diff --git a/contrib/api-development/index.md b/contrib/api-development/index.md
index 72789070..ac6abfe3 100644
--- a/contrib/api-development/index.md
+++ b/contrib/api-development/index.md
@@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
# List of sections
+- [What Is API](what-is-API.md)
- [API Methods](api-methods.md)
-- [FastAPI](fast-api.md)
\ No newline at end of file
+- [FastAPI](fast-api.md)
diff --git a/contrib/api-development/what-is-API.md b/contrib/api-development/what-is-API.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c8cc0ada
--- /dev/null
+++ b/contrib/api-development/what-is-API.md
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+# What is an API (Application Programming Interface)
+
+## Introduction
+
+An API (Application Programming Interface) is a set of rules and protocols for building and interacting with software applications. It defines the methods and data formats that applications can use to communicate with each other, enabling them to request and exchange information. APIs are used to integrate different software systems, allowing them to share data and functionality seamlessly.
+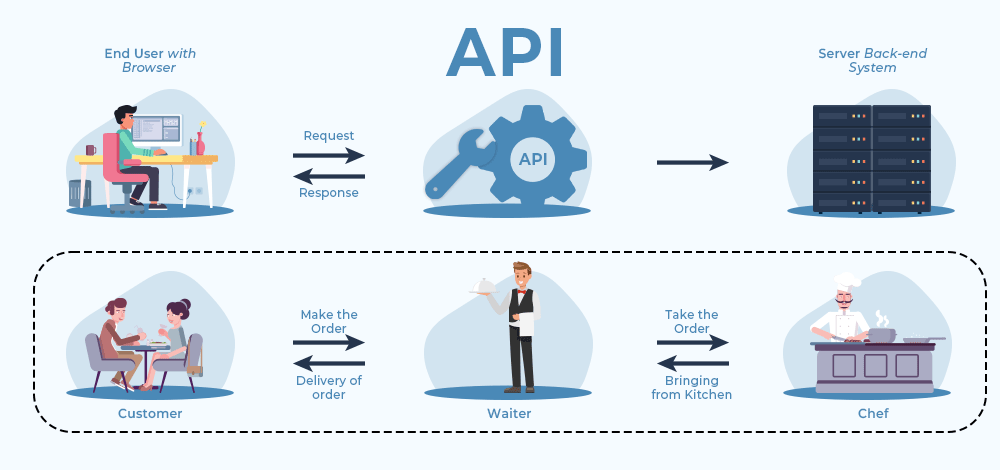
+To make you clear with the diagram of what is API, let’s take a real-life example of an API, you can think of an API as a waiter in a restaurant who listens to your order request, goes to the chef, takes the food items ordered and gets back to you with the order.
+API full form is an **Application Programming Interface** that is a collection of communication protocols and subroutines used by various programs to communicate between
them. A programmer can make use of various API tools to make their program easier and simpler. Also, an API facilitates programmers with an efficient way to develop their software programs. Thus api meaning is when an API helps two programs or applications to communicate with each other by providing them with the necessary tools and functions. It takes the request from the user and sends it to the service provider and then again sends the result generated from the service provider to the desired user.
+
+## How do APIs Work?
+
+The functioning of an API can be explained clearly with a few simple steps. Imagine a client-server architecture where the client sends a request via a medium to the server and receives the response through the same medium. An API acts as a communication bridge between two programs or systems to facilitate their interaction. In this scenario, the client represents the user or customer (who sends the request), the medium is the application programming interface, and the server is the backend (which processes the request and provides a response).
+
+
+### Here are the steps involved in the working of APIs:
+
+> The client starts the process by sending a request via the API's URI (Uniform Resource Identifier).
+> Upon receiving the request, the API makes a call to the server.
+> The server processes this request and sends back a response to the API with the required information.
+> The API then transfers the data back to the client.
+>
+> APIs are generally considered secure against attacks because they include authorization credentials and often use an API gateway to limit access, thereby minimizing security threats. To enhance data security further, HTTP headers, query string parameters, or cookies can be employed.
+
+## Types of APIs
+
+There are several types of APIs, each with its own unique features and capabilities. Some of the most
+common types of APIs include:
+
+> REST APIs: Representational State Transfer (REST) APIs are a popular type of API that uses
+> HTTP requests and responses to communicate between systems. They are often used for web
+> applications and mobile apps.
+> SOAP APIs: Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) APIs are another type of API that uses XML
+> messages to communicate between systems. They are often used for enterprise-level
+> applications and are known for their reliability and security.
+> GraphQL APIs: GraphQL APIs are a newer type of API that uses a query language to retrieve
+> data from a server. They are often used for building complex and dynamic applications.
+> Webhooks: Webhooks are a type of API that allows a system to send data to a
+> specified URL when a specific event occurs. They are often used for real-time data
+> updates and notifications.
+> RPC APIs: Remote Procedure Call (RPC) APIs are a type of API that allows a system
+> to call a procedure on a remote server. They are often used for distributed computing and
+> are known for their efficiency and scalability.
+
+## Advantages of APIs
+
+APIs offer several advantages for developers and businesses, including:
+
+> Improved efficiency: APIs allow developers to reuse existing code and functionality, reducing the time and effort required
+> to build new applications.
+> Increased flexibility: APIs allow developers to customize and extend the functionality of existing applications, making them more
+> flexible and adaptable to changing needs.
+> Improved scalability: APIs allow developers to scale applications easily by adding or removing resources as needed, making
+> them more efficient and cost-effective.
+> Enhanced security: APIs can be secured using authentication and authorization mechanisms, making them more secure and
+> reliable.
+>
+> Improved collaboration: APIs allow developers to collaborate and share resources, making it easier to build complex
+> applications.
+>
+
+## Conclusion
+
+APIs are a powerful tool for building and integrating software applications. They provide a standardized way for different
+systems to communicate and exchange data, making it easier to build complex and scalable applications. By understanding the
+different types of APIs and their advantages, developers can make informed decisions about which APIs to use in their
+applications and how to best leverage their capabilities.