Talk:Genocide: Difference between revisions
Bogazicili (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 238: | Line 238: | ||
::#The problem I bring up is not necessarily the content '''but the sourcing'''. Nothing in your comments suggests that you recognize the WP:DUE and WP:NPOV problems with relying on editors finding and citing case studies to support particular points, which by definition will involve cherry-picking some examples over others. If the examples are covered in overviews that are about genocide in general, they are much more likely to be wp:due but then you should just cite the overview. |
::#The problem I bring up is not necessarily the content '''but the sourcing'''. Nothing in your comments suggests that you recognize the WP:DUE and WP:NPOV problems with relying on editors finding and citing case studies to support particular points, which by definition will involve cherry-picking some examples over others. If the examples are covered in overviews that are about genocide in general, they are much more likely to be wp:due but then you should just cite the overview. |
||
::Furthermore, the topic is very large and so is the number of possible sources. Just because you read something in one source does not mean it is the historical consensus, majority view, or wp:due for mention in the article. Contributing effectively requires a high degree of familiarity with the scholarly literature. For example, your recent edits remove citations to the 2022 version of the Oxford genocide studies handbook, in preference to the 2010 version, which is hard to explain. ([[User talk:Buidhe|t]] · [[Special:Contributions/Buidhe|c]]) '''[[User:buidhe|<span style="color: black">buidhe</span>]]''' 03:12, 30 October 2024 (UTC) |
::Furthermore, the topic is very large and so is the number of possible sources. Just because you read something in one source does not mean it is the historical consensus, majority view, or wp:due for mention in the article. Contributing effectively requires a high degree of familiarity with the scholarly literature. For example, your recent edits remove citations to the 2022 version of the Oxford genocide studies handbook, in preference to the 2010 version, which is hard to explain. ([[User talk:Buidhe|t]] · [[Special:Contributions/Buidhe|c]]) '''[[User:buidhe|<span style="color: black">buidhe</span>]]''' 03:12, 30 October 2024 (UTC) |
||
:::1) What is this 2020 paper? Unless it's a review article, it would be considered [[WP:Primary]]. This [https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Genocide&diff=1249549941&oldid=1249469537] was used in a 2023 genocide textbook. [https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003185291] |
|||
:::2) Nope. The beginning is about European colonialism. Then it switches to {{tq|While all empires...}}. I do not read that part as being about only "European colonial empires" [https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Genocide&diff=1249933218&oldid=1249886256] Should we specifically change it to "while all empires, including non-European ones"? |
|||
:::3) That's not how I read it. Such as is just an example. |
|||
:::4) Sources??? |
|||
:::5) There are overview sources. For example, {{tq|Beginning in the 15th century, European colonialism led to genocides of indigenous peoples. This has continued under settler colonies, such as United States and Australia, between 16th and 20th centuries.[47][149][150]}} 150 is from The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies, which is an overview source. [https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Genocide&oldid=1254128280#History] |
|||
:::Overall, I am very concerned that anything mentioning Native Americans or Americas are being removed. This is also evident even in the images in the article. There are no images from Americas. You said I'm cherry-picking with examples, but your examples seem cherry picked to me as well. In the methods sections, you put: {{tq|Cultural destruction, such as Indian residential schools, is often dependent on controlling the victims at a specific location.[123]}} The source is: Basso, Andrew R. (2024). Destroy Them Gradually: Displacement as Atrocity. That's not an overview source either. |
|||
:::We seem to be discussing this since September, so I requested [[WP:DRN]] [[User:Bogazicili|Bogazicili]] ([[User talk:Bogazicili|talk]]) 04:35, 30 October 2024 (UTC) |
|||
Revision as of 04:35, 30 October 2024
| This is the talk page for discussing improvements to the Genocide article. This is not a forum for general discussion of the article's subject. |
Article policies
|
| Find sources: Google (books · news · scholar · free images · WP refs) · FENS · JSTOR · TWL |
| Archives: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8Auto-archiving period: 30 days |
| Slow genocide was nominated for deletion. The discussion was closed on 9 November 2020 with a consensus to merge. Its contents were merged into Genocide. The original page is now a redirect to this page. For the contribution history and old versions of the redirected article, please see its history; for its talk page, see here. |
| This It is of interest to the following WikiProjects: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
This article links to one or more target anchors that no longer exist.
Please help fix the broken anchors. You can remove this template after fixing the problems. | Reporting errors |
Article needs a restructure
Here are some thoughts for overhauling the article:
- Origins of the concept—including etymology, historical context, Lemkin's role
- Genocide Convention and legal definition / legal cases (including alternative legal definition) —possible sub article Genocide (crime)
- Genocide studies—including alternative non-legal definitions, criticism of the concept of genocide
- Causes of genocide (eg. colonialism and genocide, war and genocide), perpetrator studies, genocide prevention
- Effects of genocide
- Genocide in history—focusing on trends rather than individual events (prehistoric origins, European colonialism, "century of genocide")
- Genocide recognition politics and genocide denial/justification
(t · c) buidhe 03:29, 6 September 2024 (UTC)
- I applaud the (much-needed) pruning and tidying of this (somewhat bloated) article.Pincrete (talk) 05:52, 9 September 2024 (UTC)
- Buidhe, thanks for the great work!
- Right now, history section is missing Part 2 Empire-Building And State Domination in The Cambridge World History of Genocide Vol. 2. For example, chapter 5: Atrocity and Genocide in Japan’s Invasion of Korea wouldn't be covered by European colonialism. I think we should add a sentence or two about that.
- We are also missing history after WW2. I guess this would be covered by Part 3 The Nation-State System During The Cold War in The Cambridge World History of Genocide Vol. 3 Bogazicili (talk) 20:23, 12 September 2024 (UTC)
European colonialism
Bogazicili Thanks for your edits but I think they are redundant. The entire idea of settler colonialism was invented in large part to signify that European colonialism did not end with the establishment of self governing states overseas. So all of the genocides in the Americas would be considered a product of European colonialism (although perhaps it could be Western colonialism to avoid confusion on this point). (t · c) buidhe 17:36, 12 September 2024 (UTC)
- No I don't think they are redundant. It's important to recognize that it has continued after the establishment of independent states, such as California genocide. "Western colonialism" sounds confusing. Is California genocide "Western colonialism"? Bogazicili (talk) 17:41, 12 September 2024 (UTC)
- "Colonial states" is also used in other sources. The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies, p. 349:
Bogazicili (talk) 17:46, 12 September 2024 (UTC)Colonial genocide has even become a widely used distinct category. However, it is important to note that genocidal violence in most of colonial Africa differs in some considerable ways from genocides committed in North American and Australian settler colonies: European colonization of Africa did not inevitably lead to the expulsion and/or annihilation of the indigenous populations. There are two reasons for this difference: whereas colonization preceded the formation of bureaucratic colonial states in America and Australia, European settlement followed the establishment of colonial administration in Africa. As a result, the colonial states in the British New World territories were almost unlimitedly dominated by settlers’ interests. In Africa, by contrast, the settlers’ influence and ability to fight and expel the Africans on their own was more restricted because the colonial states were still weak and their power relied on the cooperation with indigenous chiefs.
- Obviously not all situations are the same, but it's still redundant the way you worded it. Especially since Adhikari is discussing both of them in the paragraph you edited. (t · c) buidhe 17:56, 12 September 2024 (UTC)
- No, I don't see it as redundant. Maybe it is for you since you have a lot of prior knowledge. But this is an encyclopedia article. It should be written for a general audience.
- You can't assume that readers will know "The entire idea of settler colonialism was invented in large part to signify that European colonialism did not end with the establishment of self governing states overseas". Why do you not explain that in the article? The article is only 2k words. I also used a different source than Adhikari. It is better to use multiple sources. Bogazicili (talk) 18:01, 12 September 2024 (UTC)
- Obviously not all situations are the same, but it's still redundant the way you worded it. Especially since Adhikari is discussing both of them in the paragraph you edited. (t · c) buidhe 17:56, 12 September 2024 (UTC)
- I was about to post here myself, I also think the addition redundant, and possibly confusing. Any state which came about as a result of European colonialism, whether it was still wholly governed by by the 'mother country' or wholly self-governing (or an intermediate state such as some British 'colonies/dominions'), would be covered by the term 'European colonialism'. They may not all be identical in other respects, but they are all the result of such colonialism.
- Why would a reader understand/know that, for example, countries in the American continent were 'colonial states', but not know that they were the product of 'European colonialism'?Pincrete (talk) 18:11, 12 September 2024 (UTC)
- Is California genocide European colonialism? Also, the source makes a distinction and clarification. Why do you want to omit that? The Cambridge World History of Genocide. Vol. 2, p. 38:
Bogazicili (talk) 18:15, 12 September 2024 (UTC)With these works, a near consensus emerged. By most scholarly definitions and consistent with the UN Convention, these scholars all asserted that genocide against at least some Indigenous peoples had occurred in North America following colonisation, perpetuated first by colonial empires and then by independent nation-states
- This is the lead which is necessarily a summary, but it doesn't make the distinction you claim, it simply says that genocide ocurred "following colonisation", both before and after the places became independent states. Our text said "It is particularly associated with European colonialism", how is that untrue or incomplete?
- California is not a state at all, in the sense of being an independent nation, colonial or otherwise. California was though colonised by people of European extraction. Are you now claiming that the reader would recognise California as being a 'colonial state'. Pincrete (talk) 18:29, 12 September 2024 (UTC)
- What would you suggest for the lead? I think just saying European colonization is insufficient.
- You assume the reader would know "Any state which came about as a result of European colonialism, whether it was still wholly governed by by the 'mother country' or wholly self-governing (or an intermediate state such as some British 'colonies/dominions'), would be covered by the term 'European colonialism'".
- Maybe we can say Western colonialism in the lead or European colonization and newly established states, or something like that. But the sentence I added into the body should stay. Bogazicili (talk) 18:35, 12 September 2024 (UTC)
- The sentence you added to the body is not particularly helpful to readers, imo. Since it is settlers on the ground who are the driving force behind anti indigenous genocide to begin with, there is no obvious reason why it should stop when the settlers give fealty to a slightly less distant authority. If the reader wrongly believes that the government is the leading perpetrator, that is the most important misconception to correct. (t · c) buidhe 21:15, 12 September 2024 (UTC)
Maybe we can say Western colonialism in the lead or European colonization and newly established states, or something like that
I personally don't have a problem with 'Western colonialism', but 'newly established states' fundamentally changes the meaning (which is that these states were, or evolved from European colonies and were largely run by 'settlers'). That they were 'new' is incidental. Pincrete (talk) 04:52, 13 September 2024 (UTC)
- Why would a reader understand/know that, for example, countries in the American continent were 'colonial states', but not know that they were the product of 'European colonialism'?Pincrete (talk) 18:11, 12 September 2024 (UTC)
. That is incorrect. State or national governments or government officials were also responsible
- The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies, p. 338:
In 1851, Governor Burnett gave official voice to the genocidal intent of settler violence against the California Indians, stating: ‘[T]he white man, to whom time is money, and who labors hard all day to create the comforts of life, cannot sit up all night to watch his property . . . after being robbed a few times he becomes desperate, and resolves upon a war of extermination.’ According to Burnett, ‘A war of extermination will continue to be waged between the races until the Indian race becomes extinct.’72
- The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies, p. 339:
The genocidal intent of California settlers and government officials was acted out in numerous battles and massacres (and aided by technological advances in weaponry, especially after the Civil War), in the abduction and sexual abuse of Indian women, and in the economic exploitation of Indian child labourers
- The Cambridge World History of Genocide. Vol. 2, p. 47:
Within twenty years of settlement, the Aboriginal population of Victoria had declined by 80 per cent. Most of Australia’s 750 Aboriginal languages lost their last speakers. In the 1930s, after a century of child stealing and family disruption, the official policy of 'breeding out the colour’ was implemented. It was genocide, exactly as Lemkin was then trying to make it understood. It was not only about killings, but also about words and actions that signified an intention to destroy a human group.2
Saying In places like North America, genocide of indigenous peoples continued after the establishment of independent states
also doesn't suggest "government is the leading perpetrator". That seems to be your personal interpretation. Bogazicili (talk) 22:12, 12 September 2024 (UTC)
- I never said that government officials weren't involved , merely that in my opinion your edits start from the premise that, for example, Canada becoming officially independent from the United Kingdom is necessarily going to make a significant difference in terms of what is happening on the ground in Manitoba. It is not correct to put so much emphasis on this in the article unless it is the driving force behind genocides. (t · c) buidhe 00:28, 13 September 2024 (UTC)
- I also have to admit that I'm not sure about the sentence "According to Mark Levene, seeing native people as "savages" and racism "played a critical role in psychocultural justifications for genocide" in areas such as Australia and North America". This was also the justification for genocide in many other cases, even non-colonial ones. I'll look for a more general source and then put it in a different section. (t · c) buidhe 05:26, 13 September 2024 (UTC)
- Buidhe, are you trying to remove any mention of Australia and North America in the History section?
- As for your earlier reply, I see the issue. You thought my premise was about drivers because of where I placed the sentence. No, I was just trying to clarify the timeline. As I said, "European colonialism" sounds too vague. We need to clarify what is meant by that term. The source makes it clear.
- The Cambridge World History of Genocide. Vol. 2. Introduction Chapter, p. 10:
This volume offers, besides other imperial expansionist cases such as those from early modern China and Japan, empirical evidence for Barta’s observation across five centuries of European settler colonial history. In Part I, ‘Settler Colonialism’, three chapters collectively survey the colonial histories of the United States, Australia, New Zealand and Southern Africa from the sixteenth to the early twentieth centuries. These chapters bring the many differences between these colonies to light, but it is what connects them that determines their histories as genocidal: the goal of imposing a new settler society on Indigenous lands. Further, these chapters articulate how genocide has shaped the nationalist historiographies of settler colonies.
- I'll reword the sentence and move it to the beginning of the paragraph, so it's clear it's clarifying what is meant by "European colonialism" Bogazicili (talk) 17:23, 13 September 2024 (UTC)
- The article is about genocide in general so the sources we cite should also be about genocide in general, rather than specific cases of genocide. The added material to the history section makes me concerned about due weight when the colonialism material is now making up more than half of the history section. I do not agree with giving North America / Australia undue prominence—this isn't even all of the Anglo-American settler colonialism as the source you just quoted makes clear—and if it's possible to cover them in combination with other cases of genocide, that structure seems more suitable for an overview article. (t · c) buidhe 17:30, 13 September 2024 (UTC)
- Buidhe, you gave Amalek as an example for the ancient period. North America and Australia should be used as examples for what is meant by colonial genocides. North America and Australia are mentioned so many times even only in the Introduction Chapter in the above source.
- The reason for UNDUE weight is your long-winded economic explanation. Economic explanation should be moved to Causes section. Bogazicili (talk) 17:41, 13 September 2024 (UTC)
- European colonialism would include ALL of America (N & S), as well as much of Africa and Asia. I don't understand why N. America and Australia would be singled out. I also don't think 'colonial state' is either clear or obvious. Would 'former colonies' not be clearer, if it is felt necessary to distinguish them from 'true' colonies? Pincrete (talk) 18:01, 13 September 2024 (UTC)
- I clarified with this sentence:
The destruction of indigenous societies as part of European colonialism, including in colonial states such as United States and Australia, was initially not recognized as a form of genocide.
based on above source. Otherwise, it's too vague. I'm ok with moving the entire paragraph starting with "According to Mohamed Adhikari, the two" to Causes section. Bogazicili (talk) 18:09, 13 September 2024 (UTC)
- I clarified with this sentence:
- European colonialism would include ALL of America (N & S), as well as much of Africa and Asia. I don't understand why N. America and Australia would be singled out. I also don't think 'colonial state' is either clear or obvious. Would 'former colonies' not be clearer, if it is felt necessary to distinguish them from 'true' colonies? Pincrete (talk) 18:01, 13 September 2024 (UTC)
- The article is about genocide in general so the sources we cite should also be about genocide in general, rather than specific cases of genocide. The added material to the history section makes me concerned about due weight when the colonialism material is now making up more than half of the history section. I do not agree with giving North America / Australia undue prominence—this isn't even all of the Anglo-American settler colonialism as the source you just quoted makes clear—and if it's possible to cover them in combination with other cases of genocide, that structure seems more suitable for an overview article. (t · c) buidhe 17:30, 13 September 2024 (UTC)
- I also have to admit that I'm not sure about the sentence "According to Mark Levene, seeing native people as "savages" and racism "played a critical role in psychocultural justifications for genocide" in areas such as Australia and North America". This was also the justification for genocide in many other cases, even non-colonial ones. I'll look for a more general source and then put it in a different section. (t · c) buidhe 05:26, 13 September 2024 (UTC)
Leading photo of 'reprisal firing squad'
Isn't the new lead photo (a Nazi firing squad shooting Polish 'hostages' as reprisal for other Poles attacking a German policeman) an example of a "violent and coercive form of rule that aim to change behavior rather than destroy groups", which we say is excluded, rather than genocide itself. I acknowledge that Nazi policy 'in the East' was consciously and systematically genocidal, but is this photo an example of that? Pincrete (talk) 06:58, 13 September 2024 (UTC)
- The previous picture was, as acknowledged by the caption, not typical of genocides because it is more common historically for men to be killed than the women and children in the picture. The new picture was chosen to illustrate the security rationale elaborated in the causes section that is behind most or all genocides. I do think that it qualifies because it is an execution of hostages for actions committed by other Poles, which is the same logic explained in the causes section. If we accept that the Nazi policy in occupied Poland and the Soviet Union was genocidal, a large part of the deaths inflicted by the occupier were in the course of German anti-partisan operations in World War II and the main victims were civilians not armed partisans (as in the picture).
- At the same time, I am open to suggestion other images that may be considered typical of genocides in general. (t · c) buidhe 07:56, 13 September 2024 (UTC)
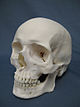
- I am curious as to why you replaced the image that references the Cambodian genocide with this image (the Nazi firing squad)? I'm still learning the ropes of Wikipedia inclusion/exclusion criteria. MSTwitch666 (talk) 14:24, 28 October 2024 (UTC)
- I am not set on a particular image, but I believe that the Cambodian skulls image is not the best choice for the lead image for several reasons :
- The image reinforces the common misconception that genocide is just about mass killing
- It is a museum /memorialized form of genocide (see Stone et al 2022), rather than showing genocide in progress
- The picture does nothing to illuminate the most commonly discussed aspects of genocide, namely what it is? Why and how does it happen?
- (t · c) buidhe 23:27, 28 October 2024 (UTC)
- I am not set on a particular image, but I believe that the Cambodian skulls image is not the best choice for the lead image for several reasons :
- I am curious as to why you replaced the image that references the Cambodian genocide with this image (the Nazi firing squad)? I'm still learning the ropes of Wikipedia inclusion/exclusion criteria. MSTwitch666 (talk) 14:24, 28 October 2024 (UTC)
"relatively uncommon"
"relatively uncommon" in comparison to what? The source is not clear on it. (t · c) buidhe 00:33, 18 September 2024 (UTC)
- The source references "Van Wees, ‘Archaic and classical Greece’, 19". I don't have that source.
- Van Wees say in The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies, p. 244: "The massacre of all inhabitants of a city was quite rare, though not unknown. More common was the killing of all men, or all men of military age, while the women and children were led away to be sold as slaves. This is described as standard procedure for dealing with a city captured by force in a range of texts from Deuteronomy and the Iliad to Livy’s history of Rome" Bogazicili (talk) 14:41, 18 September 2024 (UTC)
- Yeah I wasn't sure whether it meant "relatively uncommon" in relation to events in the era when genocide might have occurred, or in comparison to more recent times. (t · c) buidhe 18:24, 18 September 2024 (UTC)
Removal of sourced information
Buidhe, I appreciate your work on this article. But why were my recent edits, which used high quality sources, removed without any talk page discussion in this giant edit [1]?? Bogazicili (talk) 11:13, 4 October 2024 (UTC)
Incomplete information in history section
Buidhe, this is what Häussler, Stucki & Veracini 2022, pp. 212–213 say. Bolding mine:
Later, the settlers often became the state, either by acquiring self-governing capacities through territorial or colonial devolution, or by declaring their independence outright. Their state is typically aggressively expansionist but remains different from an imperial state, even if the practice of frontier massacres is eventually discontinued. Rather than managing subjected heterogeneity like imperial states do, the settler state aims to constitute demographic homogeneity by the violent application of a variety of administrative and assimilatory means against surviving indigenous peoples. Cultural genocide, a most violent practice, characterizes the operation of settler states.
This is what you put in the article. Again bolding mine:
Unlike traditional empires, settler colonialism—particularly common in the overseas empires that resulted from European colonialism—are characterized by militarized populations of settlers in remote areas beyond effective state control. Rather than labor or economic surplus, the settlers want to acquire land from indigenous people
When you say "particularly common in the overseas empires", it sounds like you are just talking about empires such as British Empire or French Empire. However, genocides did happen in settler colonies such as in United States and Australia. We have additional quotes above in European colonialism section in the talk page as well. I find the wording currently in the article misleading or incomplete. Bogazicili (talk) 11:56, 4 October 2024 (UTC)
- Hi Bogazicili, I'm trying to follow the sources. If you take a look at the ones I cited, you will find that the distinction that you keep bringing up—between empires ruled from overseas and those colonies that became independent under the control of settlers—may be mentioned, but is not emphasized. Rather, they stress the difference between types of imperialism and colonialism, with settler colonialism more prone to genocide than classical colonialism. (t · c) buidhe 13:01, 4 October 2024 (UTC)
- Hello Buidhe. I have to say I'm very concerned about coverage of indigenous genocides in English-language Wikipedia, especially after seeing this journal article [2].
- For example, United States and Australia articles seem to make no mention of this, which is rather shocking. Australia is supposed to be FA-class. That is a massive oversight.
- Now, returning to this article, I don't think your edits are helping. I disagree with your view about the source. It defines the areas very clearly:
It is only with what James Belich has called the global ‘settler revolution’ of the nineteenth century that settlers typically became respectable, even though not always: the transport and the industrial revolutions had made the temperate prairies of North America and Australia, parts of South Africa, and the southernmost parts of South America...
- And other sources also emphasize this. The Cambridge World History of Genocide. Vol. 2, there are 3 chapters under Settler Colonialism:
- Ch 1 The Centrality of Dispossession’: Native American Genocide and Settler Colonialism
- Ch 2 Very British Genocide: Acknowledgement of Indigenous Destruction in the Founding of Australia and New Zealand
- Ch 3 Settler Genocides of San Peoples of Southern Africa.
- Jones, Adam (2023). Genocide: A Comprehensive Introduction. 136-137:
Three ideological tenets stand out as justifying and facilitating European5 conquest,“pacification,” and “settlement.” The first, most prominent in the British realm (especially the United States, Canada, and Australasia), was a legal-utilitarian justification, according to which native peoples had no right to territories they inhabited, owing to their “failure” to exploit them adequately. As Benjamin Madley
...
Ironically, this modernizing ideology also resulted in the migration – as convicts or refugees from want, political persecution, and famine – of millions of “surplus” Europeans to the New World. In Australia and the United States, among other locations, these settlers would become key, often semi-autonomous instruments of genocide against indigenous peoples. Brendan Lindsay described the dynamic of “California’s Native American Genocide” in a way that echoes many others worldwide- You are keeping the wording too vague, just mentioning European colonialism and empires, which is unnecessary given that the article is only 3,704 words. Please spell out what settler colonialism is and what areas it effected. At least give examples. All above sources gives examples of North America/United States and Australia, not sure why these are omitted. Bogazicili (talk) 15:12, 4 October 2024 (UTC)
- They aren't exactly ommitted although I agree there could be more on them... In the genocide studies section we note that "The genocides of indigenous peoples as part of European colonialism, including in colonial states such as United States and Australia, were initially not recognized as a form of genocide."
- I'm aware. I added that clarification. However this is the history section. The current wording makes it sound like only empires like British Empire did colonial genocides, whereas it happened under countries like United States and Australia too. The current wording is unnecessarily vague given the short size of the article. Bogazicili (talk) 15:34, 4 October 2024 (UTC)
- Thank you for adding that clarification, I agree that the current section doesn't do a great job of summarizing all of the dedicated pages on history Genocides in history, Genocides in history (before World War I), Genocides in history (World War I through World War II), Genocides in history (1946 to 1999), and Genocides in history (21st century) but thats also a really hard job Horse Eye's Back (talk) 15:38, 4 October 2024 (UTC)
- I'm not trying to summarize those articles, which have serious content and sourcing problems. I'm trying to build a better article here based on overviews of genocide in general. (t · c) buidhe 15:59, 4 October 2024 (UTC)
- Jones, Adam (2023). Genocide: A Comprehensive Introduction is a good overview source and it is much more comprehensive in its coverage of history, with an entire chapter on indigenous genocides. The current history section is not comprehensive Bogazicili (talk) 16:13, 4 October 2024 (UTC)
- The section is a work in progress. But it cannot go into the same level of detail as more specific articles. (t · c) buidhe 02:17, 5 October 2024 (UTC)
- Thats completely backwards. Horse Eye's Back (talk) 17:53, 4 October 2024 (UTC)
- So your opinion is that I can't work on improving this article until I strip out and rewrite 6 other ones? Or else we should align this article to be like others that have known issues, rather than write an article without those issues. I don't think Wikipedia works that way. (t · c) buidhe 02:15, 5 October 2024 (UTC)
- It depends on what part of the article, that section is supposed to be a summary of another article... If the section is not a summary of another article you have much more freedom, but if it is then any significant edits should be made to the daughter page first. Horse Eye's Back (talk) 14:58, 7 October 2024 (UTC)
- I think the coverage should be better now, with more examples. Bogazicili (talk) 20:45, 7 October 2024 (UTC)
- It depends on what part of the article, that section is supposed to be a summary of another article... If the section is not a summary of another article you have much more freedom, but if it is then any significant edits should be made to the daughter page first. Horse Eye's Back (talk) 14:58, 7 October 2024 (UTC)
- So your opinion is that I can't work on improving this article until I strip out and rewrite 6 other ones? Or else we should align this article to be like others that have known issues, rather than write an article without those issues. I don't think Wikipedia works that way. (t · c) buidhe 02:15, 5 October 2024 (UTC)
- Jones, Adam (2023). Genocide: A Comprehensive Introduction is a good overview source and it is much more comprehensive in its coverage of history, with an entire chapter on indigenous genocides. The current history section is not comprehensive Bogazicili (talk) 16:13, 4 October 2024 (UTC)
- I'm not trying to summarize those articles, which have serious content and sourcing problems. I'm trying to build a better article here based on overviews of genocide in general. (t · c) buidhe 15:59, 4 October 2024 (UTC)
- Thank you for adding that clarification, I agree that the current section doesn't do a great job of summarizing all of the dedicated pages on history Genocides in history, Genocides in history (before World War I), Genocides in history (World War I through World War II), Genocides in history (1946 to 1999), and Genocides in history (21st century) but thats also a really hard job Horse Eye's Back (talk) 15:38, 4 October 2024 (UTC)
- The Haussler et al source spends several pages discussing settler colonialism and genocide while only about a paragraph on the transition from British to independent rule - because that transition is not so important to the actual fate of indigenous people. I rest my case that Bogazicili 's focus on overseas empires vs their successors is misplaced. (t · c) buidhe 15:57, 4 October 2024 (UTC)
- That answer doesn't make sense. The Haussler et al is one source. It is much more prominent in Jones, Adam (2023). Genocide: A Comprehensive Introduction and The Cambridge World History of Genocide. Vol. 2. I rest my case that using one source while ignoring others is against WP:NPOV. Bogazicili (talk) 16:10, 4 October 2024 (UTC)
- The important factor for genocide in Australia and other colonies that became independent is the arrival of European settlers, not the independence from the original metropole such as the British Empire. Although I do not have access to all of jones 2023 (do you?) I've never seen any source, including those you've quoted, that say otherwise so I'm not sure why we're still having this argument. Some that you quoted above support my argument and not yours. (t · c) buidhe 02:21, 5 October 2024 (UTC)
- The section is history. Not factors for genocide. So the fact that it happened after establishment of independent countries is how it historically happened. Your wording is therefore misleading. And the section is currently incomprehensive in terms of timeline.
- And yes, I have access to all of Jones 2023. I'll be adding more from it shortly. Bogazicili (talk) 14:08, 5 October 2024 (UTC)
- The sources I've seen say that genocides occurred both before and after the transition to independent rule so I'm not sure why you keep emphasizig this transition. If it's not relevant to the occurrence of genocides (either as a cause, method, effect, or some other thing directly relevant to actual genocides), I do not see any reason to emphasize this point, since the article has to be very concise and economical given the information it has to cover. I think the history section is a pretty good length as it is, although it can be improved I would oppose a dramatic expansion per WP:SUMMARYSTYLE. Readers looking for detailed information about history should go to one of the genocides in history articles instead. (t · c) buidhe 14:19, 5 October 2024 (UTC)
- I'm not emphasizing it. I'm just trying to give a good summary for history. It's part of history that it happened both before and after. I'm not sure why you keep trying to omit this. What is the reason?
- History section is right now pretty incomplete. I also didn't like how you summarized the part after WW2 for example, it seems a bit simplistic. Bogazicili (talk) 14:23, 5 October 2024 (UTC)
- I think there is room for improvement, and I don't oppose a change in wording, but I think we have to be clear than when it comes to colonialism the sources emphasize type of colonialism versus the distinction between overseas empires and their successors. If the relative importance is not clear to the reader we aren't doing our job. (t · c) buidhe 14:25, 5 October 2024 (UTC)
- As I said many times. Your wording implies that genocides were only done by empires such as the British Empire. This is misleading. It's also incomplete. This is the history section. Right now your wording is not doing its job. Bogazicili (talk) 14:29, 5 October 2024 (UTC)
- I think there is room for improvement, and I don't oppose a change in wording, but I think we have to be clear than when it comes to colonialism the sources emphasize type of colonialism versus the distinction between overseas empires and their successors. If the relative importance is not clear to the reader we aren't doing our job. (t · c) buidhe 14:25, 5 October 2024 (UTC)
- The sources I've seen say that genocides occurred both before and after the transition to independent rule so I'm not sure why you keep emphasizig this transition. If it's not relevant to the occurrence of genocides (either as a cause, method, effect, or some other thing directly relevant to actual genocides), I do not see any reason to emphasize this point, since the article has to be very concise and economical given the information it has to cover. I think the history section is a pretty good length as it is, although it can be improved I would oppose a dramatic expansion per WP:SUMMARYSTYLE. Readers looking for detailed information about history should go to one of the genocides in history articles instead. (t · c) buidhe 14:19, 5 October 2024 (UTC)
- The important factor for genocide in Australia and other colonies that became independent is the arrival of European settlers, not the independence from the original metropole such as the British Empire. Although I do not have access to all of jones 2023 (do you?) I've never seen any source, including those you've quoted, that say otherwise so I'm not sure why we're still having this argument. Some that you quoted above support my argument and not yours. (t · c) buidhe 02:21, 5 October 2024 (UTC)
- That answer doesn't make sense. The Haussler et al is one source. It is much more prominent in Jones, Adam (2023). Genocide: A Comprehensive Introduction and The Cambridge World History of Genocide. Vol. 2. I rest my case that using one source while ignoring others is against WP:NPOV. Bogazicili (talk) 16:10, 4 October 2024 (UTC)
- I'm aware. I added that clarification. However this is the history section. The current wording makes it sound like only empires like British Empire did colonial genocides, whereas it happened under countries like United States and Australia too. The current wording is unnecessarily vague given the short size of the article. Bogazicili (talk) 15:34, 4 October 2024 (UTC)
- They aren't exactly ommitted although I agree there could be more on them... In the genocide studies section we note that "The genocides of indigenous peoples as part of European colonialism, including in colonial states such as United States and Australia, were initially not recognized as a form of genocide."
buidhe, unlike what I thought you implied, establishment of independent states does seem to be a factor in frontier genocides. Bolding is mine
The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies, p. 334:
The emergence of a racially defined American republic in North America added a level of ideological intensity to colonial patterns of frontier violence and the Anglo-American quest for territorial and economic aggrandizement. Standing in the path of a republican settler colonial empire that stretched from the Atlantic to the Pacific were the Native American communities of the south, southwest, the Great Plains, and the west. American explorers, ranchers, settlers, and gold-seekers took to the United States’ frontiers of settlement their hopes and dreams for a better life, and a moral repugnance for indigenous peoples that expressed itself, in the words of one recent scholar, as the ‘beastilization’ of Native Americans.
And places such as United States seem to be a core area of settler colonialism. So they should be used as examples when introducing the term in history section:
The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies, p. 341:
As Richard Cole Harris observes, the ‘geographical core’ of settler colonialism—to which I include the United States—was ‘about the displacement of people from their land and its repossession by others’.87 This basic analytical premise inspired what Ben Kiernan refers to as the ‘selective threat of genocide’ against Native Americans, a threat that resulted in various forms of organized and spontaneous acts of violence since the seventeenth century was driven by the intent to exterminate the American ‘natives’.
We also have the quotes from above.
The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies, p. 349:
Colonial genocide has even become a widely used distinct category. However, it is important to note that genocidal violence in most of colonial Africa differs in some considerable ways from genocides committed in North American and Australian settler colonies: European colonization of Africa did not inevitably lead to the expulsion and/or annihilation of the indigenous populations. There are two reasons for this difference: whereas colonization preceded the formation of bureaucratic colonial states in America and Australia, European settlement followed the establishment of colonial administration in Africa. As a result, the colonial states in the British New World territories were almost unlimitedly dominated by settlers’ interests. In Africa, by contrast, the settlers’ influence and ability to fight and expel the Africans on their own was more restricted because the colonial states were still weak and their power relied on the cooperation with indigenous chiefs.
The Cambridge World History of Genocide. Vol. 2. Introduction Chapter, p. 10:
This volume offers, besides other imperial expansionist cases such as those from early modern China and Japan, empirical evidence for Barta’s observation across five centuries of European settler colonial history. In Part I, ‘Settler Colonialism’, three chapters collectively survey the colonial histories of the United States, Australia, New Zealand and Southern Africa from the sixteenth to the early twentieth centuries. These chapters bring the many differences between these colonies to light, but it is what connects them that determines their histories as genocidal: the goal of imposing a new settler society on Indigenous lands. Further, these chapters articulate how genocide has shaped the nationalist historiographies of settler colonies.
This is a new one quote. The Cambridge World History of Genocide. Vol. 2. Introduction Chapter, p. 7:
The European inflicted genocides of traditional landowners that began in the late-fifteenth-century Americas were rationalised by an evolving sense of religious righteousness, commercial drive, cultural superiority and racial supremacy that persisted into the modern era.
The first paragraph covers the period until the early modern period. The last paragraph starts from WW1. The second paragraph should cover the period in between. Given this, and considering all of the quotes above, the following should be the first sentence in the second paragraph in History section:
|
Beginning in the 15th century, European colonialism led to genocides of indigenous peoples. This has continued under settler colonies, such as United States and Australia, between 16th and 20th centuries. |
buidhe, you are welcome to adapt the rest of the paragraph with this first sentence. Or I can write the entire paragraph myself. I think we can also give some non-European examples. I think explaining the difference between empires and settler colonialism is also fine. If you disagree with all of these, we can proceed to Wikipedia:Dispute resolution noticeboard. Bogazicili (talk) 16:40, 6 October 2024 (UTC)
- Have made the changes. Bogazicili (talk) 16:06, 7 October 2024 (UTC)
- The wording is incorrect because it implies that a settler colony only becomes such when it declares independence from the metropole. In fact, a settler colony is defined by the invasion of foreign settlers, not by the political status of the territory. This wrong assumption means you have misinterpreted several of the above passages to support your viewpoint when they do no such thing. (t · c) buidhe 04:23, 26 October 2024 (UTC)
Semi-protected edit request on 26 October 2024
This edit request has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
In the body of the Wiki page there is a picture depicting Pro-Hamas supporters calling for stopping the alleged genocide in Gaza. The picture is a political statement and does not belong in an article discussing actual genocide. Moreover, the picture literally depicts genocide supporters, by transitive properties of supporting the genocidal Hamas agenda. In conclusion the picture is not only in bad taste, it is an oxymoron to include it as it is included. Orpgol (talk) 04:16, 26 October 2024 (UTC)
- There is nothing about the photo that suggests that the protestors are
Pro-Hamas
nor that they are in any sensegenocide supporters, … supporting the genocidal Hamas agenda
. There may be valid reasons to excude this pic, but crudely mischaracterising the protestors doesn't make that case. Pincrete (talk) 05:00, 26 October 2024 (UTC)- Initially the photo was included as an easy to find example of people using the term "genocide" in order to bring attention to a particular cause (in this case ending the war/genocide in Gaza). This phenomenon is discussed in sourced article text now in a different section of the article. (t · c) buidhe 05:29, 26 October 2024 (UTC)
- Understood, but using this photo in this context represents a political agenda rather than objective truth, and we should avoid that in a body representing factual information. Orpgol (talk) 17:38, 26 October 2024 (UTC)
- I disagree with your points. The main reason to exclude this picture is because it serves a political agenda and does not represent an objective truth, especially in the context in which it is presented. This lowers the standards of Wikipedia. Lower on the reason to remove scale, at the bottom right corner there is a green flag that appears to be a Hamas flag. Orpgol (talk) 17:36, 26 October 2024 (UTC)
- Initially the photo was included as an easy to find example of people using the term "genocide" in order to bring attention to a particular cause (in this case ending the war/genocide in Gaza). This phenomenon is discussed in sourced article text now in a different section of the article. (t · c) buidhe 05:29, 26 October 2024 (UTC)
 Not done: neither an uncontroversial edit request, nor one that is supported by a consensus. M.Bitton (talk) 15:10, 26 October 2024 (UTC)
Not done: neither an uncontroversial edit request, nor one that is supported by a consensus. M.Bitton (talk) 15:10, 26 October 2024 (UTC)
- See my comments above. Consensus should not be needed for objective truth. Allowing a politically motivated image to stay on the article is mean to sway public opinion. If that is the declared purpose of this picture then please state as such. Orpgol (talk) 21:42, 27 October 2024 (UTC)
at the bottom right corner there is a green flag that appears to be a Hamas flag
Actually at the bottom right corner there is some green, which might concievably be many things, including a flag of some sort. Though personally, I find it unlikely that Hamas flags would be on display in a Northern European city without comment, but neither of us could possibly know what the green is could we?- The '
objective truth
on display is that protests across the free world have taken place about Israeli action in response to the October attacks. Many of the protests and many competent commentators have recorded that 'genocide' and/or ethnic cleansing in pursuit of collective punishment is the clear and - in some instances - stated intention of Israeli actions. This is hardly some fringe PoV. Pincrete (talk) 04:06, 28 October 2024 (UTC)- Sorry to press the point but most of what you say shows some bias towards a political agenda and not objective truth. Saying things like "protests have taken place..." as a justification to supporting political symbolism on Wikipedia is in poor taste. Protests have taken place supporting both sides of the conflict have they not?
- Additionally, I reject the "many competent commentators..." reasoning. Until there is no clear cut proof that a genocidal agenda has been driving this conflict, I think we can rely on the evidence before us on how the conflict started (genocidal terrorist acts, hostages still in captivity) as a good marker for framing this conflict. Competent commentators have been recorded saying things that support either side of this war. Please do not devolve a source of knowledge to a politically motivated history rewriting attempt. Orpgol (talk) 00:19, 29 October 2024 (UTC)
- I think someone arguing that pro-Palestinian/peace protestors are inherently pro-Hamas and that a splash of green in a photo is proof of a Hamas flag isn't in a very strong position to accuse others of bias, nor to defend 'objective truth'. Hardly anyone in English speaking/European countries can be unaware that various terms have been used in the public sphere to criticise Israel's reaction to the October attacks, including 'genocide/al'. These accusations and the counterpoint vigorous defence by local sympathisers and Israeli govt spokesmen have been nightly fare on the news programmes of the free world for much of the last year. The idea that we are condoning/endorsing one side by showing a picture of a protest is pretty far fetched IMO. You don't have to endorse the accusation to acknowledge that it has been made by parties that are far-from fringe and far from pro-Hamas. But we obviously aren't going to agree on this and it is fairly tangential to the topic of 'genocide' itself, which is the purpose of the page.Pincrete (talk) 09:17, 29 October 2024 (UTC)
- Without going into the points we will not agree on here, I think what I want to convince you is that the majority opinion is not necessarily the one that needs to be endorsed as you are suggesting here. Can you see a reason why, in this case, the zeitgeist opinion may be doing harm to what I referred to here as the objective truth?
- All I am asking is that we do not intentionally or accidentally, endorse ANY side of this conflict where it does not make sense. That's it. Orpgol (talk) 17:08, 29 October 2024 (UTC)
- I think someone arguing that pro-Palestinian/peace protestors are inherently pro-Hamas and that a splash of green in a photo is proof of a Hamas flag isn't in a very strong position to accuse others of bias, nor to defend 'objective truth'. Hardly anyone in English speaking/European countries can be unaware that various terms have been used in the public sphere to criticise Israel's reaction to the October attacks, including 'genocide/al'. These accusations and the counterpoint vigorous defence by local sympathisers and Israeli govt spokesmen have been nightly fare on the news programmes of the free world for much of the last year. The idea that we are condoning/endorsing one side by showing a picture of a protest is pretty far fetched IMO. You don't have to endorse the accusation to acknowledge that it has been made by parties that are far-from fringe and far from pro-Hamas. But we obviously aren't going to agree on this and it is fairly tangential to the topic of 'genocide' itself, which is the purpose of the page.Pincrete (talk) 09:17, 29 October 2024 (UTC)
- See my comments above. Consensus should not be needed for objective truth. Allowing a politically motivated image to stay on the article is mean to sway public opinion. If that is the declared purpose of this picture then please state as such. Orpgol (talk) 21:42, 27 October 2024 (UTC)
Additional problems with recent edits
additional methods included using plague and smallpox as biological weapons, forced labor and slavery, and starvation
—the argument that plague and smallpox was used as biological weapons remains contested, and certainly cannot be stated in wiki voice (for example, this source states "No historical evidence exists that smallpox was an effective bioweapon.")- Edits to the history section subsume general analysis about the function of empires to a paragraph about European colonialism, misleadingly making it seem as if the comment applies only to European colonialism, or perhaps that European empires are the main/only ones that commit genocide (an interpretation not found in the sources)
- See above and this source for the misinterpretation of what a "settler colony" is and its actual definition
While not prevented, genocides in Bosnia, Cambodia, and Rwanda were stopped with the intervention of outside forces
If not completely wrong, this is a controversial statement, that relies at a minimum on certain definitions (eg. the extent the Bosnian genocide, what are "outside forces" in Rwanda) that are not universally acceptedIn the 20th century, genocides were committed in Africa, Asia, and Europe.
Although the twentieth century history does need more work, I cannot support this addition because it suggests that genocide did not occur elsewhere, such as Australia and North America, where some sources say it did. Given that sources don't agree on when settler genocides come to an end, I think more ambiguity is necessary to maintain NPOV.
I also see a concerning reliance on specific case studies as sources. This article is about the overarching concept of genocide, so material from sources about particular genocides should be added to the relevant articles but it does not show WP:DUE for the inclusion of content here. (t · c) buidhe 04:49, 26 October 2024 (UTC)
- The source you provided says "No historical evidence exists that smallpox was an effective bioweapon" (bolding mine). It doesn't say it wasn't a method, just that it wasn't effective. The source also notes:
Over several centuries of colonial settlement in North and South America, anecdotes, diaries, and public letters expressed intent to use smallpox against indigenous people.
. The authors are also not historians or genocide scholars. In any case, we can simply attribute that statement to Adam Jones (Canadian scholar). - What is misleading is the version you are reverting to, which suggests only empires such as British Empire did genocide. If you have a concern about
European empires are the main/only ones that commit genocide
, feel free to expand the article and fix it. More examples can be given in history section. - The source you provided defines US as a settler colony
European settler colonies existed from the beginning of European overseas expansion and even the USA can be considered a settler colony up to the end of the 19th century, because it was only then that the free space for settlement disappeared
. What is the issue here? While not prevented, genocides in Bosnia, Cambodia, and Rwanda were stopped with the intervention of outside forces
Please show sources which contradict thisIn the 20th century, genocides were committed in Africa, Asia, and Europe
. We can reword.but it does not show WP:DUE for the inclusion of content here
The examples are DUE because they are given in the introduction chapters of the sources, such as The Cambridge World History of Genocide. Vol. 2. Introduction Chapter. p. 10 (quoted above). It's also in introduction chapter in The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies, p. 4:A related consequence of the influence of the Holocaust model has been to overemphasize the role of narrow political ideology in genocide ... Such a taxonomy ignores both the concessions that the Nazis did make to practicality in their murder campaigns and, more importantly, the obviously ideological considerations that ultimately permitted, say, Europeans to murder, say, native Americans as if they were simply practical obstacles to be removed...
- It's also mentioned in WP:Tertiary sources:
- The Social Science Encyclopedia, Genocide entry, p. 411. US and Australia are given as examples to colonial genocides:
(1) Colonial genocides developed from the fifteenth century onwards as Europeans and (later on) North Americans established their domination around the globe...In the case of the Americas, the vast proportion of Native Americans died as a result of their exposure to diseases against which they had no immunological protection. But there were individual cases of genocide within the huge and complex process of European expansion, as of the California Indians in the 1840s and the Aboriginal populations in Tasmania and in Queensland, Australia.
- The Encyclopedia of Politics and Religion, Genocide entry, p. 295:
It is suspected that genocide was fairly common even in antiquity. The best-known but sometimes still contentious cases since earliest times include the Athenian destruction of Melos (416 B.C.) during the Peloponnesian War, the Roman obliteration of Carthage in 146 B.C., the ravages of the Mongols under Genghis Khan in the thirteenth century, the Albigensian Crusade in thirteenth-century Europe, the persecution of Christians in early modern Japan, the mass killings of Ndwandwe people by Shaka's Zulu armies in the 1820s, and the destruction of certain Native American and Aboriginal peoples in the New World and Australia. Critics of the British imperial regime also used the term extermination to characterize the Irish famine of the 1840s, during which at least a million people perished.
- Encyclopedia of Global Justice, Genocide entry, p. 388:
In recent years, the term "genocide" has been used to describe the United States' actions against the Native Americans during the four centuries after Columbus landed.
- The Social Science Encyclopedia, Genocide entry, p. 411. US and Australia are given as examples to colonial genocides:
- In short, these are not "reliance on specific case studies as sources." These are examples. When explaining concepts, examples are given. When explaining colonial genocides, examples of US and Australia are DUE. Bogazicili (talk) 15:05, 29 October 2024 (UTC)
- If it's not an effective method of genocide, and the idea that it was in widespread use is treated with skepticism with historians, what makes it wp:due for inclusion? Are you aware that the argument for widespread intentional disease spread originates with the plagiarist and fabricator Ward Churchill? About this, a 2020 paper states,
Most significantly, though, [Churchill] claimed that colonizers deliberately infected indigenous peoples through the distribution of smallpox-laden blankets and other items. Beyond the documented case of biological warfare at Fort Pitt in 1763, scholars had not given such claims much credibility.
- Again, you reverted to the version where the source's general comment about empires is placed later in the paragraph about European colonial empires. As I pointed out above , this is a distortion of the cited source
- Did you read what I wrote?
The wording is incorrect because it implies that a settler colony only becomes such when it declares independence from the metropole. In fact, a settler colony is defined by the invasion of foreign settlers, not by the political status of the territory.
- For example, the Bosnian genocide is most often defined as the srebrenica massacre, which came to an end when all the potential victims were killed or had escaped. The consensus view of how the Rwandan genocide ended is that Rwandan Tutsis put an end to the Rwandan genocide by capturing all of the country's territory (for both of these, see Bellamy et al 2022). All of this is well known in genocide studies and it surprises me that you are trying to substantially rewrite the article if you weren't aware of these widely known interpretations.
- The problem I bring up is not necessarily the content but the sourcing. Nothing in your comments suggests that you recognize the WP:DUE and WP:NPOV problems with relying on editors finding and citing case studies to support particular points, which by definition will involve cherry-picking some examples over others. If the examples are covered in overviews that are about genocide in general, they are much more likely to be wp:due but then you should just cite the overview.
- If it's not an effective method of genocide, and the idea that it was in widespread use is treated with skepticism with historians, what makes it wp:due for inclusion? Are you aware that the argument for widespread intentional disease spread originates with the plagiarist and fabricator Ward Churchill? About this, a 2020 paper states,
- Furthermore, the topic is very large and so is the number of possible sources. Just because you read something in one source does not mean it is the historical consensus, majority view, or wp:due for mention in the article. Contributing effectively requires a high degree of familiarity with the scholarly literature. For example, your recent edits remove citations to the 2022 version of the Oxford genocide studies handbook, in preference to the 2010 version, which is hard to explain. (t · c) buidhe 03:12, 30 October 2024 (UTC)
- 1) What is this 2020 paper? Unless it's a review article, it would be considered WP:Primary. This [3] was used in a 2023 genocide textbook. [4]
- 2) Nope. The beginning is about European colonialism. Then it switches to
While all empires...
. I do not read that part as being about only "European colonial empires" [5] Should we specifically change it to "while all empires, including non-European ones"? - 3) That's not how I read it. Such as is just an example.
- 4) Sources???
- 5) There are overview sources. For example,
Beginning in the 15th century, European colonialism led to genocides of indigenous peoples. This has continued under settler colonies, such as United States and Australia, between 16th and 20th centuries.[47][149][150]
150 is from The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies, which is an overview source. [6] - Overall, I am very concerned that anything mentioning Native Americans or Americas are being removed. This is also evident even in the images in the article. There are no images from Americas. You said I'm cherry-picking with examples, but your examples seem cherry picked to me as well. In the methods sections, you put:
Cultural destruction, such as Indian residential schools, is often dependent on controlling the victims at a specific location.[123]
The source is: Basso, Andrew R. (2024). Destroy Them Gradually: Displacement as Atrocity. That's not an overview source either. - We seem to be discussing this since September, so I requested WP:DRN Bogazicili (talk) 04:35, 30 October 2024 (UTC)
- B-Class level-3 vital articles
- Wikipedia level-3 vital articles in Society and social sciences
- B-Class vital articles in Society and social sciences
- B-Class Human rights articles
- Top-importance Human rights articles
- WikiProject Human rights articles
- B-Class Philosophy articles
- High-importance Philosophy articles
- B-Class ethics articles
- High-importance ethics articles
- Ethics task force articles
- B-Class Crime-related articles
- Top-importance Crime-related articles
- WikiProject Crime and Criminal Biography articles
- B-Class Death articles
- Top-importance Death articles
- B-Class Ethnic groups articles
- Low-importance Ethnic groups articles
- WikiProject Ethnic groups articles
- B-Class Discrimination articles
- Top-importance Discrimination articles
- WikiProject Discrimination articles
- B-Class International relations articles
- Low-importance International relations articles
- B-Class International law articles
- Mid-importance International law articles
- WikiProject International law articles
- WikiProject International relations articles