|
| 1 | +### Java Arrays |
| 2 | + |
| 3 | +Normally, an array is a collection of similar type of elements which have a contiguous memory location. |
| 4 | + |
| 5 | +Java array is an object which contains elements of a similar data type. Additionally, The elements of an array are stored in a contiguous memory location. It is a data structure where we store similar elements. We can store only a fixed set of elements in a Java array. |
| 6 | + |
| 7 | +Array in Java is index-based, the first element of the array is stored at the 0th index, 2nd element is stored on 1st index and so on. |
| 8 | + |
| 9 | +Unlike C/C++, we can get the length of the array using the length member. In C/C++, we need to use the sizeof operator. |
| 10 | + |
| 11 | +In Java, array is an object of a dynamically generated class. Java array inherits the Object class, and implements the Serializable as well as Cloneable interfaces. We can store primitive values or objects in an array in Java. Like C/C++, we can also create single dimentional or multidimentional arrays in Java. |
| 12 | + |
| 13 | +Moreover, Java provides the feature of anonymous arrays which is not available in C/C++. |
| 14 | + |
| 15 | +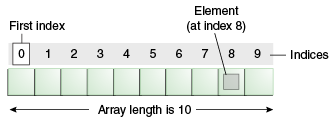 |
| 16 | + |
| 17 | +##### Advantages |
| 18 | + |
| 19 | + - Code Optimization: It makes the code optimized, we can retrieve or sort the data efficiently. |
| 20 | + - Random access: We can get any data located at an index position. |
| 21 | + |
| 22 | +##### Disadvantages |
| 23 | + |
| 24 | + - Size Limit: We can store only the fixed size of elements in the array. It doesn't grow its size at runtime. To solve this problem, collection framework is used in Java which grows automatically. |
| 25 | + |
| 26 | + |
| 27 | +##### Types of Array in java |
| 28 | + |
| 29 | +There are two types of array. |
| 30 | + |
| 31 | + - Single Dimensional Array |
| 32 | + - Multidimensional Array |
| 33 | + |
| 34 | +------- |
| 35 | + |
| 36 | +#### Example of Java Array |
| 37 | + |
| 38 | +```java |
| 39 | +//Java Program to illustrate how to declare, instantiate, initialize |
| 40 | +//and traverse the Java array. |
| 41 | +class Testarray{ |
| 42 | +public static void main(String args[]){ |
| 43 | +int a[]=new int[5];//declaration and instantiation |
| 44 | +a[0]=10;//initialization |
| 45 | +a[1]=20; |
| 46 | +a[2]=70; |
| 47 | +a[3]=40; |
| 48 | +a[4]=50; |
| 49 | +//traversing array |
| 50 | +for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)//length is the property of array |
| 51 | +System.out.println(a[i]); |
| 52 | +} |
| 53 | +} |
| 54 | +``` |
| 55 | +Ourput |
| 56 | +``` |
| 57 | + 10 |
| 58 | + 20 |
| 59 | + 70 |
| 60 | + 40 |
| 61 | + 50 |
| 62 | +``` |
| 63 | + |
| 64 | + |
| 65 | +------- |
| 66 | + |
| 67 | +##### Declaration, Instantiation and Initialization of Java Array |
| 68 | + |
| 69 | +```java |
| 70 | + int a[]={33,3,4,5};//declaration, instantiation and initialization |
| 71 | +``` |
| 72 | +Let's see the simple example to print this array. |
| 73 | +```java |
| 74 | +//Java Program to illustrate the use of declaration, instantiation |
| 75 | +//and initialization of Java array in a single line |
| 76 | +class Testarray1{ |
| 77 | +public static void main(String args[]){ |
| 78 | +int a[]={33,3,4,5};//declaration, instantiation and initialization |
| 79 | +//printing array |
| 80 | +for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)//length is the property of array |
| 81 | +System.out.println(a[i]); |
| 82 | +} |
| 83 | +} |
| 84 | +``` |
| 85 | +Output |
| 86 | +``` |
| 87 | +33 |
| 88 | +3 |
| 89 | +4 |
| 90 | +5 |
| 91 | +``` |
| 92 | + |
| 93 | +-------- |
| 94 | + |
0 commit comments