | year=2012 |
| volume=38 | issue=5 | pages=331 | year=2012 |
||
| bibcode=2012AstL...38..331A | doi=10.1134/S1063773712050015 |
| bibcode=2012AstL...38..331A | doi=10.1134/S1063773712050015 |
||
| arxiv=1108.4971 | postscript=. }}</ref> |
| arxiv=1108.4971 | s2cid=119257644 | postscript=. }}</ref> |
||
<ref name=aaa523_A73>{{citation | display-authors=1 | last1=Ehrenreich | first1=D. | last2=Lagrange | first2=A.-M. | last3=Montagnier | first3=G. | last4=Chauvin | first4=G. | last5=Galland | first5=F. | last6=Beuzit | first6=J.-L. | last7=Rameau | first7=J. | title=Deep infrared imaging of close companions to austral A- and F-type stars | journal=Astronomy and Astrophysics | volume=523 | page=A73 |date=November 2010 | doi=10.1051/0004-6361/201014763 | bibcode=2010A&A...523A..73E | postscript=. |arxiv = 1007.0002 }}</ref> |
<ref name=aaa523_A73>{{citation | display-authors=1 | last1=Ehrenreich | first1=D. | last2=Lagrange | first2=A.-M. | last3=Montagnier | first3=G. | last4=Chauvin | first4=G. | last5=Galland | first5=F. | last6=Beuzit | first6=J.-L. | last7=Rameau | first7=J. | title=Deep infrared imaging of close companions to austral A- and F-type stars | journal=Astronomy and Astrophysics | volume=523 | page=A73 |date=November 2010 | doi=10.1051/0004-6361/201014763 | bibcode=2010A&A...523A..73E | postscript=. |arxiv = 1007.0002 | s2cid=54913363 }}</ref> |
||
<ref name=mnras189_601>{{citation | display-authors=1 | last1=Underhill | first1=A. B. | last2=Divan | first2=L. | last3=Prevot-Burnichon | first3=M.-L. | last4=Doazan | first4=V. | title=Effective temperatures, angular diameters, distances and linear radii for 160 O and B stars | journal=[[Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society]] | volume=189 | pages=601–605 |date=November 1979 | bibcode=1979MNRAS.189..601U | postscript=. | doi=10.1093/mnras/189.3.601| doi-access=free }}</ref> |
<ref name=mnras189_601>{{citation | display-authors=1 | last1=Underhill | first1=A. B. | last2=Divan | first2=L. | last3=Prevot-Burnichon | first3=M.-L. | last4=Doazan | first4=V. | title=Effective temperatures, angular diameters, distances and linear radii for 160 O and B stars | journal=[[Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society]] | volume=189 | pages=601–605 |date=November 1979 | issue=3 | bibcode=1979MNRAS.189..601U | postscript=. | doi=10.1093/mnras/189.3.601| doi-access=free }}</ref> |
||
<ref name=houk1978>{{citation | last1=Houk | first1=Nancy | title=Michigan catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD stars | volume=4 | publication-place=Ann Arbor | publisher=Dept. of Astronomy, University of Michigan | year=1978 | bibcode=1988mcts.book.....H | postscript=. }}</ref> |
<ref name=houk1978>{{citation | last1=Houk | first1=Nancy | title=Michigan catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD stars | volume=4 | publication-place=Ann Arbor | publisher=Dept. of Astronomy, University of Michigan | year=1978 | bibcode=1988mcts.book.....H | postscript=. }}</ref> |
||
<ref name=scfs>{{citation | display-authors=1 | title=Sixth Catalogue of Fundamental Stars (FK6). Part I. Basic fundamental stars with direct solutions | last1=Wielen | first1=R. | last2=Schwan | first2=H. | last3=Dettbarn | first3=C. | last4=Lenhardt | first4=H. | last5=Jahreiß | first5=H. | last6=Jährling | first6=R. | publisher=Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Heidelberg | issue=35 | year=1999 | bibcode=1999VeARI..35....1W | postscript=. }}</ref> |
<ref name=scfs>{{citation | display-authors=1 | title=Sixth Catalogue of Fundamental Stars (FK6). Part I. Basic fundamental stars with direct solutions | last1=Wielen | first1=R. | last2=Schwan | first2=H. | last3=Dettbarn | first3=C. | last4=Lenhardt | first4=H. | last5=Jahreiß | first5=H. | last6=Jährling | first6=R. | journal=Veroeffentlichungen des Astronomischen Rechen-Instituts Heidelberg | publisher=Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Heidelberg | issue=35 | year=1999 | volume=35 | page=1 | bibcode=1999VeARI..35....1W | postscript=. }}</ref> |
||
<ref name=apj573_1_359>{{citation | last1=Abt | first1=Helmut A. | last2=Levato | first2=Hugo | last3=Grosso | first3=Monica | title=Rotational Velocities of B Stars | journal=The Astrophysical Journal | volume=573 | issue=1 | pages=359–365 |date=July 2002 | doi=10.1086/340590 | bibcode=2002ApJ...573..359A | postscript=. | doi-access=free }}</ref> |
<ref name=apj573_1_359>{{citation | last1=Abt | first1=Helmut A. | last2=Levato | first2=Hugo | last3=Grosso | first3=Monica | title=Rotational Velocities of B Stars | journal=The Astrophysical Journal | volume=573 | issue=1 | pages=359–365 |date=July 2002 | doi=10.1086/340590 | bibcode=2002ApJ...573..359A | postscript=. | doi-access=free }}</ref> |
||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
<ref name=SIMBAD>{{cite simbad | title=* iot Aqr | access-date=2012-06-30 }}</ref> |
<ref name=SIMBAD>{{cite simbad | title=* iot Aqr | access-date=2012-06-30 }}</ref> |
||
<ref name=aaa525_A71>{{citation | display-authors=1 | last1=Wu | first1=Yue | last2=Singh | first2=H. P. | last3=Prugniel | first3=P. | last4=Gupta | first4=R. | last5=Koleva | first5=M. | title=Coudé-feed stellar spectral library - atmospheric parameters | journal=Astronomy and Astrophysics | volume=525 | page=A71 |date=January 2011 | doi=10.1051/0004-6361/201015014 | bibcode=2011A&A...525A..71W | postscript=. |arxiv = 1009.1491 }}</ref> |
<ref name=aaa525_A71>{{citation | display-authors=1 | last1=Wu | first1=Yue | last2=Singh | first2=H. P. | last3=Prugniel | first3=P. | last4=Gupta | first4=R. | last5=Koleva | first5=M. | title=Coudé-feed stellar spectral library - atmospheric parameters | journal=Astronomy and Astrophysics | volume=525 | page=A71 |date=January 2011 | doi=10.1051/0004-6361/201015014 | bibcode=2011A&A...525A..71W | postscript=. |arxiv = 1009.1491 | s2cid=53480665 }}</ref> |
||
}} |
}} |
||
Revision as of 19:04, 19 April 2021
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Aquarius |
| Right ascension | 22h 06m 26.22742s[1] |
| Declination | –13° 52′ 10.8615″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.279[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | B8 V[3] |
| U−B color index | –0.288[2] |
| B−V color index | –0.062[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | –10.0[4] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +36.89[1] mas/yr Dec.: –58.99[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 18.62 ± 0.22 mas[1] |
| Distance | 175 ± 2 ly (53.7 ± 0.6 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | +0.64[5] |
| Details | |
| Radius | 2.7[6] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 74[5] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.09 ± 0.08[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 11,284 ± 284[6] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | –0.08 ± 0.12[7] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 135[8] km/s |
| Age | 30–60[9] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
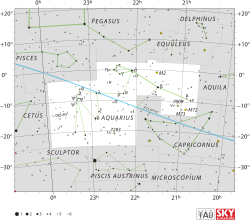
Iota Aquarii, Latinized from ι Aquarii, is the Bayer designation for a star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent magnitude of +4.279.[2] Based upon parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, the distance to this star is around 175 light-years (54 parsecs).[2]
The spectrum of this star fits a stellar classification of B8 V,[3] showing that this is a B-type main sequence star. It has 2.7[6] times the radius of the Sun and is spinning rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of 135 km/s.[8] A 2010 infrared search for companions around this star was unsuccessful.[9]
References
- ^ a b c d e van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv:0708.1752, Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, S2CID 18759600.
- ^ a b c d e Kozok, J. R. (September 1985), "Photometric observations of emission B-stars in the southern Milky Way", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series, 61: 387–405, Bibcode:1985A&AS...61..387K.
- ^ a b Houk, Nancy (1978), Michigan catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD stars, vol. 4, Ann Arbor: Dept. of Astronomy, University of Michigan, Bibcode:1988mcts.book.....H.
- ^ Wielen, R.; et al. (1999), "Sixth Catalogue of Fundamental Stars (FK6). Part I. Basic fundamental stars with direct solutions", Veroeffentlichungen des Astronomischen Rechen-Instituts Heidelberg, 35 (35), Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Heidelberg: 1, Bibcode:1999VeARI..35....1W.
- ^ a b Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters, 38 (5): 331, arXiv:1108.4971, Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015, S2CID 119257644.
- ^ a b c Underhill, A. B.; et al. (November 1979), "Effective temperatures, angular diameters, distances and linear radii for 160 O and B stars", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 189 (3): 601–605, Bibcode:1979MNRAS.189..601U, doi:10.1093/mnras/189.3.601.
- ^ a b Wu, Yue; et al. (January 2011), "Coudé-feed stellar spectral library - atmospheric parameters", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 525: A71, arXiv:1009.1491, Bibcode:2011A&A...525A..71W, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201015014, S2CID 53480665.
- ^ a b Abt, Helmut A.; Levato, Hugo; Grosso, Monica (July 2002), "Rotational Velocities of B Stars", The Astrophysical Journal, 573 (1): 359–365, Bibcode:2002ApJ...573..359A, doi:10.1086/340590.
- ^ a b Ehrenreich, D.; et al. (November 2010), "Deep infrared imaging of close companions to austral A- and F-type stars", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 523: A73, arXiv:1007.0002, Bibcode:2010A&A...523A..73E, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014763, S2CID 54913363.
- ^ "* iot Aqr". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2012-06-30.