Nakshatra: Difference between revisions
Nick Levine (talk | contribs) Reverted 1 edit by 2409:40F4:1008:AADD:8000:0:0:0 (talk): Inadequately explained text removal |
rv Corruption of Wikipedia Tags: Manual revert Reverted references removed Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web edit Disambiguation links added |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
{{Nakshatras}} |
{{Nakshatras}} |
||
'''Nakshatra''' ({{lang-sa| नक्षत्रम्|translit=Nakṣatram}}) is the term for [[ |
'''Nakshatra''' ({{lang-sa| नक्षत्रम्|translit=Nakṣatram}}) is the term for [[lunar mansion]] in [[Hindu astrology]]. A nakshatra is one of 27 sectors along the ecliptic. Their names are related to a prominent star or [[asterism (astronomy)|asterisms]] in or near the respective sectors. In essence (in Western astronomical terms), a nakshatra simply is a [[constellation]]. Every nakshatra is divided into four ''padas'' ({{lit}} "steps") related to the [[Char Dham|Chara Dhama]], a set of four pilgrimage sites in India. |
||
The starting point for the nakshatras according to |
The starting point for the nakshatras according to Vedas is "Krittika" (it has been argued because the Pleiades may have started the year at the time the Vedas were compiled, presumably at the vernal equinox), but, in more recent compilations, the start of the nakshatras list is the point on the ecliptic directly opposite to the star [[Spica]] called ''Chitra'' in [[Sanskrit]], which would be Ashvini, a part of the modern constellation Aries, and these compilations therefore may have been compiled during the centuries when the sun was passing through the area of the constellation Aries at the time of the vernal equinox. This version may have been called ''Meshādi'' or the "[[first point of Aries|start of Aries]]".<ref> |
||
{{cite book |
{{cite book |
||
|first=Vashisht |last=Vaid |
|first=Vashisht |last=Vaid |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
</ref>{{better source needed|date=June 2018}} |
</ref>{{better source needed|date=June 2018}} |
||
In classical Hindu scriptures ( |
In classical Hindu scriptures ([[Mahabharata]], [[Harivamsa]]), the creation of the nakshatras is attributed to [[Daksha]] and [[Asikni (goddess)|Asikini]].<ref>{{Cite book |last=Moor |first=Edward |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=5kJDAAAAYAAJ&dq=Daksha+Nakshatra&pg=PA291 |title=The Hindu Pantheon |date=1810 |publisher=J. Johnson |pages=291 |language=en}}</ref> They are daughters of Daksha and Asikini and are wives of [[Chandra]], who is the Moon God. |
||
==In the Atharvaveda== |
==In the Atharvaveda== |
||
| Line 83: | Line 83: | ||
# [[Ashvini]] |
# [[Ashvini]] |
||
# [[Bharani]] |
# [[Bharani]] |
||
# [[Krttika]] |
|||
# [[Kṛttikā]] (the [[Pleiades]]) |
|||
# [[Rohini (nakshatra)| |
# [[Rohini (nakshatra)|Rohini]] |
||
# [[ |
# [[Mrigashirsha]] |
||
# [[Ardra Nakshatra| |
# [[Ardra Nakshatra|Ardra]] |
||
# [[Punarvasu]] |
# [[Punarvasu]] |
||
# [[Pushya]] |
# [[Pushya]] |
||
# [[Ashlesha (nakshatra)| |
# [[Ashlesha (nakshatra)|Aslesha]] |
||
# [[Magha (nakshatra)| |
# [[Magha (nakshatra)|Magha]] |
||
# |
# Purva Phalguni |
||
# |
# Uttara Phalguni |
||
# [[Hasta (nakshatra)|Hasta]] |
# [[Hasta (nakshatra)|Hasta]] |
||
# [[Chitra]] |
|||
# [[#List of Nakshatras|Chitrā]] ([[Spica]]) |
|||
# [[Svati| |
# [[Svati|Svati]] |
||
# [[ |
# [[Vishakha]] |
||
# [[Anuradha (nakshatra)| |
# [[Anuradha (nakshatra)|Anuradha]] |
||
# [[Jyeshtha (nakshatra)| |
# [[Jyeshtha (nakshatra)|Jyeshtha]] |
||
# [[Mula (nakshatra)| |
# [[Mula (nakshatra)|Mula]] |
||
# [[ |
# [[Purva Ashadha]] |
||
# [[Uttara Ashadha]] |
# [[Uttara Ashadha]] |
||
# [[Shravana]] |
# [[Shravana]] |
||
# [[Dhanishta]] |
# [[Dhanishta]] |
||
# [[Shatabhisha |
# [[Shatabhisha]] |
||
# [[Purva Bhadrapada]] |
# [[Purva Bhadrapada]] |
||
# [[ |
# [[Uttara Bhadrapada]] |
||
# [[Revati (nakshatra)|Revati]] |
# [[Revati (nakshatra)|Revati]] |
||
}} |
}} |
||
This 27 |
This 27 day time cycle has been taken to mean a particular group of stars. The relationship to the stars really has to do with the periodicity with which the Moon travels over time and through space past the field of the specific stars called nakshatras. Hence, the stars are more like numbers on a clock through which the hands of time pass (the moon). This concept is described by J. Mercay (2012) in connection with ''[[Surya Siddhanta]]''.<ref name="mercay"> |
||
{{cite book |
{{cite book |
||
|author=Mercay, Jessie |
|author=Mercay, Jessie |
||
| Line 177: | Line 177: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
| 1 |
| 1 |
||
||'''[[Ashvini|Aśvini]]'''<br/> |
||'''[[Ashvini|Aśvini]]'''<br/> |
||
||[[Sheratan|β]] and [[Mesarthim|γ]] [[Aries (constellation)|Arietis]] |
||[[Sheratan|β]] and [[Mesarthim|γ]] [[Aries (constellation)|Arietis]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Ketu (mythology)|Ketu]] (South lunar node) |
||
*''Symbol'': Horse's head |
*''Symbol'': Horse's head |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Ashvins]], the horse-headed twins who are physicians to the gods |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 0° – 13°20′ |
*''Indian zodiac'': 0° – 13°20′ Mesha |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 26° Aries – 9°20′ Taurus |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 26° Aries – 9°20′ Taurus |
||
||[[Image:Aries constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||[[Image:Aries constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 2 |
| 2 |
||
||'''[[Bharani]]'''<br/>" |
||'''[[Bharani]]'''<br/>"the bearer" |
||
||[[35 Arietis|35]], [[39 Arietis|39]], and [[41 Arietis|41]] [[Aries (constellation)|Arietis]] |
||[[35 Arietis|35]], [[39 Arietis|39]], and [[41 Arietis|41]] [[Aries (constellation)|Arietis]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Shukra]] ([[Venus]]) |
||
*''Symbol'': [[Yoni]], the female organ of reproduction |
*''Symbol'': [[Yoni]], the female organ of reproduction |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Yama]], [[god of death]] or [[Dharma]] |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 13° 20′ – 26°40′ |
*''Indian zodiac'': 13° 20′ – 26°40′ Mesha |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 9° 20′ – 22° 40′ Taurus |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 9° 20′ – 22° 40′ Taurus |
||
||[[Image:Aries constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||[[Image:Aries constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 3 |
| 3 |
||
||'''[[Krittika|Kṛttikā]]'''<br/> |
||'''[[Krittika|Kṛttikā]]'''<br/>an old name of the Pleiades; personified as the nurses of ''Kārttikeya'', a son of Shiva. |
||
||[[Pleiades]] |
||[[Pleiades]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Surya]] ([[Solar deity|Sun]]) |
||
*''Symbol'': [[Knife]] or [[spear]] |
*''Symbol'': [[Knife]] or [[spear]] |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Agni]], god of fire |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 26°40′ |
*''Indian zodiac'': 26°40′ Mesha – 10° Vrishabha |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 22° 40′ Taurus – 6° Gemini |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 22° 40′ Taurus – 6° Gemini |
||
||[[Image:Taurus constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||[[Image:Taurus constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 4 |
| 4 |
||
||'''[[Rohini (nakshatra)|Rohiṇi]]'''<br>" |
||'''[[Rohini (nakshatra)|Rohiṇi]]'''<br>"the red one", a name of [[Aldebaran]]. Also known as ''brāhmī'' |
||
||[[Aldebaran]] |
||[[Aldebaran]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Chandra]] ([[Moon]]) |
||
*''Symbol'': Cart or [[chariot]], [[temple]], [[banyan tree]] |
*''Symbol'': Cart or [[chariot]], [[temple]], [[banyan tree]] |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Prajapati]], [[Creator deity|the Creator]] |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 10° – 23°20′ |
*''Indian zodiac'': 10° – 23°20′ Vrishabha |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 6° – 19°20′ Gemini |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 6° – 19°20′ Gemini |
||
||[[Image:Taurus constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||[[Image:Taurus constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 5 |
| 5 |
||
||'''[[Mrigashīrsha|Mṛgaśīrā]]'''<br/>" |
||'''[[Mrigashīrsha|Mṛgaśīrā]]'''<br/>"the deer's head". Also known as ''āgrahāyaṇī'' |
||
||[[Meissa|λ]], [[Phi Orionis|φ]] [[Orion (constellation)|Orionis]] |
||[[Meissa|λ]], [[Phi Orionis|φ]] [[Orion (constellation)|Orionis]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Mangala]] ([[Mars]]) |
||
*''Symbol'': Deer's head |
*''Symbol'': Deer's head |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Soma (deity)|Soma]], [[Chandra]], the Moon god |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 23° 20′ |
*''Indian zodiac'': 23° 20′ Vrishabha – 6° 40′ Mithuna |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 19° 20′ Gemini – 2° 40′ Cancer |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 19° 20′ Gemini – 2° 40′ Cancer |
||
||[[Image:Orion constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||[[Image:Orion constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 6 |
| 6 |
||
||'''[[Ardra Nakshatra|Ārdrā]]'''<br/>" |
||'''[[Ardra Nakshatra|Ārdrā]]'''<br/>"the moist one" |
||
||[[Betelgeuse]] |
||[[Betelgeuse]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Rahu]] (North lunar node) |
||
*''Symbol'': Teardrop, diamond, a human head |
*''Symbol'': Teardrop, diamond, a human head |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Rudra]], the storm god |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 6° 40′ – 20° |
*''Indian zodiac'': 6° 40′ – 20° Mithuna |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 2° 40′ – 16° Cancer |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 2° 40′ – 16° Cancer |
||
||[[Image:Orion constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||[[Image:Orion constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 7 |
| 7 |
||
||'''[[Punarvasu]]'''<br/>" |
||'''[[Punarvasu]]''' (dual)<br/>"the two restorers of goods", also known as ''yamakau'' "the two chariots" |
||
||[[Castor (star)|Castor]] and [[Pollux (star)|Pollux]] |
||[[Castor (star)|Castor]] and [[Pollux (star)|Pollux]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Bṛhaspati|Guru]] ([[Jupiter]]) |
||
*''Symbol'' : Bow and quiver |
*''Symbol'' : Bow and quiver |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Bhūmi|Aditi]], mother of the gods |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 20° |
*''Indian zodiac'': 20° Mithuna – 3°20′ Karka |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 16° – 29°20′ Cancer |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 16° – 29°20′ Cancer |
||
||[[File:Gemini constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||[[File:Gemini constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 8 |
| 8 |
||
||'''[[Pushya|Puṣya]]'''<br/>" |
||'''[[Pushya|Puṣya]]'''<br/>"the nourisher", also known as ''sidhya'' or ''tiṣya'' |
||
||[[Asellus Borealis|γ]], [[Asellus Australis|δ]] and [[Theta Cancri|θ]] [[Cancer (constellation)|Cancri]] |
||[[Asellus Borealis|γ]], [[Asellus Australis|δ]] and [[Theta Cancri|θ]] [[Cancer (constellation)|Cancri]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Shani]] ([[Saturn]]) |
||
*''Symbol'': Cow's udder, [[Lotus Flower|lotus]], arrow and circle |
*''Symbol'': Cow's udder, [[Lotus Flower|lotus]], arrow and circle |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Bṛhaspati]], priest of the gods |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 3° 20′ – 16° 40′ |
*''Indian zodiac'': 3° 20′ – 16° 40′ Karka |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 29° 20′ Cancer – 12° 40′ Leo |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 29° 20′ Cancer – 12° 40′ Leo |
||
||[[Image:Cancer constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||[[Image:Cancer constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 9 |
| 9 |
||
||'''[[Āshleshā|Āśleṣā]]'''<br/>" |
||'''[[Āshleshā|Āśleṣā]]'''<br/>"the embrace" |
||
||[[Delta Hydrae|δ]], [[Epsilon Hydrae|ε]], [[Eta Hydrae|η]], [[Rho Hydrae|ρ]], and [[Sigma Hydrae|σ]] [[Hydra (constellation)|Hydrae]] |
||[[Delta Hydrae|δ]], [[Epsilon Hydrae|ε]], [[Eta Hydrae|η]], [[Rho Hydrae|ρ]], and [[Sigma Hydrae|σ]] [[Hydra (constellation)|Hydrae]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Budha]] ([[Mercury (mythology)|Mercury]]) |
||
*''Symbol'': Serpent |
*''Symbol'': Serpent |
||
*Rigvedic name: Sarpas or [[Nāga|Nagas]], deified snakes |
|||
*''Deity'': [[Nāga|Nagas]], divine race of half-human, half-serpent beings that reside in the [[Patala]] |
|||
*''Indian zodiac'': 16° 40′ – 30° |
*''Indian zodiac'': 16° 40′ – 30° Karka |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 12° 40′ – 26° Leo |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 12° 40′ – 26° Leo |
||
||[[Image:Hydra constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||[[Image:Hydra constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 10 |
| 10 |
||
||'''[[Maghā]]'''<br/>" |
||'''[[Maghā]]'''<br/>"the bountiful" |
||
||[[Regulus]] |
||[[Regulus]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Ketu (mythology)|Ketu]] (South lunar node) |
||
*''Symbol'': Royal Throne |
*''Symbol'': Royal Throne |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Pitrs]], 'The Fathers', family ancestors |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 0° – 13° 20′ |
*''Indian zodiac'': 0° – 13° 20′ Simha |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 26° Leo – 9° 20′ Virgo |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 26° Leo – 9° 20′ Virgo |
||
||[[Image:Leo constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||[[Image:Leo constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 11 |
| 11 |
||
||''' |
||'''Pūrva Phalgunī'''<br>"first reddish one" |
||
||[[Zosma|δ]] and [[Theta Leonis|θ]] [[Leo (constellation)|Leonis]] |
||[[Zosma|δ]] and [[Theta Leonis|θ]] [[Leo (constellation)|Leonis]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Shukra]] ([[Venus]]) |
||
*''Symbol'': Front legs of bed, hammock, fig tree |
*''Symbol'': Front legs of bed, hammock, fig tree |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Aryaman]], god of marital bliss and prosperity |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 13° 20′ – 26°40′ |
*''Indian zodiac'': 13° 20′ – 26°40′ Simha |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 9° 20′ – 22°40′ Virgo |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 9° 20′ – 22°40′ Virgo |
||
|| [[Image:Leo constellation map.svg|100px]] |
|| [[Image:Leo constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 12 |
| 12 |
||
||''' |
||'''Uttara Phalgunī'''<br/>"second reddish one" |
||
||[[Denebola]] |
||[[Denebola]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Surya]] ([[Solar deity|Sun]]) |
||
*''Symbol'': Four legs of bed, hammock |
*''Symbol'': Four legs of bed, hammock |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Bhaga]], god of patronage and favours |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 26° 40′ |
*''Indian zodiac'': 26° 40′ Simha- 10° Kanya |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 22° 40′ Virgo – 6° Libra |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 22° 40′ Virgo – 6° Libra |
||
|| [[Image:Leo constellation map.svg|100px]] |
|| [[Image:Leo constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 13 |
| 13 |
||
||'''[[Hasta (nakshatra)|Hasta]]'''<br/>" |
||'''[[Hasta (nakshatra)|Hasta]]'''<br/>"the hand" |
||
||[[Alpha Corvi|α]], [[Beta Corvi|β]], [[Gienah|γ]], [[Algorab|δ]] and [[Minkar|ε]] [[Corvus (constellation)|Corvi]] |
||[[Alpha Corvi|α]], [[Beta Corvi|β]], [[Gienah|γ]], [[Algorab|δ]] and [[Minkar|ε]] [[Corvus (constellation)|Corvi]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Chandra]] ([[Moon]]) |
||
*''Symbol'': Hand or fist |
*''Symbol'': Hand or fist |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Savitr]], the Sun god |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 10° – 23° 20′ |
*''Indian zodiac'': 10° – 23° 20′ Kanya |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 6° – 19° 20′ Libra |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 6° – 19° 20′ Libra |
||
||[[Image:Corvus constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||[[Image:Corvus constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 14 |
| 14 |
||
||'''[[Chitra (nakshatra)|Chitrā]]'''<br/>" |
||'''[[Chitra (nakshatra)|Chitrā]]'''<br/>"the bright one", a name of Spica |
||
||[[Spica]] |
||[[Spica]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Mangala]] ([[Mars]]) |
||
*''Symbol'': Bright jewel or pearl |
*''Symbol'': Bright jewel or pearl |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Tvastar]], [[Vishvakarman|Vishwakarma]] |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 23° 20′ |
*''Indian zodiac'': 23° 20′ Kanya – 6° 40′ Tula |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 19° 20′ Libra – 2° 40′ Scorpio |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 19° 20′ Libra – 2° 40′ Scorpio |
||
|| [[Image:Virgo constellation map.svg|100px]] |
|| [[Image:Virgo constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 15 |
| 15 |
||
||'''[[Svati|Svātī]]'''<br/>" |
||'''[[Svati|Svātī]]'''<br/>"Su-Ati (Sanskrit) Very good" name of Arcturus |
||
||[[Arcturus]] |
||[[Arcturus]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Rahu]] (North lunar node) |
||
*''Symbol'': Shoot of plant, coral |
*''Symbol'': Shoot of plant, coral |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Vayu]], the Wind god |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 6° 40′ – 20° |
*''Indian zodiac'': 6° 40′ – 20° Tula |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 2° 40′ – 16° Scorpio |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 2° 40′ – 16° Scorpio |
||
|| [[Image:Bootes constellation map.png|100px]] |
|| [[Image:Bootes constellation map.png|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 16 |
| 16 |
||
||'''[[Vishākhā|Viśākhā]]'''<br/>" |
||'''[[Vishākhā|Viśākhā]]'''<br/>"forked, having branches"; |
||
|| [[Alpha Librae|α]], [[Beta Librae|β]], [[Gamma Librae|γ]] and [[Iota Librae|ι]] [[Libra (constellation)|Librae]] |
|| [[Alpha Librae|α]], [[Beta Librae|β]], [[Gamma Librae|γ]] and [[Iota Librae|ι]] [[Libra (constellation)|Librae]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Bṛhaspati|Guru]] ([[Jupiter]]) |
||
*''Symbol'': Triumphal arch, potter's wheel |
*''Symbol'': Triumphal arch, potter's wheel |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Indra]], chief of the gods; [[Agni]], god of Fire |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 20° |
*''Indian zodiac'': 20° Tula – 3° 20′ Vrishchika |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 16° – 29° 20′ Scorpio |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 16° – 29° 20′ Scorpio |
||
||[[Image:Libra constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||[[Image:Libra constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 17 |
| 17 |
||
||'''[[Anuradha (nakshatra)|Anurādhā]]'''<br/> " |
||'''[[Anuradha (nakshatra)|Anurādhā]]'''<br/> "following ''Indra''" |
||
|| [[Acrab|β]], [[Dschubba|δ]] and [[Pi Scorpii|π]] [[Scorpius (constellation)|Scorpionis]] |
|| [[Acrab|β]], [[Dschubba|δ]] and [[Pi Scorpii|π]] [[Scorpius (constellation)|Scorpionis]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Shani]] ([[Saturn]]) |
||
*''Symbol'': Triumphal archway, lotus, bamboo |
*''Symbol'': Triumphal archway, lotus, bamboo |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Mitra (Vedic)|Mitra]], one of Adityas of friendship and partnership |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 3° 20′ – 16° 40′ |
*''Indian zodiac'': 3° 20′ – 16° 40′ Vrishchika |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 29° 20′ Scorpio – 12° 40′ Sagittarius |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 29° 20′ Scorpio – 12° 40′ Sagittarius |
||
|| [[File:Scorpius constellation map.svg|100px]] |
|| [[File:Scorpius constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 18 |
| 18 |
||
||'''[[Jyeshtha (nakshatra)|Jyeṣṭha]]'''<br/> " |
||'''[[Jyeshtha (nakshatra)|Jyeṣṭha]]'''<br/> "the eldest, most excellent" |
||
|| [[Antares|α]], [[Sigma Scorpii|σ]], and [[Tau Scorpii|τ]] [[Scorpius (constellation)|Scorpionis]] |
|| [[Antares|α]], [[Sigma Scorpii|σ]], and [[Tau Scorpii|τ]] [[Scorpius (constellation)|Scorpionis]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Budha]] ([[Mercury (mythology)|Mercury]]) |
||
*''Symbol'': circular amulet, umbrella, earring |
*''Symbol'': circular amulet, umbrella, earring |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Indra]], chief of the gods |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 16° 40′ – 30° |
*''Indian zodiac'': 16° 40′ – 30° Vrishchika |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 12° 40′ – 26° Sagittarius |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 12° 40′ – 26° Sagittarius |
||
|| [[Image:Scorpius constellation map.svg|100px]] |
|| [[Image:Scorpius constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 19 |
| 19 |
||
||'''[[Mula (astrology)|Mūlā]]'''<br/>" |
||'''[[Mula (astrology)|Mūlā]]'''<br/>"the root" |
||
|| [[Epsilon Scorpii|ε]], [[Zeta Scorpii|ζ]], [[Eta Scorpii|η]], [[Sargas|θ]], ι, [[Girtab|κ]], [[Shaula|λ]], [[Mu Scorpii|μ]] and [[Jabbah|ν]] [[Scorpius (constellation)|Scorpionis]] |
|| [[Epsilon Scorpii|ε]], [[Zeta Scorpii|ζ]], [[Eta Scorpii|η]], [[Sargas|θ]], ι, [[Girtab|κ]], [[Shaula|λ]], [[Mu Scorpii|μ]] and [[Jabbah|ν]] [[Scorpius (constellation)|Scorpionis]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Ketu (mythology)|Ketu]] (South lunar node) |
||
*''Symbol'': Bunch of roots tied together, elephant goad |
*''Symbol'': Bunch of roots tied together, elephant goad |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Nirṛti (goddess)|Nirrti]], peak of material achievement and the beginning of the spiritual impulse |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 0° – 13° 20′ |
*''Indian zodiac'': 0° – 13° 20′ Dhanus |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 26° Sagittarius – 9° 20′ Capricorn |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 26° Sagittarius – 9° 20′ Capricorn |
||
|| [[Image:Scorpius constellation map.svg|100px]] |
|| [[Image:Scorpius constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 20 |
| 20 |
||
||'''[[Purva Ashadha|Pūrva Āṣāḍhā]]'''<br/>" |
||'''[[Purva Ashadha|Pūrva Āṣāḍhā]]'''<br/>"first of the ''aṣāḍhā''", ''aṣāḍhā'' "the invincible one" being the name of a constellation |
||
||[[Kaus Medius|δ]] and [[Kaus Australis|ε]] [[Sagittarius (constellation)|Sagittarii]] |
||[[Kaus Medius|δ]] and [[Kaus Australis|ε]] [[Sagittarius (constellation)|Sagittarii]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Shukra]] ([[Venus]]) |
||
*''Symbol'': Elephant tusk, fan, winnowing basket |
*''Symbol'': Elephant tusk, fan, winnowing basket |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Ap (water)|Apah]], god of Water |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 13° 20′ – 26° 40′ |
*''Indian zodiac'': 13° 20′ – 26° 40′ Dhanus |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 9° 20′ – 22° 40′ Capricorn |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 9° 20′ – 22° 40′ Capricorn |
||
|| [[Image:Sagittarius constellation map.svg|100px]] |
|| [[Image:Sagittarius constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 21 |
| 21 |
||
||'''[[Uttara Ashadha|Uttara Āṣāḍhā]]'''<br/>" |
||'''[[Uttara Ashadha|Uttara Āṣāḍhā]]'''<br/>"Later invincible" |
||
||[[Ascella|ζ]] and [[Sigma Sagittarii|σ]] [[Sagittarius (constellation)|Sagittarii]] |
||[[Ascella|ζ]] and [[Sigma Sagittarii|σ]] [[Sagittarius (constellation)|Sagittarii]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Surya]] ([[Solar deity|Sun]]) |
||
*''Symbol'': Elephant tusk, small bed |
*''Symbol'': Elephant tusk, small bed |
||
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Visvedevas]], universal gods |
|||
*''Deity'': [[Visvedevas]], the most comprehensive gathering of the gods, a classification in which no deity is stated to be omitted |
|||
*''Indian zodiac'': 26° 40′ |
*''Indian zodiac'': 26° 40′ Dhanus – 10° Makara |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 22° 40′ Capricorn – 6° Aquarius |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 22° 40′ Capricorn – 6° Aquarius |
||
|| [[Image:Sagittarius constellation map.svg|100px]] |
|| [[Image:Sagittarius constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 22 |
|||
| *{{refn|group=note| Abhijit is the 22nd lunar mansion in the Indian system of 28 nakshatras. According to traditional beliefs, it is not necessarily a separate nakshatra per se, but rather a division within the sidereal Capricorn sign, spanning from the fourth pada of Uttara Ashadha to the first pada of Shravana.}} |
|||
||'''[[Abhijit (nakshatra)|Abhijit]]'''<br/> |
||'''[[Abhijit (nakshatra)|Abhijit]]'''<br/> |
||
||[[Vega|ζ]] and [[Lyra|σ]] [[Lyra (constellation)|Lyrae]] |
||[[Vega|ζ]] and [[Lyra|σ]] [[Lyra (constellation)|Lyrae]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Brahma]] |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 6° 40′ – 10° 53′ |
*''Indian zodiac'': 6° 40′ Makara – 10° 53′ Makara |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 2° 40′ – 6° 53′ Aquarius |
|||
|| [[Image:Lyra constellation map.svg|100px]] |
|| [[Image:Lyra constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| 23 |
||
||'''[[Shravana|Śravaṇa]]'''<br/> |
||'''[[Shravana|Śravaṇa]]'''<br/> |
||
||[[Altair|α]], [[Alshain|β]] and [[Tarazed|γ]] [[Aquila (constellation)|Aquilae]] |
||[[Altair|α]], [[Alshain|β]] and [[Tarazed|γ]] [[Aquila (constellation)|Aquilae]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Chandra]] ([[Moon]]) |
||
*''Symbol'': Ear or Three Footprints |
*''Symbol'': Ear or Three Footprints |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Vishnu]], preserver of universe |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 10° – 23° 20′ |
*''Indian zodiac'': 10° – 23° 20′ Makara |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 6° – 19° 20′ Aquarius |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 6° – 19° 20′ Aquarius |
||
|| [[Image:Aquila constellation map.svg|100px]] |
|| [[Image:Aquila constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| 24 |
||
||'''[[Dhanishta|Dhaniṣṭhā]]''' <br/>" |
||'''[[Dhanishta|Dhaniṣṭhā]]''' <br/>"most famous", also ''Shravishthā'' "swiftest" |
||
||[[Alpha Delphini|α]], [[Beta Delphini|β]], [[Gamma Delphini|γ]] and [[Delta Delphini|δ]] [[Delphinus|Delphini]] |
||[[Alpha Delphini|α]], [[Beta Delphini|β]], [[Gamma Delphini|γ]] and [[Delta Delphini|δ]] [[Delphinus|Delphini]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Mangala]] ([[Mars]]) |
||
*''Symbol'': Drum or flute |
*''Symbol'': Drum or flute |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': Eight [[vasu]]s, deities of earthly abundance |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 23° 20′ |
*''Indian zodiac'': 23° 20′ Makara – 6° 40′ Kumbha |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'' 19° 20′ Aquarius – 2° 40′ Pisces |
*''Tropical zodiac'' 19° 20′ Aquarius – 2° 40′ Pisces |
||
|| [[Image:Delphinus constellation map.svg|100px]] |
|| [[Image:Delphinus constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| 25 |
||
||'''[[Shatabhisha|Śatabhiṣa]]'''<br/>" |
||'''[[Shatabhisha|Śatabhiṣa]]'''<br/>"Comprising a hundred physicians" |
||
|| [[Sadachbia]] |
|| [[Sadachbia]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Rahu]] (North lunar node) |
||
*''Symbol'': Empty circle, 1,000 flowers or stars |
*''Symbol'': Empty circle, 1,000 flowers or stars |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Varuna]], god of celestial waters |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 6° 40′ – 20° |
*''Indian zodiac'': 6° 40′ – 20° Kumbha |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 2° 40′ – 16° Pisces |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 2° 40′ – 16° Pisces |
||
|| [[File:Aquarius constellation map.svg|100px]] |
|| [[File:Aquarius constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| 26 |
||
||'''[[Purva Bhadrapada|Pūrva Bhādrapada]]'''<br/>" |
||'''[[Purva Bhadrapada|Pūrva Bhādrapada]]'''<br/>"the first of the blessed feet" |
||
|| [[Alpha Pegasi|α]] and [[Scheat|β]] [[Pegasus (constellation)|Pegasi]] |
|| [[Alpha Pegasi|α]] and [[Scheat|β]] [[Pegasus (constellation)|Pegasi]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Bṛhaspati|Guru]] ([[Jupiter]]) |
||
*''Symbol'': Swords or two front legs of funeral cot, man with two faces |
*''Symbol'': Swords or two front legs of funeral cot, man with two faces |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Ekapada|Ajaikapada]], an ancient fire dragon{{Citation needed|date=October 2022}} |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 20° |
*''Indian zodiac'': 20° Kumbha – 3° 20′ Meena |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 16° – 29° 20′ Pisces |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 16° – 29° 20′ Pisces |
||
|| [[Image:Pegasus constellation map.svg|100px]] |
|| [[Image:Pegasus constellation map.svg|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| 27 |
||
||'''[[Uttara Bhādrapadā|Uttara Bhādrapada]]'''<br/>" |
||'''[[Uttara Bhādrapadā|Uttara Bhādrapada]]'''<br/>"the second of the blessed feet" |
||
|| [[Gamma Pegasi|γ]] [[Pegasus (constellation)|Pegasi]] and [[Alpheratz|α]] [[Andromeda (constellation)|Andromedae]] |
|| [[Gamma Pegasi|γ]] [[Pegasus (constellation)|Pegasi]] and [[Alpheratz|α]] [[Andromeda (constellation)|Andromedae]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Shani]] ([[Saturn]]) |
||
*''Symbol'': Twins, back legs of funeral cot, snake in the water |
*''Symbol'': Twins, back legs of funeral cot, snake in the water |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': Ahirbudhnya, serpent or dragon of the deep |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 3° 20′ – 16° 40′ |
*''Indian zodiac'': 3° 20′ – 16° 40′ Meena |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 29° 20′ Pisces – 12° 40′ Aries |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 29° 20′ Pisces – 12° 40′ Aries |
||
|| [[Image:Andromeda constellation map (1).png|100px]] |
|| [[Image:Andromeda constellation map (1).png|100px]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| 28 |
||
||'''[[Revati (nakshatra)|Revatī]]'''<br/> |
||'''[[Revati (nakshatra)|Revatī]]'''<br/>"prosperous" |
||
|| [[Zeta Piscium|ζ]] [[Pisces (constellation)|Piscium]] |
|| [[Zeta Piscium|ζ]] [[Pisces (constellation)|Piscium]] |
||
|| |
|| |
||
*''Astrological |
*''Astrological Mate'': [[Budha]] ([[Mercury (mythology)|Mercury]]) |
||
*''Symbol'': Fish or a pair of fish, drum |
*''Symbol'': Fish or a pair of fish, drum |
||
*'' |
*''Rigvedic name'': [[Pushan]], nourisher, the protective deity |
||
*''Indian zodiac'': 16° 40′ – 30° |
*''Indian zodiac'': 16° 40′ – 30° Meena |
||
*''Tropical zodiac'': 12° 40′ – 26° Aries |
*''Tropical zodiac'': 12° 40′ – 26° Aries |
||
|| [[Image:Pisces constellation map.png|100px]] |
|| [[Image:Pisces constellation map.png|100px]] |
||
| Line 562: | Line 561: | ||
==Notes== |
==Notes== |
||
{{reflist|group=note}} |
|||
{{notelist}} |
{{notelist}} |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
Revision as of 08:38, 15 September 2024
| Nakshatras |
|---|
|
Nakshatra (Template:Lang-sa) is the term for lunar mansion in Hindu astrology. A nakshatra is one of 27 sectors along the ecliptic. Their names are related to a prominent star or asterisms in or near the respective sectors. In essence (in Western astronomical terms), a nakshatra simply is a constellation. Every nakshatra is divided into four padas (lit. "steps") related to the Chara Dhama, a set of four pilgrimage sites in India.
The starting point for the nakshatras according to Vedas is "Krittika" (it has been argued because the Pleiades may have started the year at the time the Vedas were compiled, presumably at the vernal equinox), but, in more recent compilations, the start of the nakshatras list is the point on the ecliptic directly opposite to the star Spica called Chitra in Sanskrit, which would be Ashvini, a part of the modern constellation Aries, and these compilations therefore may have been compiled during the centuries when the sun was passing through the area of the constellation Aries at the time of the vernal equinox. This version may have been called Meshādi or the "start of Aries".[1][full citation needed]
The first astronomical text that lists them is the Vedanga Jyotisha.[2][better source needed]
In classical Hindu scriptures (Mahabharata, Harivamsa), the creation of the nakshatras is attributed to Daksha and Asikini.[3] They are daughters of Daksha and Asikini and are wives of Chandra, who is the Moon God.
In the Atharvaveda

In the Atharvaveda (Shaunakiya recension, hymn 19.7) a list of 27 stars or asterisms is given, many of them corresponding to the later nakshatras:[4][a]
- Ashvini
- Bharani
- Krttika
- Rohini
- Mrigashirsha
- Ardra
- Punarvasu
- Pushya
- Aslesha
- Magha
- Purva Phalguni
- Uttara Phalguni
- Hasta
- Chitra
- Svati
- Vishakha
- Anuradha
- Jyeshtha
- Mula
- Purva Ashadha
- Uttara Ashadha
- Shravana
- Dhanishta
- Shatabhisha
- Purva Bhadrapada
- Uttara Bhadrapada
- Revati
This 27 day time cycle has been taken to mean a particular group of stars. The relationship to the stars really has to do with the periodicity with which the Moon travels over time and through space past the field of the specific stars called nakshatras. Hence, the stars are more like numbers on a clock through which the hands of time pass (the moon). This concept is described by J. Mercay (2012) in connection with Surya Siddhanta.[5]
List of Nakshatras

In Hindu astronomy, there was an older tradition of 28 Nakshatras which were used as celestial markers in the heavens. When these were mapped into equal divisions of the ecliptic, a division of 27 portions was adopted since that resulted in a clearer definition of each portion (i.e. segment) subtending 13° 20′ (as opposed to 12° 51+3⁄7′ in the case of 28 segments). In the process, the Nakshatra Abhijit was left out without a portion.[6]: 179 However, the Abhijit nakshatra becomes important while deciding on the timing of an auspicious event. The Surya Siddhantha concisely specifies the coordinates of the twenty-seven Nakshatras.[6]: 211
It is noted above that with the older tradition of 28 Nakshatras each equal segment would subtend 12.85 degrees or 12° 51′. But the 28 Nakshatra were chosen at a time when the Vedic month was recognised as having exactly 30 days. In India and China the original 28 lunar mansions were not equal. Weixing Nui provides a list of the extent of the original 28 Nakshatras expressed in Muhurtas (with one Muhurta = 48 minutes of arc). Hindu texts note there were 16 Nakshatras of 30 Muhurtas, 6 of 45 Muhurtas, 5 of 15 Muhurtas and one of 6 Muhurtas.
The 28 mansions of the 360° lunar zodiac total 831 Muhurtas or 27.7 days. This is sometimes described as an inaccurate estimate of our modern sidereal period of 27.3 days, but using the ancient Indian calendar with Vedic months of 30 days and a daily movement of the Moon of 13 degrees, this early designation of a sidereal month of 831 Muhurtas or 27.7 days is very precise.[b][7][full citation needed] Later some Indian savants dropped the Nakshatra named Abhijit to reduce the number of divisions to 27, but the Chinese retained all of their original 28 lunar mansions. These were grouped into four equal quarters which would have been fundamentally disrupted if it had been decided to reduce the number of divisions to 27.
Irrespective of the reason why ancient early Indian astronomers followed a Vedic calendar of exactly 12 months of 30 days it was this calendar and not a modern calendar of 365 days that they used for the astronomical calculations for the number of days taken for the Moon to complete one sidereal cycle of 360°. This is why initially they named 28 Nakshatras on their lunar zodiac.[8]
The following list of nakshatras gives the corresponding regions of sky, per Basham (1954).[9]
| No. | Name | Associated stars | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aśvini |
β and γ Arietis | 
| |
| 2 | Bharani "the bearer" |
35, 39, and 41 Arietis | 
| |
| 3 | Kṛttikā an old name of the Pleiades; personified as the nurses of Kārttikeya, a son of Shiva. |
Pleiades | 
| |
| 4 | Rohiṇi "the red one", a name of Aldebaran. Also known as brāhmī |
Aldebaran |
|

|
| 5 | Mṛgaśīrā "the deer's head". Also known as āgrahāyaṇī |
λ, φ Orionis | 
| |
| 6 | Ārdrā "the moist one" |
Betelgeuse | 
| |
| 7 | Punarvasu (dual) "the two restorers of goods", also known as yamakau "the two chariots" |
Castor and Pollux | 
| |
| 8 | Puṣya "the nourisher", also known as sidhya or tiṣya |
γ, δ and θ Cancri | 
| |
| 9 | Āśleṣā "the embrace" |
δ, ε, η, ρ, and σ Hydrae | 
| |
| 10 | Maghā "the bountiful" |
Regulus | 
| |
| 11 | Pūrva Phalgunī "first reddish one" |
δ and θ Leonis | 
| |
| 12 | Uttara Phalgunī "second reddish one" |
Denebola | 
| |
| 13 | Hasta "the hand" |
α, β, γ, δ and ε Corvi | 
| |
| 14 | Chitrā "the bright one", a name of Spica |
Spica |
|

|
| 15 | Svātī "Su-Ati (Sanskrit) Very good" name of Arcturus |
Arcturus | 
| |
| 16 | Viśākhā "forked, having branches"; |
α, β, γ and ι Librae | 
| |
| 17 | Anurādhā "following Indra" |
β, δ and π Scorpionis | 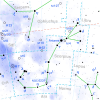
| |
| 18 | Jyeṣṭha "the eldest, most excellent" |
α, σ, and τ Scorpionis | 
| |
| 19 | Mūlā "the root" |
ε, ζ, η, θ, ι, κ, λ, μ and ν Scorpionis | 
| |
| 20 | Pūrva Āṣāḍhā "first of the aṣāḍhā", aṣāḍhā "the invincible one" being the name of a constellation |
δ and ε Sagittarii | 
| |
| 21 | Uttara Āṣāḍhā "Later invincible" |
ζ and σ Sagittarii |
|

|
| 22 | Abhijit |
ζ and σ Lyrae |
|

|
| 23 | Śravaṇa |
α, β and γ Aquilae | 
| |
| 24 | Dhaniṣṭhā "most famous", also Shravishthā "swiftest" |
α, β, γ and δ Delphini | 
| |
| 25 | Śatabhiṣa "Comprising a hundred physicians" |
Sadachbia | 
| |
| 26 | Pūrva Bhādrapada "the first of the blessed feet" |
α and β Pegasi |
|
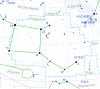
|
| 27 | Uttara Bhādrapada "the second of the blessed feet" |
γ Pegasi and α Andromedae | 
| |
| 28 | Revatī "prosperous" |
ζ Piscium | 
|
Padas (quarters)
Each of the 27 Nakshatras cover 13° 20’ of the ecliptic each. Each Nakshatra is also divided into quarters or padas of 3° 20’, and the below table lists the appropriate starting sound to name the child. The 27 nakshatras, each with 4 padas, give 108, which is the number of beads in a japa mala, representing all the elements (ansh) of Vishnu:
| # | Name | Pada 1 | Pada 2 | Pada 3 | Pada 4 | Vimsottari Lord | Ruling Deity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aśvini (अश्विनी) | चु Chu | चे Che | चो Cho | ला La | Ketu | Aswini Kumara |
| 2 | Bharaṇī (भरणी) | ली Li | लू Lu | ले Le | लो Lo | Venus | Yama |
| 3 | Kṛttikā (कृत्तिका) | अ A | ई I | उ U | ए E | Sun | Agni |
| 4 | Rohiṇī (रोहिणी) | ओ O | वा Va/Ba | वी Vi/Bi | वु Vu/Bu | Moon | Brahma |
| 5 | Mṛgaśīrṣā (मृगशीर्षा) | वे Ve/Be | वो Vo/Bo | का Ka | की Ke | Mars | Moon |
| 6 | Ārdrā (आर्द्रा) | कु Ku | घ Gha | ङ Ng/Na | छ Chha | Rahu | Shiva |
| 7 | Punarvasu (पुनर्वसु) | के Ke | को Ko | हा Ha | ही Hi | Jupiter | Aditi |
| 8 | Puṣya (पुष्य) | हु Hu | हे He | हो Ho | ड Da | Saturn | Brihaspati |
| 9 | Āśleṣā (आश्लेषा) | डी Di | डू Du | डे De | डो Do | Mercury | Rahu |
| 10 | Maghā (मघा) | मा Ma | मी Mi | मू Mu | मे Me | Ketu | Pitr |
| 11 | Pūrva or Pūrva Phālgunī (पूर्व फाल्गुनी) | नो Mo | टा Ta | टी Ti | टू Tu | Venus | Bhaga |
| 12 | Uttara or Uttara Phālgunī (उत्तर फाल्गुनी) | टे Te | टो To | पा Pa | पी Pi | Sun | Sun |
| 13 | Hasta (हस्त) | पू Pu | ष Sha | ण Na | ठ Tha | Moon | Savitr |
| 14 | Chitrā (चित्रा) | पे Pe | पो Po | रा Ra | री Ri | Mars | Vishwakarma |
| 15 | Svāti (स्वाति) | रू Ru | रे Re | रो Ro | ता Ta | Rahu | Vaayu |
| 16 | Vishākhā (विशाखा) | ती Ti | तू Tu | ते Te | तो To | Jupiter | Indra Agni |
| 17 | Anurādhā (अनुराधा) | ना Na | नी Ni | नू Nu | ने Ne | Saturn | Mitra |
| 18 | Jyeṣṭhā (ज्येष्ठा) | नो No | या Ya | यी Yi | यू Yu | Mercury | Indra |
| 19 | Mūla (मूल) | ये Ye | यो Yo | भा Bha | भी Bhi | Ketu | Varuna, Nirriti |
| 20 | Pūrva Aṣāḍhā (पूर्वाषाढ़ा) | भू Bhu | धा Dha | फा Bha/Pha | ढा Dha | Venus | Apah |
| 21 | Uttara Aṣāḍhā (उत्तराषाढ़ा) | भे Bhe | भो Bho | जा Ja | जी Ji | Sun | Brahma |
| 22 | Śrāvaṇa (श्रवण) | खी Ju/Khi | खू Je/Khu | खे Jo/Khe | खो Gha/Kho | Moon | Vishnu |
| 23 | Śrāviṣṭhā (श्रविष्ठा) or Dhaniṣṭhā (धनिष्ठा) | गा Ga | गी Gi | गु Gu | गे Ge | Mars | Vasu |
| 24 | Śatabhiṣā (शतभिषा) | गो Go | सा Sa | सी Si | सू Su | Rahu | Varuna |
| 25 | Pūrva Bhādrapadā (पूर्वभाद्रपदा) | से Se | सो So | दा Da | दी Di | Jupiter | Aja Ek Pada |
| 26 | Uttara Bhādrapadā (उत्तरभाद्रपदा) | दू Du | थ Tha | झ Jha | ञ Da/Tra | Saturn | Ahirbudhnya |
| 27 | Revati (रेवती) | दे De | दो Do | च Cha | ची Chi | Mercury | Pooshan |
See also
Nakshatra is one of the five elements of a Pañcāṅga. The other four elements:
Notes
- ^
From Griffith (1895) Hymns of the Atharva Veda:[4]
1 citrā́ṇi sākáṃ diví rocanā́ni sarīsr̥pā́ṇi bhúvane javā́ni
turmíśaṃ sumatím ichámāno áhāni gīrbhíḥ saparyāmi nā́kam
2 suhávam agne kŕ̥ttikā róhiṇī cā́stu bhadráṃ mr̥gáśiraḥ śám ārdrā́
púnarvasū sūnŕ̥tā cā́ru púṣyo bhānúr āśleṣā́ áyanaṃ maghā́ me
3 púṇyaṃ pū́rvā phálgunyau cā́tra hástaś citrā́ śivā́ svātí sukhó me astu
rā́dhe viśā́khe suhávānurādhā́ jyéṣṭhā sunákṣatram áriṣṭa mū́lam
4 ánnaṃ pū́rvā rāsatāṃ me aṣādhā́ ū́rjaṃ devy úttarā ā́ vahantu
abhijín me rāsatāṃ púṇyam evá śrávaṇaḥ śráviṣṭhāḥ kurvatāṃ supuṣṭím
5 ā́ me mahác chatábhiṣag várīya ā́ me dvayā́ próṣṭhapadā suśárma
ā́ revátī cāśvayújau bhágaṃ ma ā́ me rayíṃ bháraṇya ā́ vahantu[4]
- ^ The exact figure should be nearer 27.692308 days but 27.7 is near enough.
References
- ^ Vaid, Vashisht (2012). The Radiant Words of Love & Wisdom.
- ^ "Nakshatras and Upanakshatras". vedanet.com. American Institute of Vedic Studies. June 13, 2012. Archived from the original on March 22, 2015.
- ^ Moor, Edward (1810). The Hindu Pantheon. J. Johnson. p. 291.
- ^ a b c
Hymns of the Atharva Veda. Translated by Griffith, R.T.H. 1895.
- Original text via
- from
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)- collated with the edition of
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Original text via
- ^ Mercay, Jessie (2012). Fundamentals of Mamuni Mayans Vaastu Shastras: Building architecture of Sthapatya Veda and traditional Indian architecture. AUM Science and Technology publishers.
- ^ a b Burgess, Ebenezer (1858). Translation of the Surya Siddhantha, a Textbook of Hindu Astronomy. The American Oriental Society.
- ^ Weixing, Nui; Xiaoyuan, Jiang. Astronomy in the Sutras translated into Chinese.
- ^ Jones, H. (September 2018). "The Origin of the 28 Naksatras in Early Indian Astronomy and Astrology". Indian Journal of History of Science. 53 (3): 317–324. Bibcode:2018InJHS..53..317J. doi:10.16943/ijhs/2018/v53i3/49463.
- ^ Basham, Arthur Llewellyn (1954). "Appendix II: Astronomy". The Wonder that was India. Calcutta, IN: Rupa. p. 490.
External links
- Ahargana - The Astronomy of the Hindu Calendar: Nakshatra Explains Nakshatras by means of astronomical simulations created using Stellarium.