diff --git a/.gitignore b/.gitignore
index 4b64967..4069360 100644
--- a/.gitignore
+++ b/.gitignore
@@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
__pycache__
-.vscode
.DS_Store
+.vscode
+*.xlsx
diff --git a/LICENSE b/LICENSE
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..cbe5ad1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/LICENSE
@@ -0,0 +1,437 @@
+Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International
+
+=======================================================================
+
+Creative Commons Corporation ("Creative Commons") is not a law firm and
+does not provide legal services or legal advice. Distribution of
+Creative Commons public licenses does not create a lawyer-client or
+other relationship. Creative Commons makes its licenses and related
+information available on an "as-is" basis. Creative Commons gives no
+warranties regarding its licenses, any material licensed under their
+terms and conditions, or any related information. Creative Commons
+disclaims all liability for damages resulting from their use to the
+fullest extent possible.
+
+Using Creative Commons Public Licenses
+
+Creative Commons public licenses provide a standard set of terms and
+conditions that creators and other rights holders may use to share
+original works of authorship and other material subject to copyright
+and certain other rights specified in the public license below. The
+following considerations are for informational purposes only, are not
+exhaustive, and do not form part of our licenses.
+
+ Considerations for licensors: Our public licenses are
+ intended for use by those authorized to give the public
+ permission to use material in ways otherwise restricted by
+ copyright and certain other rights. Our licenses are
+ irrevocable. Licensors should read and understand the terms
+ and conditions of the license they choose before applying it.
+ Licensors should also secure all rights necessary before
+ applying our licenses so that the public can reuse the
+ material as expected. Licensors should clearly mark any
+ material not subject to the license. This includes other CC-
+ licensed material, or material used under an exception or
+ limitation to copyright. More considerations for licensors:
+ wiki.creativecommons.org/Considerations_for_licensors
+
+ Considerations for the public: By using one of our public
+ licenses, a licensor grants the public permission to use the
+ licensed material under specified terms and conditions. If
+ the licensor's permission is not necessary for any reason--for
+ example, because of any applicable exception or limitation to
+ copyright--then that use is not regulated by the license. Our
+ licenses grant only permissions under copyright and certain
+ other rights that a licensor has authority to grant. Use of
+ the licensed material may still be restricted for other
+ reasons, including because others have copyright or other
+ rights in the material. A licensor may make special requests,
+ such as asking that all changes be marked or described.
+ Although not required by our licenses, you are encouraged to
+ respect those requests where reasonable. More considerations
+ for the public:
+ wiki.creativecommons.org/Considerations_for_licensees
+
+=======================================================================
+
+Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International
+Public License
+
+By exercising the Licensed Rights (defined below), You accept and agree
+to be bound by the terms and conditions of this Creative Commons
+Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International Public License
+("Public License"). To the extent this Public License may be
+interpreted as a contract, You are granted the Licensed Rights in
+consideration of Your acceptance of these terms and conditions, and the
+Licensor grants You such rights in consideration of benefits the
+Licensor receives from making the Licensed Material available under
+these terms and conditions.
+
+
+Section 1 -- Definitions.
+
+ a. Adapted Material means material subject to Copyright and Similar
+ Rights that is derived from or based upon the Licensed Material
+ and in which the Licensed Material is translated, altered,
+ arranged, transformed, or otherwise modified in a manner requiring
+ permission under the Copyright and Similar Rights held by the
+ Licensor. For purposes of this Public License, where the Licensed
+ Material is a musical work, performance, or sound recording,
+ Adapted Material is always produced where the Licensed Material is
+ synched in timed relation with a moving image.
+
+ b. Adapter's License means the license You apply to Your Copyright
+ and Similar Rights in Your contributions to Adapted Material in
+ accordance with the terms and conditions of this Public License.
+
+ c. BY-NC-SA Compatible License means a license listed at
+ creativecommons.org/compatiblelicenses, approved by Creative
+ Commons as essentially the equivalent of this Public License.
+
+ d. Copyright and Similar Rights means copyright and/or similar rights
+ closely related to copyright including, without limitation,
+ performance, broadcast, sound recording, and Sui Generis Database
+ Rights, without regard to how the rights are labeled or
+ categorized. For purposes of this Public License, the rights
+ specified in Section 2(b)(1)-(2) are not Copyright and Similar
+ Rights.
+
+ e. Effective Technological Measures means those measures that, in the
+ absence of proper authority, may not be circumvented under laws
+ fulfilling obligations under Article 11 of the WIPO Copyright
+ Treaty adopted on December 20, 1996, and/or similar international
+ agreements.
+
+ f. Exceptions and Limitations means fair use, fair dealing, and/or
+ any other exception or limitation to Copyright and Similar Rights
+ that applies to Your use of the Licensed Material.
+
+ g. License Elements means the license attributes listed in the name
+ of a Creative Commons Public License. The License Elements of this
+ Public License are Attribution, NonCommercial, and ShareAlike.
+
+ h. Licensed Material means the artistic or literary work, database,
+ or other material to which the Licensor applied this Public
+ License.
+
+ i. Licensed Rights means the rights granted to You subject to the
+ terms and conditions of this Public License, which are limited to
+ all Copyright and Similar Rights that apply to Your use of the
+ Licensed Material and that the Licensor has authority to license.
+
+ j. Licensor means the individual(s) or entity(ies) granting rights
+ under this Public License.
+
+ k. NonCommercial means not primarily intended for or directed towards
+ commercial advantage or monetary compensation. For purposes of
+ this Public License, the exchange of the Licensed Material for
+ other material subject to Copyright and Similar Rights by digital
+ file-sharing or similar means is NonCommercial provided there is
+ no payment of monetary compensation in connection with the
+ exchange.
+
+ l. Share means to provide material to the public by any means or
+ process that requires permission under the Licensed Rights, such
+ as reproduction, public display, public performance, distribution,
+ dissemination, communication, or importation, and to make material
+ available to the public including in ways that members of the
+ public may access the material from a place and at a time
+ individually chosen by them.
+
+ m. Sui Generis Database Rights means rights other than copyright
+ resulting from Directive 96/9/EC of the European Parliament and of
+ the Council of 11 March 1996 on the legal protection of databases,
+ as amended and/or succeeded, as well as other essentially
+ equivalent rights anywhere in the world.
+
+ n. You means the individual or entity exercising the Licensed Rights
+ under this Public License. Your has a corresponding meaning.
+
+
+Section 2 -- Scope.
+
+ a. License grant.
+
+ 1. Subject to the terms and conditions of this Public License,
+ the Licensor hereby grants You a worldwide, royalty-free,
+ non-sublicensable, non-exclusive, irrevocable license to
+ exercise the Licensed Rights in the Licensed Material to:
+
+ a. reproduce and Share the Licensed Material, in whole or
+ in part, for NonCommercial purposes only; and
+
+ b. produce, reproduce, and Share Adapted Material for
+ NonCommercial purposes only.
+
+ 2. Exceptions and Limitations. For the avoidance of doubt, where
+ Exceptions and Limitations apply to Your use, this Public
+ License does not apply, and You do not need to comply with
+ its terms and conditions.
+
+ 3. Term. The term of this Public License is specified in Section
+ 6(a).
+
+ 4. Media and formats; technical modifications allowed. The
+ Licensor authorizes You to exercise the Licensed Rights in
+ all media and formats whether now known or hereafter created,
+ and to make technical modifications necessary to do so. The
+ Licensor waives and/or agrees not to assert any right or
+ authority to forbid You from making technical modifications
+ necessary to exercise the Licensed Rights, including
+ technical modifications necessary to circumvent Effective
+ Technological Measures. For purposes of this Public License,
+ simply making modifications authorized by this Section 2(a)
+ (4) never produces Adapted Material.
+
+ 5. Downstream recipients.
+
+ a. Offer from the Licensor -- Licensed Material. Every
+ recipient of the Licensed Material automatically
+ receives an offer from the Licensor to exercise the
+ Licensed Rights under the terms and conditions of this
+ Public License.
+
+ b. Additional offer from the Licensor -- Adapted Material.
+ Every recipient of Adapted Material from You
+ automatically receives an offer from the Licensor to
+ exercise the Licensed Rights in the Adapted Material
+ under the conditions of the Adapter's License You apply.
+
+ c. No downstream restrictions. You may not offer or impose
+ any additional or different terms or conditions on, or
+ apply any Effective Technological Measures to, the
+ Licensed Material if doing so restricts exercise of the
+ Licensed Rights by any recipient of the Licensed
+ Material.
+
+ 6. No endorsement. Nothing in this Public License constitutes or
+ may be construed as permission to assert or imply that You
+ are, or that Your use of the Licensed Material is, connected
+ with, or sponsored, endorsed, or granted official status by,
+ the Licensor or others designated to receive attribution as
+ provided in Section 3(a)(1)(A)(i).
+
+ b. Other rights.
+
+ 1. Moral rights, such as the right of integrity, are not
+ licensed under this Public License, nor are publicity,
+ privacy, and/or other similar personality rights; however, to
+ the extent possible, the Licensor waives and/or agrees not to
+ assert any such rights held by the Licensor to the limited
+ extent necessary to allow You to exercise the Licensed
+ Rights, but not otherwise.
+
+ 2. Patent and trademark rights are not licensed under this
+ Public License.
+
+ 3. To the extent possible, the Licensor waives any right to
+ collect royalties from You for the exercise of the Licensed
+ Rights, whether directly or through a collecting society
+ under any voluntary or waivable statutory or compulsory
+ licensing scheme. In all other cases the Licensor expressly
+ reserves any right to collect such royalties, including when
+ the Licensed Material is used other than for NonCommercial
+ purposes.
+
+
+Section 3 -- License Conditions.
+
+Your exercise of the Licensed Rights is expressly made subject to the
+following conditions.
+
+ a. Attribution.
+
+ 1. If You Share the Licensed Material (including in modified
+ form), You must:
+
+ a. retain the following if it is supplied by the Licensor
+ with the Licensed Material:
+
+ i. identification of the creator(s) of the Licensed
+ Material and any others designated to receive
+ attribution, in any reasonable manner requested by
+ the Licensor (including by pseudonym if
+ designated);
+
+ ii. a copyright notice;
+
+ iii. a notice that refers to this Public License;
+
+ iv. a notice that refers to the disclaimer of
+ warranties;
+
+ v. a URI or hyperlink to the Licensed Material to the
+ extent reasonably practicable;
+
+ b. indicate if You modified the Licensed Material and
+ retain an indication of any previous modifications; and
+
+ c. indicate the Licensed Material is licensed under this
+ Public License, and include the text of, or the URI or
+ hyperlink to, this Public License.
+
+ 2. You may satisfy the conditions in Section 3(a)(1) in any
+ reasonable manner based on the medium, means, and context in
+ which You Share the Licensed Material. For example, it may be
+ reasonable to satisfy the conditions by providing a URI or
+ hyperlink to a resource that includes the required
+ information.
+ 3. If requested by the Licensor, You must remove any of the
+ information required by Section 3(a)(1)(A) to the extent
+ reasonably practicable.
+
+ b. ShareAlike.
+
+ In addition to the conditions in Section 3(a), if You Share
+ Adapted Material You produce, the following conditions also apply.
+
+ 1. The Adapter's License You apply must be a Creative Commons
+ license with the same License Elements, this version or
+ later, or a BY-NC-SA Compatible License.
+
+ 2. You must include the text of, or the URI or hyperlink to, the
+ Adapter's License You apply. You may satisfy this condition
+ in any reasonable manner based on the medium, means, and
+ context in which You Share Adapted Material.
+
+ 3. You may not offer or impose any additional or different terms
+ or conditions on, or apply any Effective Technological
+ Measures to, Adapted Material that restrict exercise of the
+ rights granted under the Adapter's License You apply.
+
+
+Section 4 -- Sui Generis Database Rights.
+
+Where the Licensed Rights include Sui Generis Database Rights that
+apply to Your use of the Licensed Material:
+
+ a. for the avoidance of doubt, Section 2(a)(1) grants You the right
+ to extract, reuse, reproduce, and Share all or a substantial
+ portion of the contents of the database for NonCommercial purposes
+ only;
+
+ b. if You include all or a substantial portion of the database
+ contents in a database in which You have Sui Generis Database
+ Rights, then the database in which You have Sui Generis Database
+ Rights (but not its individual contents) is Adapted Material,
+ including for purposes of Section 3(b); and
+
+ c. You must comply with the conditions in Section 3(a) if You Share
+ all or a substantial portion of the contents of the database.
+
+For the avoidance of doubt, this Section 4 supplements and does not
+replace Your obligations under this Public License where the Licensed
+Rights include other Copyright and Similar Rights.
+
+
+Section 5 -- Disclaimer of Warranties and Limitation of Liability.
+
+ a. UNLESS OTHERWISE SEPARATELY UNDERTAKEN BY THE LICENSOR, TO THE
+ EXTENT POSSIBLE, THE LICENSOR OFFERS THE LICENSED MATERIAL AS-IS
+ AND AS-AVAILABLE, AND MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES OF
+ ANY KIND CONCERNING THE LICENSED MATERIAL, WHETHER EXPRESS,
+ IMPLIED, STATUTORY, OR OTHER. THIS INCLUDES, WITHOUT LIMITATION,
+ WARRANTIES OF TITLE, MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
+ PURPOSE, NON-INFRINGEMENT, ABSENCE OF LATENT OR OTHER DEFECTS,
+ ACCURACY, OR THE PRESENCE OR ABSENCE OF ERRORS, WHETHER OR NOT
+ KNOWN OR DISCOVERABLE. WHERE DISCLAIMERS OF WARRANTIES ARE NOT
+ ALLOWED IN FULL OR IN PART, THIS DISCLAIMER MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
+
+ b. TO THE EXTENT POSSIBLE, IN NO EVENT WILL THE LICENSOR BE LIABLE
+ TO YOU ON ANY LEGAL THEORY (INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION,
+ NEGLIGENCE) OR OTHERWISE FOR ANY DIRECT, SPECIAL, INDIRECT,
+ INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE, EXEMPLARY, OR OTHER LOSSES,
+ COSTS, EXPENSES, OR DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THIS PUBLIC LICENSE OR
+ USE OF THE LICENSED MATERIAL, EVEN IF THE LICENSOR HAS BEEN
+ ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH LOSSES, COSTS, EXPENSES, OR
+ DAMAGES. WHERE A LIMITATION OF LIABILITY IS NOT ALLOWED IN FULL OR
+ IN PART, THIS LIMITATION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
+
+ c. The disclaimer of warranties and limitation of liability provided
+ above shall be interpreted in a manner that, to the extent
+ possible, most closely approximates an absolute disclaimer and
+ waiver of all liability.
+
+
+Section 6 -- Term and Termination.
+
+ a. This Public License applies for the term of the Copyright and
+ Similar Rights licensed here. However, if You fail to comply with
+ this Public License, then Your rights under this Public License
+ terminate automatically.
+
+ b. Where Your right to use the Licensed Material has terminated under
+ Section 6(a), it reinstates:
+
+ 1. automatically as of the date the violation is cured, provided
+ it is cured within 30 days of Your discovery of the
+ violation; or
+
+ 2. upon express reinstatement by the Licensor.
+
+ For the avoidance of doubt, this Section 6(b) does not affect any
+ right the Licensor may have to seek remedies for Your violations
+ of this Public License.
+
+ c. For the avoidance of doubt, the Licensor may also offer the
+ Licensed Material under separate terms or conditions or stop
+ distributing the Licensed Material at any time; however, doing so
+ will not terminate this Public License.
+
+ d. Sections 1, 5, 6, 7, and 8 survive termination of this Public
+ License.
+
+
+Section 7 -- Other Terms and Conditions.
+
+ a. The Licensor shall not be bound by any additional or different
+ terms or conditions communicated by You unless expressly agreed.
+
+ b. Any arrangements, understandings, or agreements regarding the
+ Licensed Material not stated herein are separate from and
+ independent of the terms and conditions of this Public License.
+
+
+Section 8 -- Interpretation.
+
+ a. For the avoidance of doubt, this Public License does not, and
+ shall not be interpreted to, reduce, limit, restrict, or impose
+ conditions on any use of the Licensed Material that could lawfully
+ be made without permission under this Public License.
+
+ b. To the extent possible, if any provision of this Public License is
+ deemed unenforceable, it shall be automatically reformed to the
+ minimum extent necessary to make it enforceable. If the provision
+ cannot be reformed, it shall be severed from this Public License
+ without affecting the enforceability of the remaining terms and
+ conditions.
+
+ c. No term or condition of this Public License will be waived and no
+ failure to comply consented to unless expressly agreed to by the
+ Licensor.
+
+ d. Nothing in this Public License constitutes or may be interpreted
+ as a limitation upon, or waiver of, any privileges and immunities
+ that apply to the Licensor or You, including from the legal
+ processes of any jurisdiction or authority.
+
+=======================================================================
+
+Creative Commons is not a party to its public
+licenses. Notwithstanding, Creative Commons may elect to apply one of
+its public licenses to material it publishes and in those instances
+will be considered the “Licensor.” The text of the Creative Commons
+public licenses is dedicated to the public domain under the CC0 Public
+Domain Dedication. Except for the limited purpose of indicating that
+material is shared under a Creative Commons public license or as
+otherwise permitted by the Creative Commons policies published at
+creativecommons.org/policies, Creative Commons does not authorize the
+use of the trademark "Creative Commons" or any other trademark or logo
+of Creative Commons without its prior written consent including,
+without limitation, in connection with any unauthorized modifications
+to any of its public licenses or any other arrangements,
+understandings, or agreements concerning use of licensed material. For
+the avoidance of doubt, this paragraph does not form part of the
+public licenses.
+
+Creative Commons may be contacted at creativecommons.org.
diff --git a/LICENSE.md b/LICENSE.md
deleted file mode 100644
index d379d94..0000000
--- a/LICENSE.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,173 +0,0 @@
-# Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International
-
-Creative Commons Corporation (“Creative Commons”) is not a law firm and does not provide legal services or legal advice. Distribution of Creative Commons public licenses does not create a lawyer-client or other relationship. Creative Commons makes its licenses and related information available on an “as-is” basis. Creative Commons gives no warranties regarding its licenses, any material licensed under their terms and conditions, or any related information. Creative Commons disclaims all liability for damages resulting from their use to the fullest extent possible.
-
-### Using Creative Commons Public Licenses
-
-Creative Commons public licenses provide a standard set of terms and conditions that creators and other rights holders may use to share original works of authorship and other material subject to copyright and certain other rights specified in the public license below. The following considerations are for informational purposes only, are not exhaustive, and do not form part of our licenses.
-
-* __Considerations for licensors:__ Our public licenses are intended for use by those authorized to give the public permission to use material in ways otherwise restricted by copyright and certain other rights. Our licenses are irrevocable. Licensors should read and understand the terms and conditions of the license they choose before applying it. Licensors should also secure all rights necessary before applying our licenses so that the public can reuse the material as expected. Licensors should clearly mark any material not subject to the license. This includes other CC-licensed material, or material used under an exception or limitation to copyright. [More considerations for licensors](http://wiki.creativecommons.org/Considerations_for_licensors_and_licensees#Considerations_for_licensors).
-
-* __Considerations for the public:__ By using one of our public licenses, a licensor grants the public permission to use the licensed material under specified terms and conditions. If the licensor’s permission is not necessary for any reason–for example, because of any applicable exception or limitation to copyright–then that use is not regulated by the license. Our licenses grant only permissions under copyright and certain other rights that a licensor has authority to grant. Use of the licensed material may still be restricted for other reasons, including because others have copyright or other rights in the material. A licensor may make special requests, such as asking that all changes be marked or described. Although not required by our licenses, you are encouraged to respect those requests where reasonable. [More considerations for the public](http://wiki.creativecommons.org/Considerations_for_licensors_and_licensees#Considerations_for_licensees).
-
-## Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International Public License
-
-By exercising the Licensed Rights (defined below), You accept and agree to be bound by the terms and conditions of this Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International Public License ("Public License"). To the extent this Public License may be interpreted as a contract, You are granted the Licensed Rights in consideration of Your acceptance of these terms and conditions, and the Licensor grants You such rights in consideration of benefits the Licensor receives from making the Licensed Material available under these terms and conditions.
-
-### Section 1 – Definitions.
-
-a. __Adapted Material__ means material subject to Copyright and Similar Rights that is derived from or based upon the Licensed Material and in which the Licensed Material is translated, altered, arranged, transformed, or otherwise modified in a manner requiring permission under the Copyright and Similar Rights held by the Licensor. For purposes of this Public License, where the Licensed Material is a musical work, performance, or sound recording, Adapted Material is always produced where the Licensed Material is synched in timed relation with a moving image.
-
-b. __Adapter's License__ means the license You apply to Your Copyright and Similar Rights in Your contributions to Adapted Material in accordance with the terms and conditions of this Public License.
-
-c. __BY-NC-SA Compatible License__ means a license listed at [creativecommons.org/compatiblelicenses](http://creativecommons.org/compatiblelicenses), approved by Creative Commons as essentially the equivalent of this Public License.
-
-d. __Copyright and Similar Rights__ means copyright and/or similar rights closely related to copyright including, without limitation, performance, broadcast, sound recording, and Sui Generis Database Rights, without regard to how the rights are labeled or categorized. For purposes of this Public License, the rights specified in Section 2(b)(1)-(2) are not Copyright and Similar Rights.
-
-e. __Effective Technological Measures__ means those measures that, in the absence of proper authority, may not be circumvented under laws fulfilling obligations under Article 11 of the WIPO Copyright Treaty adopted on December 20, 1996, and/or similar international agreements.
-
-f. __Exceptions and Limitations__ means fair use, fair dealing, and/or any other exception or limitation to Copyright and Similar Rights that applies to Your use of the Licensed Material.
-
-g. __License Elements__ means the license attributes listed in the name of a Creative Commons Public License. The License Elements of this Public License are Attribution, NonCommercial, and ShareAlike.
-
-h. __Licensed Material__ means the artistic or literary work, database, or other material to which the Licensor applied this Public License.
-
-i. __Licensed Rights__ means the rights granted to You subject to the terms and conditions of this Public License, which are limited to all Copyright and Similar Rights that apply to Your use of the Licensed Material and that the Licensor has authority to license.
-
-j. __Licensor__ means the individual(s) or entity(ies) granting rights under this Public License.
-
-k. __NonCommercial__ means not primarily intended for or directed towards commercial advantage or monetary compensation. For purposes of this Public License, the exchange of the Licensed Material for other material subject to Copyright and Similar Rights by digital file-sharing or similar means is NonCommercial provided there is no payment of monetary compensation in connection with the exchange.
-
-l. __Share__ means to provide material to the public by any means or process that requires permission under the Licensed Rights, such as reproduction, public display, public performance, distribution, dissemination, communication, or importation, and to make material available to the public including in ways that members of the public may access the material from a place and at a time individually chosen by them.
-
-m. __Sui Generis Database Rights__ means rights other than copyright resulting from Directive 96/9/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 11 March 1996 on the legal protection of databases, as amended and/or succeeded, as well as other essentially equivalent rights anywhere in the world.
-
-n. __You__ means the individual or entity exercising the Licensed Rights under this Public License. __Your__ has a corresponding meaning.
-
-### Section 2 – Scope.
-
-a. ___License grant.___
-
- 1. Subject to the terms and conditions of this Public License, the Licensor hereby grants You a worldwide, royalty-free, non-sublicensable, non-exclusive, irrevocable license to exercise the Licensed Rights in the Licensed Material to:
-
- A. reproduce and Share the Licensed Material, in whole or in part, for NonCommercial purposes only; and
-
- B. produce, reproduce, and Share Adapted Material for NonCommercial purposes only.
-
- 2. __Exceptions and Limitations.__ For the avoidance of doubt, where Exceptions and Limitations apply to Your use, this Public License does not apply, and You do not need to comply with its terms and conditions.
-
- 3. __Term.__ The term of this Public License is specified in Section 6(a).
-
- 4. __Media and formats; technical modifications allowed.__ The Licensor authorizes You to exercise the Licensed Rights in all media and formats whether now known or hereafter created, and to make technical modifications necessary to do so. The Licensor waives and/or agrees not to assert any right or authority to forbid You from making technical modifications necessary to exercise the Licensed Rights, including technical modifications necessary to circumvent Effective Technological Measures. For purposes of this Public License, simply making modifications authorized by this Section 2(a)(4) never produces Adapted Material.
-
- 5. __Downstream recipients.__
-
- A. __Offer from the Licensor – Licensed Material.__ Every recipient of the Licensed Material automatically receives an offer from the Licensor to exercise the Licensed Rights under the terms and conditions of this Public License.
-
- B. __Additional offer from the Licensor – Adapted Material.__ Every recipient of Adapted Material from You automatically receives an offer from the Licensor to exercise the Licensed Rights in the Adapted Material under the conditions of the Adapter’s License You apply.
-
- C. __No downstream restrictions.__ You may not offer or impose any additional or different terms or conditions on, or apply any Effective Technological Measures to, the Licensed Material if doing so restricts exercise of the Licensed Rights by any recipient of the Licensed Material.
-
- 6. __No endorsement.__ Nothing in this Public License constitutes or may be construed as permission to assert or imply that You are, or that Your use of the Licensed Material is, connected with, or sponsored, endorsed, or granted official status by, the Licensor or others designated to receive attribution as provided in Section 3(a)(1)(A)(i).
-
-b. ___Other rights.___
-
- 1. Moral rights, such as the right of integrity, are not licensed under this Public License, nor are publicity, privacy, and/or other similar personality rights; however, to the extent possible, the Licensor waives and/or agrees not to assert any such rights held by the Licensor to the limited extent necessary to allow You to exercise the Licensed Rights, but not otherwise.
-
- 2. Patent and trademark rights are not licensed under this Public License.
-
- 3. To the extent possible, the Licensor waives any right to collect royalties from You for the exercise of the Licensed Rights, whether directly or through a collecting society under any voluntary or waivable statutory or compulsory licensing scheme. In all other cases the Licensor expressly reserves any right to collect such royalties, including when the Licensed Material is used other than for NonCommercial purposes.
-
-### Section 3 – License Conditions.
-
-Your exercise of the Licensed Rights is expressly made subject to the following conditions.
-
-a. ___Attribution.___
-
- 1. If You Share the Licensed Material (including in modified form), You must:
-
- A. retain the following if it is supplied by the Licensor with the Licensed Material:
-
- i. identification of the creator(s) of the Licensed Material and any others designated to receive attribution, in any reasonable manner requested by the Licensor (including by pseudonym if designated);
-
- ii. a copyright notice;
-
- iii. a notice that refers to this Public License;
-
- iv. a notice that refers to the disclaimer of warranties;
-
- v. a URI or hyperlink to the Licensed Material to the extent reasonably practicable;
-
- B. indicate if You modified the Licensed Material and retain an indication of any previous modifications; and
-
- C. indicate the Licensed Material is licensed under this Public License, and include the text of, or the URI or hyperlink to, this Public License.
-
- 2. You may satisfy the conditions in Section 3(a)(1) in any reasonable manner based on the medium, means, and context in which You Share the Licensed Material. For example, it may be reasonable to satisfy the conditions by providing a URI or hyperlink to a resource that includes the required information.
-
- 3. If requested by the Licensor, You must remove any of the information required by Section 3(a)(1)(A) to the extent reasonably practicable.
-
-b. ___ShareAlike.___
-
-In addition to the conditions in Section 3(a), if You Share Adapted Material You produce, the following conditions also apply.
-
-1. The Adapter’s License You apply must be a Creative Commons license with the same License Elements, this version or later, or a BY-NC-SA Compatible License.
-
-2. You must include the text of, or the URI or hyperlink to, the Adapter's License You apply. You may satisfy this condition in any reasonable manner based on the medium, means, and context in which You Share Adapted Material.
-
-3. You may not offer or impose any additional or different terms or conditions on, or apply any Effective Technological Measures to, Adapted Material that restrict exercise of the rights granted under the Adapter's License You apply.
-
-### Section 4 – Sui Generis Database Rights.
-
-Where the Licensed Rights include Sui Generis Database Rights that apply to Your use of the Licensed Material:
-
-a. for the avoidance of doubt, Section 2(a)(1) grants You the right to extract, reuse, reproduce, and Share all or a substantial portion of the contents of the database for NonCommercial purposes only;
-
-b. if You include all or a substantial portion of the database contents in a database in which You have Sui Generis Database Rights, then the database in which You have Sui Generis Database Rights (but not its individual contents) is Adapted Material, including for purposes of Section 3(b); and
-
-c. You must comply with the conditions in Section 3(a) if You Share all or a substantial portion of the contents of the database.
-
-For the avoidance of doubt, this Section 4 supplements and does not replace Your obligations under this Public License where the Licensed Rights include other Copyright and Similar Rights.
-
-### Section 5 – Disclaimer of Warranties and Limitation of Liability.
-
-a. __Unless otherwise separately undertaken by the Licensor, to the extent possible, the Licensor offers the Licensed Material as-is and as-available, and makes no representations or warranties of any kind concerning the Licensed Material, whether express, implied, statutory, or other. This includes, without limitation, warranties of title, merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, non-infringement, absence of latent or other defects, accuracy, or the presence or absence of errors, whether or not known or discoverable. Where disclaimers of warranties are not allowed in full or in part, this disclaimer may not apply to You.__
-
-b. __To the extent possible, in no event will the Licensor be liable to You on any legal theory (including, without limitation, negligence) or otherwise for any direct, special, indirect, incidental, consequential, punitive, exemplary, or other losses, costs, expenses, or damages arising out of this Public License or use of the Licensed Material, even if the Licensor has been advised of the possibility of such losses, costs, expenses, or damages. Where a limitation of liability is not allowed in full or in part, this limitation may not apply to You.__
-
-c. The disclaimer of warranties and limitation of liability provided above shall be interpreted in a manner that, to the extent possible, most closely approximates an absolute disclaimer and waiver of all liability.
-
-### Section 6 – Term and Termination.
-
-a. This Public License applies for the term of the Copyright and Similar Rights licensed here. However, if You fail to comply with this Public License, then Your rights under this Public License terminate automatically.
-
-b. Where Your right to use the Licensed Material has terminated under Section 6(a), it reinstates:
-
- 1. automatically as of the date the violation is cured, provided it is cured within 30 days of Your discovery of the violation; or
-
- 2. upon express reinstatement by the Licensor.
-
- For the avoidance of doubt, this Section 6(b) does not affect any right the Licensor may have to seek remedies for Your violations of this Public License.
-
-c. For the avoidance of doubt, the Licensor may also offer the Licensed Material under separate terms or conditions or stop distributing the Licensed Material at any time; however, doing so will not terminate this Public License.
-
-d. Sections 1, 5, 6, 7, and 8 survive termination of this Public License.
-
-### Section 7 – Other Terms and Conditions.
-
-a. The Licensor shall not be bound by any additional or different terms or conditions communicated by You unless expressly agreed.
-
-b. Any arrangements, understandings, or agreements regarding the Licensed Material not stated herein are separate from and independent of the terms and conditions of this Public License.
-
-### Section 8 – Interpretation.
-
-a. For the avoidance of doubt, this Public License does not, and shall not be interpreted to, reduce, limit, restrict, or impose conditions on any use of the Licensed Material that could lawfully be made without permission under this Public License.
-
-b. To the extent possible, if any provision of this Public License is deemed unenforceable, it shall be automatically reformed to the minimum extent necessary to make it enforceable. If the provision cannot be reformed, it shall be severed from this Public License without affecting the enforceability of the remaining terms and conditions.
-
-c. No term or condition of this Public License will be waived and no failure to comply consented to unless expressly agreed to by the Licensor.
-
-d. Nothing in this Public License constitutes or may be interpreted as a limitation upon, or waiver of, any privileges and immunities that apply to the Licensor or You, including from the legal processes of any jurisdiction or authority.
-
-> Creative Commons is not a party to its public licenses. Notwithstanding, Creative Commons may elect to apply one of its public licenses to material it publishes and in those instances will be considered the “Licensor.” Except for the limited purpose of indicating that material is shared under a Creative Commons public license or as otherwise permitted by the Creative Commons policies published at [creativecommons.org/policies](http://creativecommons.org/policies), Creative Commons does not authorize the use of the trademark “Creative Commons” or any other trademark or logo of Creative Commons without its prior written consent including, without limitation, in connection with any unauthorized modifications to any of its public licenses or any other arrangements, understandings, or agreements concerning use of licensed material. For the avoidance of doubt, this paragraph does not form part of the public licenses.
->
-> Creative Commons may be contacted at creativecommons.org
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
old mode 100644
new mode 100755
index 395d94c..1163fa5
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -1,186 +1,74 @@
-# :book: 图解算法数据结构
+
+
+  +
+
+
+
-[](https://github.com/krahets/LeetCode-Book) [](https://github.com/krahets/LeetCode-Book) [](https://github.com/krahets)
+
+  +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+
- [](https://github.com/krahets/LeetCode-Book/tree/main/python) [](https://github.com/krahets/LeetCode-Book/tree/main/java) [](https://github.com/krahets/LeetCode-Book/tree/main/cpp)
+[《图解算法数据结构》](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/detail/illustration-of-algorithm/)是一本面向算法初学者和互联网求职者编写的 LeetBook 手册。
-[ ](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/detail/illustration-of-algorithm/)
+- 图文详解 75 道题目,覆盖主要算法知识点。
+- 题目活跃于各大互联网公司招聘中,可使笔面试准备事半功倍。
+- 致力于行文深入浅出、图文搭配,提供简洁的 Python, Java, C++ 解题代码。
-LeetBook《图解算法数据结构》面向算法初学者、互联网求职者设计,主要内容包括:
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> 本仓库包含“图解算法数据结构”、“Krahets 笔面试精选 88 题”和“剑指 Offer”的题解内容:
+>
+> ```python
+> LeetCode-Book
+> ├── leetbook_ioa # 《图解算法数据结构》题解和专栏文档
+> ├── selected_coding_interview # 《Krahets 笔面试精选 88 题》题解文档
+> └── sword_for_offer # 《剑指 Offer》题解文档、代码、刷题计划
+> ```
-### :green_book: 剑指 Offer 图文题解
+> 若本仓库对您有所帮助,请在页面右上角点个 **Star** :star: 支持一下,谢谢!
-- 图文详解 75 道题目,覆盖主要算法知识点,非常适合作为算法学习的 **第一份题库** 。
-- 题库活跃于各大互联网公司招聘中,可使笔面试准备事半功倍。
-- 致力于行文深入浅出、图文搭配,提供简洁的 **Python3, Java, C++** 解题代码。
-- 笔者整理了 **30 天刷题计划**、**题目分类**,让刷题有迹可循。
-
-### :blue_book: 数据结构与算法专栏
-
-- **基础知识:** 时间复杂度、空间复杂度等算法知识。
-- **数据结构:** 数组、栈、队列、字符串、链表、树、图、堆、哈希表。
-- **算法专题:** 分治算法、动态规划、搜索与回溯算法、查找算法、贪心算法、排序、位运算、双指针、模拟、数学。
-
-## :student: 适合人群
-
-- 互联网算法、软件岗位求职者。
-- 从零开始接触数据结构与算法的同学。
-- 具有一定编程基础,计划系统学习算法的同学。
-
----
-
-## :ledger: 算法专栏
-
-### 「[数据结构](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50e446/)」
-
-> 建议对数据结构不熟悉的同学,先看这篇熟悉用法。
-
-- 常用数据结构的**分类**和**基本特点**。
-- 在算法解题中,数据结构的**常用操作**。
-- 在 Python3 , Java , C++ 语言中,各数据结构的**初始化与构建方法**。
-
-### 「[算法复杂度](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/r84gmi/)」
-
-> 复杂度是算法优劣性的有力评价指标,对于理解算法起着至关重要的作用。
-
-- 什么是时间复杂度、空间复杂度?
-- 时间复杂度和空间复杂度的**概念定义**、**符号表示**、**常见种类**、**时空权衡**。
-- 时间与空间复杂度的**示例题目与解析**。
-
-### 「[动态规划](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/m5zfc1/)」
-
-> 动态规划是算法重难点,也是笔面试重要考点,需要重点理解与练习。
-
-- 动态规划问题特点,动态规划和分治算法的联系与区别;
-- 借助例题介绍**重叠子问题**和**最优子结构**分别是什么,以及动态规划是如何解决它们的;
-- 动态规划的**解题框架**总结;
-- 动态规划的**练习例题**,从易到难排序;
-
-### 「[排序算法](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/pxal47/)」
-
-> 排序是最经典的算法问题之一,由浅入深的多种算法涵盖多个算法知识点(例如暴力搜索、分治算法、堆数据结构等)。
-
-- 排序算法分类方法,包括稳定性 、就地性 、自适应性;
-- 排序算法与二分查找、双指针算法之间的关系;
-- 各主要排序算法的时间复杂度与空间复杂度;
-
----
-
-## :hourglass: 刷题计划
-
-笔者整理了《剑指 Offer 》刷题计划,核心理念为从易到难、从基础类题目到综合类题目,供希望按照知识点类型顺序刷题的小伙伴们参考。行百里者半九十,坚持一个月刷完,一起加油!
-
-| 日程 | 题目 |
-| :--------: | :------------------------------------------------ |
-| **Day 1** | **栈与队列(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 09. 用两个栈实现队列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5d3i87/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 30. 包含 min 函数的栈](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50bp33/) |
-| **Day 2** | **链表(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dt66m/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9pdjbm/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9p0yy1/) |
-| **Day 3** | **字符串(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 05. 替换空格](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50ywkd/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 58 - II. 左旋转字符串](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/589fz2/) |
-| **Day 4** | **查找算法(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 03. 数组中重复的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/59bjss/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 53 - I. 在排序数组中查找数字 I](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5874p1/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 53 - II. 0~n-1 中缺失的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58iqo5/) |
-| **Day 5** | **查找算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 04. 二维数组中的查找](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5v76yi/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 11. 旋转数组的最小数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50xofm/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 50. 第一个只出现一次的字符](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5viisg/) |
-| **Day 6** | **搜索与回溯算法(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9ackoe/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vawr3/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vnp91/) |
-| **Day 7** | **搜索与回溯算法(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 26. 树的子结构](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dshwe/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 27. 二叉树的镜像](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/59zt5i/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 28. 对称的二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5d412v/) |
-| **Day 8** | **动态规划(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 10- I. 斐波那契数列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50fxu1/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 10- II. 青蛙跳台阶问题](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57hyl5/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 63. 股票的最大利润](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58nn7r/) |
-| **Day 9** | **动态规划(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 42. 连续子数组的最大和](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/59gq9c/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 47. 礼物的最大价值](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vokvr/) |
-| **Day 10** | **动态规划(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 46. 把数字翻译成字符串](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/99wd55/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 48. 最长不含重复字符的子字符串](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dgr0c/) |
-| **Day 11** | **双指针(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/505fc7/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第 k 个节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58tl52/) |
-| **Day 12** | **双指针(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vq98s/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/oe5os3/) |
-| **Day 13** | **双指针(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 21. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5v8a6t/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 57. 和为 s 的两个数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5832fi/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 58 - I. 翻转单词顺序](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/586ecg/) |
-| **Day 14** | **搜索与回溯算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 12. 矩阵中的路径](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58wowd/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 13. 机器人的运动范围](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9h6vo2/) |
-| **Day 15** | **搜索与回溯算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dy6pt/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dbies/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 54. 二叉搜索树的第 k 大节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58df23/) |
-| **Day 16** | **排序(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 45. 把数组排成最小的数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/59ypcj/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 61. 扑克牌中的顺子](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57mpoj/) |
-| **Day 17** | **排序(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 40. 最小的 k 个数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/ohvl0d/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 41. 数据流中的中位数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vd1j2/) |
-| **Day 18** | **搜索与回溯算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 55 - I. 二叉树的深度](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9hgr5i/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 55 - II. 平衡二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9hzffg/) |
-| **Day 19** | **搜索与回溯算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 64. 求 1 + 2 + … + n](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9h44cj/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/575kd2/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 68 - II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57euni/) |
-| **Day 20** | **分治算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 07. 重建二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/99lxci/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 16. 数值的整数次方](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57rwmg/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vwxx5/) |
-| **Day 21** | **位运算(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 15. 二进制中 1 的个数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vk1l3/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 65. 不用加减乘除做加法](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vz6d1/) |
-| **Day 22** | **位运算(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 56 - I. 数组中数字出现的次数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/eubbnm/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 56 - II. 数组中数字出现的次数 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9hyq1r/) |
-| **Day 23** | **数学(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/99iy4g/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 66. 构建乘积数组](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57d8cm/) |
-| **Day 24** | **数学(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 14- I. 剪绳子](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5v1026/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 57 - II. 和为 s 的连续正数序列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/eufzm7/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 62. 圆圈中最后剩下的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/oxrkot/) |
-| **Day 25** | **模拟(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 29. 顺时针打印矩阵](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vfh9g/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 31. 栈的压入、弹出序列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5wh1hj/) |
-| **Day 26** | **字符串(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 20. 表示数值的字符串](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5d6vi6/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 67. 把字符串转换成整数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58pq8g/) |
-| **Day 27** | **栈与队列(困难)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 59 - I. 滑动窗口的最大值](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58o46i/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 59 - II. 队列的最大值](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/e2t5ug/) |
-| **Day 28** | **搜索与回溯算法(困难)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 37. 序列化二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/990pf2/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 38. 字符串的排列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dfv5h/) |
-| **Day 29** | **动态规划(困难)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 19. 正则表达式匹配](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9a1ypc/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 49. 丑数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9h3im5/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 60. n 个骰子的点数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/ozzl1r/) |
-| **Day 30** | **分治算法(困难)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 17. 打印从 1 到最大的 n 位数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/594wfg/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 51. 数组中的逆序对](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/o58jfs/) |
-| **Day 31** | **数学(困难)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 14- II. 剪绳子 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vcapc/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 43. 1~n 整数中 1 出现的次数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/572jxs/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 44. 数字序列中某一位的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57vzfh/) |
-
----
-
-若本书对您有所帮助,麻烦请您点个 Star :star: 啦,谢谢!
-
-
](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/detail/illustration-of-algorithm/)
+- 图文详解 75 道题目,覆盖主要算法知识点。
+- 题目活跃于各大互联网公司招聘中,可使笔面试准备事半功倍。
+- 致力于行文深入浅出、图文搭配,提供简洁的 Python, Java, C++ 解题代码。
-LeetBook《图解算法数据结构》面向算法初学者、互联网求职者设计,主要内容包括:
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> 本仓库包含“图解算法数据结构”、“Krahets 笔面试精选 88 题”和“剑指 Offer”的题解内容:
+>
+> ```python
+> LeetCode-Book
+> ├── leetbook_ioa # 《图解算法数据结构》题解和专栏文档
+> ├── selected_coding_interview # 《Krahets 笔面试精选 88 题》题解文档
+> └── sword_for_offer # 《剑指 Offer》题解文档、代码、刷题计划
+> ```
-### :green_book: 剑指 Offer 图文题解
+> 若本仓库对您有所帮助,请在页面右上角点个 **Star** :star: 支持一下,谢谢!
-- 图文详解 75 道题目,覆盖主要算法知识点,非常适合作为算法学习的 **第一份题库** 。
-- 题库活跃于各大互联网公司招聘中,可使笔面试准备事半功倍。
-- 致力于行文深入浅出、图文搭配,提供简洁的 **Python3, Java, C++** 解题代码。
-- 笔者整理了 **30 天刷题计划**、**题目分类**,让刷题有迹可循。
-
-### :blue_book: 数据结构与算法专栏
-
-- **基础知识:** 时间复杂度、空间复杂度等算法知识。
-- **数据结构:** 数组、栈、队列、字符串、链表、树、图、堆、哈希表。
-- **算法专题:** 分治算法、动态规划、搜索与回溯算法、查找算法、贪心算法、排序、位运算、双指针、模拟、数学。
-
-## :student: 适合人群
-
-- 互联网算法、软件岗位求职者。
-- 从零开始接触数据结构与算法的同学。
-- 具有一定编程基础,计划系统学习算法的同学。
-
----
-
-## :ledger: 算法专栏
-
-### 「[数据结构](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50e446/)」
-
-> 建议对数据结构不熟悉的同学,先看这篇熟悉用法。
-
-- 常用数据结构的**分类**和**基本特点**。
-- 在算法解题中,数据结构的**常用操作**。
-- 在 Python3 , Java , C++ 语言中,各数据结构的**初始化与构建方法**。
-
-### 「[算法复杂度](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/r84gmi/)」
-
-> 复杂度是算法优劣性的有力评价指标,对于理解算法起着至关重要的作用。
-
-- 什么是时间复杂度、空间复杂度?
-- 时间复杂度和空间复杂度的**概念定义**、**符号表示**、**常见种类**、**时空权衡**。
-- 时间与空间复杂度的**示例题目与解析**。
-
-### 「[动态规划](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/m5zfc1/)」
-
-> 动态规划是算法重难点,也是笔面试重要考点,需要重点理解与练习。
-
-- 动态规划问题特点,动态规划和分治算法的联系与区别;
-- 借助例题介绍**重叠子问题**和**最优子结构**分别是什么,以及动态规划是如何解决它们的;
-- 动态规划的**解题框架**总结;
-- 动态规划的**练习例题**,从易到难排序;
-
-### 「[排序算法](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/pxal47/)」
-
-> 排序是最经典的算法问题之一,由浅入深的多种算法涵盖多个算法知识点(例如暴力搜索、分治算法、堆数据结构等)。
-
-- 排序算法分类方法,包括稳定性 、就地性 、自适应性;
-- 排序算法与二分查找、双指针算法之间的关系;
-- 各主要排序算法的时间复杂度与空间复杂度;
-
----
-
-## :hourglass: 刷题计划
-
-笔者整理了《剑指 Offer 》刷题计划,核心理念为从易到难、从基础类题目到综合类题目,供希望按照知识点类型顺序刷题的小伙伴们参考。行百里者半九十,坚持一个月刷完,一起加油!
-
-| 日程 | 题目 |
-| :--------: | :------------------------------------------------ |
-| **Day 1** | **栈与队列(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 09. 用两个栈实现队列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5d3i87/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 30. 包含 min 函数的栈](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50bp33/) |
-| **Day 2** | **链表(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dt66m/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9pdjbm/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9p0yy1/) |
-| **Day 3** | **字符串(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 05. 替换空格](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50ywkd/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 58 - II. 左旋转字符串](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/589fz2/) |
-| **Day 4** | **查找算法(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 03. 数组中重复的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/59bjss/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 53 - I. 在排序数组中查找数字 I](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5874p1/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 53 - II. 0~n-1 中缺失的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58iqo5/) |
-| **Day 5** | **查找算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 04. 二维数组中的查找](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5v76yi/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 11. 旋转数组的最小数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50xofm/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 50. 第一个只出现一次的字符](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5viisg/) |
-| **Day 6** | **搜索与回溯算法(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9ackoe/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vawr3/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vnp91/) |
-| **Day 7** | **搜索与回溯算法(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 26. 树的子结构](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dshwe/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 27. 二叉树的镜像](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/59zt5i/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 28. 对称的二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5d412v/) |
-| **Day 8** | **动态规划(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 10- I. 斐波那契数列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50fxu1/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 10- II. 青蛙跳台阶问题](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57hyl5/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 63. 股票的最大利润](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58nn7r/) |
-| **Day 9** | **动态规划(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 42. 连续子数组的最大和](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/59gq9c/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 47. 礼物的最大价值](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vokvr/) |
-| **Day 10** | **动态规划(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 46. 把数字翻译成字符串](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/99wd55/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 48. 最长不含重复字符的子字符串](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dgr0c/) |
-| **Day 11** | **双指针(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/505fc7/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第 k 个节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58tl52/) |
-| **Day 12** | **双指针(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vq98s/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/oe5os3/) |
-| **Day 13** | **双指针(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 21. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5v8a6t/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 57. 和为 s 的两个数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5832fi/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 58 - I. 翻转单词顺序](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/586ecg/) |
-| **Day 14** | **搜索与回溯算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 12. 矩阵中的路径](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58wowd/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 13. 机器人的运动范围](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9h6vo2/) |
-| **Day 15** | **搜索与回溯算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dy6pt/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dbies/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 54. 二叉搜索树的第 k 大节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58df23/) |
-| **Day 16** | **排序(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 45. 把数组排成最小的数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/59ypcj/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 61. 扑克牌中的顺子](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57mpoj/) |
-| **Day 17** | **排序(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 40. 最小的 k 个数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/ohvl0d/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 41. 数据流中的中位数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vd1j2/) |
-| **Day 18** | **搜索与回溯算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 55 - I. 二叉树的深度](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9hgr5i/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 55 - II. 平衡二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9hzffg/) |
-| **Day 19** | **搜索与回溯算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 64. 求 1 + 2 + … + n](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9h44cj/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/575kd2/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 68 - II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57euni/) |
-| **Day 20** | **分治算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 07. 重建二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/99lxci/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 16. 数值的整数次方](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57rwmg/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vwxx5/) |
-| **Day 21** | **位运算(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 15. 二进制中 1 的个数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vk1l3/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 65. 不用加减乘除做加法](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vz6d1/) |
-| **Day 22** | **位运算(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 56 - I. 数组中数字出现的次数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/eubbnm/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 56 - II. 数组中数字出现的次数 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9hyq1r/) |
-| **Day 23** | **数学(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/99iy4g/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 66. 构建乘积数组](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57d8cm/) |
-| **Day 24** | **数学(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 14- I. 剪绳子](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5v1026/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 57 - II. 和为 s 的连续正数序列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/eufzm7/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 62. 圆圈中最后剩下的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/oxrkot/) |
-| **Day 25** | **模拟(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 29. 顺时针打印矩阵](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vfh9g/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 31. 栈的压入、弹出序列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5wh1hj/) |
-| **Day 26** | **字符串(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 20. 表示数值的字符串](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5d6vi6/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 67. 把字符串转换成整数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58pq8g/) |
-| **Day 27** | **栈与队列(困难)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 59 - I. 滑动窗口的最大值](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58o46i/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 59 - II. 队列的最大值](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/e2t5ug/) |
-| **Day 28** | **搜索与回溯算法(困难)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 37. 序列化二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/990pf2/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 38. 字符串的排列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dfv5h/) |
-| **Day 29** | **动态规划(困难)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 19. 正则表达式匹配](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9a1ypc/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 49. 丑数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9h3im5/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 60. n 个骰子的点数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/ozzl1r/) |
-| **Day 30** | **分治算法(困难)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 17. 打印从 1 到最大的 n 位数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/594wfg/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 51. 数组中的逆序对](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/o58jfs/) |
-| **Day 31** | **数学(困难)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 14- II. 剪绳子 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vcapc/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 43. 1~n 整数中 1 出现的次数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/572jxs/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 44. 数字序列中某一位的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57vzfh/) |
-
----
-
-若本书对您有所帮助,麻烦请您点个 Star :star: 啦,谢谢!
-
-
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
+## 如何学习算法
+
+### 第一步:看入门书
+
+
+  +
+
+
+
+ 《Hello 算法》 —— 动画图解、一键运行的数据结构与算法教程
+
+
+此书旨在引导初学者探索数据结构与算法的知识地图,掌握刷题需要的前置知识与工具库。
+
+> [!TIP]
+> 建议先读完这本书(概括且全面地了解数据结构与算法),再开始刷题(深入探索各类算法和数据结构)。
+
+### 第二步:刷算法题
+
+推荐以下 LeetCode 题单:
+
+1. [Krahets 笔面试精选 88 题](https://leetcode.cn/studyplan/selected-coding-interview/):从“剑指 Offer”和“热题 100”精选出的 88 道高频算法笔试题,适合初学者入门。
+2. [图解算法数据结构](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/detail/illustration-of-algorithm/)([Interview-75](https://leetcode.cn/studyplan/coding-interviews/)):题目更贴近实际应用,相较于“剑指 Offer”难度有所增加。
+3. [LeetCode 热题 100](https://leetcode.cn/studyplan/top-100-liked/):力扣用户最喜爱的 100 道题。
+4. [面试经典 150 题](https://leetcode.cn/studyplan/top-interview-150/):150 道经典面试力扣题。
+5. [LeetCode-75](https://leetcode.cn/studyplan/leetcode-75/):精选 75 道面试核心题目。
+
+> [!TIP]
+> 第 `1.` `2.` 项的题目分类与《Hello 算法》的章节内容对应,且提供 [@krahets](https://leetcode.cn/u/jyd/) 写的题解,适合作为配套习题。
+
+对初学者刷题的一些建议:
+
+1. 建议每日刷 2~3 题。若能轻松完成,可以尝试增加至 5~8 题。
+2. 刷题的质量比数量更加重要。请确保你真正理解了每个题目的解法及背后的算法原理。
+3. 建议你按照题单目录的顺序做题。如果感觉一道题很难,可以先跳过,后续再攻克。
+4. 题目通常有不止一种解法,请你注意比较和探讨各种方法的特点和适用情况。
+5. 如果你发现自己遗忘了题目解法,不必灰心;我们通常需要复习三次以上,才能真正掌握一个知识点。
+6. 行百里者半九十。坚持至关重要,加油!
+
+## License
+
+The texts, code, and images in this repository are licensed under [CC BY-NC-SA-4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/).
diff --git a/cpp/include/PrintUtil.hpp b/cpp/include/PrintUtil.hpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 34e8b86..0000000
--- a/cpp/include/PrintUtil.hpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,197 +0,0 @@
-/*
- * File: PrintUtil.hpp
- * Created Time: 2021-12-19
- * Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
- */
-
-#pragma once
-
-#include
-#include
-#include
-#include "ListNode.hpp"
-#include "TreeNode.hpp"
-
-class PrintUtil {
- public:
- /**
- * @brief Find an element in a vector
- *
- * @tparam T
- * @param vec
- * @param ele
- * @return int
- */
- template
- static int vecFind(const vector& vec, T ele) {
- int j = INT_MAX;
- for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++) {
- if (vec[i] == ele) {
- j = i;
- }
- }
- return j;
- }
-
- /**
- * @brief Concatenate a vector with a delim
- *
- * @tparam T
- * @param delim
- * @param vec
- * @return string
- */
- template
- static string strJoin(const string& delim, const T& vec) {
- ostringstream s;
- for (const auto& i : vec) {
- if (&i != &vec[0]) {
- s << delim;
- }
- s << i;
- }
- return s.str();
- }
-
- /**
- * @brief Repeat a string for n times
- *
- * @param str
- * @param n
- * @return string
- */
- static string strRepeat(string str, int n) {
- ostringstream os;
- for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
- os << str;
- return os.str();
- }
-
- /**
- * @brief Get the Vector String object
- *
- * @tparam T
- * @param list
- * @return string
- */
- template
- static string getVectorString(vector &list) {
- return "[" + strJoin(", ", list) + "]";
- }
-
- /**
- * @brief Print a vector
- *
- * @tparam T
- * @param list
- */
- template
- static void printVector(vector &list) {
- cout << getVectorString(list) << '\n';
- }
-
- /**
- * @brief Print a vector matrix
- *
- * @tparam T
- * @param matrix
- */
- template
- static void printVectorMatrix(vector> &matrix) {
- cout << "[" << '\n';
- for (vector &list : matrix)
- cout << " " + getVectorString(list) + "," << '\n';
- cout << "]" << '\n';
- }
-
- /**
- * @brief Print a linked list
- *
- * @param head
- */
- static void printLinkedList(ListNode *head) {
- vector list;
- while (head != nullptr) {
- list.push_back(head->val);
- head = head->next;
- }
-
- cout << strJoin(" -> ", list) << '\n';
- }
-
- /**
- * @brief This tree printer is borrowed from TECHIE DELIGHT
- * https://www.techiedelight.com/c-program-print-binary-tree/
- */
- struct Trunk {
- Trunk *prev;
- string str;
- Trunk(Trunk *prev, string str) {
- this->prev = prev;
- this->str = str;
- }
- };
-
- /**
- * @brief Helper function to print branches of the binary tree
- *
- * @param p
- */
- static void showTrunks(Trunk *p) {
- if (p == nullptr) {
- return;
- }
-
- showTrunks(p->prev);
- cout << p->str;
- }
-
- /**
- * @brief The interface of the tree printer
- *
- * @param root
- */
- static void printTree(TreeNode *root) {
- printTree(root, nullptr, false);
- }
-
- /**
- * @brief Print a binary tree
- *
- * @param root
- * @param prev
- * @param isLeft
- */
- static void printTree(TreeNode *root, Trunk *prev, bool isLeft) {
- if (root == nullptr) {
- return;
- }
-
- string prev_str = " ";
- Trunk *trunk = new Trunk(prev, prev_str);
-
- printTree(root->right, trunk, true);
-
- if (!prev) {
- trunk->str = "———";
- }
- else if (isLeft) {
- trunk->str = "/———";
- prev_str = " |";
- }
- else {
- trunk->str = "\\———";
- prev->str = prev_str;
- }
-
- showTrunks(trunk);
- cout << " " << root->val << endl;
-
- if (prev) {
- prev->str = prev_str;
- }
- trunk->str = " |";
-
- printTree(root->left, trunk, false);
- }
-};
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_03_find_duplicate_numbers_in_an_array_s2/sfo_03_find_duplicate_numbers_in_an_array_s2.cpp b/cpp/sfo_03_find_duplicate_numbers_in_an_array_s2/sfo_03_find_duplicate_numbers_in_an_array_s2.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 7975201..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_03_find_duplicate_numbers_in_an_array_s2/sfo_03_find_duplicate_numbers_in_an_array_s2.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_03_find_duplicate_numbers_in_an_array_s2.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- int findRepeatNumber(vector& nums) {
- int i = 0;
- while(i < nums.size()) {
- if(nums[i] == i) {
- i++;
- continue;
- }
- if(nums[nums[i]] == nums[i])
- return nums[i];
- swap(nums[i],nums[nums[i]]);
- }
- return -1;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- vector nums = { 2, 3, 1, 0, 2, 5, 3 };
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- int res = slt->findRepeatNumber(nums);
- cout << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_04_find_a_number_in_2d_matrix_s1/sfo_04_find_a_number_in_2d_matrix_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_04_find_a_number_in_2d_matrix_s1/sfo_04_find_a_number_in_2d_matrix_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index af7a76c..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_04_find_a_number_in_2d_matrix_s1/sfo_04_find_a_number_in_2d_matrix_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_04_find_a_number_in_2d_matrix_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- bool findNumberIn2DArray(vector>& matrix, int target) {
- int i = matrix.size() - 1, j = 0;
- while(i >= 0 && j < matrix[0].size())
- {
- if(matrix[i][j] > target) i--;
- else if(matrix[i][j] < target) j++;
- else return true;
- }
- return false;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- vector> matrix = {
- { 1, 4, 7, 11, 15 },
- { 2, 5, 8, 12, 19 },
- { 3, 6, 9, 16, 22 },
- { 10, 13, 14, 17, 24 },
- { 18, 21, 23, 26, 30 }
-};
- int target = 5;
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- bool res = slt->findNumberIn2DArray(matrix, target);
- cout << boolalpha << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_11_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array_s1/sfo_11_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_11_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array_s1/sfo_11_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index b23919d..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_11_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array_s1/sfo_11_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_11_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- int minArray(vector& numbers) {
- int i = 0, j = numbers.size() - 1;
- while (i < j) {
- int m = (i + j) / 2;
- if (numbers[m] > numbers[j]) i = m + 1;
- else if (numbers[m] < numbers[j]) j = m;
- else j--;
- }
- return numbers[i];
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- vector numbers = { 3, 4, 5, 1, 2 };
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- int res = slt->minArray(numbers);
- cout << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_11_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array_s2/sfo_11_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array_s2.cpp b/cpp/sfo_11_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array_s2/sfo_11_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array_s2.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index a910d92..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_11_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array_s2/sfo_11_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array_s2.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_11_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array_s2.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- int minArray(vector& numbers) {
- int i = 0, j = numbers.size() - 1;
- while (i < j) {
- int m = (i + j) / 2;
- if (numbers[m] > numbers[j]) i = m + 1;
- else if (numbers[m] < numbers[j]) j = m;
- else {
- int x = i;
- for(int k = i + 1; k < j; k++) {
- if(numbers[k] < numbers[x]) x = k;
- }
- return numbers[x];
- }
- }
- return numbers[i];
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- vector numbers = { 3, 4, 5, 1, 2 };
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- int res = slt->minArray(numbers);
- cout << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_12_word_search_s1/sfo_12_word_search_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_12_word_search_s1/sfo_12_word_search_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 2018e0e..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_12_word_search_s1/sfo_12_word_search_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,49 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_12_word_search_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- bool exist(vector>& board, string word) {
- rows = board.size();
- cols = board[0].size();
- for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
- for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
- if(dfs(board, word, i, j, 0)) return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
-private:
- int rows, cols;
- bool dfs(vector>& board, string word, int i, int j, int k) {
- if(i >= rows || i < 0 || j >= cols || j < 0 || board[i][j] != word[k]) return false;
- if(k == word.size() - 1) return true;
- board[i][j] = '\0';
- bool res = dfs(board, word, i + 1, j, k + 1) || dfs(board, word, i - 1, j, k + 1) ||
- dfs(board, word, i, j + 1, k + 1) || dfs(board, word, i , j - 1, k + 1);
- board[i][j] = word[k];
- return res;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- vector> board = {
- { 'A', 'B', 'C', 'E' },
- { 'S', 'F', 'C', 'S' },
- { 'A', 'D', 'E', 'E' }
-};
- string word = "ABCCED";
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- bool res = slt->exist(board, word);
- cout << boolalpha << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_18_delete_a_node_from_a_linked_list_s1/sfo_18_delete_a_node_from_a_linked_list_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_18_delete_a_node_from_a_linked_list_s1/sfo_18_delete_a_node_from_a_linked_list_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 37dbc00..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_18_delete_a_node_from_a_linked_list_s1/sfo_18_delete_a_node_from_a_linked_list_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,34 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_18_delete_a_node_from_a_linked_list_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- ListNode* deleteNode(ListNode* head, int val) {
- if(head->val == val) return head->next;
- ListNode *pre = head, *cur = head->next;
- while(cur != nullptr && cur->val != val) {
- pre = cur;
- cur = cur->next;
- }
- if(cur != nullptr) pre->next = cur->next;
- return head;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- ListNode* head = vectorToLinkedList(vector { 4, 5, 1, 9 });
- int val = 5;
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- ListNode* res = slt->deleteNode(head, val);
- PrintUtil::printLinkedList(res);
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_19_regular_expression_matching_s2/sfo_19_regular_expression_matching_s2.cpp b/cpp/sfo_19_regular_expression_matching_s2/sfo_19_regular_expression_matching_s2.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index abad706..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_19_regular_expression_matching_s2/sfo_19_regular_expression_matching_s2.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_19_regular_expression_matching_s2.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- bool isMatch(string s, string p) {
- int m = s.size() + 1, n = p.size() + 1;
- vector> dp(m, vector(n, false));
- dp[0][0] = true;
- // 初始化首行
- for(int j = 2; j < n; j += 2)
- dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 2] && p[j - 1] == '*';
- // 状态转移
- for(int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
- for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
- if(p[j - 1] == '*') {
- if(dp[i][j - 2]) dp[i][j] = true; // 1.
- else if(dp[i - 1][j] && s[i - 1] == p[j - 2]) dp[i][j] = true; // 2.
- else if(dp[i - 1][j] && p[j - 2] == '.') dp[i][j] = true; // 3.
- } else {
- if(dp[i - 1][j - 1] && s[i - 1] == p[j - 1]) dp[i][j] = true; // 1.
- else if(dp[i - 1][j - 1] && p[j - 1] == '.') dp[i][j] = true; // 2.
- }
- }
- }
- return dp[m - 1][n - 1];
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- string s = "mississippi";
- string p = "mis*is*p*.";
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- bool res = slt->isMatch(s, p);
- cout << boolalpha << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_21_adjust_the_order_of_numbers_in_an_array_s1/sfo_21_adjust_the_order_of_numbers_in_an_array_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_21_adjust_the_order_of_numbers_in_an_array_s1/sfo_21_adjust_the_order_of_numbers_in_an_array_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index cc74780..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_21_adjust_the_order_of_numbers_in_an_array_s1/sfo_21_adjust_the_order_of_numbers_in_an_array_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_21_adjust_the_order_of_numbers_in_an_array_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- vector exchange(vector& nums) {
- int i = 0, j = nums.size() - 1;
- while (i < j)
- {
- while(i < j && (nums[i] & 1) == 1) i++;
- while(i < j && (nums[j] & 1) == 0) j--;
- swap(nums[i], nums[j]);
- }
- return nums;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- vector nums = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- vector res = slt->exchange(nums);
- PrintUtil::printVector(res);
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_22_the_kth_node_from_the_end_of_a_linked_list_s2/sfo_22_the_kth_node_from_the_end_of_a_linked_list_s2.cpp b/cpp/sfo_22_the_kth_node_from_the_end_of_a_linked_list_s2/sfo_22_the_kth_node_from_the_end_of_a_linked_list_s2.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 1c80e0d..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_22_the_kth_node_from_the_end_of_a_linked_list_s2/sfo_22_the_kth_node_from_the_end_of_a_linked_list_s2.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_22_the_kth_node_from_the_end_of_a_linked_list_s2.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- ListNode* getKthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int k) {
- ListNode *former = head, *latter = head;
- for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
- if(former == nullptr) return nullptr;
- former = former->next;
- }
- while(former != nullptr) {
- former = former->next;
- latter = latter->next;
- }
- return latter;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- ListNode* head = vectorToLinkedList(vector { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 });
- int k = 2;
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- ListNode* res = slt->getKthFromEnd(head, k);
- PrintUtil::printLinkedList(res);
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_24_reverse_a_linked_list_s2/sfo_24_reverse_a_linked_list_s2.cpp b/cpp/sfo_24_reverse_a_linked_list_s2/sfo_24_reverse_a_linked_list_s2.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 2ec993e..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_24_reverse_a_linked_list_s2/sfo_24_reverse_a_linked_list_s2.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_24_reverse_a_linked_list_s2.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
- return recur(head, nullptr); // 调用递归并返回
- }
-private:
- ListNode* recur(ListNode* cur, ListNode* pre) {
- if (cur == nullptr) return pre; // 终止条件
- ListNode* res = recur(cur->next, cur); // 递归后继节点
- cur->next = pre; // 修改节点引用指向
- return res; // 返回反转链表的头节点
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- ListNode* head = vectorToLinkedList(vector { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 });
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- ListNode* res = slt->reverseList(head);
- PrintUtil::printLinkedList(res);
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_25_combine_two_sorted_linked_lists_s1/sfo_25_combine_two_sorted_linked_lists_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_25_combine_two_sorted_linked_lists_s1/sfo_25_combine_two_sorted_linked_lists_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 5ca2443..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_25_combine_two_sorted_linked_lists_s1/sfo_25_combine_two_sorted_linked_lists_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_25_combine_two_sorted_linked_lists_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
- ListNode* dum = new ListNode(0);
- ListNode* cur = dum;
- while(l1 != nullptr && l2 != nullptr) {
- if(l1->val < l2->val) {
- cur->next = l1;
- l1 = l1->next;
- }
- else {
- cur->next = l2;
- l2 = l2->next;
- }
- cur = cur->next;
- }
- cur->next = l1 != nullptr ? l1 : l2;
- return dum->next;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- ListNode* l1 = vectorToLinkedList(vector { 1, 2, 4 });
- ListNode* l2 = vectorToLinkedList(vector { 1, 3, 4 });
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- ListNode* res = slt->mergeTwoLists(l1, l2);
- PrintUtil::printLinkedList(res);
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_26_substructure_of_a_binary_tree_s1/sfo_26_substructure_of_a_binary_tree_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_26_substructure_of_a_binary_tree_s1/sfo_26_substructure_of_a_binary_tree_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 9714f94..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_26_substructure_of_a_binary_tree_s1/sfo_26_substructure_of_a_binary_tree_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_26_substructure_of_a_binary_tree_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- bool isSubStructure(TreeNode* A, TreeNode* B) {
- return (A != nullptr && B != nullptr) && (recur(A, B) || isSubStructure(A->left, B) || isSubStructure(A->right, B));
- }
-private:
- bool recur(TreeNode* A, TreeNode* B) {
- if(B == nullptr) return true;
- if(A == nullptr || A->val != B->val) return false;
- return recur(A->left, B->left) && recur(A->right, B->right);
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- TreeNode* A = vectorToTree(vector { 3, 4, 5, 1, 2, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX });
- TreeNode* B = vectorToTree(vector { 4, 1, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX });
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- bool res = slt->isSubStructure(A, B);
- cout << boolalpha << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_27_mirror_of_a_binary_tree_s1/sfo_27_mirror_of_a_binary_tree_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_27_mirror_of_a_binary_tree_s1/sfo_27_mirror_of_a_binary_tree_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 700f2cd..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_27_mirror_of_a_binary_tree_s1/sfo_27_mirror_of_a_binary_tree_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,30 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_27_mirror_of_a_binary_tree_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- TreeNode* mirrorTree(TreeNode* root) {
- if (root == nullptr) return nullptr;
- TreeNode* tmp = root->left;
- root->left = mirrorTree(root->right);
- root->right = mirrorTree(tmp);
- return root;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- TreeNode* root = vectorToTree(vector { 4, 2, 7, 1, 3, 6, 9, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX });
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- TreeNode* res = slt->mirrorTree(root);
- PrintUtil::printTree(res);
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_27_mirror_of_a_binary_tree_s2/sfo_27_mirror_of_a_binary_tree_s2.cpp b/cpp/sfo_27_mirror_of_a_binary_tree_s2/sfo_27_mirror_of_a_binary_tree_s2.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index a406e23..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_27_mirror_of_a_binary_tree_s2/sfo_27_mirror_of_a_binary_tree_s2.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_27_mirror_of_a_binary_tree_s2.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- TreeNode* mirrorTree(TreeNode* root) {
- if(root == nullptr) return nullptr;
- stack stack;
- stack.push(root);
- while (!stack.empty())
- {
- TreeNode* node = stack.top();
- stack.pop();
- if (node->left != nullptr) stack.push(node->left);
- if (node->right != nullptr) stack.push(node->right);
- TreeNode* tmp = node->left;
- node->left = node->right;
- node->right = tmp;
- }
- return root;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- TreeNode* root = vectorToTree(vector { 4, 2, 7, 1, 3, 6, 9, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX });
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- TreeNode* res = slt->mirrorTree(root);
- PrintUtil::printTree(res);
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_28_symmetric_binary_tree_s1/sfo_28_symmetric_binary_tree_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_28_symmetric_binary_tree_s1/sfo_28_symmetric_binary_tree_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index a893e2a..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_28_symmetric_binary_tree_s1/sfo_28_symmetric_binary_tree_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_28_symmetric_binary_tree_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
- return root == nullptr || recur(root->left, root->right);
- }
-private:
- bool recur(TreeNode* L, TreeNode* R) {
- if(L == nullptr && R == nullptr) return true;
- if(L == nullptr || R == nullptr || L->val != R->val) return false;
- return recur(L->left, R->right) && recur(L->right, R->left);
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- TreeNode* root = vectorToTree(vector { 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 3, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX });
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- bool res = slt->isSymmetric(root);
- cout << boolalpha << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_29_print_a_given_matrix_in_spiral_form_s1/sfo_29_print_a_given_matrix_in_spiral_form_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_29_print_a_given_matrix_in_spiral_form_s1/sfo_29_print_a_given_matrix_in_spiral_form_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index d4d303b..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_29_print_a_given_matrix_in_spiral_form_s1/sfo_29_print_a_given_matrix_in_spiral_form_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,44 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_29_print_a_given_matrix_in_spiral_form_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- vector spiralOrder(vector>& matrix) {
- if (matrix.empty()) return {};
- int l = 0, r = matrix[0].size() - 1, t = 0, b = matrix.size() - 1;
- vector res;
- while(true)
- {
- for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) res.push_back(matrix[t][i]); // left to right
- if (++t > b) break;
- for (int i = t; i <= b; i++) res.push_back(matrix[i][r]); // top to bottom
- if (l > --r) break;
- for (int i = r; i >= l; i--) res.push_back(matrix[b][i]); // right to left
- if (t > --b) break;
- for (int i = b; i >= t; i--) res.push_back(matrix[i][l]); // bottom to top
- if (++l > r) break;
- }
- return res;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- vector> matrix = {
- { 1, 2, 3 },
- { 4, 5, 6 },
- { 7, 8, 9 }
-};
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- vector res = slt->spiralOrder(matrix);
- PrintUtil::printVector(res);
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_31_validate_stack_sequences_s1/sfo_31_validate_stack_sequences_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_31_validate_stack_sequences_s1/sfo_31_validate_stack_sequences_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index aaf210b..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_31_validate_stack_sequences_s1/sfo_31_validate_stack_sequences_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_31_validate_stack_sequences_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- bool validateStackSequences(vector& pushed, vector& popped) {
- stack stk;
- int i = 0;
- for(int num : pushed) {
- stk.push(num); // num 入栈
- while(!stk.empty() && stk.top() == popped[i]) { // 循环判断与出栈
- stk.pop();
- i++;
- }
- }
- return stk.empty();
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- vector pushed = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
- vector popped = { 4, 5, 3, 2, 1 };
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- bool res = slt->validateStackSequences(pushed, popped);
- cout << boolalpha << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_32i_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_i_s1/sfo_32i_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_i_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_32i_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_i_s1/sfo_32i_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_i_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index e7ebcd1..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_32i_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_i_s1/sfo_32i_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_i_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_32i_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_i_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- vector levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
- vector res;
- if(!root) return res;
- queue que;
- que.push(root);
- while(!que.empty()){
- TreeNode* node = que.front();
- que.pop();
- res.push_back(node->val);
- if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
- if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
- }
- return res;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- TreeNode* root = vectorToTree(vector { 3, 9, 20, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, 15, 7, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX });
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- vector res = slt->levelOrder(root);
- PrintUtil::printVector(res);
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_32ii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_ii_s1/sfo_32ii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_ii_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_32ii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_ii_s1/sfo_32ii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_ii_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 98e77e6..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_32ii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_ii_s1/sfo_32ii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_ii_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_32ii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_ii_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- vector> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
- queue que;
- vector> res;
- int cnt = 0;
- if(root != NULL) que.push(root);
- while(!que.empty()) {
- vector tmp;
- for(int i = que.size(); i > 0; --i) {
- root = que.front();
- que.pop();
- tmp.push_back(root->val);
- if(root->left != NULL) que.push(root->left);
- if(root->right != NULL) que.push(root->right);
- }
- res.push_back(tmp);
- }
- return res;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- TreeNode* root = vectorToTree(vector { 3, 9, 20, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, 15, 7, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX });
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- vector> res = slt->levelOrder(root);
- PrintUtil::printVectorMatrix(res);
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_32iii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_iii_s1/sfo_32iii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_iii_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_32iii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_iii_s1/sfo_32iii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_iii_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 1d90ac8..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_32iii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_iii_s1/sfo_32iii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_iii_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,56 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_32iii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_iii_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- vector> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
- deque deque;
- vector> res;
- if(root != NULL) deque.push_back(root);
- while(!deque.empty()) {
- // 打印奇数层
- vector tmp;
- for(int i = deque.size(); i > 0; i--) {
- // 从左向右打印
- TreeNode* node = deque.front();
- deque.pop_front();
- tmp.push_back(node->val);
- // 先左后右加入下层节点
- if(node->left != NULL) deque.push_back(node->left);
- if(node->right != NULL) deque.push_back(node->right);
- }
- res.push_back(tmp);
- if(deque.empty()) break; // 若为空则提前跳出
- // 打印偶数层
- tmp.clear();
- for(int i = deque.size(); i > 0; i--) {
- // 从右向左打印
- TreeNode* node = deque.back();
- deque.pop_back();
- tmp.push_back(node->val);
- // 先右后左加入下层节点
- if(node->right != NULL) deque.push_front(node->right);
- if(node->left != NULL) deque.push_front(node->left);
- }
- res.push_back(tmp);
- }
- return res;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- TreeNode* root = vectorToTree(vector { 3, 9, 20, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, 15, 7, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX });
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- vector> res = slt->levelOrder(root);
- PrintUtil::printVectorMatrix(res);
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_32iii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_iii_s2/sfo_32iii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_iii_s2.cpp b/cpp/sfo_32iii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_iii_s2/sfo_32iii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_iii_s2.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 660d0e9..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_32iii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_iii_s2/sfo_32iii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_iii_s2.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_32iii_print_a_binary_tree_topbottom_iii_s2.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- vector> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
- queue que;
- vector> res;
- if(root != NULL) que.push(root);
- while(!que.empty()) {
- vector tmp;
- for(int i = que.size(); i > 0; i--) {
- TreeNode* node = que.front();
- que.pop();
- tmp.push_back(node->val);
- if(node->left != NULL) que.push(node->left);
- if(node->right != NULL) que.push(node->right);
- }
- if(res.size() % 2 == 1) reverse(tmp.begin(),tmp.end());
- res.push_back(tmp);
- }
- return res;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- TreeNode* root = vectorToTree(vector { 3, 9, 20, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, 15, 7, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX });
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- vector> res = slt->levelOrder(root);
- PrintUtil::printVectorMatrix(res);
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_33_postorder_traversal_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1/sfo_33_postorder_traversal_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_33_postorder_traversal_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1/sfo_33_postorder_traversal_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 8f159e0..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_33_postorder_traversal_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1/sfo_33_postorder_traversal_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_33_postorder_traversal_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- bool verifyPostorder(vector& postorder) {
- return recur(postorder, 0, postorder.size() - 1);
- }
-private:
- bool recur(vector& postorder, int i, int j) {
- if(i >= j) return true;
- int p = i;
- while(postorder[p] < postorder[j]) p++;
- int m = p;
- while(postorder[p] > postorder[j]) p++;
- return p == j && recur(postorder, i, m - 1) && recur(postorder, m, j - 1);
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- vector postorder = { 1, 6, 3, 2, 5 };
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- bool res = slt->verifyPostorder(postorder);
- cout << boolalpha << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_34_all_xsum_paths_in_a_binary_tree_s1/sfo_34_all_xsum_paths_in_a_binary_tree_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_34_all_xsum_paths_in_a_binary_tree_s1/sfo_34_all_xsum_paths_in_a_binary_tree_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 301b13e..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_34_all_xsum_paths_in_a_binary_tree_s1/sfo_34_all_xsum_paths_in_a_binary_tree_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_34_all_xsum_paths_in_a_binary_tree_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- vector> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
- recur(root, sum);
- return res;
- }
-private:
- vector> res;
- vector path;
- void recur(TreeNode* root, int tar) {
- if(root == nullptr) return;
- path.push_back(root->val);
- tar -= root->val;
- if(tar == 0 && root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr)
- res.push_back(path);
- recur(root->left, tar);
- recur(root->right, tar);
- path.pop_back();
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- TreeNode* root = vectorToTree(vector { 5, 4, 8, 11, INT_MAX, 13, 4, 7, 2, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, 5, 1, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX });
- int sum = 22;
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- vector> res = slt->pathSum(root, sum);
- PrintUtil::printVectorMatrix(res);
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_38_all_permutations_of_a_string_s1/sfo_38_all_permutations_of_a_string_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_38_all_permutations_of_a_string_s1/sfo_38_all_permutations_of_a_string_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 6ab23af..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_38_all_permutations_of_a_string_s1/sfo_38_all_permutations_of_a_string_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,43 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_38_all_permutations_of_a_string_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- vector permutation(string s) {
- dfs(s, 0);
- return res;
- }
-private:
- vector res;
- void dfs(string s, int x) {
- if(x == s.size() - 1) {
- res.push_back(s); // 添加排列方案
- return;
- }
- set st;
- for(int i = x; i < s.size(); i++) {
- if(st.find(s[i]) != st.end()) continue; // 重复,因此剪枝
- st.insert(s[i]);
- swap(s[i], s[x]); // 交换,将 s[i] 固定在第 x 位
- dfs(s, x + 1); // 开启固定第 x + 1 位字符
- swap(s[i], s[x]); // 恢复交换
- }
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- string s = "abc";
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- vector res = slt->permutation(s);
- PrintUtil::printVector(res);
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_40_the_smallest_k_numbers_s2/sfo_40_the_smallest_k_numbers_s2.cpp b/cpp/sfo_40_the_smallest_k_numbers_s2/sfo_40_the_smallest_k_numbers_s2.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index efb0ab6..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_40_the_smallest_k_numbers_s2/sfo_40_the_smallest_k_numbers_s2.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,43 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_40_the_smallest_k_numbers_s2.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- vector getLeastNumbers(vector& arr, int k) {
- if (k >= arr.size()) return arr;
- return quickSort(arr, k, 0, arr.size() - 1);
- }
-private:
- vector quickSort(vector& arr, int k, int l, int r) {
- int i = l, j = r;
- while (i < j) {
- while (i < j && arr[j] >= arr[l]) j--;
- while (i < j && arr[i] <= arr[l]) i++;
- swap(arr[i], arr[j]);
- }
- swap(arr[i], arr[l]);
- if (i > k) return quickSort(arr, k, l, i - 1);
- if (i < k) return quickSort(arr, k, i + 1, r);
- vector res;
- res.assign(arr.begin(), arr.begin() + k);
- return res;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- vector arr = { 3, 2, 1 };
- int k = 2;
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- vector res = slt->getLeastNumbers(arr, k);
- PrintUtil::printVector(res);
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_42_largest_sum_contiguous_subarray_s1/sfo_42_largest_sum_contiguous_subarray_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_42_largest_sum_contiguous_subarray_s1/sfo_42_largest_sum_contiguous_subarray_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index eb667c6..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_42_largest_sum_contiguous_subarray_s1/sfo_42_largest_sum_contiguous_subarray_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_42_largest_sum_contiguous_subarray_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- int maxSubArray(vector& nums) {
- int res = nums[0];
- for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
- if(nums[i - 1] > 0) nums[i] += nums[i - 1];
- if(nums[i] > res) res = nums[i];
- }
- return res;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- vector nums = { -2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4 };
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- int res = slt->maxSubArray(nums);
- cout << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_45_arrange_an_array_into_the_smallest_number_s1/sfo_45_arrange_an_array_into_the_smallest_number_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_45_arrange_an_array_into_the_smallest_number_s1/sfo_45_arrange_an_array_into_the_smallest_number_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 4b724a2..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_45_arrange_an_array_into_the_smallest_number_s1/sfo_45_arrange_an_array_into_the_smallest_number_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_45_arrange_an_array_into_the_smallest_number_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- string minNumber(vector& nums) {
- vector strs;
- for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)
- strs.push_back(to_string(nums[i]));
- quickSort(strs, 0, strs.size() - 1);
- string res;
- for(string s : strs)
- res.append(s);
- return res;
- }
-private:
- void quickSort(vector& strs, int l, int r) {
- if(l >= r) return;
- int i = l, j = r;
- while(i < j) {
- while(strs[j] + strs[l] >= strs[l] + strs[j] && i < j) j--;
- while(strs[i] + strs[l] <= strs[l] + strs[i] && i < j) i++;
- swap(strs[i], strs[j]);
- }
- swap(strs[i], strs[l]);
- quickSort(strs, l, i - 1);
- quickSort(strs, i + 1, r);
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- vector nums = { 3, 30, 34, 5, 9 };
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- string res = slt->minNumber(nums);
- cout << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_45_arrange_an_array_into_the_smallest_number_s2/sfo_45_arrange_an_array_into_the_smallest_number_s2.cpp b/cpp/sfo_45_arrange_an_array_into_the_smallest_number_s2/sfo_45_arrange_an_array_into_the_smallest_number_s2.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index e1723f2..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_45_arrange_an_array_into_the_smallest_number_s2/sfo_45_arrange_an_array_into_the_smallest_number_s2.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_45_arrange_an_array_into_the_smallest_number_s2.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- string minNumber(vector& nums) {
- vector strs;
- string res;
- for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)
- strs.push_back(to_string(nums[i]));
- sort(strs.begin(), strs.end(), [](string& x, string& y){ return x + y < y + x; });
- for(int i = 0; i < strs.size(); i++)
- res.append(strs[i]);
- return res;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- vector nums = { 3, 30, 34, 5, 9 };
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- string res = slt->minNumber(nums);
- cout << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_47_the_maximum_value_of_gifts_s1/sfo_47_the_maximum_value_of_gifts_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_47_the_maximum_value_of_gifts_s1/sfo_47_the_maximum_value_of_gifts_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index c4d9f4b..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_47_the_maximum_value_of_gifts_s1/sfo_47_the_maximum_value_of_gifts_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_47_the_maximum_value_of_gifts_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- int maxValue(vector>& grid) {
- int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
- for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
- for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
- if(i == 0 && j == 0) continue;
- if(i == 0) grid[i][j] += grid[i][j - 1] ;
- else if(j == 0) grid[i][j] += grid[i - 1][j];
- else grid[i][j] += max(grid[i][j - 1], grid[i - 1][j]);
- }
- }
- return grid[m - 1][n - 1];
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- vector> grid = {
- { 1, 3, 1 },
- { 1, 5, 1 },
- { 4, 2, 1 }
-};
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- int res = slt->maxValue(grid);
- cout << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_48_the_longest_substring_without_repeated_characters_s1/sfo_48_the_longest_substring_without_repeated_characters_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_48_the_longest_substring_without_repeated_characters_s1/sfo_48_the_longest_substring_without_repeated_characters_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 50cd7c1..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_48_the_longest_substring_without_repeated_characters_s1/sfo_48_the_longest_substring_without_repeated_characters_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_48_the_longest_substring_without_repeated_characters_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
- unordered_map dic;
- int res = 0, tmp = 0, len = s.size(), i;
- for(int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
- if(dic.find(s[j]) == dic.end()) i = - 1;
- else i = dic.find(s[j])->second; // 获取索引 i
- dic[s[j]] = j; // 更新哈希表
- tmp = tmp < j - i ? tmp + 1 : j - i; // dp[j - 1] -> dp[j]
- res = max(res, tmp); // max(dp[j - 1], dp[j])
- }
- return res;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- string s = "abcabcbb";
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- int res = slt->lengthOfLongestSubstring(s);
- cout << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_53i_find_a_number_in_a_sorted_array_s1/sfo_53i_find_a_number_in_a_sorted_array_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_53i_find_a_number_in_a_sorted_array_s1/sfo_53i_find_a_number_in_a_sorted_array_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index eaa9ee2..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_53i_find_a_number_in_a_sorted_array_s1/sfo_53i_find_a_number_in_a_sorted_array_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,45 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_53i_find_a_number_in_a_sorted_array_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- int search(vector& nums, int target) {
- // 搜索右边界 right
- int i = 0, j = nums.size() - 1;
- while(i <= j) {
- int m = (i + j) / 2;
- if(nums[m] <= target) i = m + 1;
- else j = m - 1;
- }
- int right = i;
- // 若数组中无 target ,则提前返回
- if(j >= 0 && nums[j] != target) return 0;
- // 搜索左边界 right
- i = 0; j = nums.size() - 1;
- while(i <= j) {
- int m = (i + j) / 2;
- if(nums[m] < target) i = m + 1;
- else j = m - 1;
- }
- int left = j;
- return right - left - 1;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- vector nums = { 5, 7, 7, 8, 8, 10 };
- int target = 8;
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- int res = slt->search(nums, target);
- cout << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_53i_find_a_number_in_a_sorted_array_s2/sfo_53i_find_a_number_in_a_sorted_array_s2.cpp b/cpp/sfo_53i_find_a_number_in_a_sorted_array_s2/sfo_53i_find_a_number_in_a_sorted_array_s2.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index a7b8921..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_53i_find_a_number_in_a_sorted_array_s2/sfo_53i_find_a_number_in_a_sorted_array_s2.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_53i_find_a_number_in_a_sorted_array_s2.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- int search(vector& nums, int target) {
- return helper(nums, target) - helper(nums, target - 1);
- }
-private:
- int helper(vector& nums, int tar) {
- int i = 0, j = nums.size() - 1;
- while(i <= j) {
- int m = (i + j) / 2;
- if(nums[m] <= tar) i = m + 1;
- else j = m - 1;
- }
- return i;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- vector nums = { 5, 7, 7, 8, 8, 10 };
- int target = 8;
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- int res = slt->search(nums, target);
- cout << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_53ii_the_missing_number_from_0_to_n1_s1/sfo_53ii_the_missing_number_from_0_to_n1_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_53ii_the_missing_number_from_0_to_n1_s1/sfo_53ii_the_missing_number_from_0_to_n1_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 59182cf..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_53ii_the_missing_number_from_0_to_n1_s1/sfo_53ii_the_missing_number_from_0_to_n1_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_53ii_the_missing_number_from_0_to_n1_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- int missingNumber(vector& nums) {
- int i = 0, j = nums.size() - 1;
- while(i <= j) {
- int m = (i + j) / 2;
- if(nums[m] == m) i = m + 1;
- else j = m - 1;
- }
- return i;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- vector nums = { 0, 1, 3 };
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- int res = slt->missingNumber(nums);
- cout << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_54_the_kth_largest_node_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1/sfo_54_the_kth_largest_node_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_54_the_kth_largest_node_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1/sfo_54_the_kth_largest_node_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 1f7a32d..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_54_the_kth_largest_node_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1/sfo_54_the_kth_largest_node_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_54_the_kth_largest_node_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- int kthLargest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
- this->k = k;
- dfs(root);
- return res;
- }
-private:
- int res, k;
- void dfs(TreeNode* root) {
- if(root == nullptr) return;
- dfs(root->right);
- if(k == 0) return;
- if(--k == 0) res = root->val;
- dfs(root->left);
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- TreeNode* root = vectorToTree(vector { 3, 1, 4, INT_MAX, 2, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX });
- int k = 1;
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- int res = slt->kthLargest(root, k);
- cout << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_55i_depth_of_a_binary_tree_s1/sfo_55i_depth_of_a_binary_tree_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_55i_depth_of_a_binary_tree_s1/sfo_55i_depth_of_a_binary_tree_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 282b207..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_55i_depth_of_a_binary_tree_s1/sfo_55i_depth_of_a_binary_tree_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,27 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_55i_depth_of_a_binary_tree_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
- if(root == nullptr) return 0;
- return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- TreeNode* root = vectorToTree(vector { 3, 9, 20, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, 15, 7, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX });
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- int res = slt->maxDepth(root);
- cout << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_55i_depth_of_a_binary_tree_s2/sfo_55i_depth_of_a_binary_tree_s2.cpp b/cpp/sfo_55i_depth_of_a_binary_tree_s2/sfo_55i_depth_of_a_binary_tree_s2.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 7c79f40..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_55i_depth_of_a_binary_tree_s2/sfo_55i_depth_of_a_binary_tree_s2.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_55i_depth_of_a_binary_tree_s2.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
- if(root == nullptr) return 0;
- vector que;
- que.push_back(root);
- int res = 0;
- while(!que.empty()) {
- vector tmp;
- for(TreeNode* node : que) {
- if(node->left != nullptr) tmp.push_back(node->left);
- if(node->right != nullptr) tmp.push_back(node->right);
- }
- que = tmp;
- res++;
- }
- return res;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- TreeNode* root = vectorToTree(vector { 3, 9, 20, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, 15, 7, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX });
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- int res = slt->maxDepth(root);
- cout << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_55ii_balanced_binary_tree_s1/sfo_55ii_balanced_binary_tree_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_55ii_balanced_binary_tree_s1/sfo_55ii_balanced_binary_tree_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 1eecb32..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_55ii_balanced_binary_tree_s1/sfo_55ii_balanced_binary_tree_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_55ii_balanced_binary_tree_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
- return recur(root) != -1;
- }
-private:
- int recur(TreeNode* root) {
- if (root == nullptr) return 0;
- int left = recur(root->left);
- if(left == -1) return -1;
- int right = recur(root->right);
- if(right == -1) return -1;
- return abs(left - right) < 2 ? max(left, right) + 1 : -1;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- TreeNode* root = vectorToTree(vector { 3, 9, 20, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, 15, 7, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX });
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- bool res = slt->isBalanced(root);
- cout << boolalpha << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_55ii_balanced_binary_tree_s2/sfo_55ii_balanced_binary_tree_s2.cpp b/cpp/sfo_55ii_balanced_binary_tree_s2/sfo_55ii_balanced_binary_tree_s2.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 065893c..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_55ii_balanced_binary_tree_s2/sfo_55ii_balanced_binary_tree_s2.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_55ii_balanced_binary_tree_s2.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
- if (root == nullptr) return true;
- return abs(depth(root->left) - depth(root->right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(root->left) && isBalanced(root->right);
- }
-private:
- int depth(TreeNode* root) {
- if (root == nullptr) return 0;
- return max(depth(root->left), depth(root->right)) + 1;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- TreeNode* root = vectorToTree(vector { 3, 9, 20, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, 15, 7, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX });
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- bool res = slt->isBalanced(root);
- cout << boolalpha << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_56i_single_number_i_s1/sfo_56i_single_number_i_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_56i_single_number_i_s1/sfo_56i_single_number_i_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 8ea515e..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_56i_single_number_i_s1/sfo_56i_single_number_i_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_56i_single_number_i_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- vector singleNumbers(vector& nums) {
- int x = 0, y = 0, n = 0, m = 1;
- for(int num : nums) // 1. 遍历异或
- n ^= num;
- while((n & m) == 0) // 2. 循环左移,计算 m
- m <<= 1;
- for(int num : nums) { // 3. 遍历 nums 分组
- if(num & m) x ^= num; // 4. 当 num & m != 0
- else y ^= num; // 4. 当 num & m == 0
- }
- return vector {x, y}; // 5. 返回出现一次的数字
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- vector nums = { 4, 1, 4, 6 };
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- vector res = slt->singleNumbers(nums);
- PrintUtil::printVector(res);
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_57_two_numbers_with_sum_s_s1/sfo_57_two_numbers_with_sum_s_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_57_two_numbers_with_sum_s_s1/sfo_57_two_numbers_with_sum_s_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index cea8b07..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_57_two_numbers_with_sum_s_s1/sfo_57_two_numbers_with_sum_s_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,34 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_57_two_numbers_with_sum_s_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- vector twoSum(vector& nums, int target) {
- int i = 0, j = nums.size() - 1;
- while(i < j) {
- int s = nums[i] + nums[j];
- if(s < target) i++;
- else if(s > target) j--;
- else return { nums[i], nums[j] };
- }
- return {};
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- vector nums = { 2, 7, 11, 15 };
- int target = 9;
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- vector res = slt->twoSum(nums, target);
- PrintUtil::printVector(res);
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_61_straight_in_poker_s2/sfo_61_straight_in_poker_s2.cpp b/cpp/sfo_61_straight_in_poker_s2/sfo_61_straight_in_poker_s2.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 1e862ca..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_61_straight_in_poker_s2/sfo_61_straight_in_poker_s2.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_61_straight_in_poker_s2.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- bool isStraight(vector& nums) {
- int joker = 0;
- sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); // 数组排序
- for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
- if(nums[i] == 0) joker++; // 统计大小王数量
- else if(nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) return false; // 若有重复,提前返回 false
- }
- return nums[4] - nums[joker] < 5; // 最大牌 - 最小牌 < 5 则可构成顺子
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- vector nums = { 0, 0, 1, 2, 5 };
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- bool res = slt->isStraight(nums);
- cout << boolalpha << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_67_convert_string_to_int_s1/sfo_67_convert_string_to_int_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_67_convert_string_to_int_s1/sfo_67_convert_string_to_int_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 60ab737..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_67_convert_string_to_int_s1/sfo_67_convert_string_to_int_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_67_convert_string_to_int_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- int strToInt(string str) {
- int res = 0, bndry = INT_MAX / 10;
- int i = 0, sign = 1, length = str.size();
- if(length == 0) return 0;
- while(str[i] == ' ')
- if(++i == length) return 0;
- if(str[i] == '-') sign = -1;
- if(str[i] == '-' || str[i] == '+') i++;
- for(int j = i; j < length; j++) {
- if(str[j] < '0' || str[j] > '9') break;
- if(res > bndry || res == bndry && str[j] > '7')
- return sign == 1 ? INT_MAX : INT_MIN;
- res = res * 10 + (str[j] - '0');
- }
- return sign * res;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- string str = "42";
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- int res = slt->strToInt(str);
- cout << res << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1/sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1/sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 55b9a7c..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1/sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
- while(root != nullptr) {
- if(root->val < p->val && root->val < q->val) // p,q 都在 root 的右子树中
- root = root->right; // 遍历至右子节点
- else if(root->val > p->val && root->val > q->val) // p,q 都在 root 的左子树中
- root = root->left; // 遍历至左子节点
- else break;
- }
- return root;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- TreeNode* root = vectorToTree(vector { 6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, 3, 5, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX });
- TreeNode* p = new TreeNode(2);
- TreeNode* q = new TreeNode(8);
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- TreeNode* res = slt->lowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q);
- cout << res->val << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s2/sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s2.cpp b/cpp/sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s2/sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s2.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 5c03b89..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s2/sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s2.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s2.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
- if(p->val > q->val)
- swap(p, q);
- while(root != nullptr) {
- if(root->val < p->val) // p,q 都在 root 的右子树中
- root = root->right; // 遍历至右子节点
- else if(root->val > q->val) // p,q 都在 root 的左子树中
- root = root->left; // 遍历至左子节点
- else break;
- }
- return root;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- TreeNode* root = vectorToTree(vector { 6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, 3, 5, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX });
- TreeNode* p = new TreeNode(2);
- TreeNode* q = new TreeNode(8);
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- TreeNode* res = slt->lowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q);
- cout << res->val << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s3/sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s3.cpp b/cpp/sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s3/sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s3.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 4568d73..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s3/sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s3.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_68i_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree_s3.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
- if(root->val < p->val && root->val < q->val)
- return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
- if(root->val > p->val && root->val > q->val)
- return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
- return root;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- TreeNode* root = vectorToTree(vector { 6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, 3, 5, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX });
- TreeNode* p = new TreeNode(2);
- TreeNode* q = new TreeNode(8);
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- TreeNode* res = slt->lowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q);
- cout << res->val << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_68ii_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_tree_s1/sfo_68ii_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_tree_s1.cpp b/cpp/sfo_68ii_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_tree_s1/sfo_68ii_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_tree_s1.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 7adc63a..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_68ii_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_tree_s1/sfo_68ii_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_tree_s1.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_68ii_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_tree_s1.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
- if(root == nullptr || root == p || root == q) return root;
- TreeNode *left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
- TreeNode *right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
- if(left == nullptr) return right;
- if(right == nullptr) return left;
- return root;
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- TreeNode* root = vectorToTree(vector { 3, 5, 1, 6, 2, 0, 8, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, 7, 4, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX });
- TreeNode* p = getTreeNode(root, 5);
- TreeNode* q = getTreeNode(root, 1);
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- TreeNode* res = slt->lowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q);
- cout << res->val << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/cpp/sfo_68ii_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_tree_s2/sfo_68ii_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_tree_s2.cpp b/cpp/sfo_68ii_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_tree_s2/sfo_68ii_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_tree_s2.cpp
deleted file mode 100644
index 6e57b95..0000000
--- a/cpp/sfo_68ii_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_tree_s2/sfo_68ii_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_tree_s2.cpp
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,34 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_68ii_the_nearest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_tree_s2.cpp
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-#include "../include/include.hpp"
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
-public:
- TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
- if(root == nullptr || root == p || root == q) return root;
- TreeNode *left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
- TreeNode *right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
- if(left == nullptr && right == nullptr) return nullptr; // 1.
- if(left == nullptr) return right; // 3.
- if(right == nullptr) return left; // 4.
- return root; // 2. if(left != null and right != null)
- }
-};
-
-int main() {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- TreeNode* root = vectorToTree(vector { 3, 5, 1, 6, 2, 0, 8, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, 7, 4, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX, INT_MAX });
- TreeNode* p = getTreeNode(root, 5);
- TreeNode* q = getTreeNode(root, 1);
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution* slt = new Solution();
- TreeNode* res = slt->lowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q);
- cout << res->val << endl;
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/java/sfo_20_a_string_representing_a_numeric_value_s1/sfo_20_a_string_representing_a_numeric_value_s1.java b/java/sfo_20_a_string_representing_a_numeric_value_s1/sfo_20_a_string_representing_a_numeric_value_s1.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 63fda1a..0000000
--- a/java/sfo_20_a_string_representing_a_numeric_value_s1/sfo_20_a_string_representing_a_numeric_value_s1.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,50 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* File: sfo_20_a_string_representing_a_numeric_value_s1.java
-* Created Time: 2021-12-09
-* Author: Krahets (krahets@163.com)
-*/
-
-package sfo_20_a_string_representing_a_numeric_value_s1;
-
-import include.*;
-import java.util.*;
-
-// ===== Solution Code =====
-class Solution {
- public boolean isNumber(String s) {
- HashMap[] states = {
- new HashMap() {{ put(' ', 0); put('s', 1); put('d', 2); put('.', 4); }}, // 0.
- new HashMap() {{ put('d', 2); put('.', 4); }}, // 1.
- new HashMap() {{ put('d', 2); put('.', 3); put('e', 5); put(' ', 8); }}, // 2.
- new HashMap() {{ put('d', 3); put('e', 5); put(' ', 8); }}, // 3.
- new HashMap() {{ put('d', 3); }}, // 4.
- new HashMap() {{ put('s', 6); put('d', 7); }}, // 5.
- new HashMap() {{ put('d', 7); }}, // 6.
- new HashMap() {{ put('d', 7); put(' ', 8); }}, // 7.
- new HashMap() {{ put(' ', 8); }} // 8.
- };
- int p = 0;
- char t;
- for(char c : s.toCharArray()) {
- if(c >= '0' && c <= '9') t = 'd';
- else if(c == '+' || c == '-') t = 's';
- else if(c == 'e' || c == 'E') t = 'e';
- else if(c == '.' || c == ' ') t = c;
- else t = '?';
- if(!states[p].containsKey(t)) return false;
- p = (int)states[p].get(t);
- }
- return p == 2 || p == 3 || p == 7 || p == 8;
- }
-}
-
-public class sfo_20_a_string_representing_a_numeric_value_s1 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- // ======= Test Case =======
- String s = " .1 ";
- // ====== Driver Code ======
- Solution slt = new Solution();
- boolean res = slt.isNumber(s);
- System.out.println(res);
- }
-}
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 0 \345\274\225\350\250\200.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 0 \345\274\225\350\250\200.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..b3f6ee9
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 0 \345\274\225\350\250\200.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
+# 引言
+
+《图解算法数据结构》面向算法初学者、互联网求职者设计,主要内容包括:
+
+### 精选面试题图文解析
+
+- 图文详解 75 道题目,覆盖主要算法知识点,非常适合作为算法学习的 **第一份题库**。
+- 题库活跃于各大互联网公司招聘中,可使笔面试准备事半功倍。
+- 致力于行文深入浅出、图文搭配,提供简洁的 **Python, Java, C++** 解题代码。
+- 笔者整理了 **题目分类** 和 **刷题计划** ,让刷题有迹可循。
+
+### 数据结构与算法专栏
+
+- **基础知识:** 时间复杂度、空间复杂度等算法知识。
+- **数据结构:** 数组、链表、字符串、栈、队列、哈希表、树、图、堆。
+- **算法专题:** 搜索与回溯、分治、动态规划、贪心、排序、位运算、模拟、数学。
+
+## 配套代码
+
+为方便各位 Debug 算法题目,笔者整理了本 LeetBook 的配套代码,包括:
+
+- 「题解代码」提供 Python, Java, C++ 语言。
+- 「测试样例」与运行调用代码。
+- 「数据结构」封装,提升 LeetCode 刷题效率。
+
+与本 LeetBook 配合食用更佳,仓库链接:https://github.com/krahets/LeetCode-Book
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 0.1 \345\210\267\351\242\230\345\273\272\350\256\256.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 0.1 \345\210\267\351\242\230\345\273\272\350\256\256.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..a2e4c90
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 0.1 \345\210\267\351\242\230\345\273\272\350\256\256.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+# 刷题建议
+
+本书专为算法初学者设计,特别针对有意进入互联网行业的求职者。内容覆盖如下主题:
+
+- **算法**:搜索、查找、排序、双指针、回溯、分治、动态规划、贪心、位运算、数学等。
+- **数据结构**:数组、栈、队列、字符串、链表、树、图、堆、哈希表等。
+
+所有题目已经进行分类,并按照难易程度排序。对于初学者,这里提供几条刷题建议:
+
+1. 建议每日刷 2~3 题。若能轻松完成,可以尝试增加至 5~8 题,但请记住:刷题的质量远重要于数量。务必确保你真正理解了每个题目的解法及背后的算法原理。
+2. 建议你按照目录顺序逐题解答。如果碰到某些难以解决的题目,可以先跳过,稍后回顾时再挑战。
+3. 很多题目都有不止一种解法,请你注意比较和探讨各种方法的特点和适用情况。
+4. 如果你发现自己忘记了某个题目的解法,不必灰心。艾宾浩斯遗忘曲线指出,为了真正掌握一个知识点,通常需要复习至少3次。
+5. 行百里者半九十。坚持至关重要,加油,相信你可以做到!
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 0.2 \351\242\230\347\233\256\345\210\206\347\261\273.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 0.2 \351\242\230\347\233\256\345\210\206\347\261\273.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..3bfb3e9
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 0.2 \351\242\230\347\233\256\345\210\206\347\261\273.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+# 题目分类
+
+题目可能存在多种解法,下表仅列举最优解法(时间与空间复杂度最低)的算法和数据结构分类。
+
+| 题目 | 算法分类 | 数据结构分类 |
+| -------------------------------- | ---------------- | -------------- |
+| 寻找文件副本 | 查找 | 数组 |
+| 寻找目标值 - 二维数组 | 查找 | 数组 |
+| 路径加密 | | 字符串 |
+| 图书整理 I | | 栈与队列,链表 |
+| 推理二叉树 | 分治 | 树,哈希表 |
+| 图书整理 II | | 栈与队列 |
+| 斐波那契数 | 动态规划 | 数组 |
+| 跳跃训练 | 动态规划 | 数组 |
+| 库存管理 I | 查找 | 数组 |
+| 字母迷宫 | 回溯,搜索 | 数组,图 |
+| 衣橱整理 | 回溯,搜索 | 数组,图 |
+| 砍竹子 I | 贪心,数学 | |
+| 砍竹子 II | 贪心,分治,数学 | |
+| 位 1 的个数 | 位运算 | |
+| Pow(x, n) | 分治,位运算 | |
+| 报数 | | 数组 |
+| 删除链表节点 | 双指针 | 链表 |
+| 模糊搜索验证 | 动态规划 | 字符串 |
+| 有效数字 | | 字符串 |
+| 训练计划 I | 双指针 | 数组 |
+| 训练计划 II | 双指针 | 链表 |
+| 训练计划 III | 双指针 | 链表 |
+| 训练计划 IV | 双指针 | 链表 |
+| 子结构判断 | 搜索 | 树 |
+| 翻转二叉树 | 搜索 | 栈与队列,树 |
+| 判断对称二叉树 | 搜索 | 树 |
+| 螺旋遍历二维数组 | 模拟 | 数组 |
+| 最小栈 | 排序 | 栈与队列 |
+| 验证图书取出顺序 | 模拟 | 栈与队列 |
+| 彩灯装饰记录 I | 搜索 | 栈与队列,树 |
+| 彩灯装饰记录 II | 搜索 | 栈与队列,树 |
+| 彩灯装饰记录 III | 搜索 | 栈与队列,树 |
+| 验证二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列 | 分治 | 栈与队列,树 |
+| 二叉树中和为目标值的路径 | 回溯,搜索 | 树 |
+| 随机链表的复制 | | 链表 |
+| 将二叉搜索树转化为排序的双向链表 | 搜索,双指针 | 树 |
+| 序列化与反序列化二叉树 | 搜索 | 树 |
+| 套餐内商品的排列顺序 | 回溯 | 字符串,哈希表 |
+| 库存管理 II | | 数组 |
+| 库存管理 III | 排序 | 数组,堆 |
+| 数据流中的中位数 | 排序 | 堆 |
+| 连续天数的最高销售额 | 动态规划 | 数组 |
+| 数字 1 的个数 | 数学 | |
+| 找到第 k 位数字 | 数学 | |
+| 破解闯关密码 | 排序 | 字符串 |
+| 解密数字 | 动态规划 | 字符串 |
+| 珠宝的最高价值 | 动态规划 | 数组 |
+| 招式拆解 I | 动态规划,双指针 | 哈希表 |
+| 丑数 | 动态规划 | |
+| 招式拆解 II | | 哈希表 |
+| 交易逆序对的总数 | 分治 | 数组 |
+| 训练计划 V | 双指针 | 链表 |
+| 统计目标成绩的出现次数 | 查找 | 数组 |
+| 点名 | 查找 | 数组 |
+| 寻找二叉搜索树中的目标节点 | 搜索 | 树 |
+| 计算二叉树的深度 | 搜索 | 树 |
+| 判断是否为平衡二叉树 | 搜索 | 树 |
+| 撞色搭配 | 位运算 | 数组 |
+| 训练计划 VI | 位运算 | 数组 |
+| 查找总价格为目标值的两个商品 | 双指针 | 数组 |
+| 文件组合 | 双指针 | 数组 |
+| 字符串中的单词反转 | 双指针 | 字符串 |
+| 动态口令 | | 字符串 |
+| 望远镜中最高的海拔 | 排序 | 数组,栈与队列 |
+| 设计自助结算系统 | 排序 | 数组,栈与队列 |
+| 统计结果概率 | 动态规划 | |
+| 文物朝代判断 | 排序 | 数组,哈希表 |
+| 破冰游戏 | 数学 | |
+| 买卖芯片的最佳时机 | 动态规划 | 数组 |
+| 设计机械累加器 | | |
+| 加密运算 | 位运算 | |
+| 按规则计算统计结果 | 数学 | 数组 |
+| 不使用库函数的字符串转整数 | | 字符串 |
+| 求二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先 | 搜索 | 树 |
+| 寻找二叉树的最近公共祖先 | 搜索 | 树 |
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 1.1 \346\225\260\346\215\256\347\273\223\346\236\204\347\256\200\344\273\213.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 1.1 \346\225\260\346\215\256\347\273\223\346\236\204\347\256\200\344\273\213.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..9b4e077
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 1.1 \346\225\260\346\215\256\347\273\223\346\236\204\347\256\200\344\273\213.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,629 @@
+# 数据结构简介
+
+数据结构是为实现对计算机数据有效使用的各种数据组织形式,服务于各类计算机操作。不同的数据结构具有各自对应的适用场景,旨在降低各种算法计算的时间与空间复杂度,达到最佳的任务执行效率。
+
+如下图所示,常见的数据结构可分为「线性数据结构」与「非线性数据结构」,具体为:「数组」、「链表」、「栈」、「队列」、「树」、「图」、「散列表」、「堆」。
+
+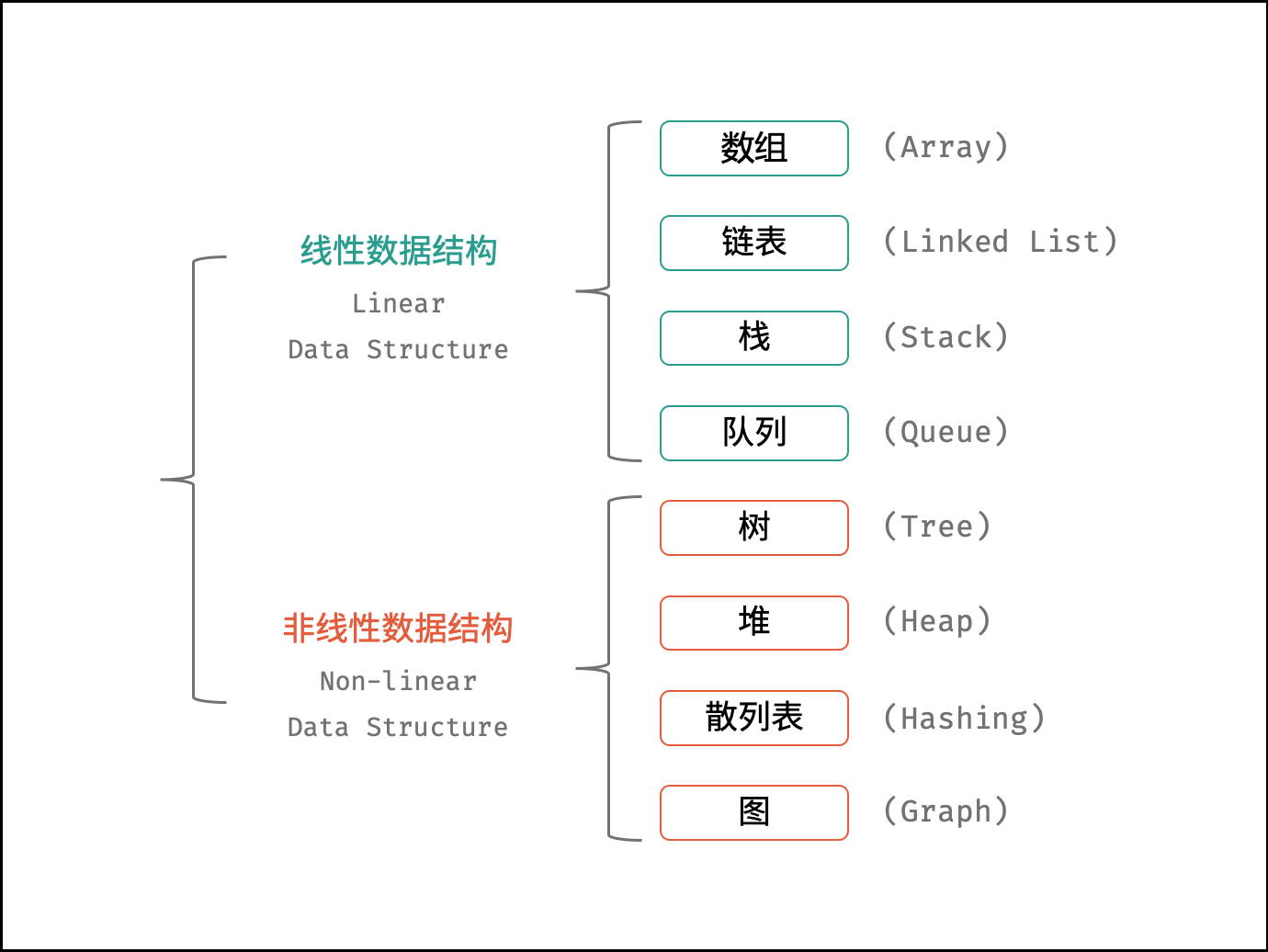{:width=500}
+
+从零开始学习算法的同学对数据结构的使用方法可能尚不熟悉,本节将初步介绍各数据结构的基本特点,与 Python3 , Java , C++ 语言中各数据结构的初始化与构建方法。
+
+> 代码运行可使用本地 IDE 或 [力扣 PlayGround](https://leetcode-cn.com/playground/) 。
+
+---
+
+## 数组
+
+数组是将相同类型的元素存储于连续内存空间的数据结构,其长度不可变。
+
+如下图所示,构建此数组需要在初始化时给定长度,并对数组每个索引元素赋值,代码如下:
+
+```Java []
+// 初始化一个长度为 5 的数组 array
+int[] array = new int[5];
+// 元素赋值
+array[0] = 2;
+array[1] = 3;
+array[2] = 1;
+array[3] = 0;
+array[4] = 2;
+```
+
+```C++ []
+// 初始化一个长度为 5 的数组 array
+int array[5];
+// 元素赋值
+array[0] = 2;
+array[1] = 3;
+array[2] = 1;
+array[3] = 0;
+array[4] = 2;
+```
+
+或者可以使用直接赋值的初始化方式,代码如下:
+
+```Java []
+int[] array = {2, 3, 1, 0, 2};
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int array[] = {2, 3, 1, 0, 2};
+```
+
+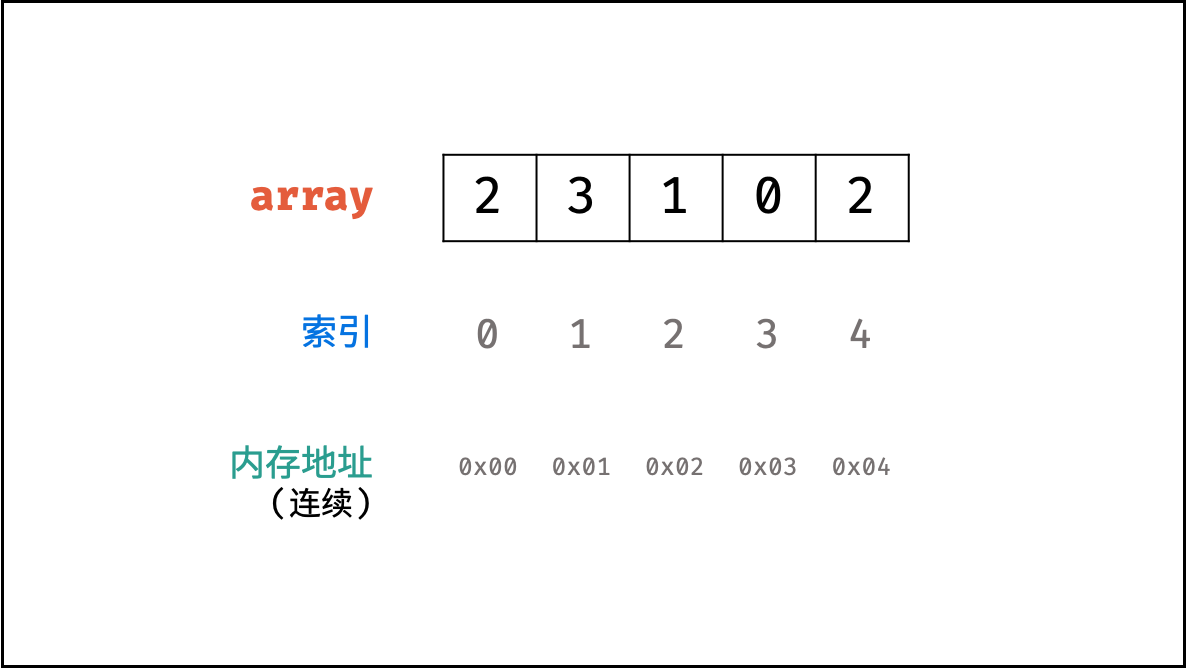{:width=500}
+
+「可变数组」是经常使用的数据结构,其基于数组和扩容机制实现,相比普通数组更加灵活。常用操作有:访问元素、添加元素、删除元素。
+
+```Java []
+// 初始化可变数组
+List array = new ArrayList<>();
+
+// 向尾部添加元素
+array.add(2);
+array.add(3);
+array.add(1);
+array.add(0);
+array.add(2);
+```
+
+```Python []
+# 初始化可变数组
+array = []
+
+# 向尾部添加元素
+array.append(2)
+array.append(3)
+array.append(1)
+array.append(0)
+array.append(2)
+```
+
+```C++ []
+// 初始化可变数组
+vector array;
+
+// 向尾部添加元素
+array.push_back(2);
+array.push_back(3);
+array.push_back(1);
+array.push_back(0);
+array.push_back(2);
+```
+
+---
+
+## 链表
+
+链表以节点为单位,每个元素都是一个独立对象,在内存空间的存储是非连续的。链表的节点对象具有两个成员变量:「值 `val`」,「后继节点引用 `next`」 。
+
+```Java []
+class ListNode {
+ int val; // 节点值
+ ListNode next; // 后继节点引用
+ ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
+}
+```
+
+```Python []
+class ListNode:
+ def __init__(self, x):
+ self.val = x # 节点值
+ self.next = None # 后继节点引用
+```
+
+```C++ []
+struct ListNode {
+ int val; // 节点值
+ ListNode *next; // 后继节点引用
+ ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
+};
+```
+
+如下图所示,建立此链表需要实例化每个节点,并构建各节点的引用指向。
+
+```Java []
+// 实例化节点
+ListNode n1 = new ListNode(4); // 节点 head
+ListNode n2 = new ListNode(5);
+ListNode n3 = new ListNode(1);
+
+// 构建引用指向
+n1.next = n2;
+n2.next = n3;
+```
+
+```Python []
+# 实例化节点
+n1 = ListNode(4) # 节点 head
+n2 = ListNode(5)
+n3 = ListNode(1)
+
+# 构建引用指向
+n1.next = n2
+n2.next = n3
+```
+
+```C++ []
+// 实例化节点
+ListNode *n1 = new ListNode(4); // 节点 head
+ListNode *n2 = new ListNode(5);
+ListNode *n3 = new ListNode(1);
+
+// 构建引用指向
+n1->next = n2;
+n2->next = n3;
+```
+
+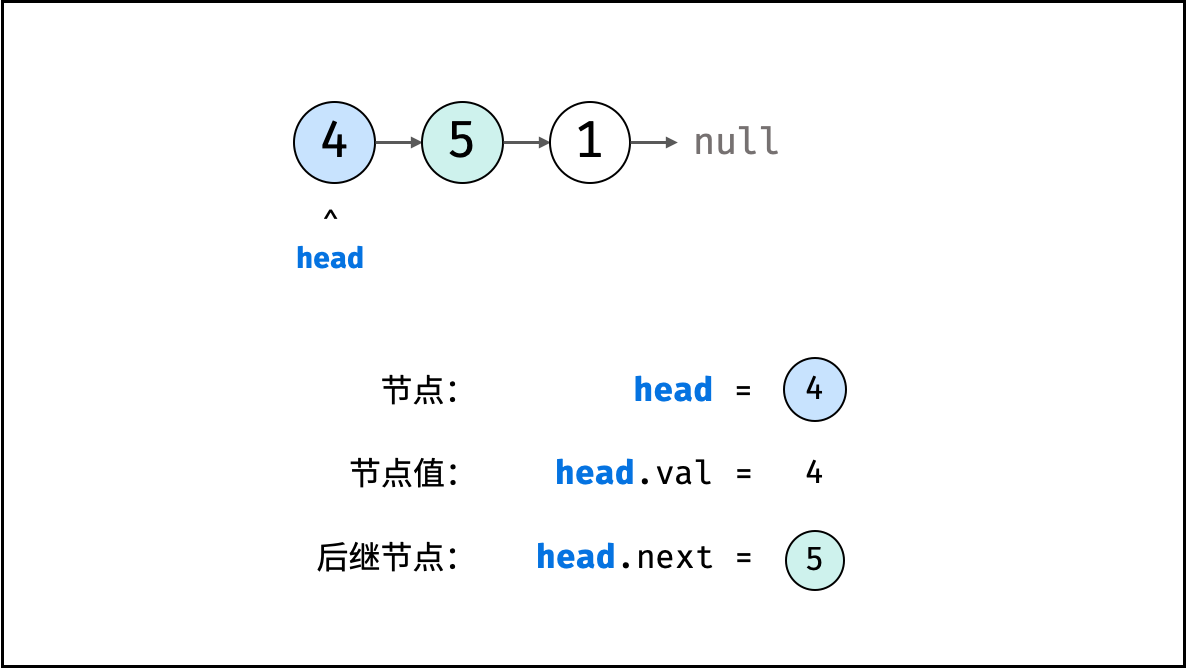{:width=500}
+
+---
+
+## 栈
+
+栈是一种具有 「先入后出」 特点的抽象数据结构,可使用数组或链表实现。
+
+```Java []
+Stack stack = new Stack<>();
+```
+
+```Python []
+stack = [] # Python 可将列表作为栈使用
+```
+
+```C++ []
+stack stk;
+```
+
+如下图所示,通过常用操作「入栈 `push()`」,「出栈 `pop()`」,展示了栈的先入后出特性。
+
+```Java []
+stack.push(1); // 元素 1 入栈
+stack.push(2); // 元素 2 入栈
+stack.pop(); // 出栈 -> 元素 2
+stack.pop(); // 出栈 -> 元素 1
+```
+
+```Python []
+stack.append(1) # 元素 1 入栈
+stack.append(2) # 元素 2 入栈
+stack.pop() # 出栈 -> 元素 2
+stack.pop() # 出栈 -> 元素 1
+```
+
+```C++ []
+stk.push(1); // 元素 1 入栈
+stk.push(2); // 元素 2 入栈
+stk.pop(); // 出栈 -> 元素 2
+stk.pop(); // 出栈 -> 元素 1
+```
+
+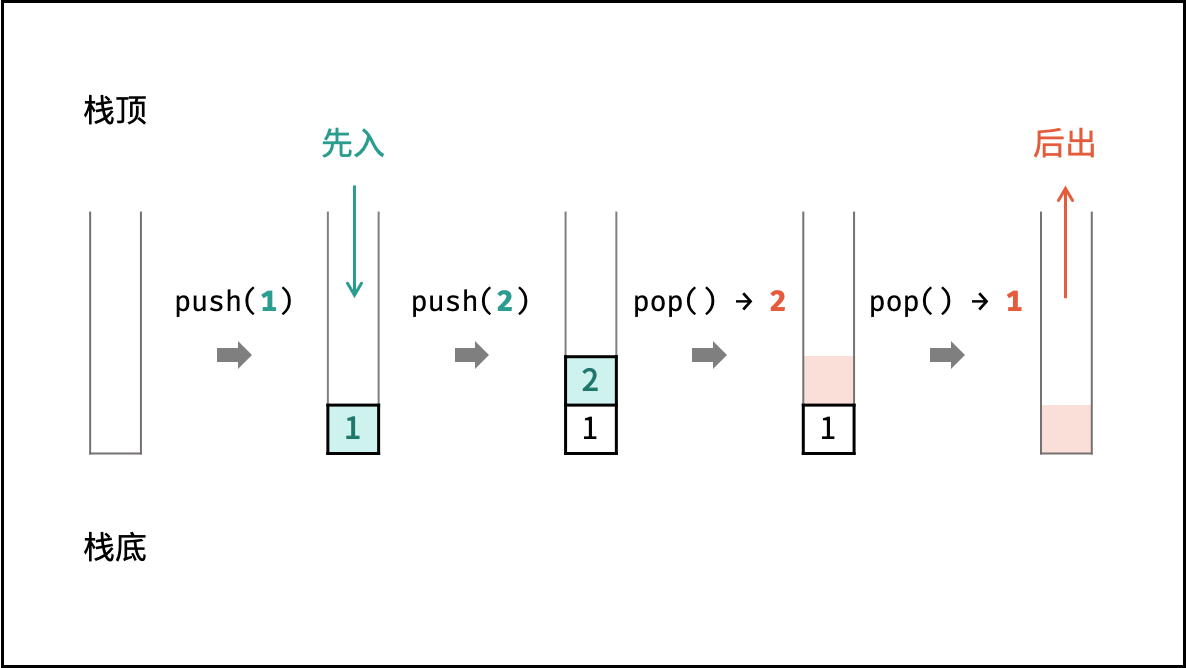{:width=500}
+
+> 注意:通常情况下,不推荐使用 Java 的 `Vector` 以及其子类 `Stack` ,而一般将 `LinkedList` 作为栈来使用。详细说明请见:[Stack,ArrayDeque,LinkedList 的区别](https://blog.csdn.net/cartoon_/article/details/87992743) 。
+
+```Java []
+LinkedList stack = new LinkedList<>();
+
+stack.addLast(1); // 元素 1 入栈
+stack.addLast(2); // 元素 2 入栈
+stack.removeLast(); // 出栈 -> 元素 2
+stack.removeLast(); // 出栈 -> 元素 1
+```
+
+---
+
+## 队列
+
+队列是一种具有 「先入先出」 特点的抽象数据结构,可使用链表实现。
+
+```Java []
+Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
+```
+
+```Python []
+# Python 通常使用双端队列 collections.deque
+from collections import deque
+
+queue = deque()
+```
+
+```C++ []
+queue que;
+```
+
+如下图所示,通过常用操作「入队 `push()`」,「出队 `pop()`」,展示了队列的先入先出特性。
+
+```Java []
+queue.offer(1); // 元素 1 入队
+queue.offer(2); // 元素 2 入队
+queue.poll(); // 出队 -> 元素 1
+queue.poll(); // 出队 -> 元素 2
+```
+
+```Python []
+queue.append(1) # 元素 1 入队
+queue.append(2) # 元素 2 入队
+queue.popleft() # 出队 -> 元素 1
+queue.popleft() # 出队 -> 元素 2
+```
+
+```C++ []
+que.push(1); // 元素 1 入队
+que.push(2); // 元素 2 入队
+que.pop(); // 出队 -> 元素 1
+que.pop(); // 出队 -> 元素 2
+```
+
+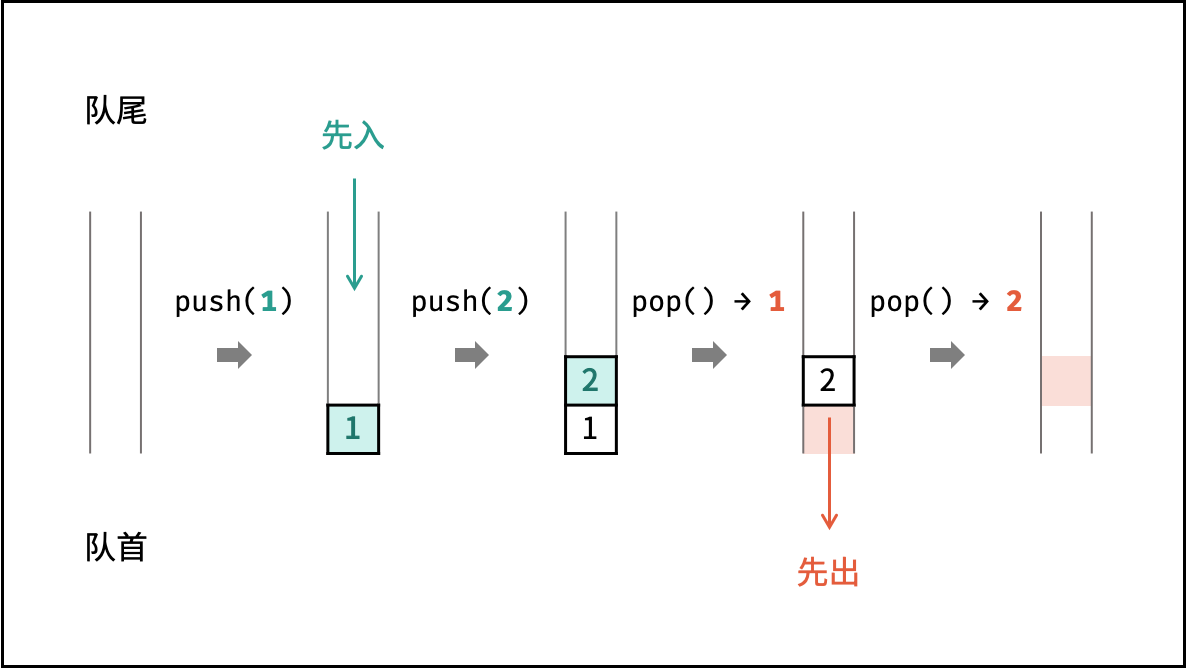{:width=500}
+
+---
+
+## 树
+
+树是一种非线性数据结构,根据子节点数量可分为 「二叉树」 和 「多叉树」,最顶层的节点称为「根节点 `root`」。以二叉树为例,每个节点包含三个成员变量:「值 `val`」、「左子节点 `left`」、「右子节点 `right`」 。
+
+```Java []
+class TreeNode {
+ int val; // 节点值
+ TreeNode left; // 左子节点
+ TreeNode right; // 右子节点
+ TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
+}
+```
+
+```Python []
+class TreeNode:
+ def __init__(self, x):
+ self.val = x # 节点值
+ self.left = None # 左子节点
+ self.right = None # 右子节点
+```
+
+```C++ []
+struct TreeNode {
+ int val; // 节点值
+ TreeNode *left; // 左子节点
+ TreeNode *right; // 右子节点
+ TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
+};
+```
+
+如下图所示,建立此二叉树需要实例化每个节点,并构建各节点的引用指向。
+
+```Java []
+// 初始化节点
+TreeNode n1 = new TreeNode(3); // 根节点 root
+TreeNode n2 = new TreeNode(4);
+TreeNode n3 = new TreeNode(5);
+TreeNode n4 = new TreeNode(1);
+TreeNode n5 = new TreeNode(2);
+
+// 构建引用指向
+n1.left = n2;
+n1.right = n3;
+n2.left = n4;
+n2.right = n5;
+```
+
+```Python []
+# 初始化节点
+n1 = TreeNode(3) # 根节点 root
+n2 = TreeNode(4)
+n3 = TreeNode(5)
+n4 = TreeNode(1)
+n5 = TreeNode(2)
+
+# 构建引用指向
+n1.left = n2
+n1.right = n3
+n2.left = n4
+n2.right = n5
+```
+
+```C++ []
+// 初始化节点
+TreeNode *n1 = new TreeNode(3); // 根节点 root
+TreeNode *n2 = new TreeNode(4);
+TreeNode *n3 = new TreeNode(5);
+TreeNode *n4 = new TreeNode(1);
+TreeNode *n5 = new TreeNode(2);
+
+// 构建引用指向
+n1->left = n2;
+n1->right = n3;
+n2->left = n4;
+n2->right = n5;
+```
+
+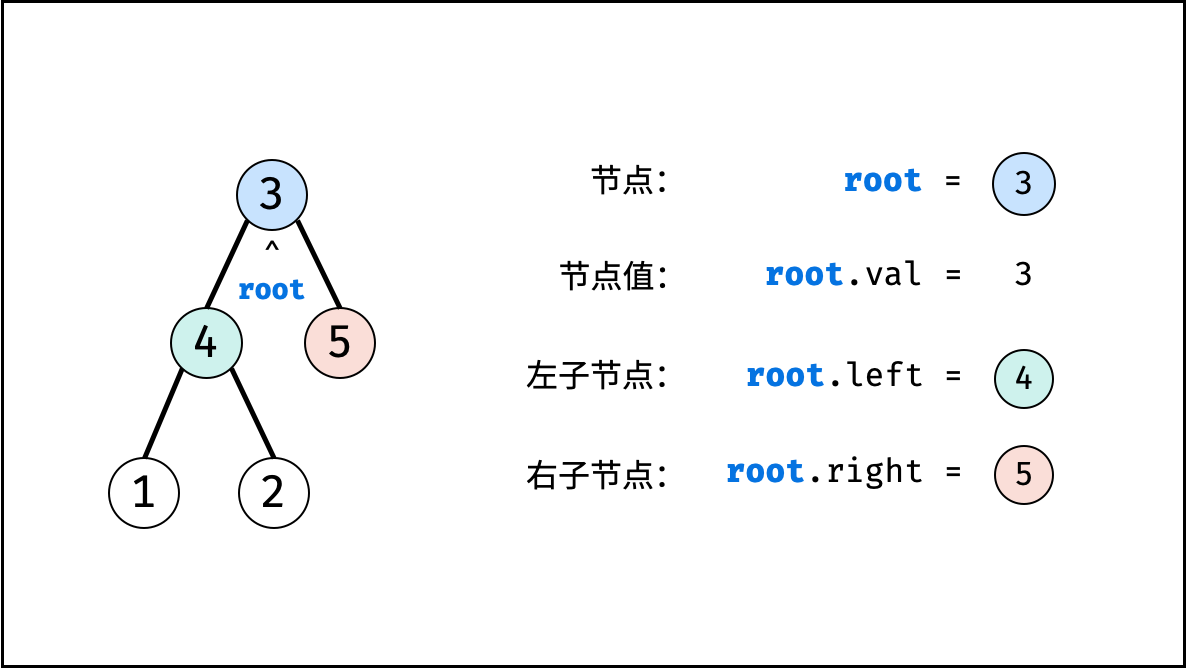{:width=500}
+
+---
+
+## 图
+
+图是一种非线性数据结构,由「节点(顶点)`vertex`」和「边 `edge`」组成,每条边连接一对顶点。根据边的方向有无,图可分为「有向图」和「无向图」。本文 **以无向图为例** 开展介绍。
+
+如下图所示,此无向图的 **顶点** 和 **边** 集合分别为:
+
+- 顶点集合: `vertices = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}`
+- 边集合: `edges = {(1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (2, 4), (3, 5), (4, 5)}`
+
+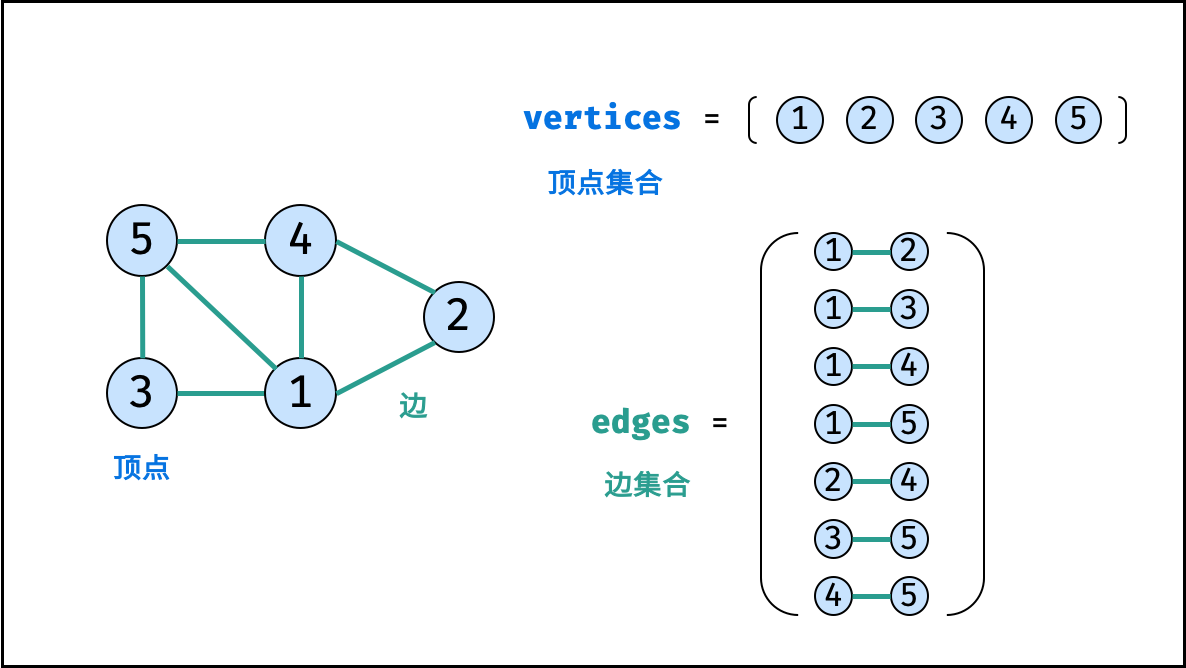{:width=500}
+
+表示图的方法通常有两种:
+
+1. **邻接矩阵:** 使用数组 $vertices$ 存储顶点,邻接矩阵 $edges$ 存储边; $edges[i][j]$ 代表节点 $i + 1$ 和 节点 $j + 1$ 之间是否有边。
+
+$$
+vertices = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] \\
+
+edges = \left[ \begin{matrix} 0 & 1 & 1 & 1 & 1 \\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 0 & 1 & 1 & 0 \\ \end{matrix} \right]
+$$
+
+```Python []
+vertices = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
+edges = [[0, 1, 1, 1, 1],
+ [1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
+ [1, 0, 0, 0, 1],
+ [1, 1, 0, 0, 1],
+ [1, 0, 1, 1, 0]]
+```
+
+```Java []
+int[] vertices = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
+int[][] edges = {{0, 1, 1, 1, 1},
+ {1, 0, 0, 1, 0},
+ {1, 0, 0, 0, 1},
+ {1, 1, 0, 0, 1},
+ {1, 0, 1, 1, 0}};
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int vertices[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
+int edges[5][5] = {{0, 1, 1, 1, 1},
+ {1, 0, 0, 1, 0},
+ {1, 0, 0, 0, 1},
+ {1, 1, 0, 0, 1},
+ {1, 0, 1, 1, 0}};
+```
+
+2. **邻接表:** 使用数组 $vertices$ 存储顶点,邻接表 $edges$ 存储边。 $edges$ 为一个二维容器,第一维 $i$ 代表顶点索引,第二维 $edges[i]$ 存储此顶点对应的边集和;例如 $edges[0] = [1, 2, 3, 4]$ 代表 $vertices[0]$ 的边集合为 $[1, 2, 3, 4]$ 。
+
+$$
+vertices = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] \\
+
+edges = \left[ \begin{matrix} [ & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 & ] \\ [ & 0 & 3 & ] \\ [ & 0 & 4 & ] \\ [ & 0 & 1 & 4 & ] \\ [ & 0 & 2 & 3 & ] \end{matrix} \right]
+$$
+
+```Python []
+vertices = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
+edges = [[1, 2, 3, 4],
+ [0, 3],
+ [0, 4],
+ [0, 1, 4],
+ [0, 2, 3]]
+```
+
+```Java []
+int[] vertices = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
+List> edges = new ArrayList<>();
+
+List edge_1 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4));
+List edge_2 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(0, 3));
+List edge_3 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(0, 4));
+List edge_4 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(0, 1, 4));
+List edge_5 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(0, 2, 3));
+edges.add(edge_1);
+edges.add(edge_2);
+edges.add(edge_3);
+edges.add(edge_4);
+edges.add(edge_5);
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int vertices[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
+vector> edges;
+
+vector edge_1 = {1, 2, 3, 4};
+vector edge_2 = {0, 3};
+vector edge_3 = {0, 4};
+vector edge_4 = {0, 1, 4};
+vector edge_5 = {0, 2, 3};
+edges.push_back(edge_1);
+edges.push_back(edge_2);
+edges.push_back(edge_3);
+edges.push_back(edge_4);
+edges.push_back(edge_5);
+```
+
+> **邻接矩阵 VS 邻接表 :**
+>
+> 邻接矩阵的大小只与节点数量有关,即 $N^2$ ,其中 $N$ 为节点数量。因此,当边数量明显少于节点数量时,使用邻接矩阵存储图会造成较大的内存浪费。
+> 因此,**邻接表** 适合存储稀疏图(顶点较多、边较少); **邻接矩阵** 适合存储稠密图(顶点较少、边较多)。
+
+---
+
+## 散列表
+
+散列表是一种非线性数据结构,通过利用 Hash 函数将指定的「键 `key`」映射至对应的「值 `value`」,以实现高效的元素查找。
+
+> 设想一个简单场景:小力、小特、小扣的学号分别为 10001, 10002, 10003 。
+> 现需求从「姓名」查找「学号」。
+
+则可通过建立姓名为 `key` ,学号为 `value` 的散列表实现此需求,代码如下:
+
+```Java []
+// 初始化散列表
+Map dic = new HashMap<>();
+
+// 添加 key -> value 键值对
+dic.put("小力", 10001);
+dic.put("小特", 10002);
+dic.put("小扣", 10003);
+
+// 从姓名查找学号
+dic.get("小力"); // -> 10001
+dic.get("小特"); // -> 10002
+dic.get("小扣"); // -> 10003
+```
+
+```Python []
+# 初始化散列表
+dic = {}
+
+# 添加 key -> value 键值对
+dic["小力"] = 10001
+dic["小特"] = 10002
+dic["小扣"] = 10003
+
+# 从姓名查找学号
+dic["小力"] # -> 10001
+dic["小特"] # -> 10002
+dic["小扣"] # -> 10003
+```
+
+```C++ []
+// 初始化散列表
+unordered_map dic;
+
+// 添加 key -> value 键值对
+dic["小力"] = 10001;
+dic["小特"] = 10002;
+dic["小扣"] = 10003;
+
+// 从姓名查找学号
+dic.find("小力")->second; // -> 10001
+dic.find("小特")->second; // -> 10002
+dic.find("小扣")->second; // -> 10003
+```
+
+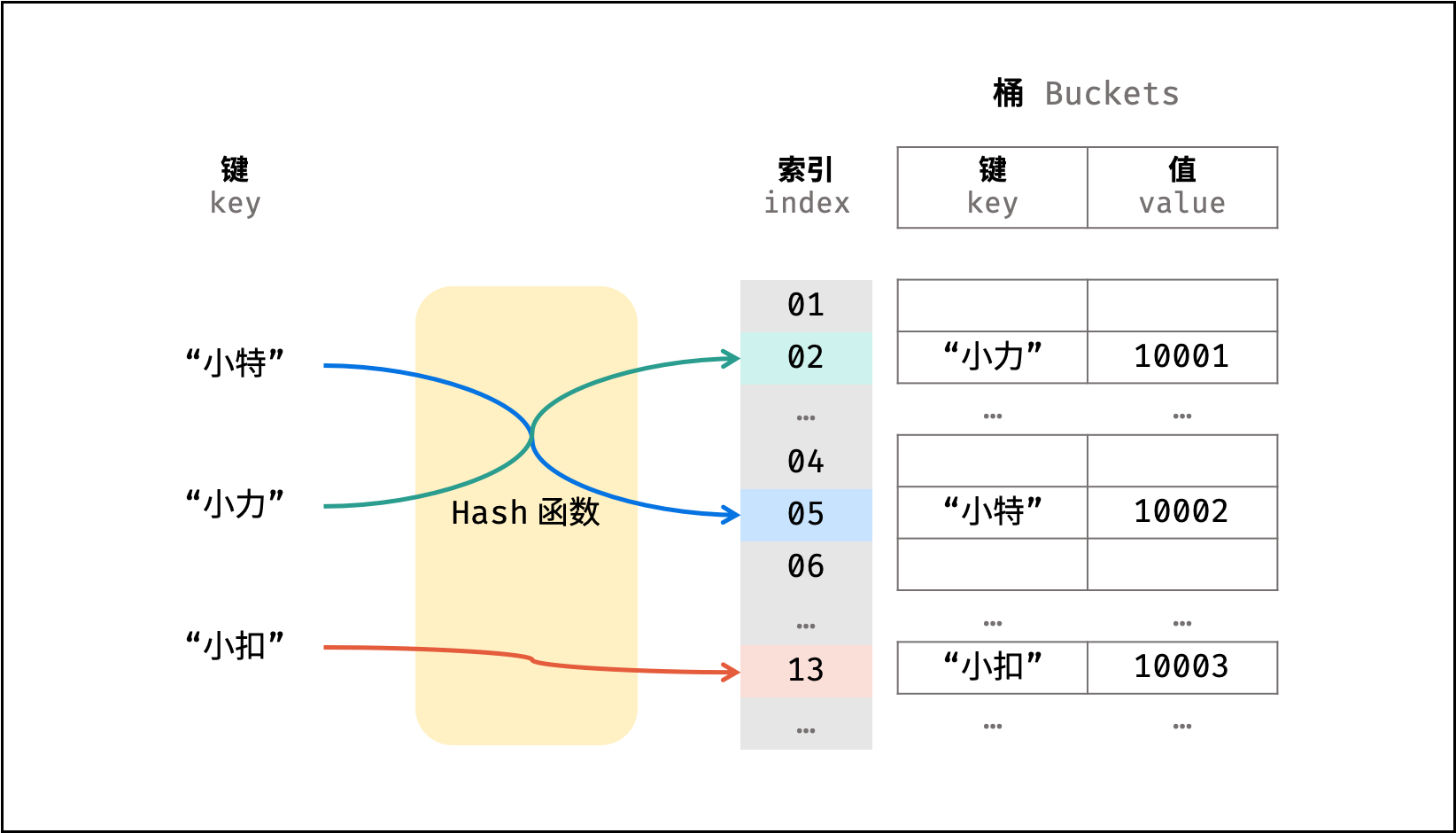{:width=550}
+
+### Hash 函数设计示例 :
+
+> 假设需求:从「学号」查找「姓名」。
+
+将三人的姓名存储至以下数组中,则各姓名在数组中的索引分别为 0, 1, 2 。
+
+```Java []
+String[] names = { "小力", "小特", "小扣" };
+```
+
+```Python []
+names = [ "小力", "小特", "小扣" ]
+```
+
+```C++ []
+string names[] = { "小力", "小特", "小扣" };
+```
+
+此时,我们构造一个简单的 Hash 函数( $\%$ 为取余符号 ),公式和封装函数如下所示:
+
+$$
+hash(key) = (key - 1) \% 10000
+$$
+
+```Java []
+int hash(int id) {
+ int index = (id - 1) % 10000;
+ return index;
+}
+```
+
+```Python []
+def hash(id):
+ index = (id - 1) % 10000
+ return index
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int hash(int id) {
+ int index = (id - 1) % 10000;
+ return index;
+}
+```
+
+则我们构建了以学号为 `key` 、姓名对应的数组索引为 `value` 的散列表。利用此 Hash 函数,则可在 $O(1)$ 时间复杂度下通过学号查找到对应姓名,即:
+
+```Java
+names[hash(10001)] // 小力
+names[hash(10002)] // 小特
+names[hash(10003)] // 小扣
+```
+
+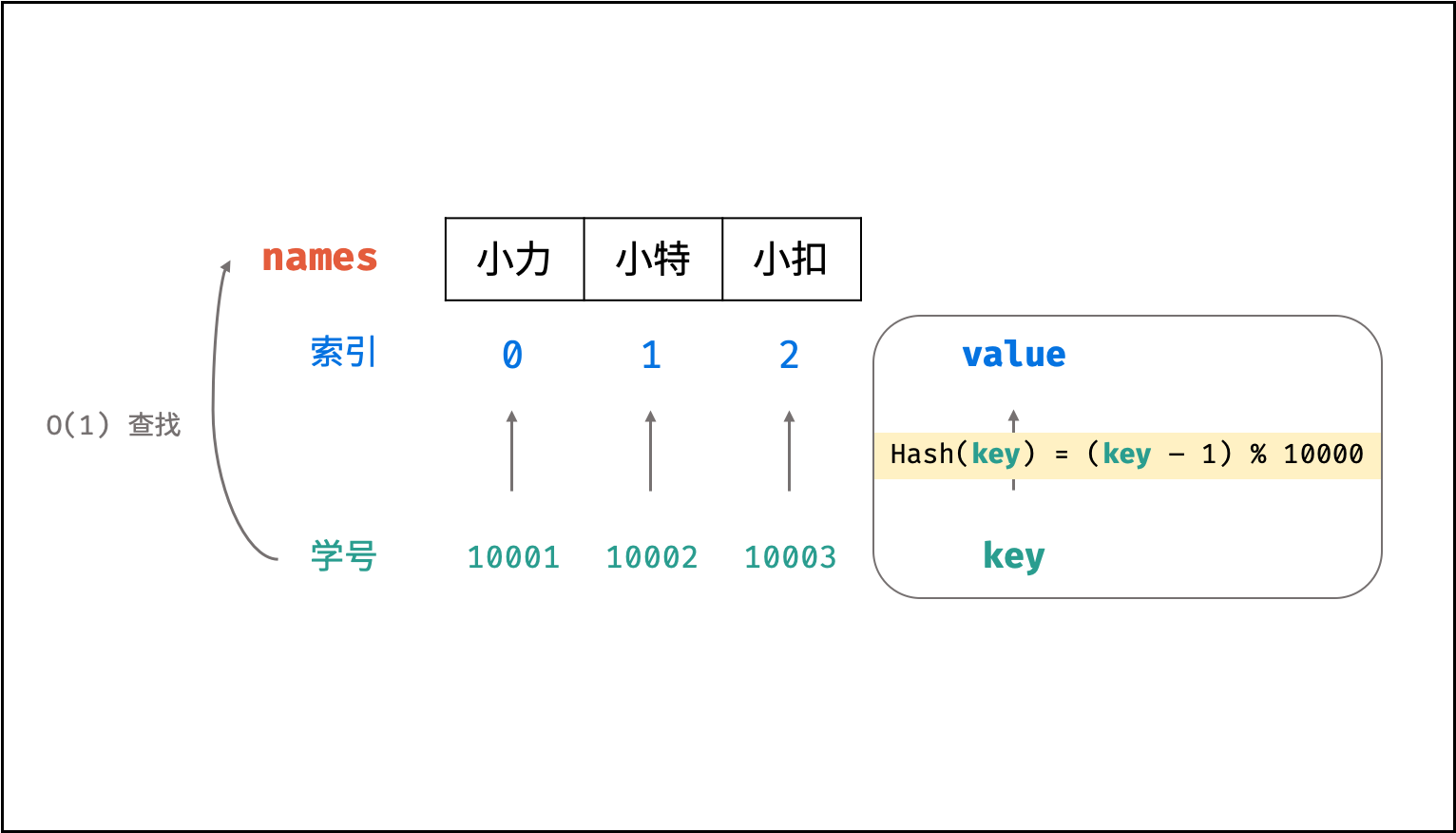{:width=550}
+
+以上设计只适用于此示例,实际的 Hash 函数需保证低碰撞率、 高鲁棒性等,以适用于各类数据和场景。
+
+---
+
+## 堆:
+
+堆是一种基于「完全二叉树」的数据结构,可使用数组实现。以堆为原理的排序算法称为「堆排序」,基于堆实现的数据结构为「优先队列」。堆分为「大顶堆」和「小顶堆」,大(小)顶堆:任意节点的值不大于(小于)其父节点的值。
+
+> **完全二叉树定义:** 设二叉树深度为 $k$ ,若二叉树除第 $k$ 层外的其它各层(第 $1$ 至 $k-1$ 层)的节点达到最大个数,且处于第 $k$ 层的节点都连续集中在最左边,则称此二叉树为完全二叉树。
+
+如下图所示,为包含 `1, 4, 2, 6, 8` 元素的小顶堆。将堆(完全二叉树)中的结点按层编号,即可映射到右边的数组存储形式。
+
+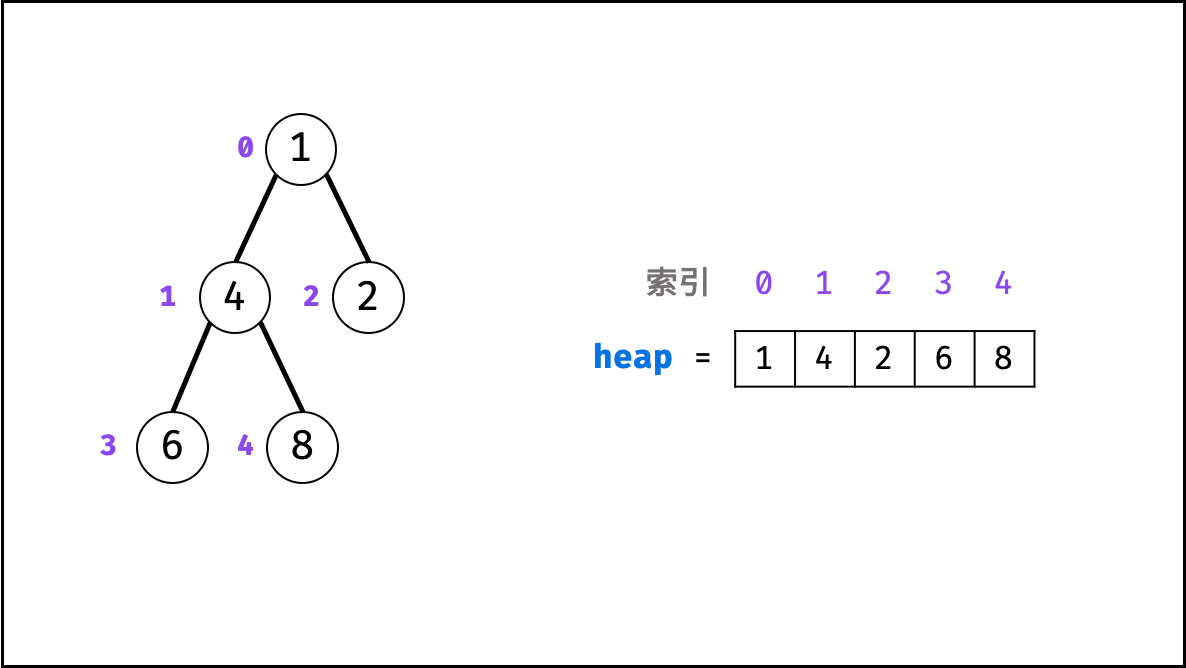{:width=550}
+
+通过使用「优先队列」的「压入 `push()`」和「弹出 `pop()`」操作,即可完成堆排序,实现代码如下:
+
+```Java []
+// 初始化小顶堆
+Queue heap = new PriorityQueue<>();
+
+// 元素入堆
+heap.add(1);
+heap.add(4);
+heap.add(2);
+heap.add(6);
+heap.add(8);
+
+// 元素出堆(从小到大)
+heap.poll(); // -> 1
+heap.poll(); // -> 2
+heap.poll(); // -> 4
+heap.poll(); // -> 6
+heap.poll(); // -> 8
+```
+
+```Python []
+from heapq import heappush, heappop
+
+# 初始化小顶堆
+heap = []
+
+# 元素入堆
+heappush(heap, 1)
+heappush(heap, 4)
+heappush(heap, 2)
+heappush(heap, 6)
+heappush(heap, 8)
+
+# 元素出堆(从小到大)
+heappop(heap) # -> 1
+heappop(heap) # -> 2
+heappop(heap) # -> 4
+heappop(heap) # -> 6
+heappop(heap) # -> 8
+```
+
+```C++ []
+// 初始化小顶堆
+priority_queue, greater> heap;
+
+// 元素入堆
+heap.push(1);
+heap.push(4);
+heap.push(2);
+heap.push(6);
+heap.push(8);
+
+// 元素出堆(从小到大)
+heap.pop(); // -> 1
+heap.pop(); // -> 2
+heap.pop(); // -> 4
+heap.pop(); // -> 6
+heap.pop(); // -> 8
+```
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 1.2 \347\256\227\346\263\225\345\244\215\346\235\202\345\272\246.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 1.2 \347\256\227\346\263\225\345\244\215\346\235\202\345\272\246.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..8e3bc55
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 1.2 \347\256\227\346\263\225\345\244\215\346\235\202\345\272\246.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
+# 算法复杂度
+
+算法复杂度旨在计算在输入数据量 $N$ 的情况下,算法的「时间使用」和「空间使用」情况;体现算法运行使用的时间和空间随「数据大小 $N$ 」而增大的速度。
+
+算法复杂度主要可从 **时间** 、**空间** 两个角度评价:
+
+- **时间:** 假设各操作的运行时间为固定常数,统计算法运行的「计算操作的数量」 ,以代表算法运行所需时间;
+- **空间:** 统计在最差情况下,算法运行所需使用的「最大空间」;
+
+「输入数据大小 $N$ 」指算法处理的输入数据量;根据不同算法,具有不同定义,例如:
+
+- **排序算法:** $N$ 代表需要排序的元素数量;
+- **搜索算法:** $N$ 代表搜索范围的元素总数,例如数组大小、矩阵大小、二叉树节点数、图节点和边数等;
+
+接下来,我们将分别从概念定义、符号表示、常见种类、时空权衡、示例解析、示例题目等角度入手,学习「时间复杂度」和「空间复杂度」。
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 1.3 \346\227\266\351\227\264\345\244\215\346\235\202\345\272\246.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 1.3 \346\227\266\351\227\264\345\244\215\346\235\202\345\272\246.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..fd3a46f
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 1.3 \346\227\266\351\227\264\345\244\215\346\235\202\345\272\246.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,514 @@
+# 时间复杂度
+
+根据定义,时间复杂度指输入数据大小为 $N$ 时,算法运行所需花费的时间。需要注意:
+
+- 统计的是算法的「计算操作数量」,而不是「运行的绝对时间」。计算操作数量和运行绝对时间呈正相关关系,并不相等。算法运行时间受到「编程语言 、计算机处理器速度、运行环境」等多种因素影响。例如,同样的算法使用 Python 或 C++ 实现、使用 CPU 或 GPU 、使用本地 IDE 或力扣平台提交,运行时间都不同。
+- 体现的是计算操作随数据大小 $N$ 变化时的变化情况。假设算法运行总共需要「 $1$ 次操作」、「 $100$ 次操作」,此两情况的时间复杂度都为常数级 $O(1)$ ;需要「 $N$ 次操作」、「 $100N$ 次操作」的时间复杂度都为 $O(N)$ 。
+
+---
+
+## 符号表示
+
+根据输入数据的特点,时间复杂度具有「最差」、「平均」、「最佳」三种情况,分别使用 $O$ , $\Theta$ , $\Omega$ 三种符号表示。以下借助一个查找算法的示例题目帮助理解。
+
+> **题目:** 输入长度为 $N$ 的整数数组 `nums` ,判断此数组中是否有数字 $7$ ,若有则返回 `true` ,否则返回 $\text{false}$ 。
+>
+> **解题算法:** 线性查找,即遍历整个数组,遇到 $7$ 则返回 `true` 。
+>
+> **代码:**
+>
+> ```Python []
+> def find_seven(nums):
+> for num in nums:
+> if num == 7:
+> return True
+> return False
+> ```
+>
+> ```Java []
+> boolean findSeven(int[] nums) {
+> for (int num : nums) {
+> if (num == 7)
+> return true;
+> }
+> return false;
+> }
+> ```
+>
+> ```C++ []
+> bool findSeven(vector& nums) {
+> for (int num : nums) {
+> if (num == 7)
+> return true;
+> }
+> return false;
+> }
+> ```
+
+- **最佳情况 $\Omega(1)$ :** `nums = [7, a, b, c, ...]` ,即当数组首个数字为 $7$ 时,无论 `nums` 有多少元素,线性查找的循环次数都为 $1$ 次;
+- **最差情况 $O(N)$ :** `nums = [a, b, c, ...]` 且 `nums` 中所有数字都不为 $7$ ,此时线性查找会遍历整个数组,循环 $N$ 次;
+- **平均情况 $\Theta$ :** 需要考虑输入数据的分布情况,计算所有数据情况下的平均时间复杂度;例如本题目,需要考虑数组长度、数组元素的取值范围等;
+
+> 大 $O$ 是最常使用的时间复杂度评价渐进符号,下文示例与本 LeetBook 题目解析皆使用 $O$ 。
+
+---
+
+## 常见种类
+
+根据从小到大排列,常见的算法时间复杂度主要有:
+
+$$
+O(1) < O(\log N) < O(N) < O(N\log N) < O(N^2) < O(2^N) < O(N!)
+$$
+
+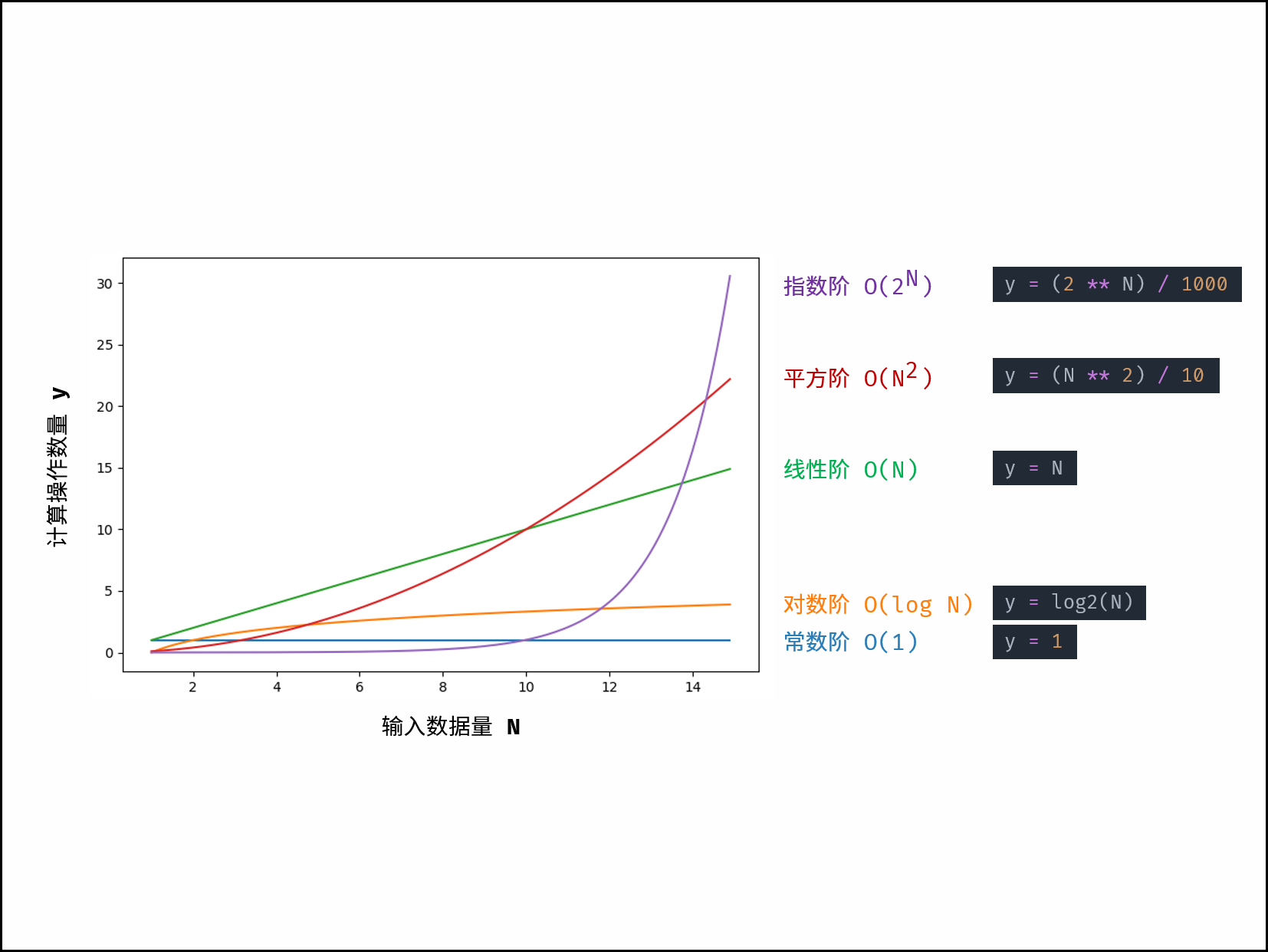
+
+对于以下所有示例,设输入数据大小为 $N$ ,计算操作数量为 $count$ 。图中每个「**蓝色方块**」代表一个单元计算操作。
+
+### 常数 $O(1)$ :
+
+运行次数与 $N$ 大小呈常数关系,即不随输入数据大小 $N$ 的变化而变化。
+
+```Python []
+def algorithm(N):
+ a = 1
+ b = 2
+ x = a * b + N
+ return 1
+```
+
+```Java []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ int a = 1;
+ int b = 2;
+ int x = a * b + N;
+ return 1;
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ int a = 1;
+ int b = 2;
+ int x = a * b + N;
+ return 1;
+}
+```
+
+对于以下代码,无论 $a$ 取多大,都与输入数据大小 $N$ 无关,因此时间复杂度仍为 $O(1)$ 。
+
+```Python []
+def algorithm(N):
+ count = 0
+ a = 10000
+ for i in range(a):
+ count += 1
+ return count
+```
+
+```Java []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ int count = 0;
+ int a = 10000;
+ for (int i = 0; i < a; i++) {
+ count++;
+ }
+ return count;
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ int count = 0;
+ int a = 10000;
+ for (int i = 0; i < a; i++) {
+ count++;
+ }
+ return count;
+}
+```
+
+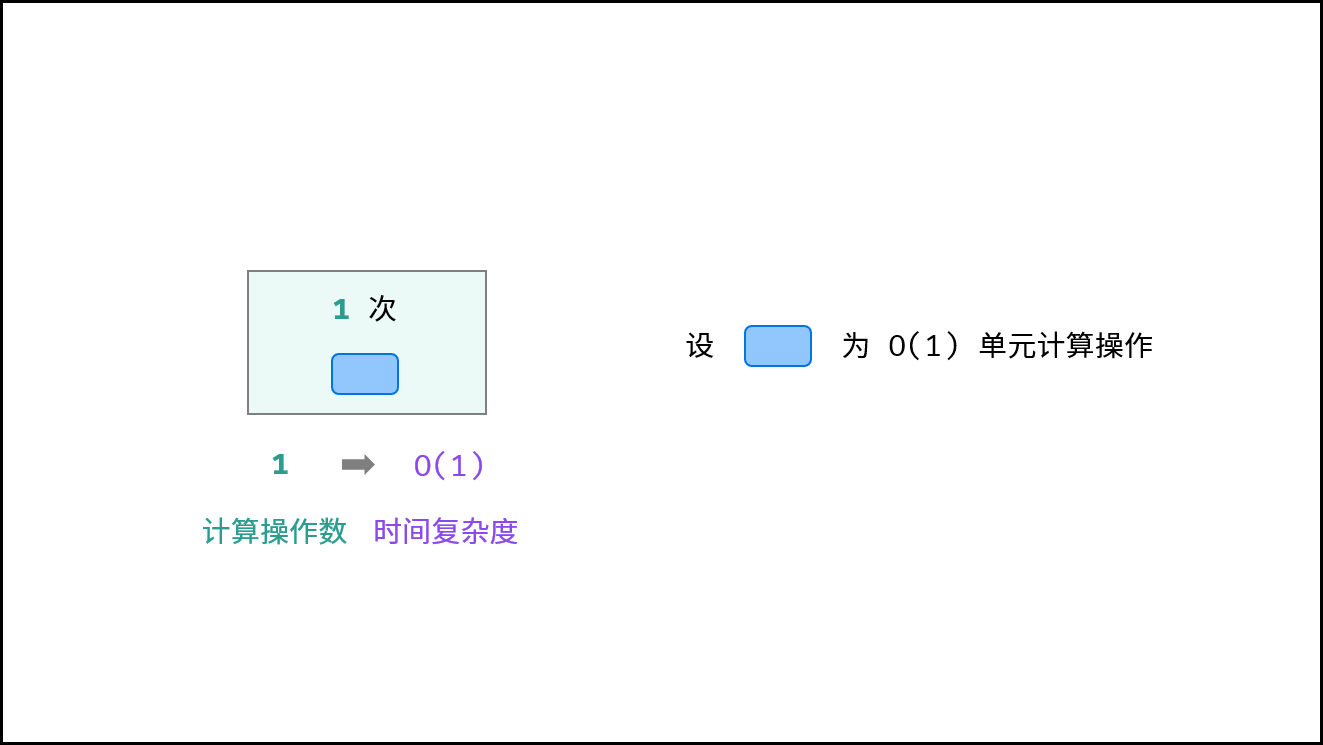{:width=500}
+
+### 线性 $O(N)$ :
+
+循环运行次数与 $N$ 大小呈线性关系,时间复杂度为 $O(N)$ 。
+
+```Python []
+def algorithm(N):
+ count = 0
+ for i in range(N):
+ count += 1
+ return count
+```
+
+```Java []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ int count = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
+ count++;
+ return count;
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ int count = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
+ count++;
+ return count;
+}
+```
+
+对于以下代码,虽然是两层循环,但第二层与 $N$ 大小无关,因此整体仍与 $N$ 呈线性关系。
+
+```Python []
+def algorithm(N):
+ count = 0
+ a = 10000
+ for i in range(N):
+ for j in range(a):
+ count += 1
+ return count
+```
+
+```Java []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ int count = 0;
+ int a = 10000;
+ for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < a; j++) {
+ count++;
+ }
+ }
+ return count;
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ int count = 0;
+ int a = 10000;
+ for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < a; j++) {
+ count++;
+ }
+ }
+ return count;
+}
+```
+
+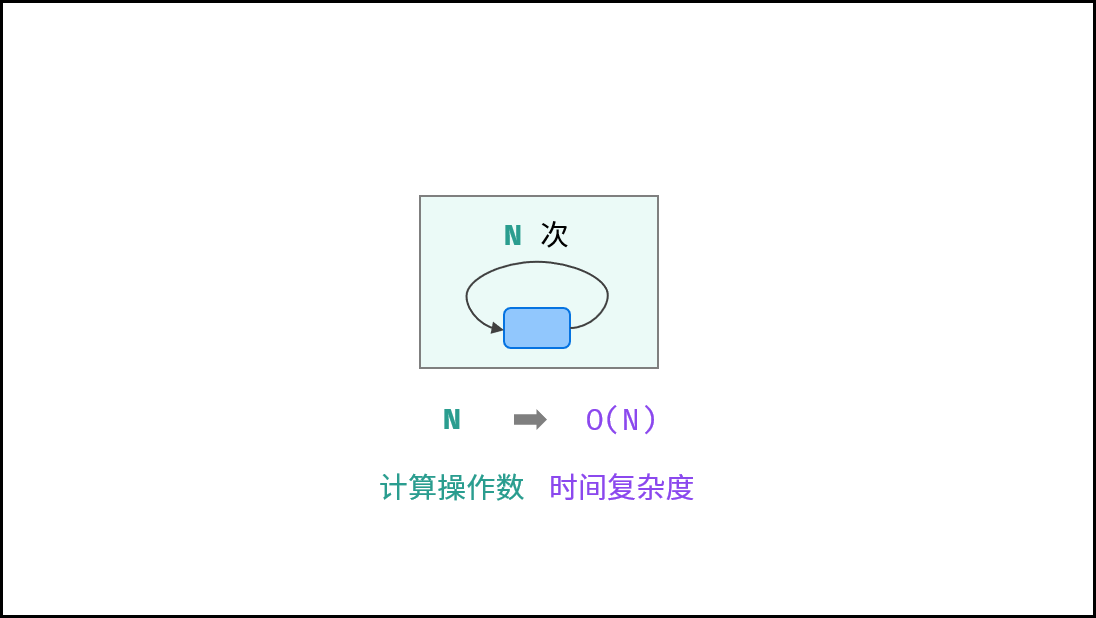{:width=500}
+
+### 平方 $O(N^2)$ :
+
+两层循环相互独立,都与 $N$ 呈线性关系,因此总体与 $N$ 呈平方关系,时间复杂度为 $O(N^2)$ 。
+
+```Python []
+def algorithm(N):
+ count = 0
+ for i in range(N):
+ for j in range(N):
+ count += 1
+ return count
+```
+
+```Java []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ int count = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
+ count++;
+ }
+ }
+ return count;
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ int count = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
+ count++;
+ }
+ }
+ return count;
+}
+```
+
+以「冒泡排序」为例,其包含两层独立循环:
+
+1. 第一层复杂度为 $O(N)$ ;
+2. 第二层平均循环次数为 $\frac{N}{2}$ ,复杂度为 $O(N)$ ,推导过程如下:
+
+$$
+O(\frac{N}{2}) = O(\frac{1}{2})O(N) = O(1)O(N) = O(N)
+$$
+
+因此,冒泡排序的总体时间复杂度为 $O(N^2)$ ,代码如下所示。
+
+```Python []
+def bubble_sort(nums):
+ N = len(nums)
+ for i in range(N - 1):
+ for j in range(N - 1 - i):
+ if nums[j] > nums[j + 1]:
+ nums[j], nums[j + 1] = nums[j + 1], nums[j]
+ return nums
+```
+
+```Java []
+int[] bubbleSort(int[] nums) {
+ int N = nums.length;
+ for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < N - 1 - i; j++) {
+ if (nums[j] > nums[j + 1]) {
+ int tmp = nums[j];
+ nums[j] = nums[j + 1];
+ nums[j + 1] = tmp;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return nums;
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+vector bubbleSort(vector& nums) {
+ int N = nums.size();
+ for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < N - 1 - i; j++) {
+ if (nums[j] > nums[j + 1]) {
+ swap(nums[j], nums[j + 1]);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return nums;
+}
+```
+
+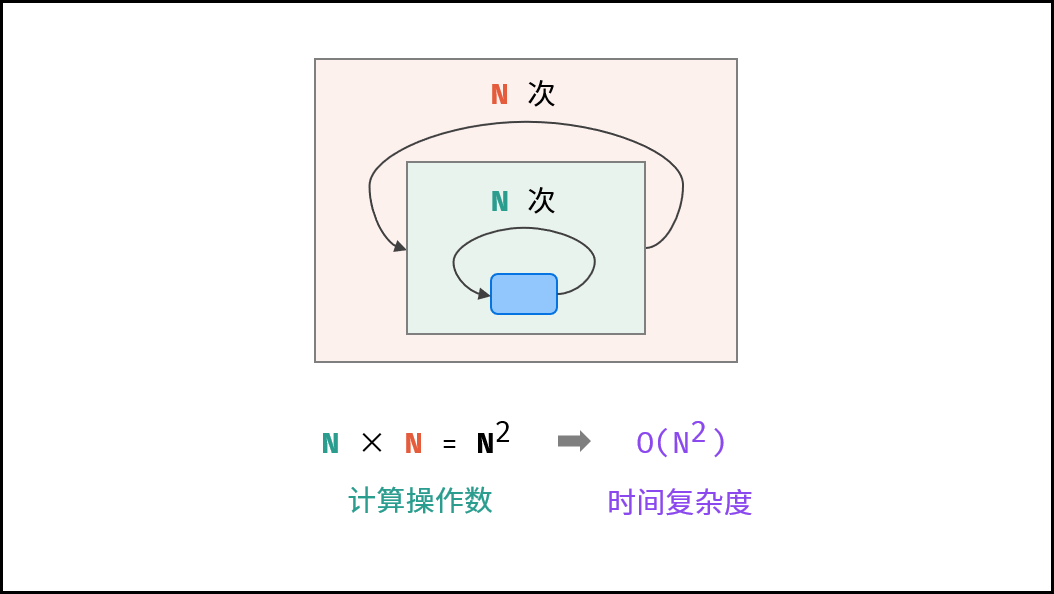{:width=450}
+
+### 指数 $O(2^N)$ :
+
+生物学科中的 “细胞分裂” 即是指数级增长。初始状态为 $1$ 个细胞,分裂一轮后为 $2$ 个,分裂两轮后为 $4$ 个,……,分裂 $N$ 轮后有 $2^N$ 个细胞。
+
+算法中,指数阶常出现于递归,算法原理图与代码如下所示。
+
+```Python []
+def algorithm(N):
+ if N <= 0: return 1
+ count_1 = algorithm(N - 1)
+ count_2 = algorithm(N - 1)
+ return count_1 + count_2
+```
+
+```Java []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ if (N <= 0) return 1;
+ int count_1 = algorithm(N - 1);
+ int count_2 = algorithm(N - 1);
+ return count_1 + count_2;
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ if (N <= 0) return 1;
+ int count_1 = algorithm(N - 1);
+ int count_2 = algorithm(N - 1);
+ return count_1 + count_2;
+}
+```
+
+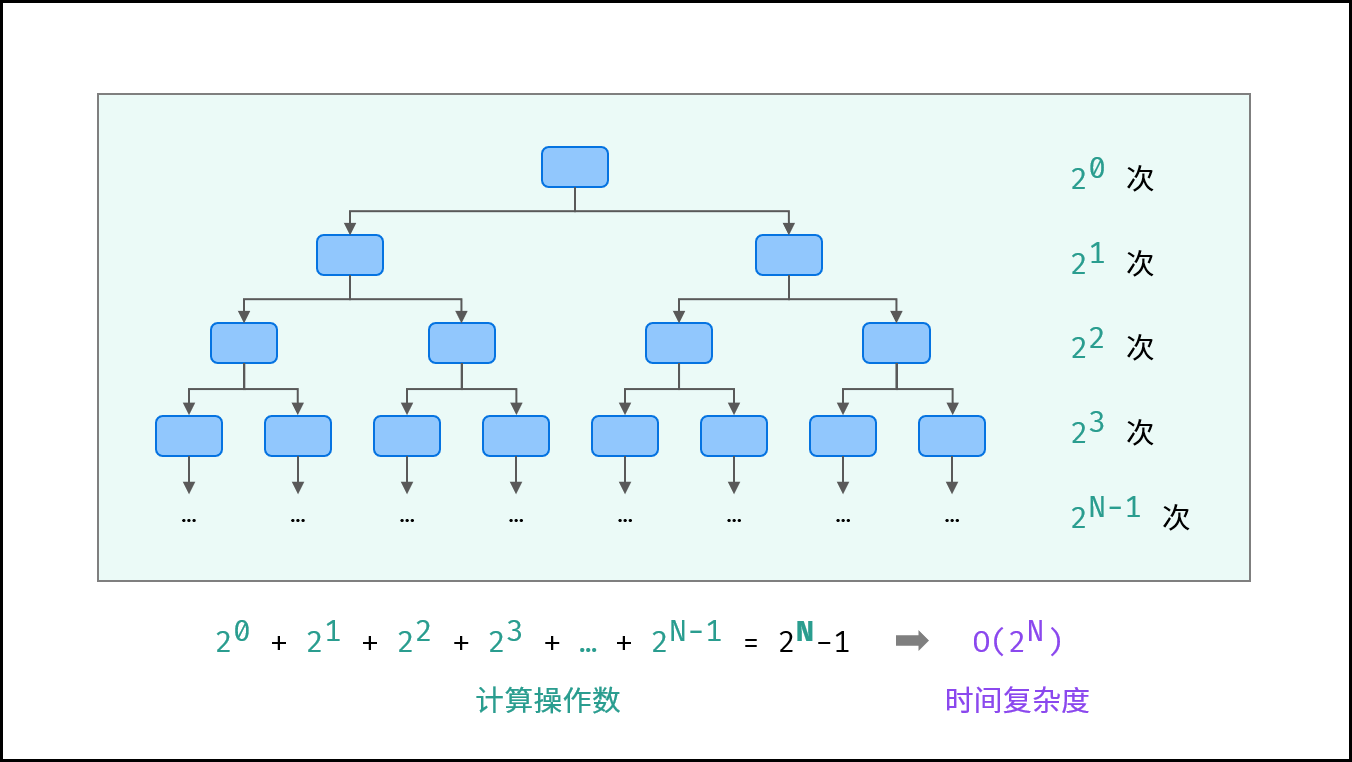{:width=600}
+
+### 阶乘 $O(N!)$ :
+
+阶乘阶对应数学上常见的 “全排列” 。即给定 $N$ 个互不重复的元素,求其所有可能的排列方案,则方案数量为:
+
+$$
+N \times (N - 1) \times (N - 2) \times \cdots \times 2 \times 1 = N!
+$$
+
+如下图与代码所示,阶乘常使用递归实现,算法原理:第一层分裂出 $N$ 个,第二层分裂出 $N - 1$ 个,…… ,直至到第 $N$ 层时终止并回溯。
+
+```Python []
+def algorithm(N):
+ if N <= 0: return 1
+ count = 0
+ for _ in range(N):
+ count += algorithm(N - 1)
+ return count
+```
+
+```Java []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ if (N <= 0) return 1;
+ int count = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
+ count += algorithm(N - 1);
+ }
+ return count;
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ if (N <= 0) return 1;
+ int count = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
+ count += algorithm(N - 1);
+ }
+ return count;
+}
+```
+
+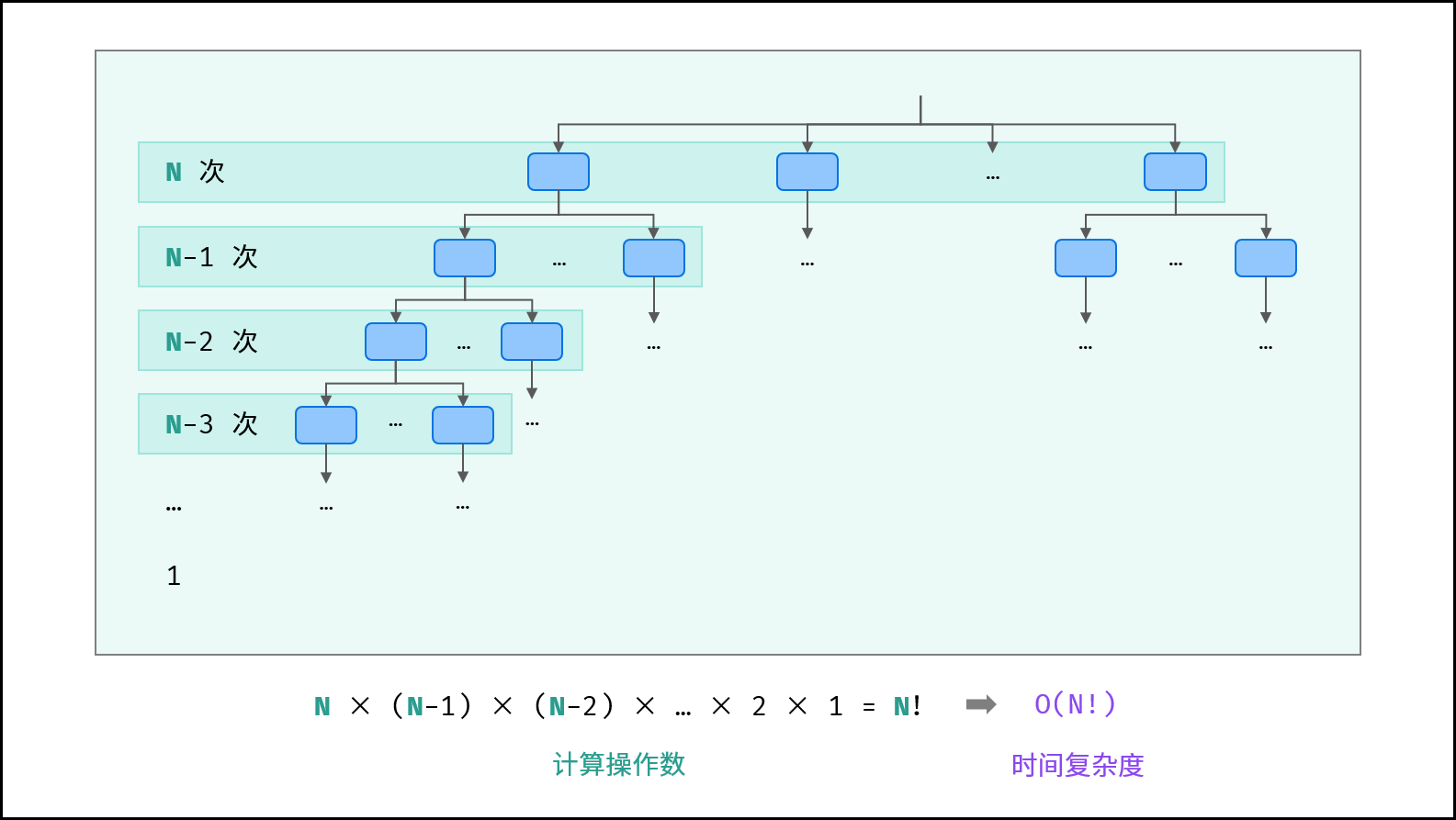{:width=600}
+
+### 对数 $O(\log N)$ :
+
+对数阶与指数阶相反,指数阶为 “每轮分裂出两倍的情况” ,而对数阶是 “每轮排除一半的情况” 。对数阶常出现于「二分法」、「分治」等算法中,体现着 “一分为二” 或 “一分为多” 的算法思想。
+
+设循环次数为 $m$ ,则输入数据大小 $N$ 与 $2 ^ m$ 呈线性关系,两边同时取 $log_2$ 对数,则得到循环次数 $m$ 与 $\log_2 N$ 呈线性关系,即时间复杂度为 $O(\log N)$ 。
+
+```Python []
+def algorithm(N):
+ count = 0
+ i = N
+ while i > 1:
+ i = i / 2
+ count += 1
+ return count
+```
+
+```Java []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ int count = 0;
+ float i = N;
+ while (i > 1) {
+ i = i / 2;
+ count++;
+ }
+ return count;
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ int count = 0;
+ float i = N;
+ while (i > 1) {
+ i = i / 2;
+ count++;
+ }
+ return count;
+}
+```
+
+如以下代码所示,对于不同 $a$ 的取值,循环次数 $m$ 与 $\log_a N$ 呈线性关系 ,时间复杂度为 $O(\log_a N)$ 。而无论底数 $a$ 取值,时间复杂度都可记作 $O(\log N)$ ,根据对数换底公式的推导如下:
+
+$$
+O(\log_a N) = \frac{O(\log_2 N)}{O(\log_2 a)} = O(\log N)
+$$
+
+```Python []
+def algorithm(N):
+ count = 0
+ i = N
+ a = 3
+ while i > 1:
+ i = i / a
+ count += 1
+ return count
+```
+
+```Java []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ int count = 0;
+ float i = N;
+ int a = 3;
+ while (i > 1) {
+ i = i / a;
+ count++;
+ }
+ return count;
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ int count = 0;
+ float i = N;
+ int a = 3;
+ while (i > 1) {
+ i = i / a;
+ count++;
+ }
+ return count;
+}
+```
+
+> 如下图所示,为二分查找的时间复杂度示意图,每次二分将搜索区间缩小一半。
+
+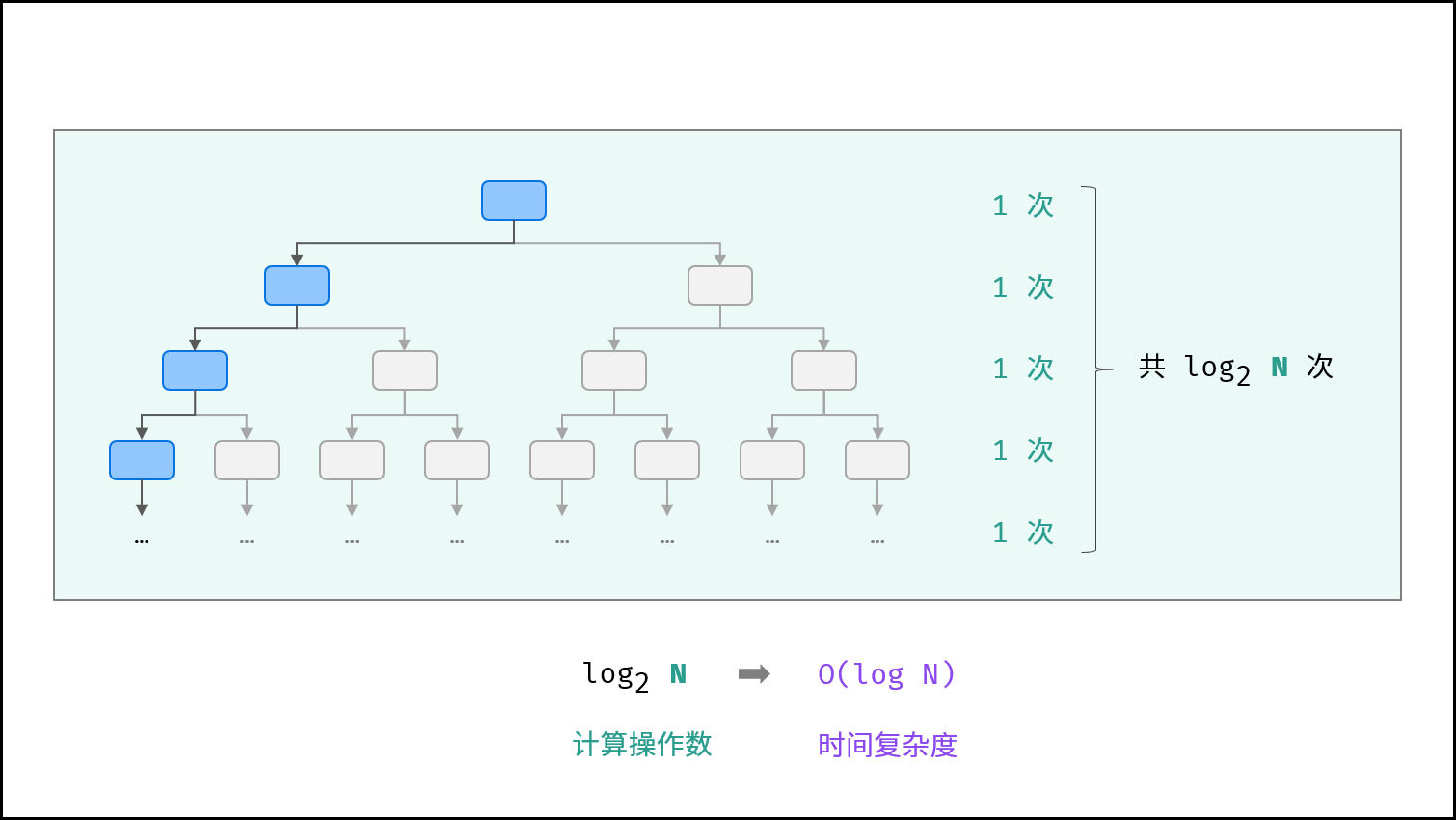{:width=600}
+
+### 线性对数 $O(N \log N)$ :
+
+两层循环相互独立,第一层和第二层时间复杂度分别为 $O(\log N)$ 和 $O(N)$ ,则总体时间复杂度为 $O(N \log N)$ ;
+
+```Python []
+def algorithm(N):
+ count = 0
+ i = N
+ while i > 1:
+ i = i / 2
+ for j in range(N):
+ count += 1
+```
+
+```Java []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ int count = 0;
+ float i = N;
+ while (i > 1) {
+ i = i / 2;
+ for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
+ count++;
+ }
+ return count;
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ int count = 0;
+ float i = N;
+ while (i > 1) {
+ i = i / 2;
+ for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
+ count++;
+ }
+ return count;
+}
+```
+
+线性对数阶常出现于排序算法,例如「快速排序」、「归并排序」、「堆排序」等,其时间复杂度原理如下图所示。
+
+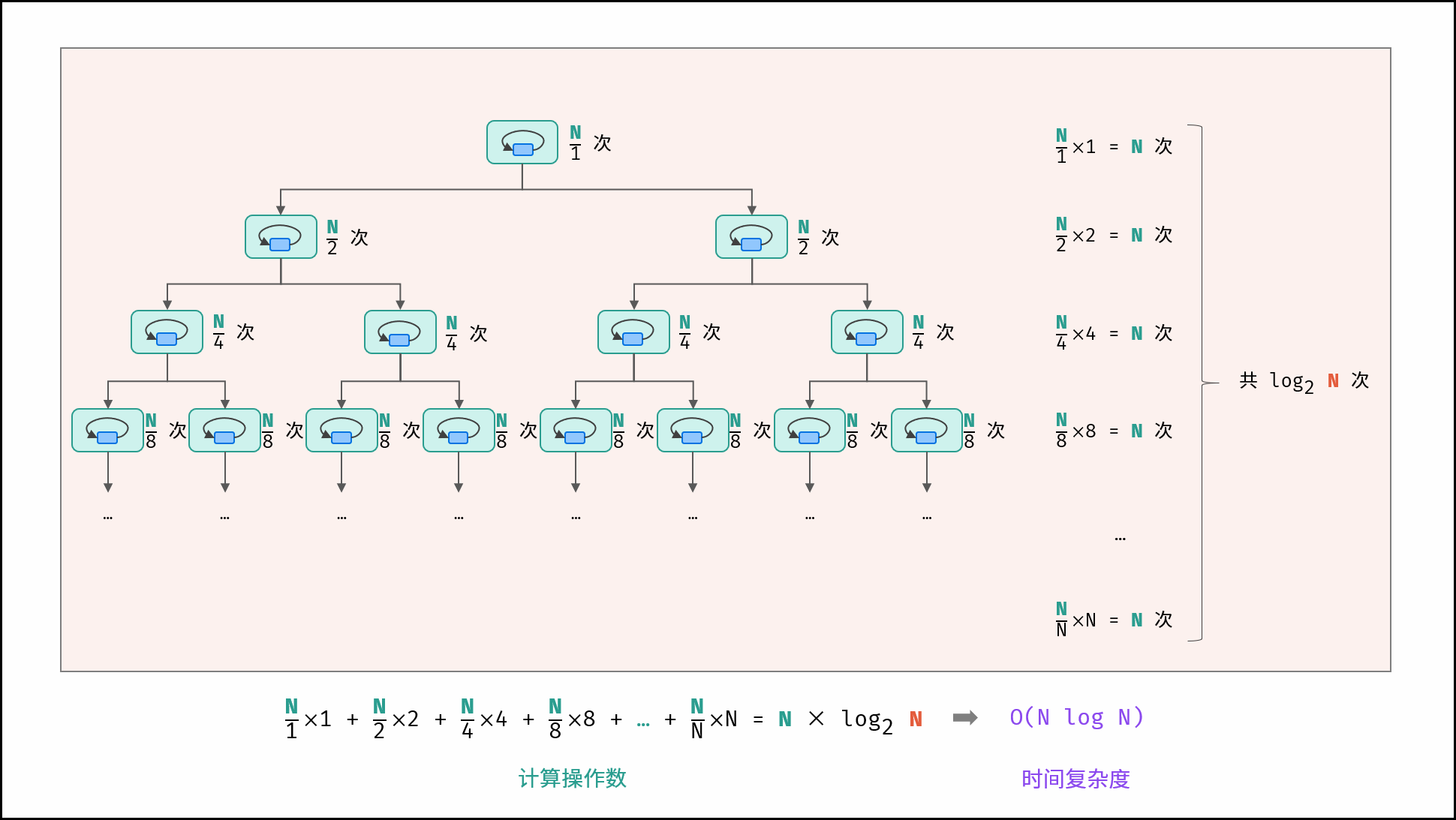
+
+---
+
+## 示例题目
+
+以下列举本 LeetBook 中各时间复杂度的对应示例题解,以帮助加深理解。
+
+| 时间复杂度 | 示例题解 |
+| ------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| $O(1)$ | [砍竹子 I](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vyva2/)、[文物朝代判断](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/572x9r/) |
+| $O(\log N)$ | [Pow(x, n)](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57p2pv/)、[统计目标成绩的出现次数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58lgr7/) |
+| $O(N)$ | [训练计划 III](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9p7s17/)、[斐波那契数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50fji7/) |
+| $O(N \log N)$ | [破解闯关密码](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/59ceyt/)、[交易逆序对的总数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/o53yjd/) |
+| $O(N^2)$ | [验证二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vwbf6/)、[招式拆解 I](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dz9di/) |
+| $O(N!)$ | [套餐内商品的排列顺序](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50hah3/) |
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 1.4 \347\251\272\351\227\264\345\244\215\346\235\202\345\272\246.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 1.4 \347\251\272\351\227\264\345\244\215\346\235\202\345\272\246.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..646ae0a
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 1.4 \347\251\272\351\227\264\345\244\215\346\235\202\345\272\246.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,547 @@
+# 空间复杂度
+
+空间复杂度涉及的空间类型有:
+
+- **输入空间:** 存储输入数据所需的空间大小;
+- **暂存空间:** 算法运行过程中,存储所有中间变量和对象等数据所需的空间大小;
+- **输出空间:** 算法运行返回时,存储输出数据所需的空间大小;
+
+通常情况下,空间复杂度指在输入数据大小为 $N$ 时,算法运行所使用的「暂存空间」+「输出空间」的总体大小。
+
+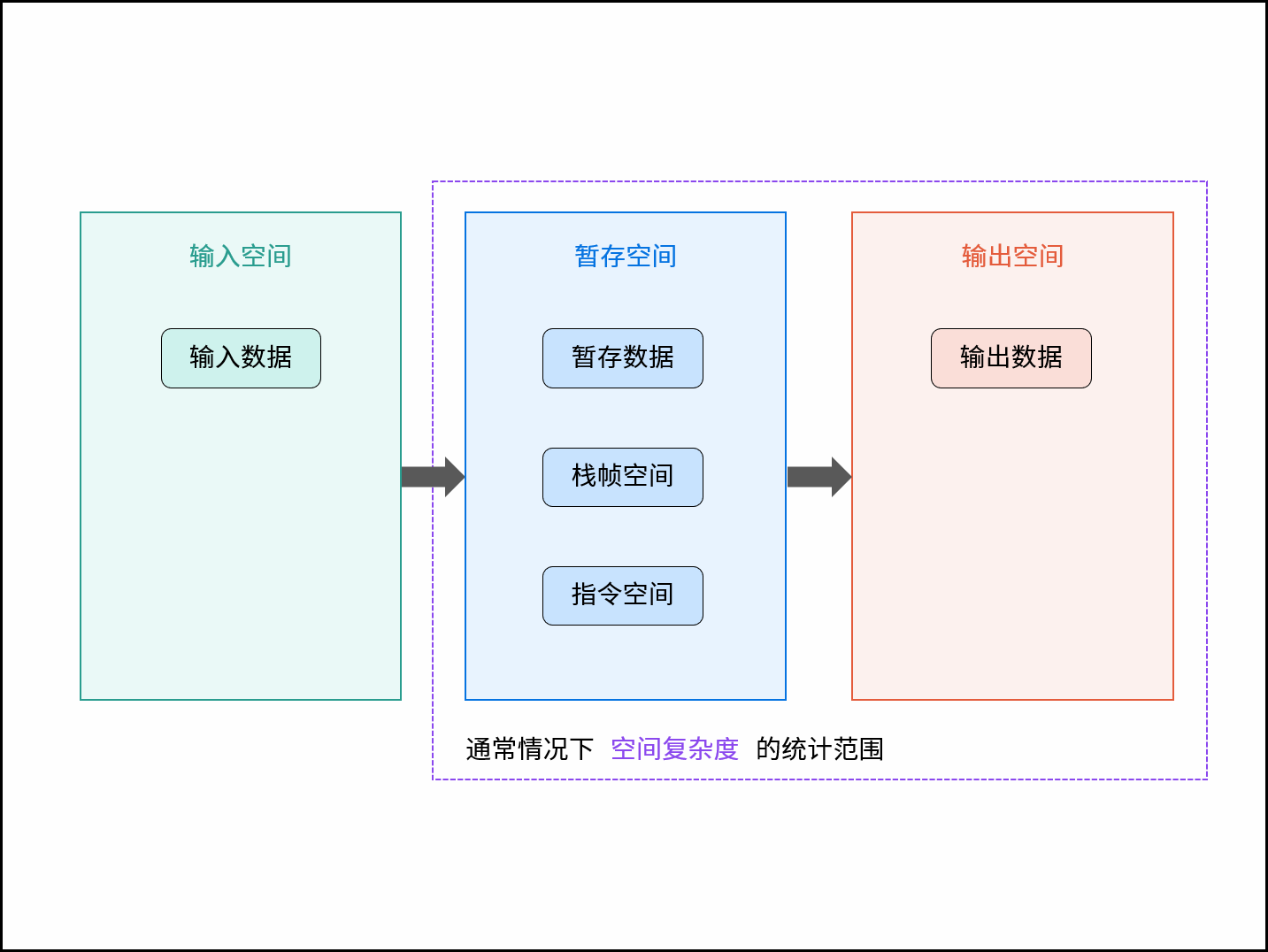{:width=500}
+
+而根据不同来源,算法使用的内存空间分为三类:
+
+**指令空间:**
+
+编译后,程序指令所使用的内存空间。
+
+**数据空间:**
+
+算法中的各项变量使用的空间,包括:声明的常量、变量、动态数组、动态对象等使用的内存空间。
+
+```Python []
+class Node:
+ def __init__(self, val):
+ self.val = val
+ self.next = None
+
+def algorithm(N):
+ num = N # 变量
+ nums = [0] * N # 动态数组
+ node = Node(N) # 动态对象
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Node {
+ int val;
+ Node next;
+ Node(int x) { val = x; }
+}
+
+void algorithm(int N) {
+ int num = N; // 变量
+ int[] nums = new int[N]; // 动态数组
+ Node node = new Node(N); // 动态对象
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+struct Node {
+ int val;
+ Node *next;
+ Node(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
+};
+
+void algorithm(int N) {
+ int num = N; // 变量
+ int nums[N]; // 动态数组
+ Node* node = new Node(N); // 动态对象
+}
+```
+
+**栈帧空间:**
+
+程序调用函数是基于栈实现的,函数在调用期间,占用常量大小的栈帧空间,直至返回后释放。如以下代码所示,在循环中调用函数,每轮调用 `test()` 返回后,栈帧空间已被释放,因此空间复杂度仍为 $O(1)$ 。
+
+```Python []
+def test():
+ return 0
+
+def algorithm(N):
+ for _ in range(N):
+ test()
+```
+
+```Java []
+int test() {
+ return 0;
+}
+
+void algorithm(int N) {
+ for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
+ test();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int test() {
+ return 0;
+}
+
+void algorithm(int N) {
+ for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
+ test();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+算法中,栈帧空间的累计常出现于递归调用。如以下代码所示,通过递归调用,会同时存在 $N$ 个未返回的函数 `algorithm()` ,此时累计使用 $O(N)$ 大小的栈帧空间。
+
+```Python []
+def algorithm(N):
+ if N <= 1: return 1
+ return algorithm(N - 1) + 1
+```
+
+```Java []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ if (N <= 1) return 1;
+ return algorithm(N - 1) + 1;
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ if (N <= 1) return 1;
+ return algorithm(N - 1) + 1;
+}
+```
+
+---
+
+## 符号表示
+
+通常情况下,空间复杂度统计算法在 “最差情况” 下使用的空间大小,以体现算法运行所需预留的空间量,使用符号 $O$ 表示。
+
+最差情况有两层含义,分别为「最差输入数据」、算法运行中的「最差运行点」。例如以下代码:
+
+> 输入整数 $N$ ,取值范围 $N \geq 1$ ;
+
+- **最差输入数据:** 当 $N \leq 10$ 时,数组 `nums` 的长度恒定为 10 ,空间复杂度为 $O(10) = O(1)$ ;当 $N > 10$ 时,数组 $nums$ 长度为 $N$ ,空间复杂度为 $O(N)$ ;因此,空间复杂度应为最差输入数据情况下的 $O(N)$ 。
+- **最差运行点:** 在执行 `nums = [0] * 10` 时,算法仅使用 $O(1)$ 大小的空间;而当执行 `nums = [0] * N` 时,算法使用 $O(N)$ 的空间;因此,空间复杂度应为最差运行点的 $O(N)$ 。
+
+```Python []
+def algorithm(N):
+ num = 5 # O(1)
+ nums = [0] * 10 # O(1)
+ if N > 10:
+ nums = [0] * N # O(N)
+```
+
+```Java []
+void algorithm(int N) {
+ int num = 5; // O(1)
+ int[] nums = new int[10]; // O(1)
+ if (N > 10) {
+ nums = new int[N]; // O(N)
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+void algorithm(int N) {
+ int num = 5; // O(1)
+ vector nums(10); // O(1)
+ if (N > 10) {
+ nums.resize(N); // O(N)
+ }
+}
+```
+
+---
+
+## 常见种类
+
+根据从小到大排列,常见的算法空间复杂度有:
+
+$$
+O(1) < O(\log N) < O(N) < O(N^2) < O(2^N)
+$$
+
+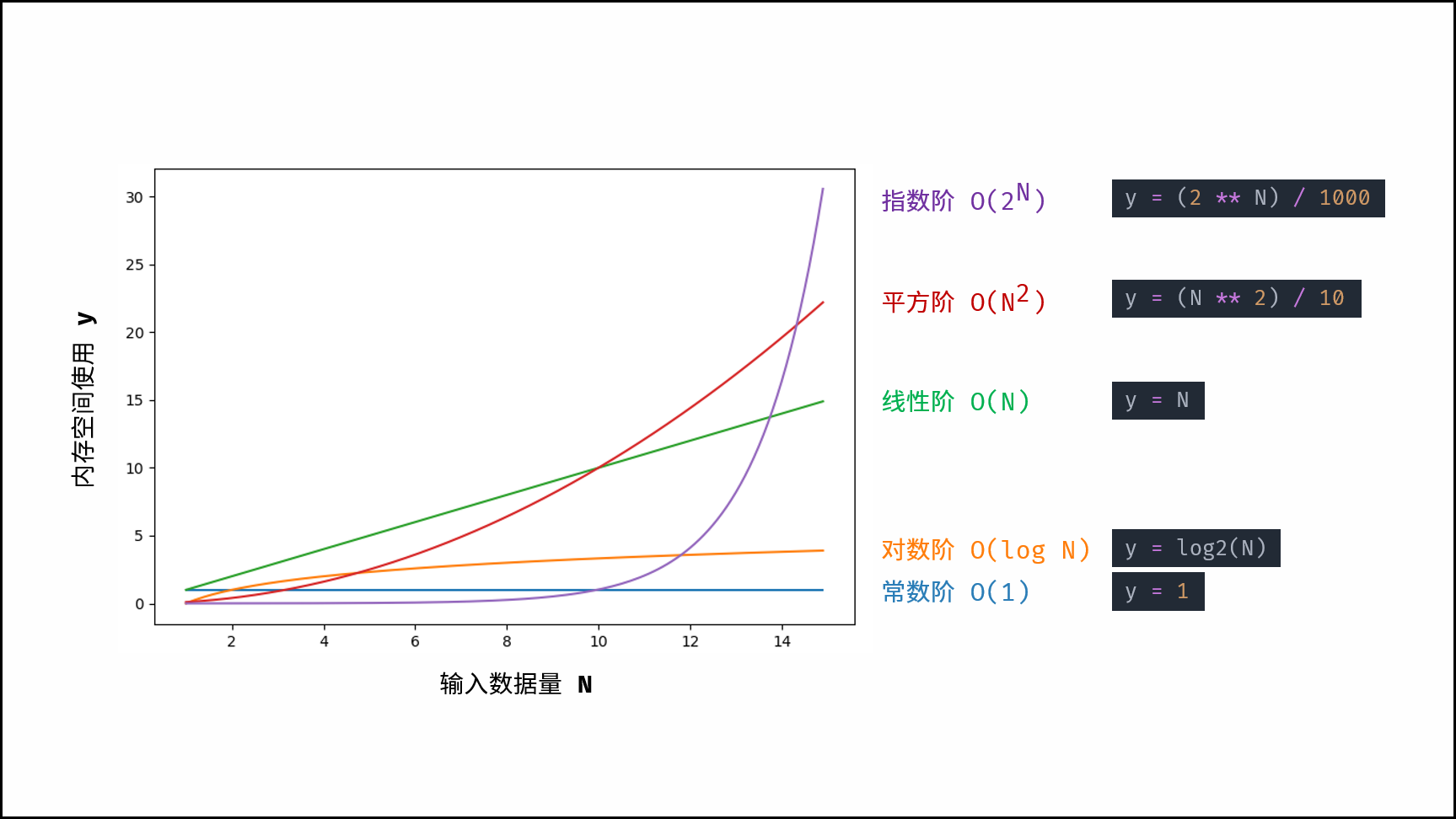
+
+对于以下所有示例,设输入数据大小为正整数 $N$ ,节点类 `Node` 、函数 `test()` 如以下代码所示。
+
+```Python []
+# 节点类 Node
+class Node:
+ def __init__(self, val):
+ self.val = val
+ self.next = None
+
+# 函数 test()
+def test():
+ return 0
+```
+
+```Java []
+// 节点类 Node
+class Node {
+ int val; // 变量
+ Node next; // 动态数组
+ Node(int x) { val = x; } // 动态对象
+}
+
+// 函数 test()
+int test() {
+ return 0;
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+// 节点类 Node
+struct Node {
+ int val;
+ Node *next;
+ Node(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
+};
+
+// 函数 test()
+int test() {
+ return 0;
+}
+```
+
+### 常数 $O(1)$ :
+
+普通常量、变量、对象、元素数量与输入数据大小 $N$ 无关的集合,皆使用常数大小的空间。
+
+```Python []
+def algorithm(N):
+ num = 0
+ nums = [0] * 10000
+ node = Node(0)
+ dic = { 0: '0' }
+```
+
+```Java []
+void algorithm(int N) {
+ int num = 0;
+ int[] nums = new int[10000];
+ Node node = new Node(0);
+ Map dic = new HashMap<>() {{ put(0, "0"); }};
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+void algorithm(int N) {
+ int num = 0;
+ int nums[10000];
+ Node* node = new Node(0);
+ unordered_map dic;
+ dic.emplace(0, "0");
+}
+```
+
+如以下代码所示,虽然函数 `test()` 调用了 $N$ 次,但每轮调用后 `test()` 已返回,无累计栈帧空间使用,因此空间复杂度仍为 $O(1)$ 。
+
+```Python []
+def algorithm(N):
+ for _ in range(N):
+ test()
+```
+
+```Java []
+void algorithm(int N) {
+ for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
+ test();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+void algorithm(int N) {
+ for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
+ test();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### 线性 $O(N)$ :
+
+元素数量与 $N$ 呈线性关系的任意类型集合(常见于一维数组、链表、哈希表等),皆使用线性大小的空间。
+
+```Python []
+def algorithm(N):
+ nums_1 = [0] * N
+ nums_2 = [0] * (N // 2)
+
+ nodes = [Node(i) for i in range(N)]
+
+ dic = {}
+ for i in range(N):
+ dic[i] = str(i)
+```
+
+```Java []
+void algorithm(int N) {
+ int[] nums_1 = new int[N];
+ int[] nums_2 = new int[N / 2];
+
+ List nodes = new ArrayList<>();
+ for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
+ nodes.add(new Node(i));
+ }
+
+ Map dic = new HashMap<>();
+ for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
+ dic.put(i, String.valueOf(i));
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+void algorithm(int N) {
+ int nums_1[N];
+ int nums_2[N / 2 + 1];
+
+ vector nodes;
+ for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
+ nodes.push_back(new Node(i));
+ }
+
+ unordered_map dic;
+ for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
+ dic.emplace(i, to_string(i));
+ }
+}
+```
+
+如下图与代码所示,此递归调用期间,会同时存在 $N$ 个未返回的 `algorithm()` 函数,因此使用 $O(N)$ 大小的栈帧空间。
+
+```Python []
+def algorithm(N):
+ if N <= 1: return 1
+ return algorithm(N - 1) + 1
+```
+
+```Java []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ if (N <= 1) return 1;
+ return algorithm(N - 1) + 1;
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ if (N <= 1) return 1;
+ return algorithm(N - 1) + 1;
+}
+```
+
+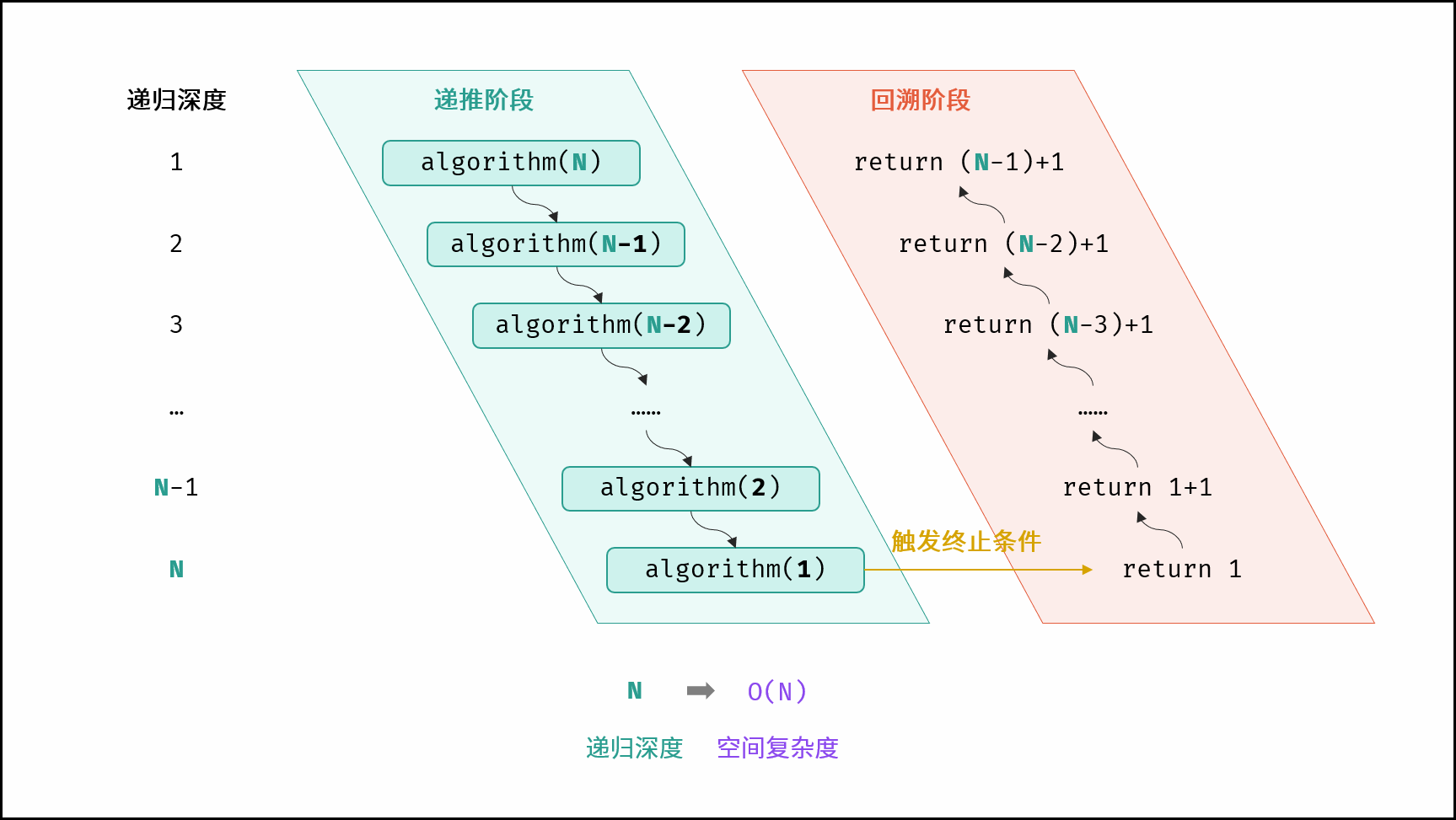
+
+### 平方 $O(N^2)$ :
+
+元素数量与 $N$ 呈平方关系的任意类型集合(常见于矩阵),皆使用平方大小的空间。
+
+```Python []
+def algorithm(N):
+ num_matrix = [[0 for j in range(N)] for i in range(N)]
+ node_matrix = [[Node(j) for j in range(N)] for i in range(N)]
+```
+
+```Java []
+void algorithm(int N) {
+ int num_matrix[][] = new int[N][N];
+
+ List> node_matrix = new ArrayList<>();
+ for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
+ List nodes = new ArrayList<>();
+ for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
+ nodes.add(new Node(j));
+ }
+ node_matrix.add(nodes);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+void algorithm(int N) {
+ vector> num_matrix;
+ for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
+ vector nums;
+ for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
+ nums.push_back(0);
+ }
+ num_matrix.push_back(nums);
+ }
+
+ vector> node_matrix;
+ for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
+ vector nodes;
+ for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
+ nodes.push_back(new Node(j));
+ }
+ node_matrix.push_back(nodes);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+如下图与代码所示,递归调用时同时存在 $N$ 个未返回的 `algorithm()` 函数,使用 $O(N)$ 栈帧空间;每层递归函数中声明了数组,平均长度为 $\frac{N}{2}$ ,使用 $O(N)$ 空间;因此总体空间复杂度为 $O(N^2)$ 。
+
+```Python []
+def algorithm(N):
+ if N <= 0: return 0
+ nums = [0] * N
+ return algorithm(N - 1)
+```
+
+```Java []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ if (N <= 0) return 0;
+ int[] nums = new int[N];
+ return algorithm(N - 1);
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int algorithm(int N) {
+ if (N <= 0) return 0;
+ int nums[N];
+ return algorithm(N - 1);
+}
+```
+
+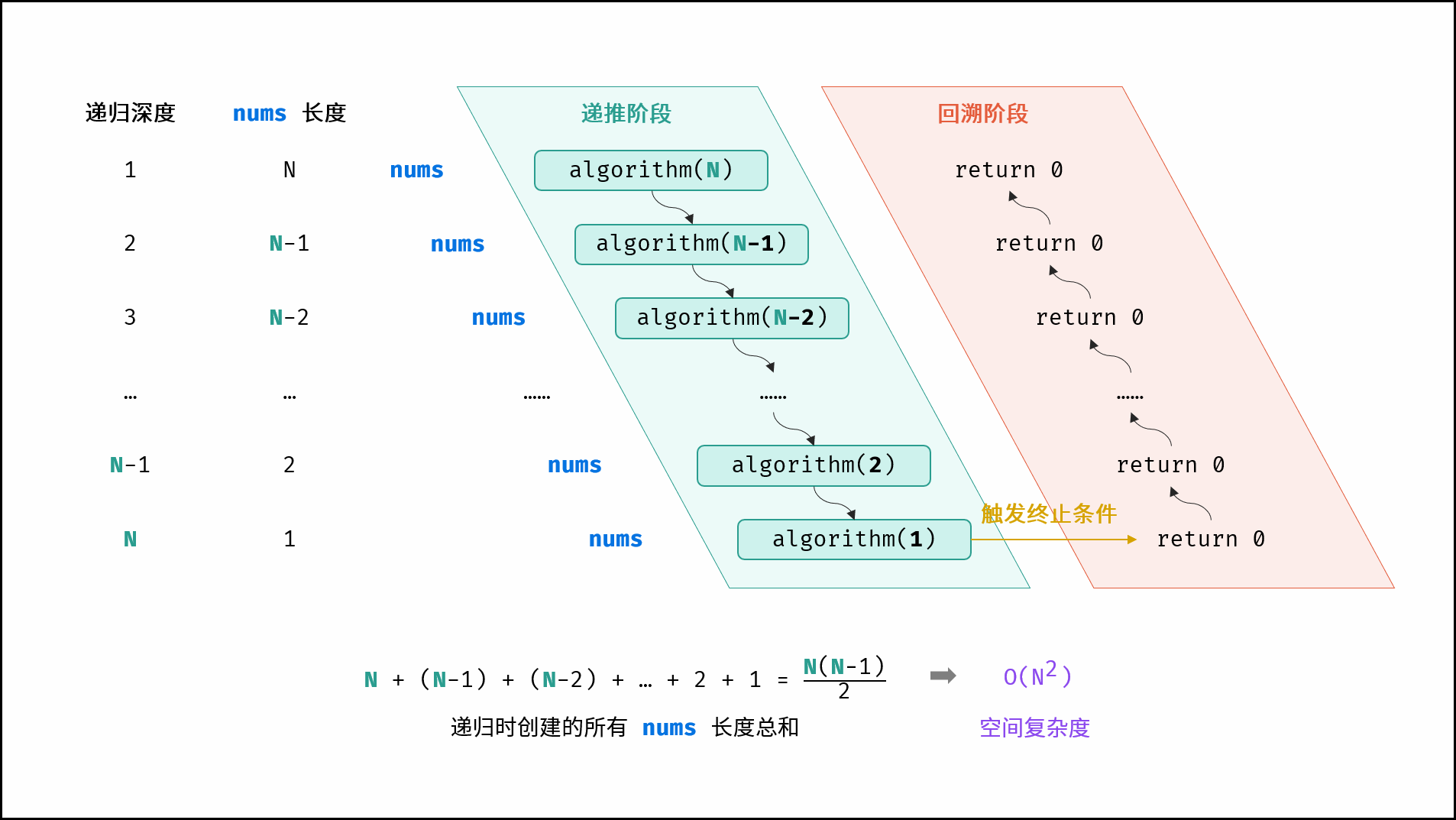
+
+### 指数 $O(2^N)$ :
+
+指数阶常见于二叉树、多叉树。例如,高度为 $N$ 的「满二叉树」的节点数量为 $2^N$ ,占用 $O(2^N)$ 大小的空间;同理,高度为 $N$ 的「满 $m$ 叉树」的节点数量为 $m^N$ ,占用 $O(m^N) = O(2^N)$ 大小的空间。
+
+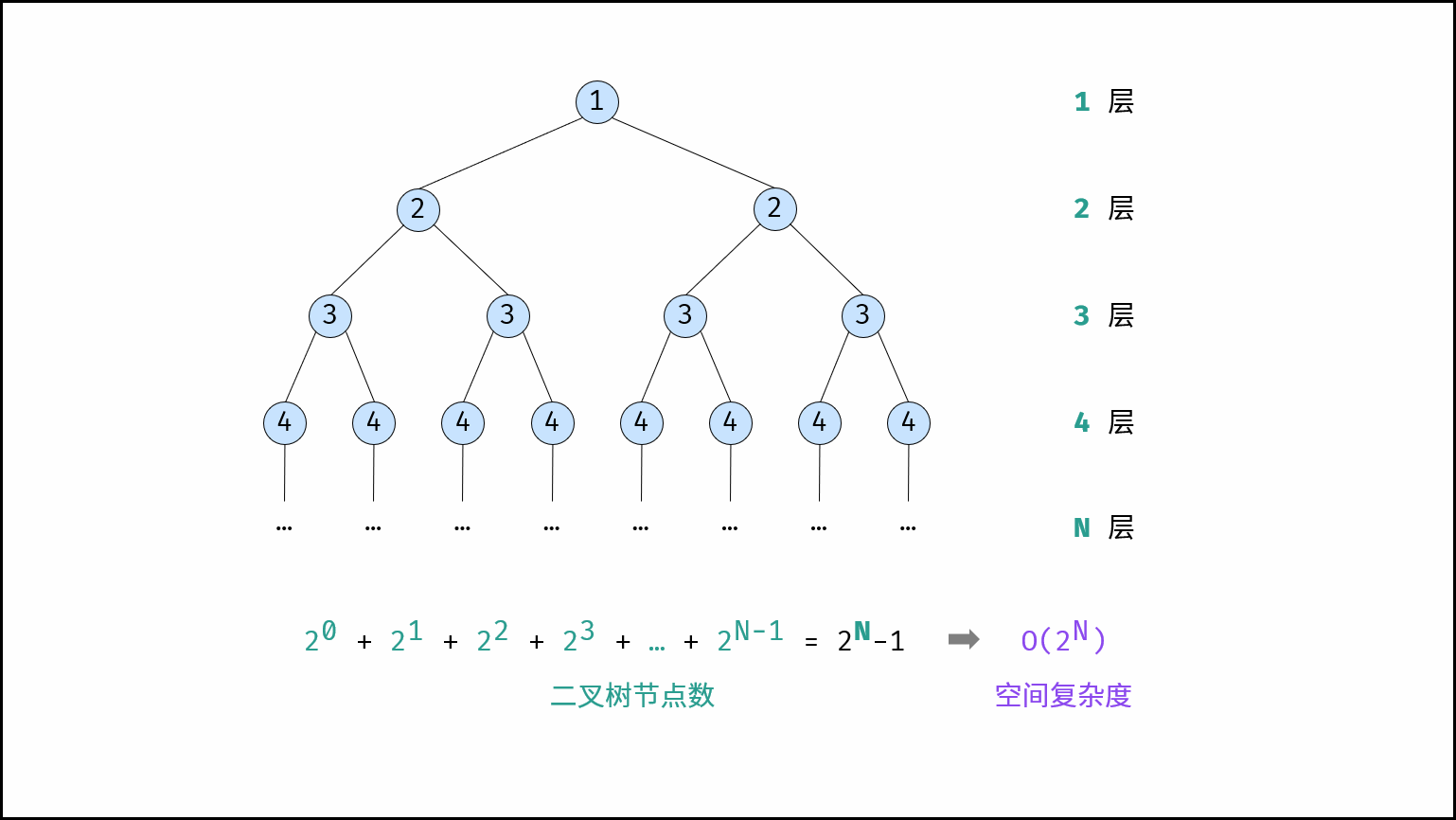{:width=600}
+
+### 对数 $O(\log N)$ :
+
+对数阶常出现于分治算法的栈帧空间累计、数据类型转换等,例如:
+
+- **快速排序** ,平均空间复杂度为 $\Theta(\log N)$ ,最差空间复杂度为 $O(N)$ 。拓展知识:通过应用 [尾递归优化](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/310974/what-is-tail-call-optimization) ,可以将快速排序的最差空间复杂度限定至 $O(N)$ 。
+- **数字转化为字符串** ,设某正整数为 $N$ ,则字符串的空间复杂度为 $O(\log N)$ 。推导如下:正整数 $N$ 的位数为 $log_{10} N$ ,即转化的字符串长度为 $\log_{10} N$ ,因此空间复杂度为 $O(\log N)$ 。
+
+---
+
+## 时空权衡
+
+对于算法的性能,需要从时间和空间的使用情况来综合评价。优良的算法应具备两个特性,即时间和空间复杂度皆较低。而实际上,对于某个算法问题,同时优化时间复杂度和空间复杂度是非常困难的。降低时间复杂度,往往是以提升空间复杂度为代价的,反之亦然。
+
+> 由于当代计算机的内存充足,通常情况下,算法设计中一般会采取「空间换时间」的做法,即牺牲部分计算机存储空间,来提升算法的运行速度。
+
+以 LeetCode 全站第一题 [两数之和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum/) 为例,「暴力枚举」和「辅助哈希表」分别为「空间最优」和「时间最优」的两种算法。
+
+### 方法一:暴力枚举
+
+时间复杂度 $O(N^2)$ ,空间复杂度 $O(1)$ ;属于「时间换空间」,虽然仅使用常数大小的额外空间,但运行速度过慢。
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
+ for i in range(len(nums) - 1):
+ for j in range(i + 1, len(nums)):
+ if nums[i] + nums[j] == target:
+ return i, j
+ return
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
+ int size = nums.length;
+ for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
+ for (int j = i + 1; j < size; j++) {
+ if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target)
+ return new int[] { i, j };
+ }
+ }
+ return new int[0];
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ vector twoSum(vector& nums, int target) {
+ int size = nums.size();
+ for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
+ for (int j = i + 1; j < size; j++) {
+ if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target)
+ return { i, j };
+ }
+ }
+ return {};
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### 方法二:辅助哈希表
+
+时间复杂度 $O(N)$ ,空间复杂度 $O(N)$ ;属于「空间换时间」,借助辅助哈希表 `dic` ,通过保存数组元素值与索引的映射来提升算法运行效率,是本题的最佳解法。
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
+ dic = {}
+ for i in range(len(nums)):
+ if target - nums[i] in dic:
+ return dic[target - nums[i]], i
+ dic[nums[i]] = i
+ return []
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
+ int size = nums.length;
+ Map dic = new HashMap<>();
+ for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
+ if (dic.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {
+ return new int[] { dic.get(target - nums[i]), i };
+ }
+ dic.put(nums[i], i);
+ }
+ return new int[0];
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ vector twoSum(vector& nums, int target) {
+ int size = nums.size();
+ unordered_map dic;
+ for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
+ if (dic.find(target - nums[i]) != dic.end()) {
+ return { dic[target - nums[i]], i };
+ }
+ dic.emplace(nums[i], i);
+ }
+ return {};
+ }
+};
+```
+
+---
+
+## 示例题目
+
+在 LeetCode 题目中,「输入空间」和「输出空间」往往是固定的,是必须使用的内存空间。因希望专注于算法性能对比,本 LeetBook 的题目解析的空间复杂度仅统计「暂存空间」大小。
+
+| 空间复杂度 | 示例题解 |
+| ----------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+| $O(1)$ | [斐波那契数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50fji7/)、[训练计划 III](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9p7s17/) |
+| $O(\log N)$ | [库存管理 III](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/ohwddh/)、[找到第 k 位数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57w6b3/) |
+| $O(N)$ | [图书整理 I](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5d8831/)、[动态口令](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58eckc/) |
+| $O(N^2)$ | [衣橱整理](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9hka9c/)、[套餐内商品的排列顺序](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50hah3/) |
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 11.1 \345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\350\247\243\351\242\230\346\241\206\346\236\266.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 11.1 \345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\350\247\243\351\242\230\346\241\206\346\236\266.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..af0b0cd
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 11.1 \345\212\250\346\200\201\350\247\204\345\210\222\350\247\243\351\242\230\346\241\206\346\236\266.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,482 @@
+# 动态规划解题框架
+
+动态规划是算法与数据结构的重难点之一,其包含了「分治思想」、「空间换时间」、「最优解」等多种基石算法思想,常作为笔面试中的中等困难题出现。为帮助读者全面理解动态规划,知晓其来龙去脉,本文将从以下几个角度切入介绍:
+
+1. 动态规划问题特点,**动态规划**和**分治算法**的联系与区别;
+2. 借助例题介绍**重叠子问题**和**最优子结构**分别是什么,以及动态规划是如何解决它们的;
+3. 动态规划的**解题框架**总结;
+4. 动态规划的**练习例题**,从易到难排序;
+
+---
+
+## 动态规划特点
+
+「分治」是算法中的一种基本思想,其通过**将原问题分解为子问题**,不断递归地将子问题分解为更小的子问题,并通过**组合子问题的解**来得到原问题的解。
+
+类似于分治算法,「动态规划」也通过组合子问题的解得到原问题的解。不同的是,适合用动态规划解决的问题具有「重叠子问题」和「最优子结构」两大特性。
+
+### 重叠子问题
+
+动态规划的子问题是有**重叠的**,即各个子问题中包含**重复的更小子问题**。若使用暴力法穷举,求解这些相同子问题会产生大量的重复计算,效率低下。
+
+动态规划在第一次求解某子问题时,会将子问题的解保存;后续遇到重叠子问题时,则直接通过查表获取解,保证每个**独立子问题只被计算一次**,从而降低算法的时间复杂度。
+
+### 最优子结构
+
+如果一个问题的最优解可以由其子问题的最优解组合构成,并且这些子问题可以独立求解,那么称此问题具有最优子结构。
+
+动态规划从基础问题的解开始,不断迭代**组合、选择子问题的最优解**,最终得到原问题最优解。
+
+---
+
+## 重叠子问题示例:斐波那契数列
+
+> 斐波那契数形成的数列为 $[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, \cdots]$ ,数学定义如下:
+> $$
+> \begin{aligned}
+> & F_0 = 0 \\
+> & F_1 = 1 \\
+> & F_n = F_{n-1} + F_{n-2}
+> \end{aligned}
+> $$
+> **题目:** 求取第 $n$ 个斐波那契数(从第 0 个斐波那契数开始)。
+
+以下,本文从「暴力递归」$\rightarrow$「记忆化递归」$\rightarrow$「动态规划」三种解法,介绍**重叠子问题**的概念与解决方案。
+
+### 方法一:暴力递归
+
+设斐波那契数列第 $n$ 个数字为 $f(n)$ 。根据数列定义,可得 $f(n) = f(n - 1) + f(n - 2)$ ,且第 0 , 1 个斐波那契数分别为 $f(0) = 0$ , $f(1) = 1$ 。
+
+我们很容易联想到使用分治思想来求取 $f(n)$ ,即将求原问题 $f(n)$ 分解为求子问题 $f(n-1)$ 和 $f(n-2)$ ,向下递归直至已知的 $f(0)$ 和 $f(1)$ ,最终组合这些子问题求取原问题 $f(n)$ 。
+
+```Python []
+# 求第 n 个斐波那契数
+def fibonacci(n):
+ if n == 0: return 0 # 返回 f(0)
+ if n == 1: return 1 # 返回 f(1)
+ return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2) # 分解为两个子问题求解
+```
+
+```Java []
+// 求第 n 个斐波那契数
+int fibonacci(int n) {
+ if (n == 0) return 0; // 返回 f(0)
+ if (n == 1) return 1; // 返回 f(1)
+ return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2); // 分解为两个子问题求解
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int fibonacci(int n) {
+ if (n == 0) return 0; // 返回 f(0)
+ if (n == 1) return 1; // 返回 f(1)
+ return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2); // 分解为两个子问题求解
+}
+```
+
+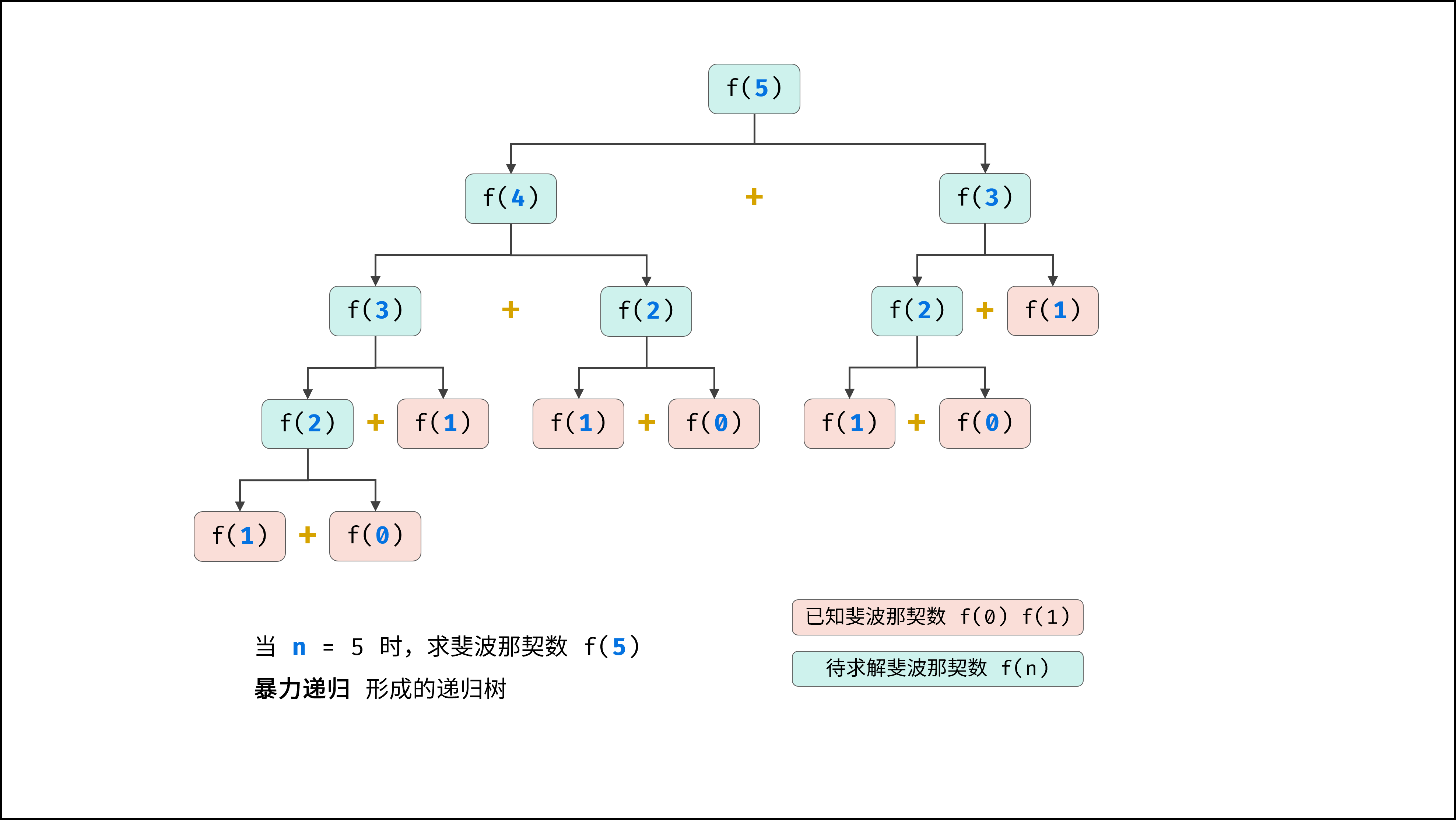
+
+如上图所示,为暴力递归求斐波那契数 $f(5)$ 形成的二叉树,树中的每个节点代表着执行了一次 `fibonacci()` 函数,且有:
+
+- 执行一次 `fibonacci()` 函数的时间复杂度为 $O(1)$ ;
+- 二叉树节点数为指数级 $O(2^n)$ ;
+
+因此,暴力递归的总体时间复杂度为 $O(2^n)$ 。此方法效率低下,随着 $n$ 的增长产生指数级爆炸。
+
+### 方法二:记忆化递归
+
+观察发现,暴力递归中的子问题多数都是**重叠子问题**,即:
+
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+& f(n) = f(n - 1) + f(n - 2) & 包含 f(n - 2) \\
+& f(n - 1) = f(n - 2) + f(n - 3) & 重复 f(n - 2) \\
+& f(n - 2) = f(n - 3) + f(n - 4) & 重复 f(n - 3) \\
+& \cdots &以此类推
+\end{aligned}
+$$
+
+这些重叠子问题产生了大量的递归树节点,其**不应被重复计算**。实际上,可以在递归中**第一次求解子问题**时,就将它们**保存**;后续递归中再次遇到相同子问题时,直接访问内存赋值即可。记忆化递归的代码如下所示。
+
+```Python []
+def fibonacci(n, dp):
+ if n == 0: return 0 # 返回 f(0)
+ if n == 1: return 1 # 返回 f(1)
+ if dp[n] != 0: return dp[n] # 若 f(n) 以前已经计算过,则直接返回记录的解
+ dp[n] = fibonacci(n - 1, dp) + fibonacci(n - 2, dp) # 将 f(n) 则记录至 dp
+ return dp[n]
+
+# 求第 n 个斐波那契数
+def fibonacci_memorized(n):
+ dp = [0] * (n + 1) # 用于保存 f(0) 至 f(n) 问题的解
+ return fibonacci(n, dp)
+```
+
+```Java []
+int fibonacci(int n, int[] dp) {
+ if (n == 0) return 0; // 返回 f(0)
+ if (n == 1) return 1; // 返回 f(1)
+ if (dp[n] != 0) return dp[n]; // 若 f(n) 以前已经计算过,则直接返回记录的解
+ dp[n] = fibonacci(n - 1, dp) + fibonacci(n - 2, dp); // 将 f(n) 则记录至 dp
+ return dp[n];
+}
+
+
+// 求第 n 个斐波那契数
+int fibonacciMemorized(int n) {
+ int[] dp = new int[n + 1]; // 用于保存 f(0) 至 f(n) 问题的解
+ return fibonacci(n, dp);
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int fibonacci(int n, vector dp) {
+ if (n == 0) return 0; // 返回 f(0)
+ if (n == 1) return 1; // 返回 f(1)
+ if (dp[n] != 0) return dp[n]; // 若 f(n) 以前已经计算过,则直接返回记录的解
+ dp[n] = fibonacci(n - 1, dp) + fibonacci(n - 2, dp); // 将 f(n) 则记录至 dp
+ return dp[n];
+}
+
+
+// 求第 n 个斐波那契数
+int fibonacciMemorized(int n) {
+ vector dp(n + 1, 0); // 用于保存 f(0) 至 f(n) 问题的解
+ return fibonacci(n, dp);
+}
+```
+
+如下图所示,应用记忆化递归方法后,递归树中绝大部分节点被**剪枝**。此时,`fibonacci()` 函数的调用次数从 $O(2^n)$ 指数级别降低至 $O(n)$ 线性级别,时间复杂度大大降低。
+
+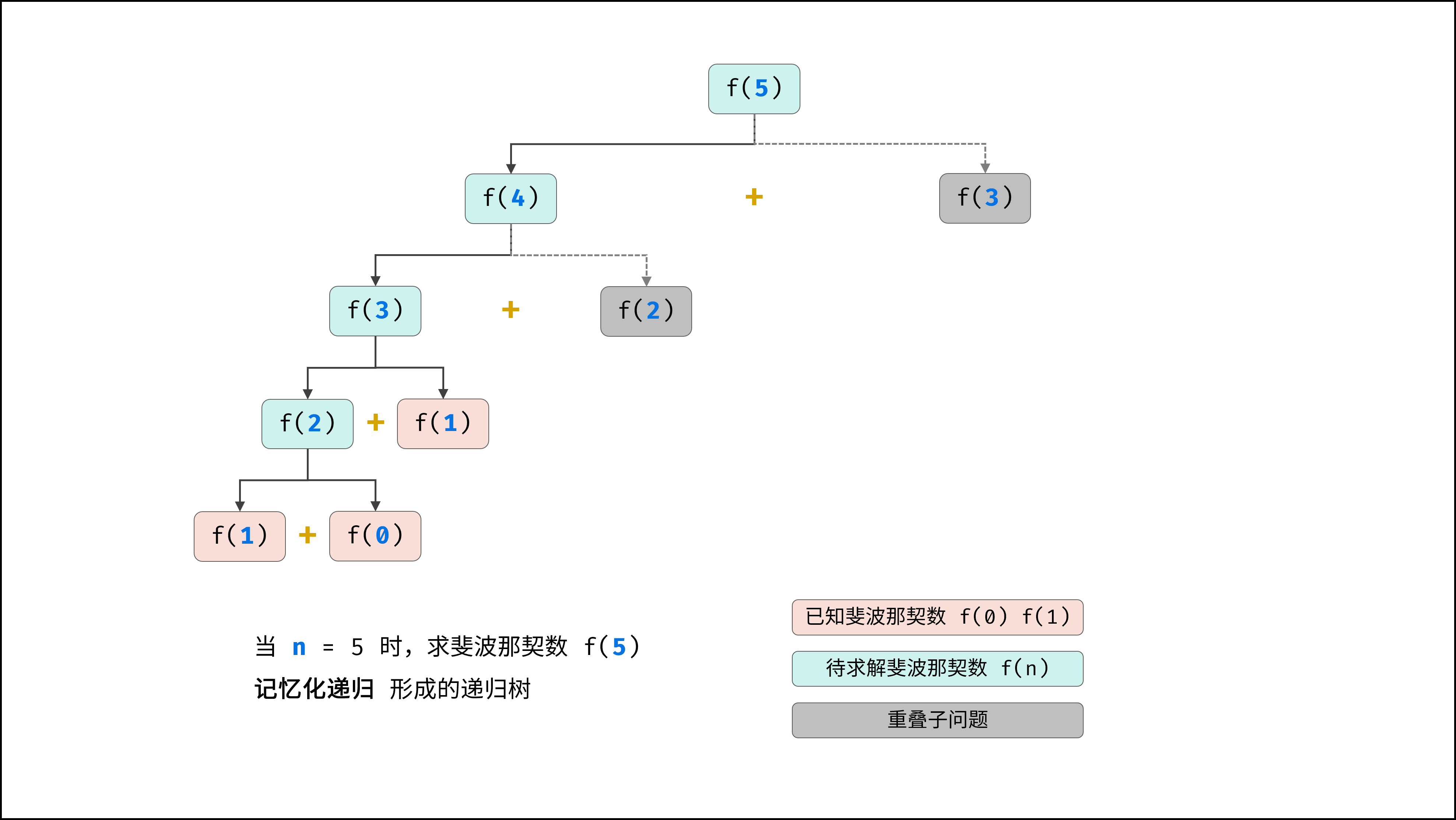
+
+### 方法三:动态规划
+
+递归本质上是基于分治思想的从顶至底的解法。借助记忆化递归思想,可应用动态规划从底至顶求取 $f(n)$ ,代码如下所示。
+
+```Python []
+# 求第 n 个斐波那契数
+def fibonacci(n):
+ if n == 0: return 0 # 若求 f(0) 则直接返回 0
+ dp = [0] * (n + 1) # 初始化 dp 列表
+ dp[0], dp[1] = 0, 1 # 初始化 f(0), f(1)
+ for i in range(2, n + 1): # 状态转移求取 f(2), f(3), ..., f(n)
+ dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]
+ return dp[n] # 返回 f(n)
+```
+
+```Java []
+// 求第 n 个斐波那契数
+int fibonacci(int n) {
+ if (n == 0) return 0; // 若求 f(0) 则直接返回 0
+ int[] dp = new int[n + 1]; // 初始化 dp 列表
+ dp[1] = 1; // 初始化 f(0), f(1)
+ for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) { // 状态转移求取 f(2), f(3), ..., f(n)
+ dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
+ }
+ return dp[n]; // 返回 f(n)
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+// 求第 n 个斐波那契数
+int fibonacci(int n) {
+ if (n == 0) return 0; // 若求 f(0) 则直接返回 0
+ vector dp(n + 1, 0); // 初始化 dp 列表
+ dp[1] = 1; // 初始化 f(0), f(1)
+ for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) { // 状态转移求取 f(2), f(3), ..., f(n)
+ dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
+ }
+ return dp[n]; // 返回 f(n)
+}
+```
+
+如下图所示,为动态规划求解 $f(5)$ 的迭代流程,其是转移方程 $f(n) = f(n - 1) + f(n - 2)$ 的体现。
+
+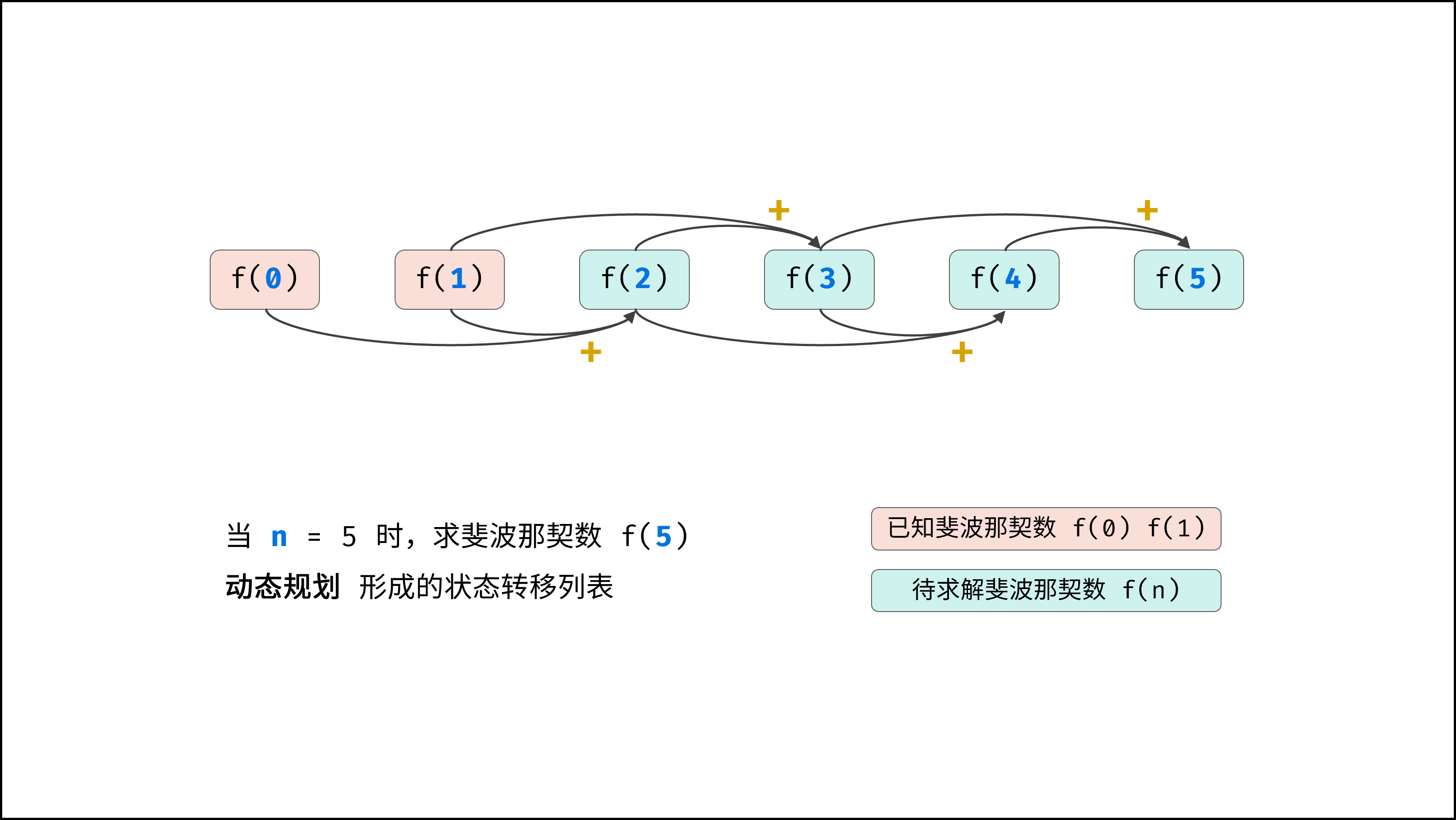
+
+上述动态规划解法借助了一个 `dp` 数组保存子问题的解,其空间复杂度为 $O(N)$ 。而由于 $f(n)$ 只与 $f(n - 1)$ 和 $f(n - 2)$ 有关,因此我们可以仅使用两个变量 $a$ , $b$ 交替前进计算即可。此时动态规划的空间复杂度降低至 $O(1)$ ,代码如下所示。
+
+```Python []
+# 求第 n 个斐波那契数
+def fibonacci(n):
+ if n == 0: return 0 # 若求 f(0) 则直接返回 0
+ a, b = 0, 1 # 初始化 f(0), f(1)
+ for i in range(2, n + 1): # 状态转移求取 f(2), f(3), ..., f(n)
+ a, b = b, a + b
+ return b # 返回 f(n)
+```
+
+```Java []
+// 求第 n 个斐波那契数
+int fibonacci(int n) {
+ if (n == 0) return 0; // 若求 f(0) 则直接返回 0
+ int a = 0, b = 1; // 初始化 f(0), f(1)
+ for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) { // 状态转移求取 f(2), f(3), ..., f(n)
+ int tmp = a;
+ a = b;
+ b = tmp + b;
+ }
+ return b; // 返回 f(n)
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+// 求第 n 个斐波那契数
+int fibonacci(int n) {
+ if (n == 0) return 0; // 若求 f(0) 则直接返回 0
+ int a = 0, b = 1; // 初始化 f(0), f(1)
+ for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) { // 状态转移求取 f(2), f(3), ..., f(n)
+ int tmp = a;
+ a = b;
+ b = tmp + b;
+ }
+ return b; // 返回 f(n)
+}
+```
+
+### 示例小结
+
+记忆化递归和动态规划的本质思想是一致的,是对斐波那契数列定义的不同表现形式:
+
+- **记忆化递归 — 从顶至低:** 求 $f(n)$ 需要 $f(n - 1)$ 和 $f(n - 2)$ ; $\cdots$ ;求 $f(2)$ 需要 $f(1)$ 和 $f(0)$ ;而 $f(1)$ 和 $f(0)$ 已知;
+- **动态规划 — 从底至顶:** 将已知 $f(0)$ 和 $f(1)$ 组合得到 $f(2)$ ;$\cdots$ ;将 $f(n - 2)$ 和 $f(n - 1)$ 组合得到 $f(n)$ ;
+
+斐波那契数列问题不包含「最优子结构」,只需计算每个子问题的解,避免重复计算即可,并不需要从子问题组合中**选择最优组合**。接下来,本文借助「最高蛋糕售价方案」,介绍动态规划的**最优子结构**概念。
+
+---
+
+## 最优子结构示例:蛋糕最高售价
+
+> 小力开了一家蛋糕店,并针对不同重量的蛋糕设定了不同售价,分别为:
+>
+> | 蛋糕重量 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
+> | :------: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: |
+> | 售价 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 7 | 11 | 15 |
+>
+> **问题:** 现给定一个重量为 $n$ 的蛋糕,问小力应该如何切分蛋糕,达到最高的蛋糕总售价。
+
+设重量为 $n$ 蛋糕的售价为 $p(n)$ ,切分的最高总售价为 $f(n)$ 。
+
+- **子问题:** $f(n)$ 的子问题包括 $f(0), f(1), f(2), \cdots, f(n - 1)$ ,分别代表重量为 $0, 1, 2, \cdots, n - 1$ 蛋糕的最高售价。 已知无蛋糕时 $f(0) = 0$ ,蛋糕重量为 1 时不可切分 $f(1) = p(1)$ ;
+- **最优子结构:**
+ - **定义:** 如果一个问题最优解可以由其子问题最优解组合构成,那么称此问题具有最优子结构。
+ - **对于本题:** 重量为 $n$ 的蛋糕的总售价可切分为 $n$ 种组合,即重量为 $0, 1, 2, ..., n - 1$ 蛋糕**最高售价**加上 $n, n - 1, n - 2, \cdots, 1$ 剩余重量蛋糕的**售价**;从这些组合中,售价最高的组合便是原问题的解 $f(n)$ ,这便是本题的最优子结构。
+
+- **状态转移方程:** 找出最优子结构后,易构建出如下的状态转移方程。
+
+$$
+f(n) = \max_{0 \leq i < n} (f(i) + p(n - i))
+$$
+
+根据以上推导,本题也能使用「暴力递归」$\rightarrow$「记忆化递归」$\rightarrow$「动态规划」三种方法解决。
+
+### 方法一:暴力递归
+
+暴力递归解法的代码如下,其时间复杂度为指数级 $O(2^n)$ 。
+
+```Python []
+# 输入蛋糕价格列表 price_list ,求重量为 n 蛋糕的最高售价
+def max_cake_price(n, price_list):
+ if n <= 1: return price_list[n] # 蛋糕重量 <= 1 时直接返回
+ f_n = 0
+ for i in range(n): # 从 n 种组合种选择最高售价的组合作为 f(n)
+ f_n = max(f_n, max_cake_price(i, price_list) + price_list[n - i])
+ return f_n # 返回 f(n)
+
+max_cake_price(4, [0, 2, 3, 6, 7, 11, 15])
+```
+
+```Java []
+// 输入蛋糕价格列表 priceList ,求重量为 n 蛋糕的最高售价
+int maxCakePrice(int n, int[] priceList) {
+ if (n <= 1) return priceList[n]; // 蛋糕重量 <= 1 时直接返回
+ int f_n = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) // 从 n 种组合种选择最高售价的组合作为 f(n)
+ f_n = Math.max(f_n, maxCakePrice(i, priceList) + priceList[n - i]);
+ return f_n; // 返回 f(n)
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+// 输入蛋糕价格列表 priceList ,求重量为 n 蛋糕的最高售价
+int maxCakePrice(int n, vector priceList) {
+ if (n <= 1) return priceList[n]; // 蛋糕重量 <= 1 时直接返回
+ int f_n = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) // 从 n 种组合种选择最高售价的组合作为 f(n)
+ f_n = max(f_n, maxCakePrice(i, priceList) + priceList[n - i]);
+ return f_n; // 返回 f(n)
+}
+```
+
+如下图所示,为暴力递归求解 $f(4)$ 形成的多叉树。
+
+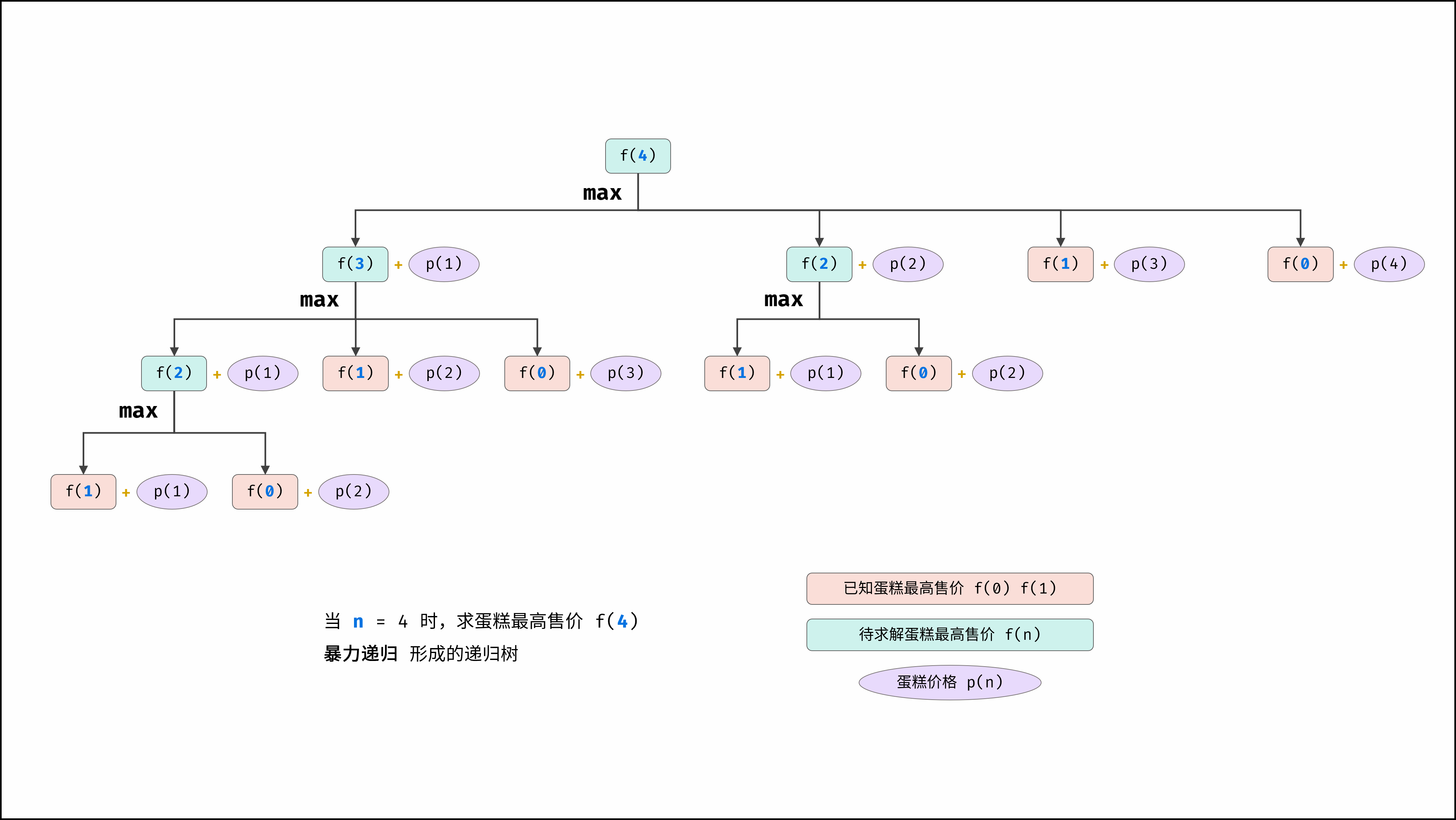
+
+### 方法二:记忆化递归
+
+观察发现,递归树中存在大量**重叠子问题**,可通过记忆化处理避免重复计算。记忆化递归的算法的时间复杂度为 $O(n^2)$ ,包括:
+
+- $f(2)$ 至 $f(n)$ 共 $n - 1$ 个待计算子问题,使用 $O(n)$ 时间;
+- 计算某 $f(i)$ 需遍历 $i - 1$ 种子问题组合,使用 $O(n)$ 时间;
+
+```Python []
+# 输入蛋糕价格列表 price_list ,求重量为 n 蛋糕的最高售价
+def max_cake_price(n, price_list, dp):
+ if n <= 1: return price_list[n] # 蛋糕重量 <= 1 时直接返回
+ f_n = 0
+ for i in range(n): # 从 n 种组合种选择最高售价的组合作为 f(n)
+ # 若 f(i) 以前已经计算过,则调取记录的解;否则,递归计算 f(i)
+ f_i = dp[i] if dp[i] != 0 else max_cake_price(i, price_list, dp)
+ f_n = max(f_n, f_i + price_list[n - i])
+ dp[n] = f_n # 记录 f(n) 至 dp 数组
+ return f_n # 返回 f(n)
+
+def max_cake_price_memorized(n, price_list):
+ dp = [0] * (n + 1)
+ return max_cake_price(n, price_list, dp)
+```
+
+```Java []
+// 输入蛋糕价格列表 priceList ,求重量为 n 蛋糕的最高售价
+int maxCakePrice(int n, int[] priceList, int[] dp) {
+ if (n <= 1) return priceList[n]; // 蛋糕重量 <= 1 时直接返回
+ int f_n = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // 从 n 种组合种选择最高售价的组合作为 f(n)
+ int f_i = dp[i] != 0 ? dp[i] : maxCakePrice(i, priceList, dp);
+ f_n = Math.max(f_n, f_i + priceList[n - i]);
+ }
+ dp[n] = f_n; // 记录 f(n) 至 dp 数组
+ return f_n; // 返回 f(n)
+}
+
+int maxCakePriceMemorized(int n, int[] priceList) {
+ int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
+ return maxCakePrice(n, priceList, dp);
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+// 输入蛋糕价格列表 priceList ,求重量为 n 蛋糕的最高售价
+int maxCakePrice(int n, vector &priceList, vector dp) {
+ if (n <= 1) return priceList[n]; // 蛋糕重量 <= 1 时直接返回
+ int f_n = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // 从 n 种组合种选择最高售价的组合作为 f(n)
+ int f_i = dp[i] != 0 ? dp[i] : maxCakePrice(i, priceList, dp);
+ f_n = max(f_n, f_i + priceList[n - i]);
+ }
+ dp[n] = f_n; // 记录 f(n) 至 dp 数组
+ return f_n; // 返回 f(n)
+}
+
+int maxCakePriceMemorized(int n, vector priceList) {
+ vector dp(n + 1, 0);
+ return maxCakePrice(n, priceList, dp);
+}
+```
+
+如下图所示,为记忆化递归求解 $f(4)$ 形成的多叉树。观察得知,重叠子问题皆被**剪枝**。
+
+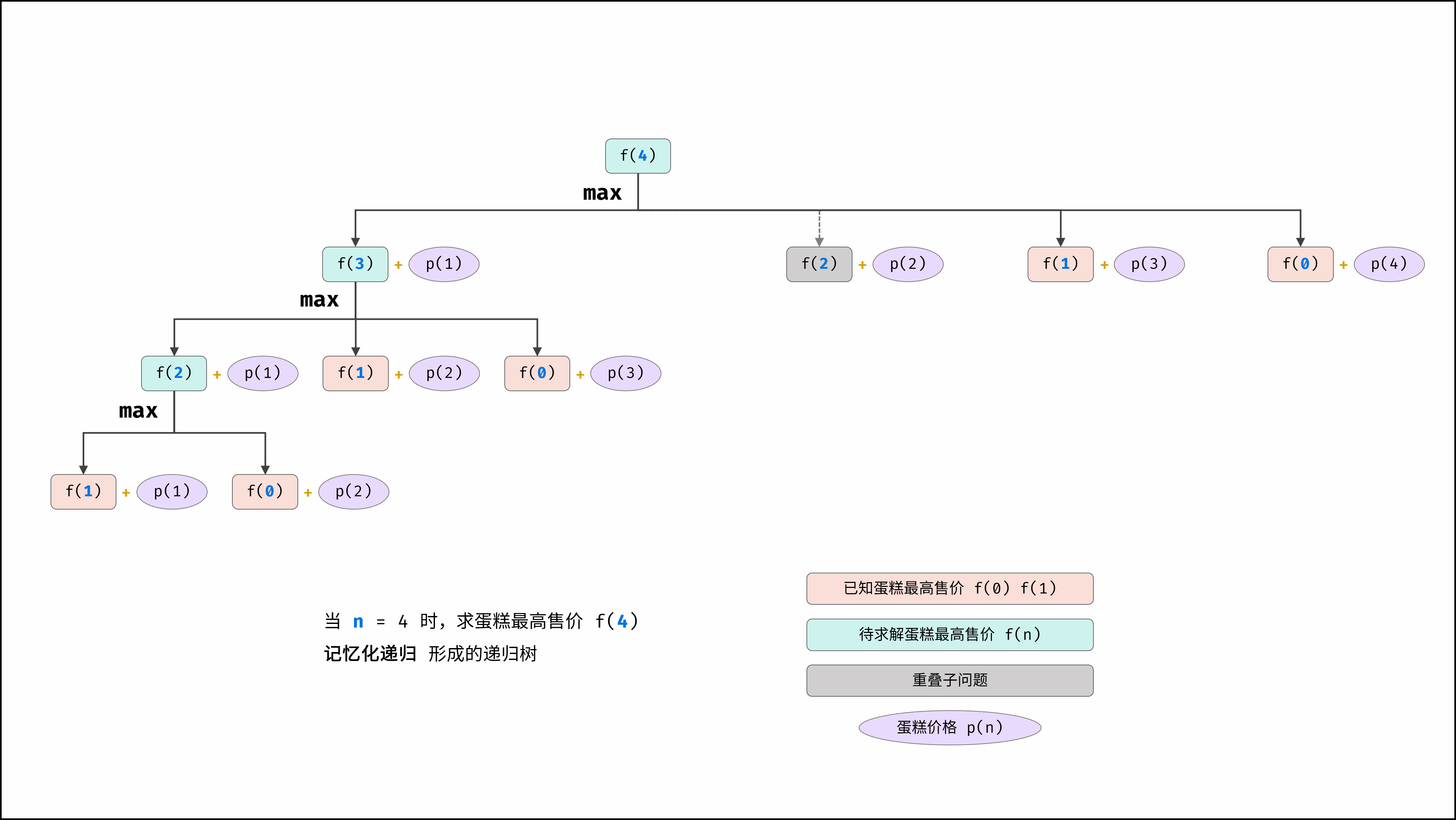
+
+### 方法三:动态规划
+
+相较于记忆化递归的从顶至底方法,易得动态规划的从底至顶方法,代码如下所示。
+
+```Python []
+# 输入蛋糕价格列表 price_list ,求重量为 n 蛋糕的最高售价
+def max_cake_price(n, price_list):
+ if n <= 1: return price_list[n] # 蛋糕重量 <= 1 时直接返回
+ dp = [0] * (n + 1) # 初始化 dp 列表
+ for j in range(1, n + 1): # 按顺序计算 f(1), f(2), ..., f(n)
+ for i in range(j): # 从 j 种组合种选择最高售价的组合作为 f(j)
+ dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[i] + price_list[j - i])
+ return dp[n]
+```
+
+```Java []
+// 输入蛋糕价格列表 priceList ,求重量为 n 蛋糕的最高售价
+int maxCakePrice(int n, int[] priceList) {
+ if (n <= 1) return priceList[n]; // 蛋糕重量 <= 1 时直接返回
+ int[] dp = new int[n + 1]; // 初始化 dp 列表
+ for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { // 按顺序计算 f(1), f(2), ..., f(n)
+ for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) // 从 j 种组合种选择最高售价的组合作为 f(j)
+ dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[i] + priceList[j - i]);
+ }
+ return dp[n];
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+// 输入蛋糕价格列表 priceList ,求重量为 n 蛋糕的最高售价
+int maxCakePrice(int n, vector priceList) {
+ if (n <= 1) return priceList[n]; // 蛋糕重量 <= 1 时直接返回
+ vector dp(n + 1, 0); // 初始化 dp 列表
+ for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { // 按顺序计算 f(1), f(2), ..., f(n)
+ for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) // 从 j 种组合种选择最高售价的组合作为 f(j)
+ dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[i] + priceList[j - i]);
+ }
+ return dp[n];
+}
+```
+
+如下图所示,为动态规划求解 $f(4)$ 的迭代流程,其是转移方程 $f(n) = \max_{0 \leq i < n} (f(i) + p(n - i))$ 的体现。
+
+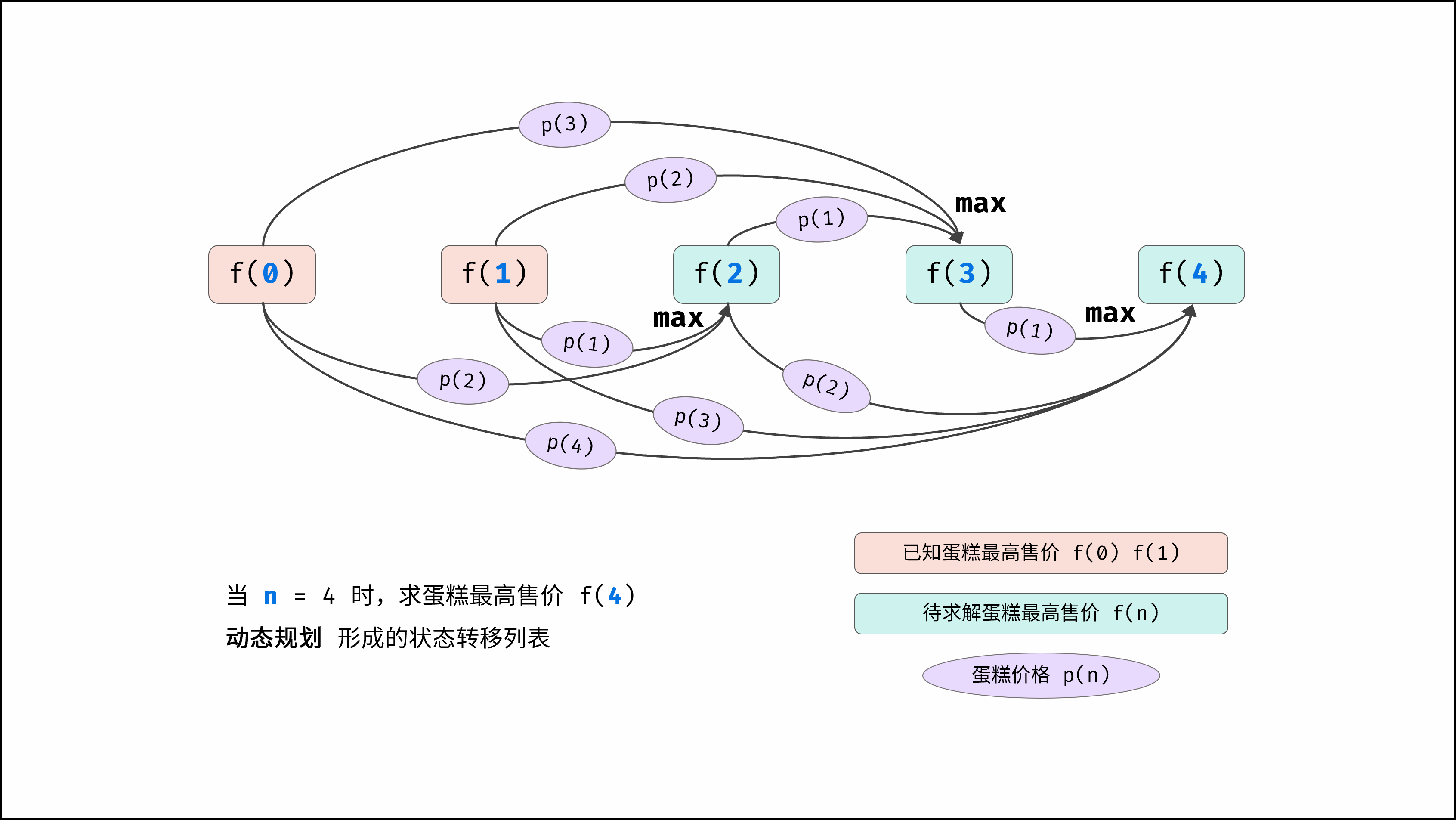
+
+### 示例小结
+
+本题同时包含「重叠子问题」和「最优子结构」,为动态规划的典型问题。动态规划通过填表避免了重复计算问题,并通过状态转移方程、初始状态实现对问题的迭代求解。
+
+普遍来看,**求最值** 的问题一般都具有「重叠子问题」和「最优子结构」特点,因此此类问题往往适合用动态规划解决。
+
+---
+
+## 动态规划解题框架
+
+若确定给定问题具有重叠子问题和最优子结构,那么就可以使用动态规划求解。总体上看,求解可分为四步:
+
+1. **状态定义:** 构建问题最优解模型,包括问题**最优解的定义**、有哪些**计算解的自变量**;
+2. **初始状态:** 确定**基础子问题的解**(即已知解),原问题和子问题的解都是以基础子问题的解为起始点,在迭代计算中得到的;
+3. **转移方程:** 确定原问题的解与子问题的解之间的关系是什么,以及使用何种**选择规则**从子问题最优解组合中选出原问题最优解;
+4. **返回值:** 确定应返回的问题的解是什么,即动态规划**在何处停止迭代**;
+
+完成以上步骤后,便容易写出对应的解题代码。
+
+### 示例:斐波那契数列
+
+- 状态定义:一维 $dp$ 列表,设第 $i$ 个斐波那契数为 $dp[i]$ ;
+- 初始状态:已知第 $0$ , $1$ 个斐波那契数分别为 $dp[0] = 0$ , $dp[1] = 1$ ;
+- 转移方程:后一个数字等于前两个数字之和,即
+
+$$
+dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]
+$$
+
+- 返回值:需求取的第 $n$ 个斐波那契数 $dp[n]$ ;
+
+### 示例:蛋糕最高售价
+
+- 状态定义:一维 $dp$ 列表,设重量为 $i$ 蛋糕的售价为 $p(i)$ ,重量为 $i$ 蛋糕切分后的最高售价为 $dp[i]$ ;
+- 初始状态:已知重量为 0 蛋糕的最高售价为 0 ,重量为 1 的蛋糕最高售价为 $p(1)$ ;
+- 转移方程:$dp[n]$ 为 $n$ 种切分组合中的最高售价组合,即
+
+$$
+dp[n] = \max_{0 \leq i < n} (dp[i] + p(n - i))
+$$
+
+- 返回值:需求取的重量为 $n$ 的蛋糕最高售价 $dp[n]$ ;
+
+---
+
+## 例题练习
+
+动态规划的问题种类多,难度跨度较大,需要充足练习、熟能生巧。以下给出若干典型例题,供读者巩固理解本文内容。
+
+| 题目 | 难度 | 描述 |
+| ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ---- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [跳跃训练](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57hyl5/) | 简单 | 与本文的斐波那契数列例题等价 |
+| [连续天数的最高销售额](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/59gq9c/) | 简单 | 求最大值问题,关键点在于状态定义 |
+| [珠宝的最高价值](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vokvr/) | 简单 | 求最大值问题,特点是其 $dp$ 列表是二维的 |
+| [统计结果概率](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/ozzl1r/) | 中等 | 容易想到暴力枚举方法,难点为列出状态转移方程,且正向递推方法比较 tricky |
+| [模糊搜索验证](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9a1ypc/) | 困难 | 状态定义容易得出,但状态转移方程复杂、选择规则分支多 |
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 7.1 \346\216\222\345\272\217\347\256\227\346\263\225\347\256\200\344\273\213.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 7.1 \346\216\222\345\272\217\347\256\227\346\263\225\347\256\200\344\273\213.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..47df189
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 7.1 \346\216\222\345\272\217\347\256\227\346\263\225\347\256\200\344\273\213.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
+# 排序算法简介
+
+排序算法用作实现列表的排序,列表元素可以是整数,也可以是浮点数、字符串等其他数据类型。生活中有许多需要排序算法的场景,例如:
+
+- **整数排序:** 对于一个整数数组,我们希望将所有数字从小到大排序;
+- **字符串排序:** 对于一个姓名列表,我们希望将所有单词按照字符先后排序;
+- **自定义排序:** 对于任意一个 **已定义比较规则** 的集合,我们希望将其按规则排序;
+
+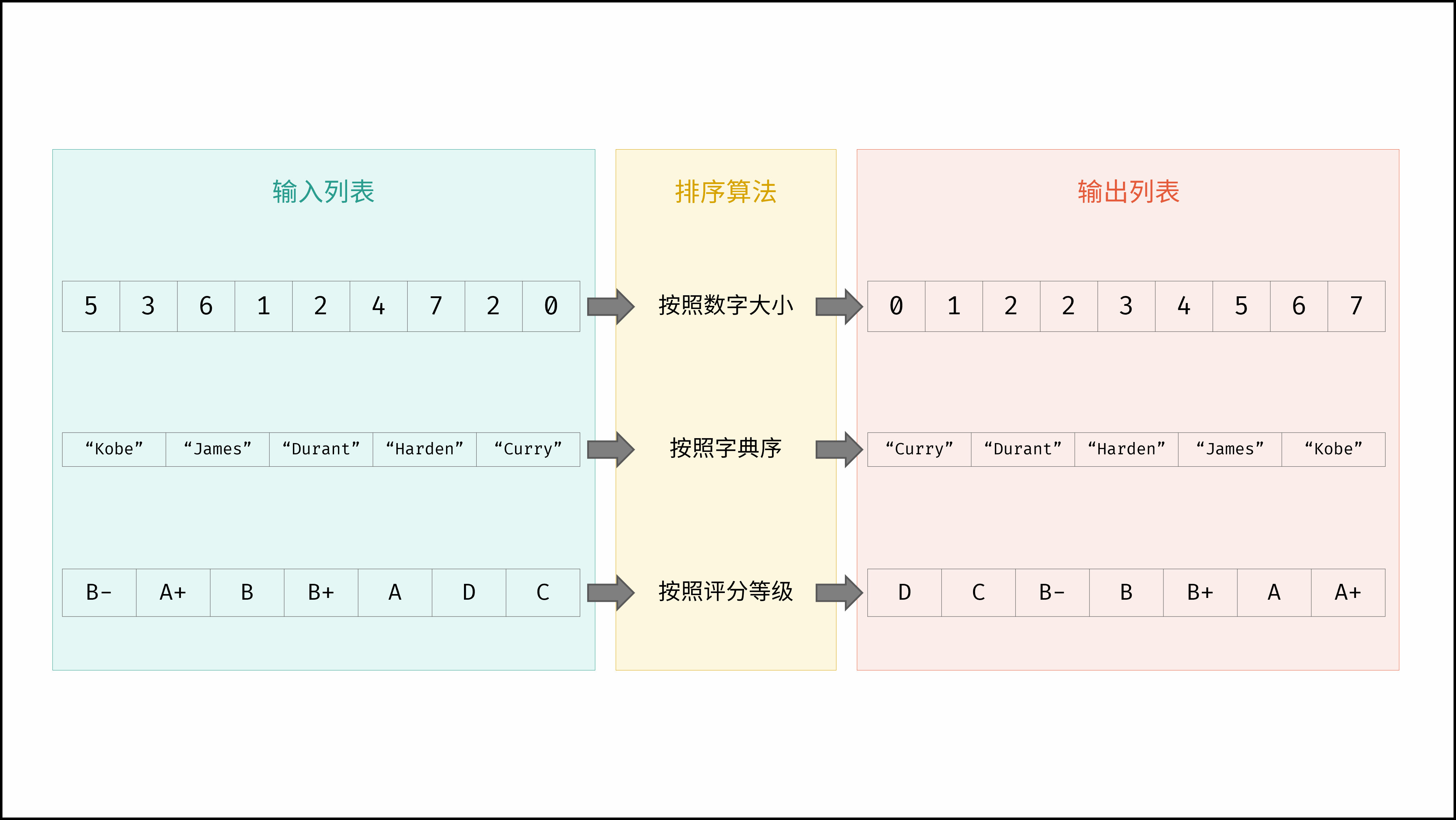
+
+同时,某些算法需要在排序算法的基础上使用(即在排序数组上运行),例如:
+
+- **二分查找:** 根据数组已排序的特性,才能每轮确定排除两部分中的哪一部分;
+- **双指针:** 例如合并两个排序链表,根据已排序特性,才能通过双指针移动在线性时间内将其合并为一个排序链表。
+
+> 接下来,本文将从「常见排序算法」、「分类方法」、「时间与空间复杂度」三方面入手,简要介绍排序算法。「各排序算法详细介绍」请见后续专栏文章。
+
+---
+
+## 常见算法
+
+常见排序算法包括「冒泡排序」、「插入排序」、「选择排序」、「快速排序」、「归并排序」、「堆排序」、「基数排序」、「桶排ss序」。如下图所示,为各排序算法的核心特性与时空复杂度总结。
+
+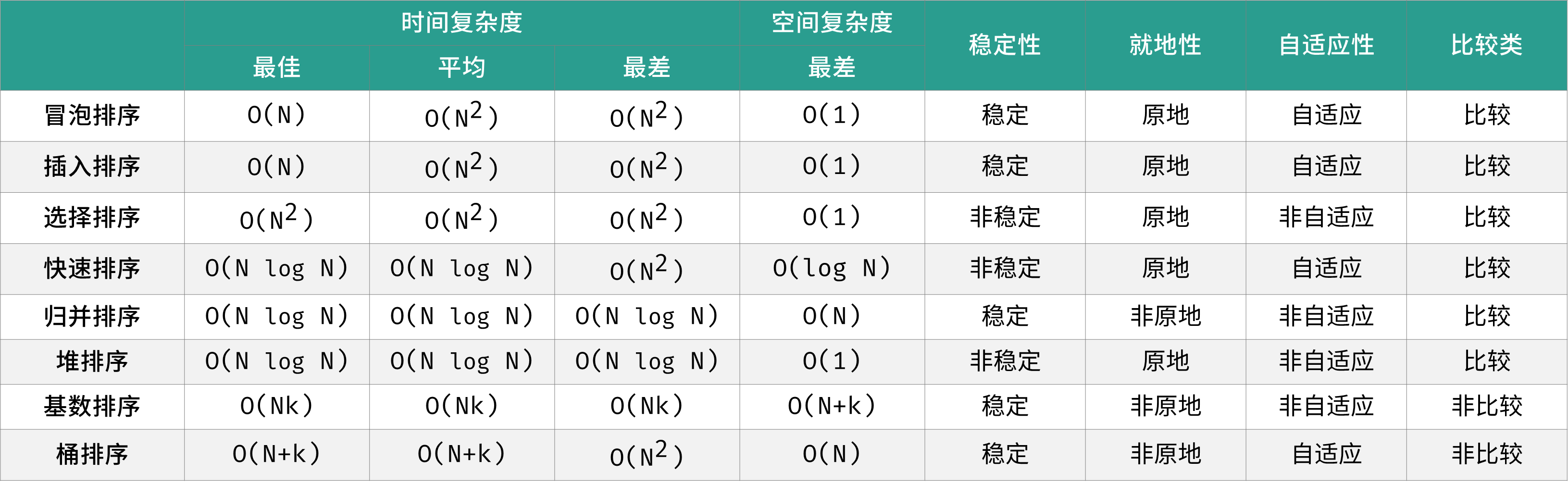
+
+如下图所示,为在 「随机乱序」、「接近有序」、「完全倒序」、「少数独特」四类输入数据下,各常见排序算法的排序过程。
+
+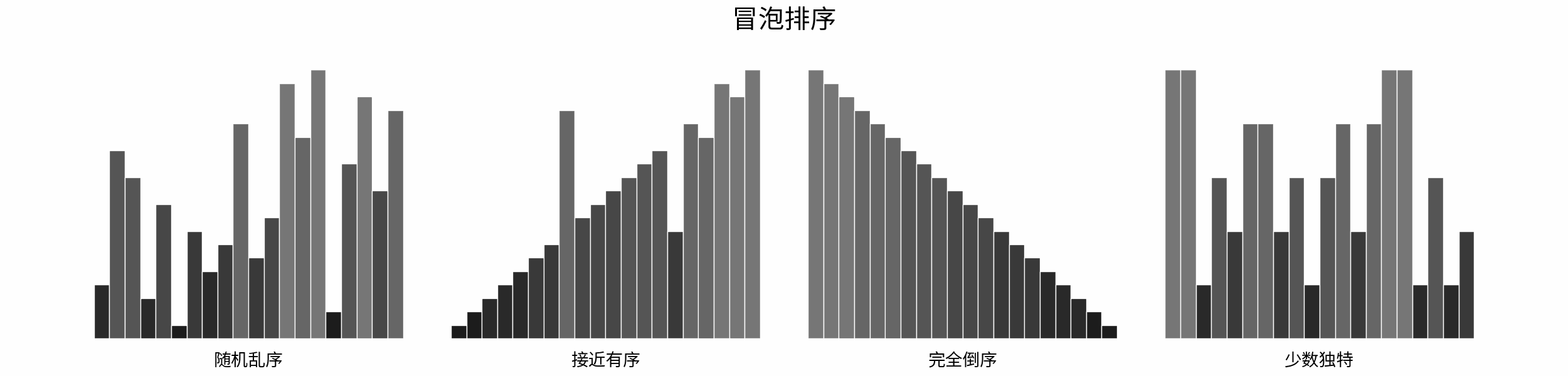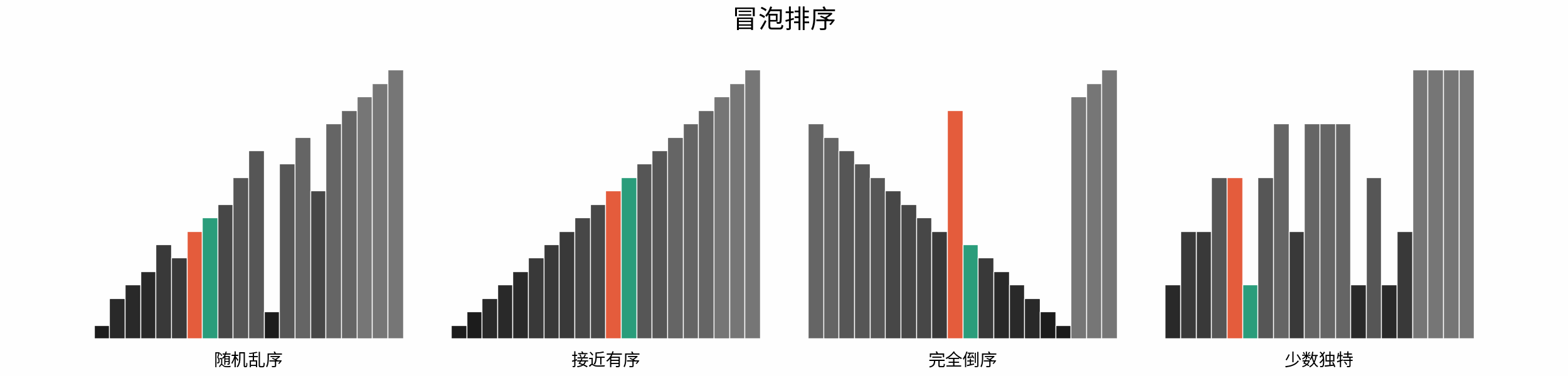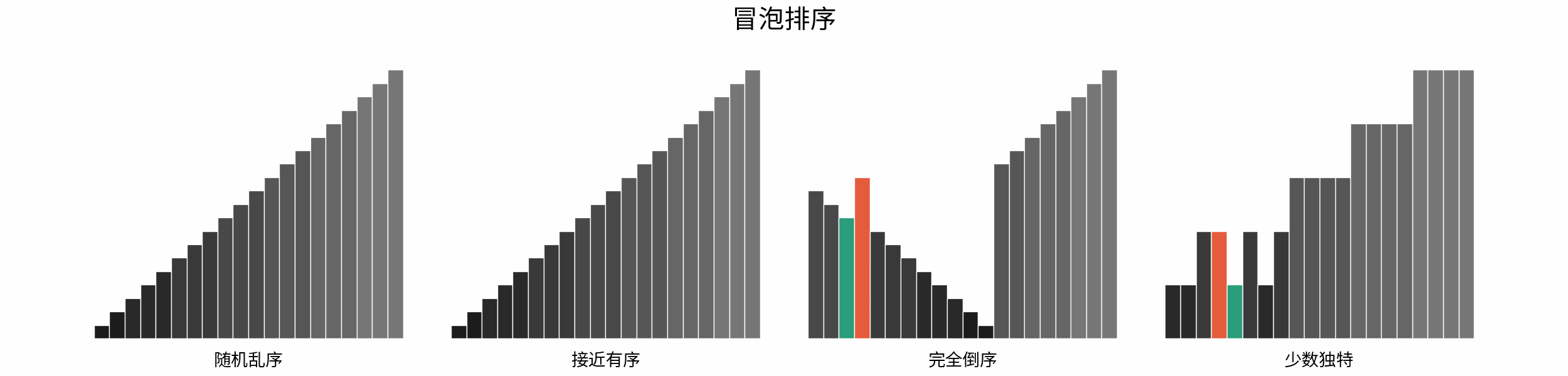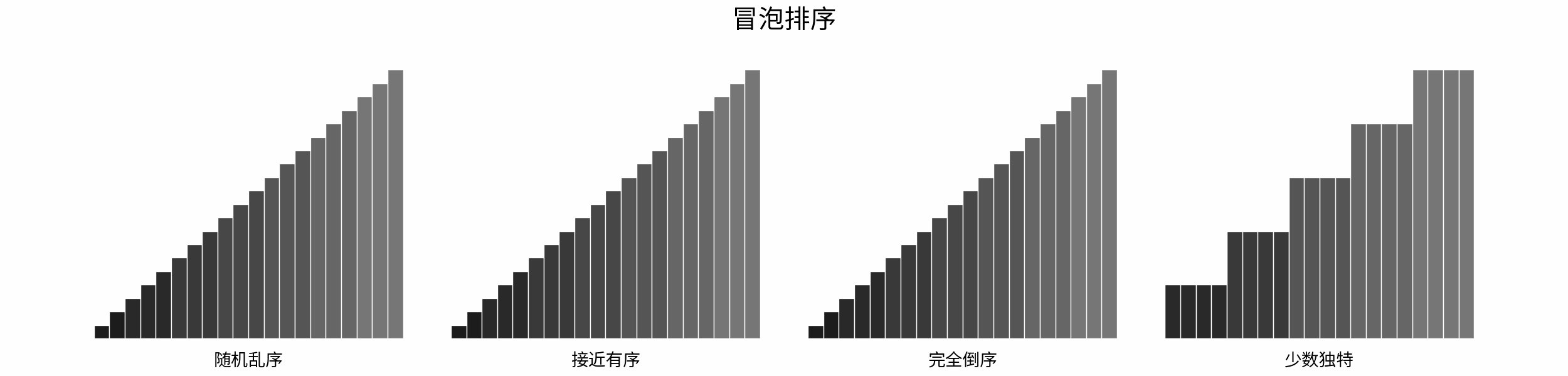
+
+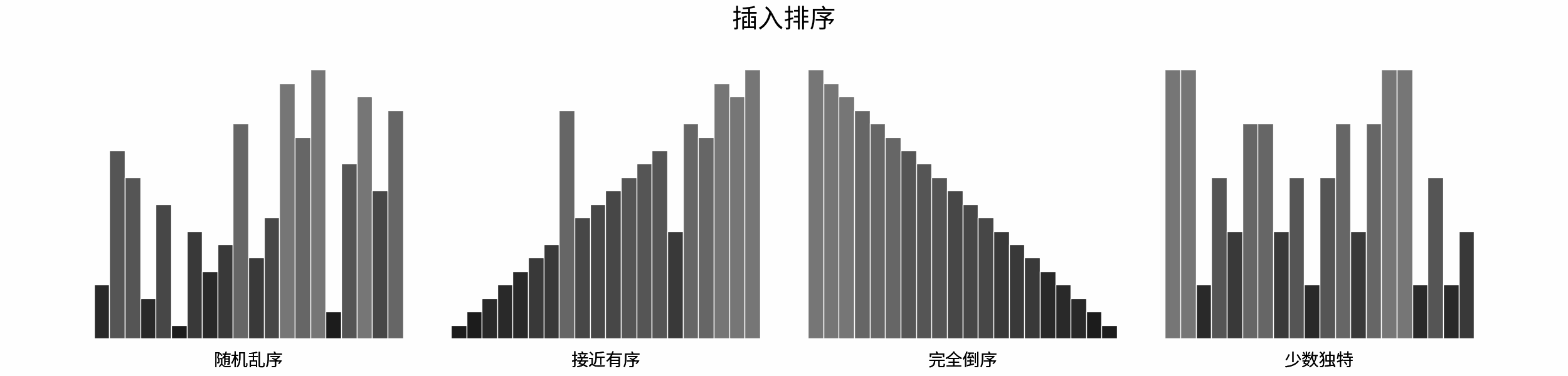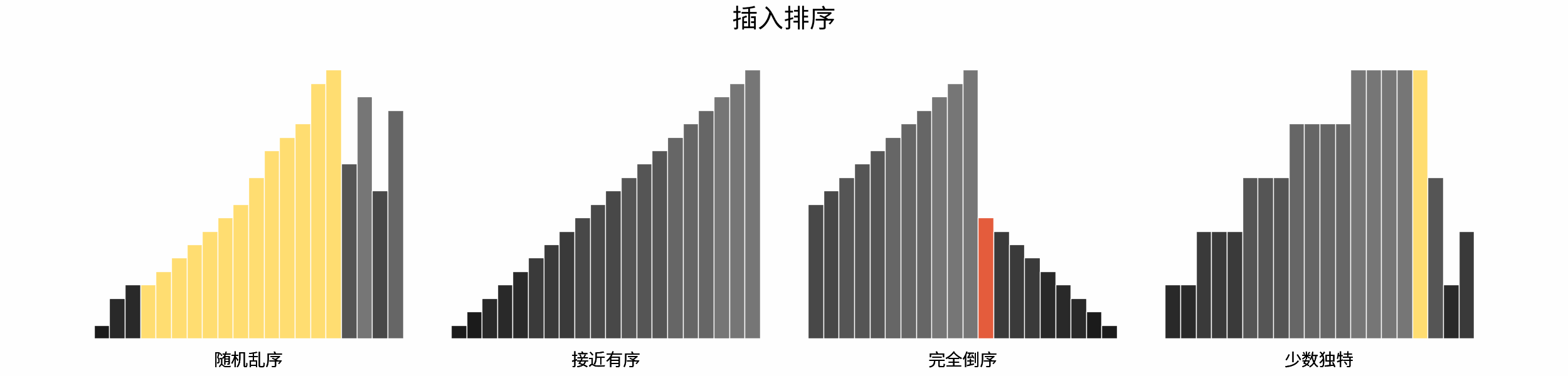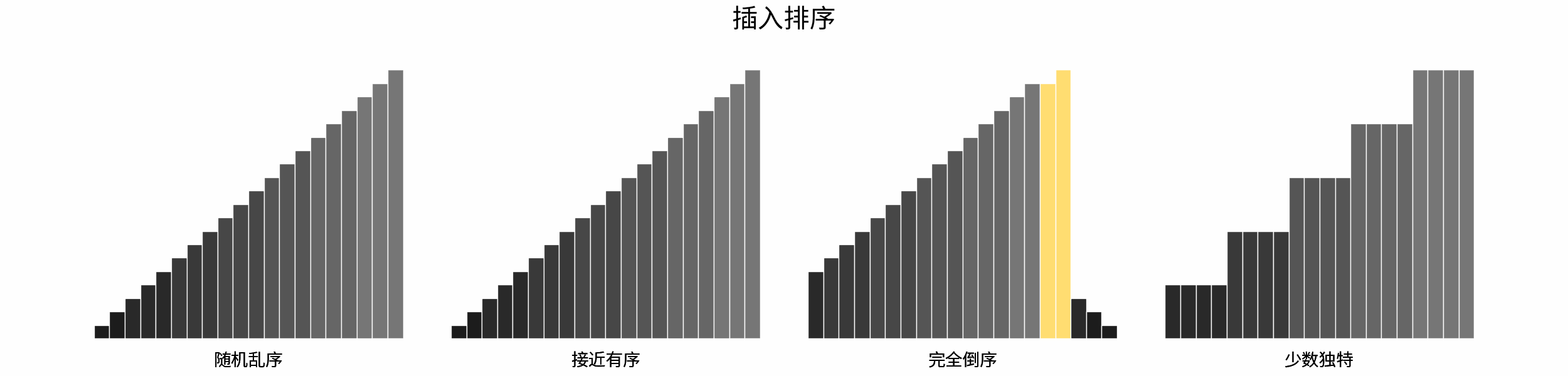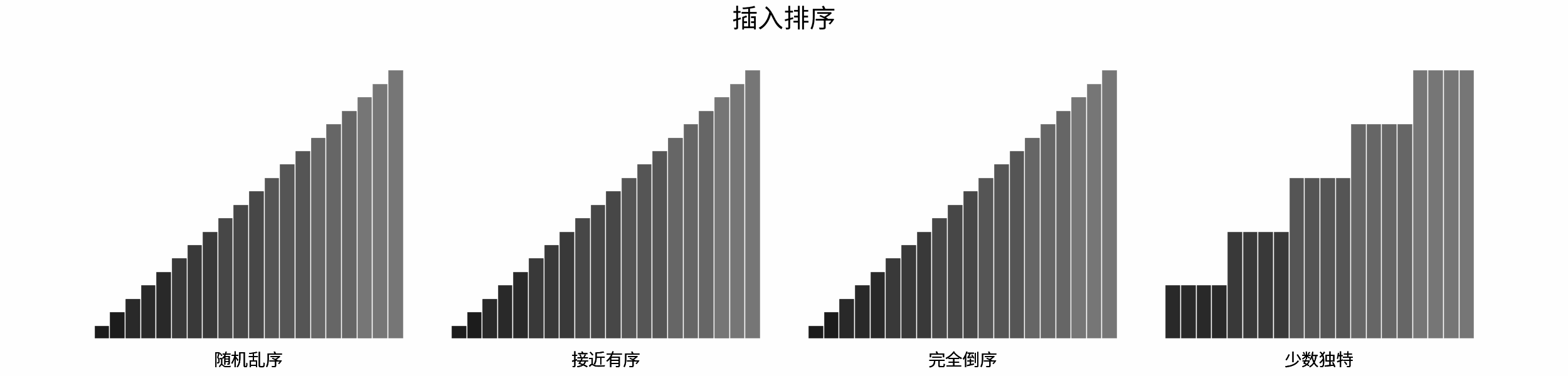
+
+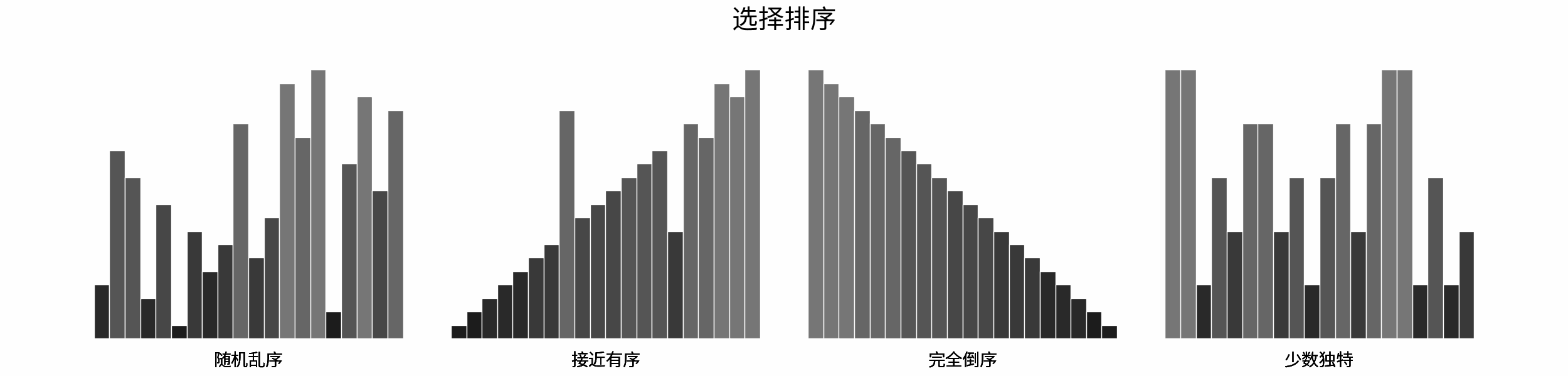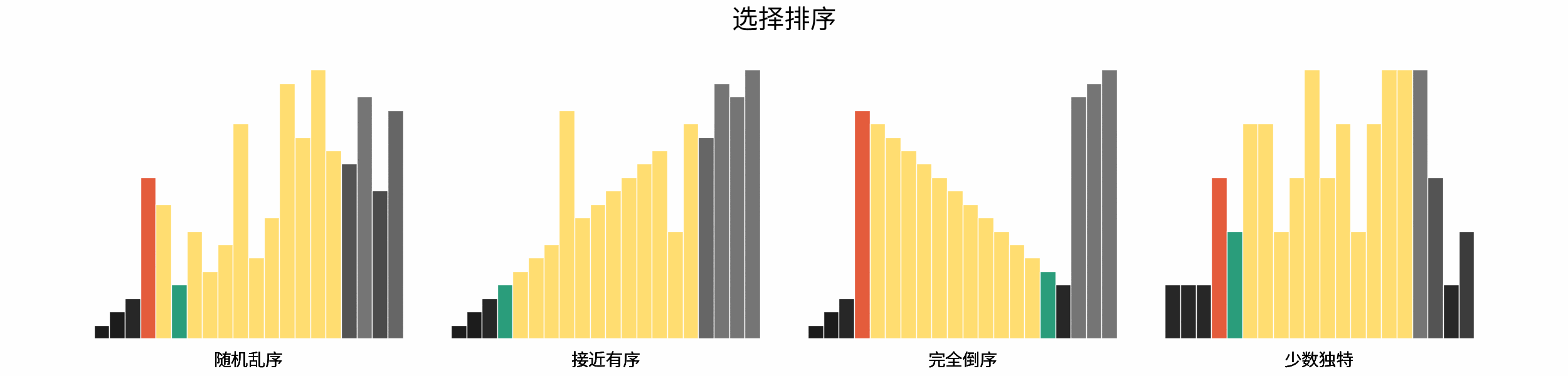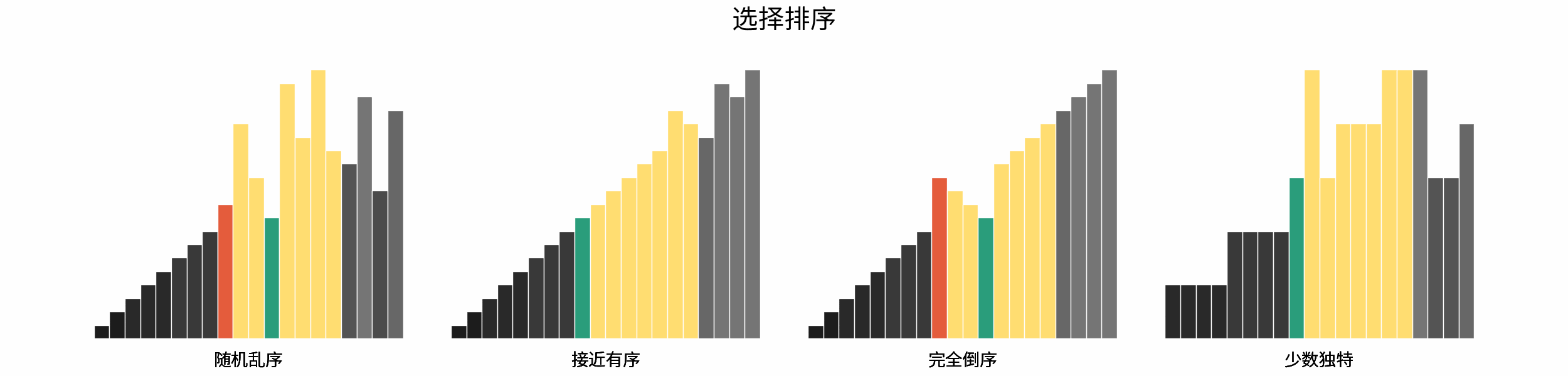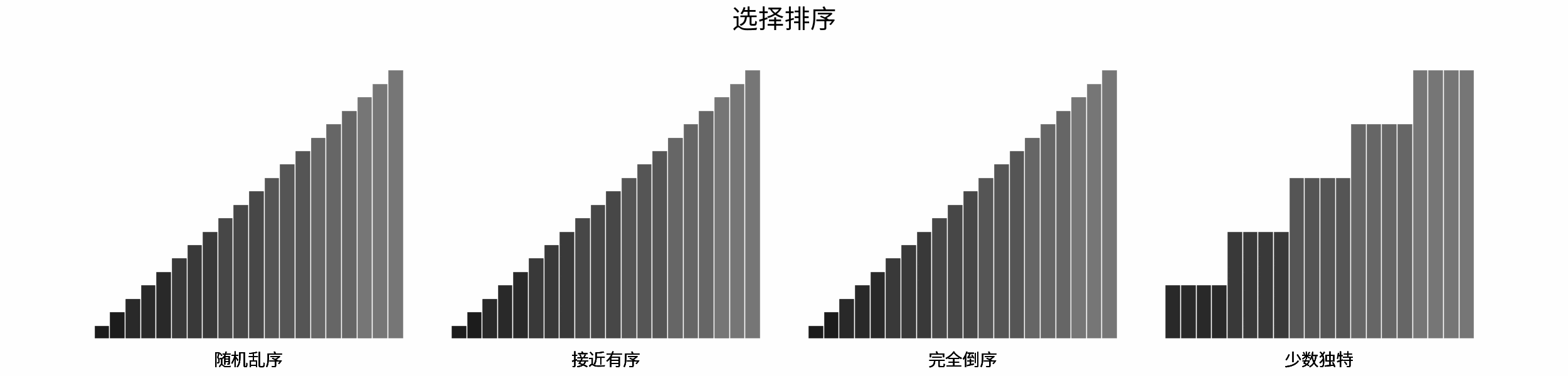
+
+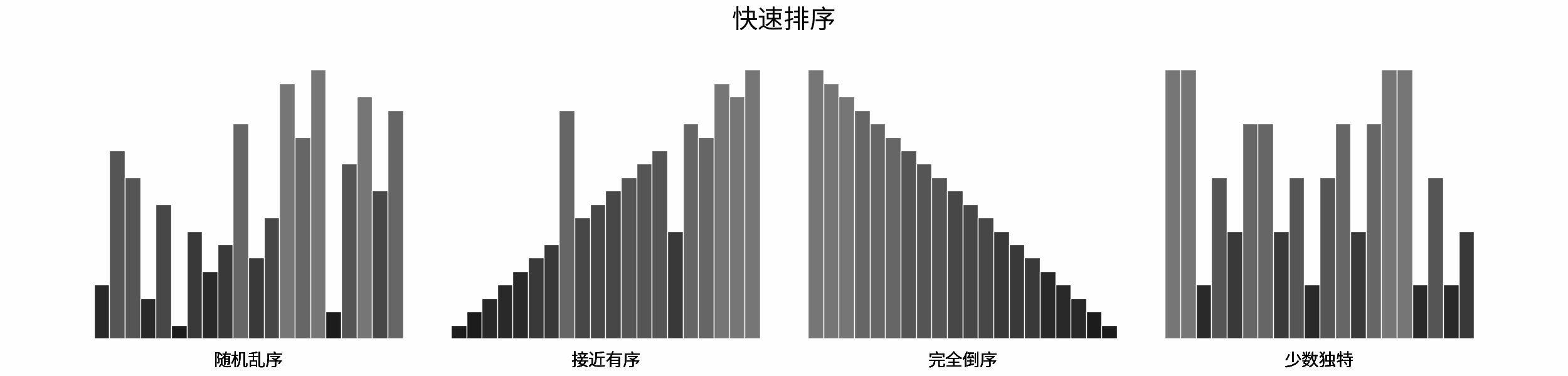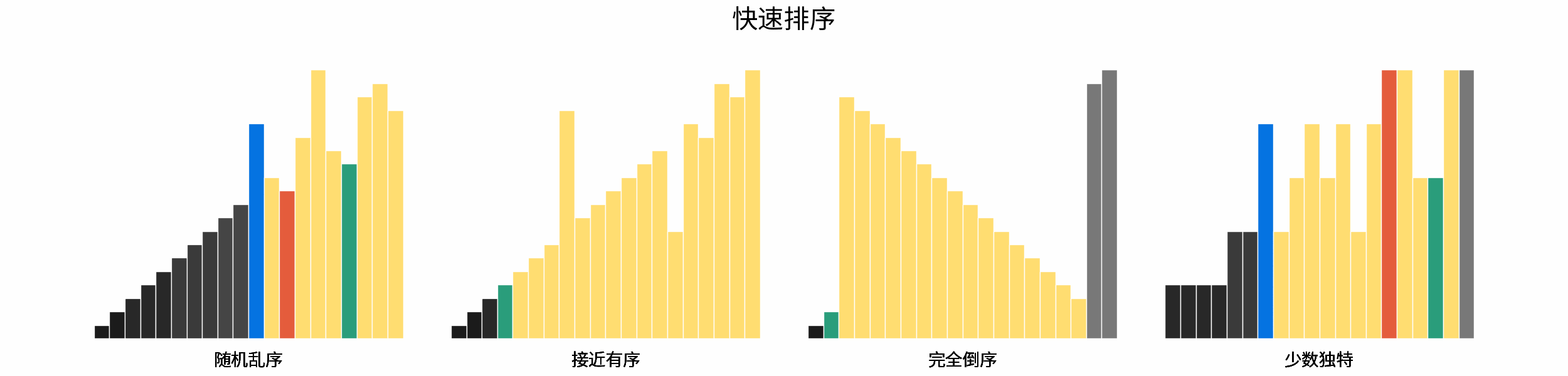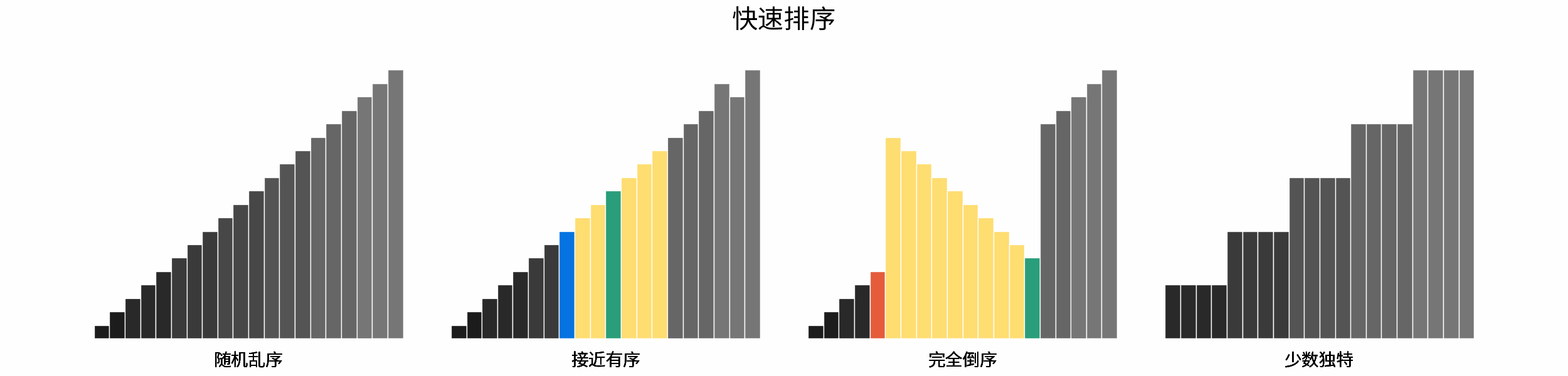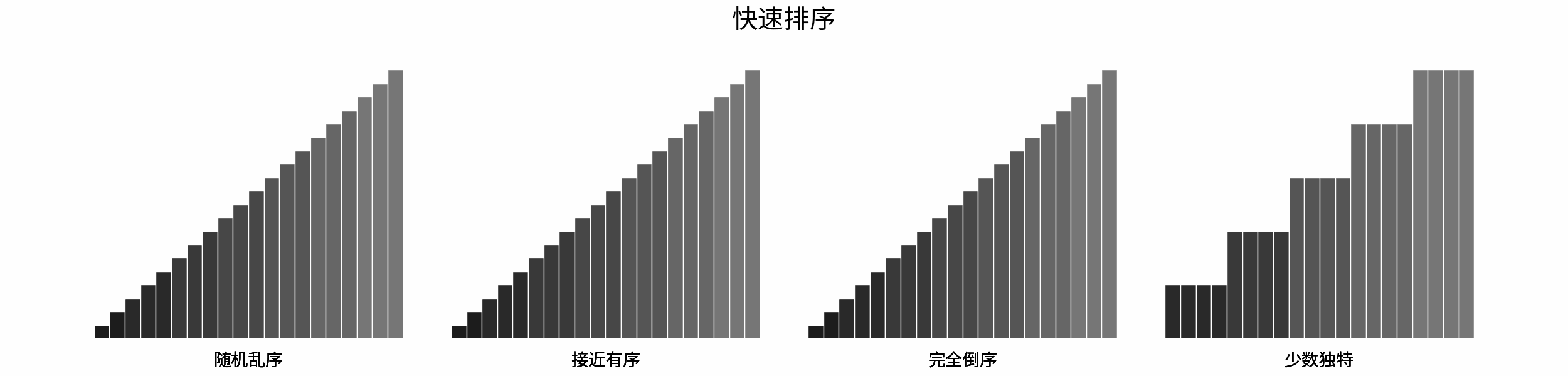
+
+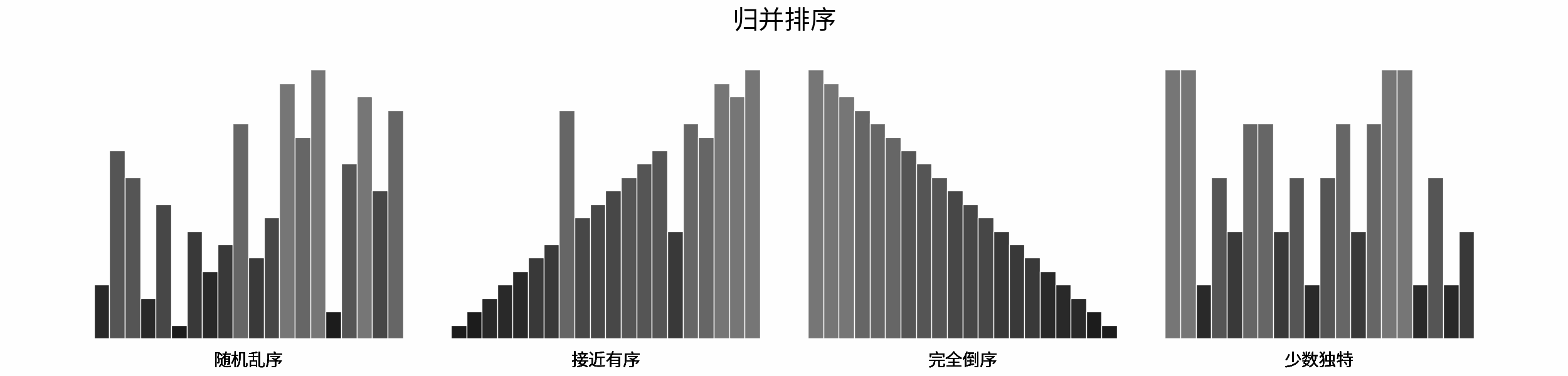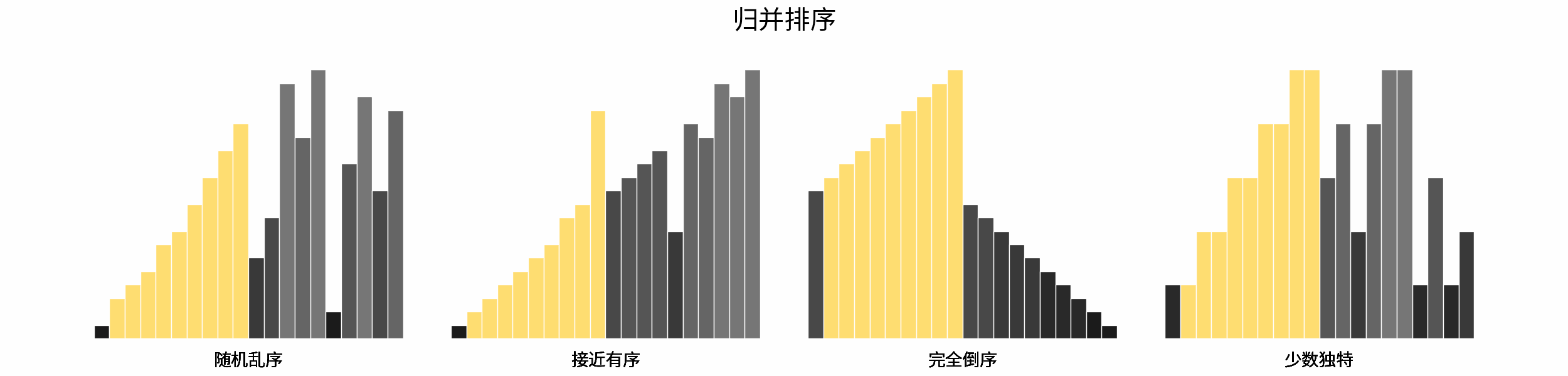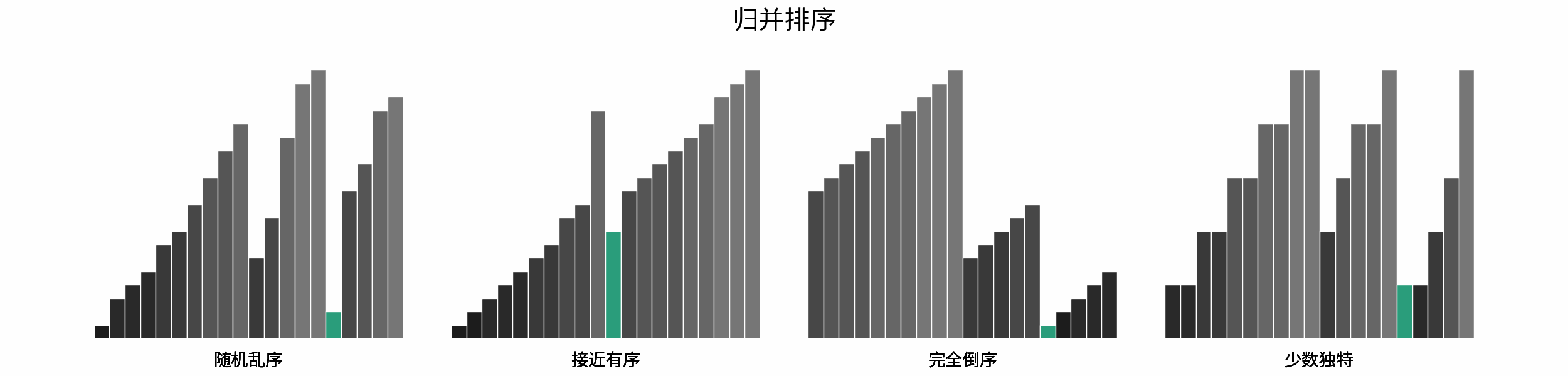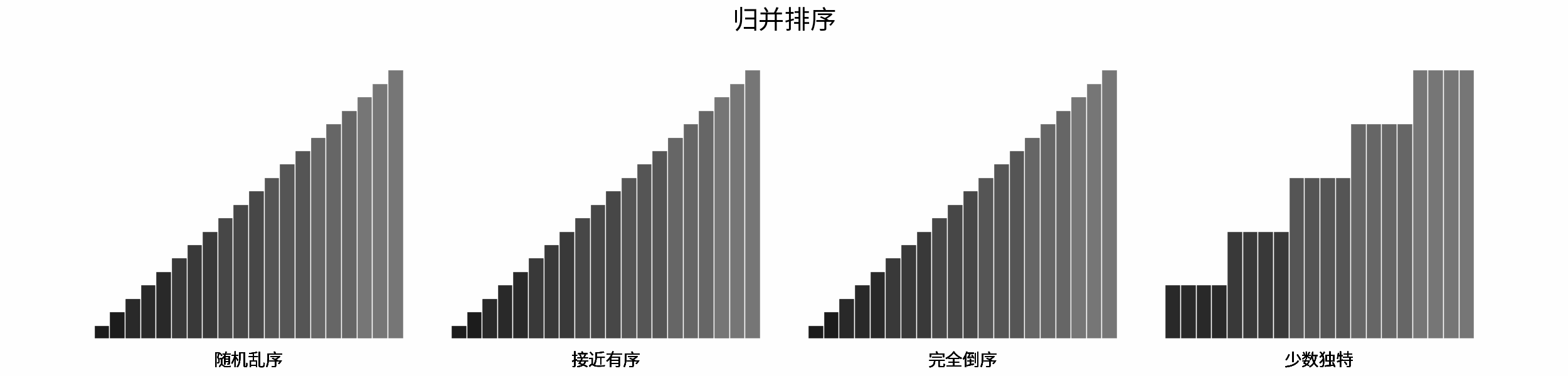
+
+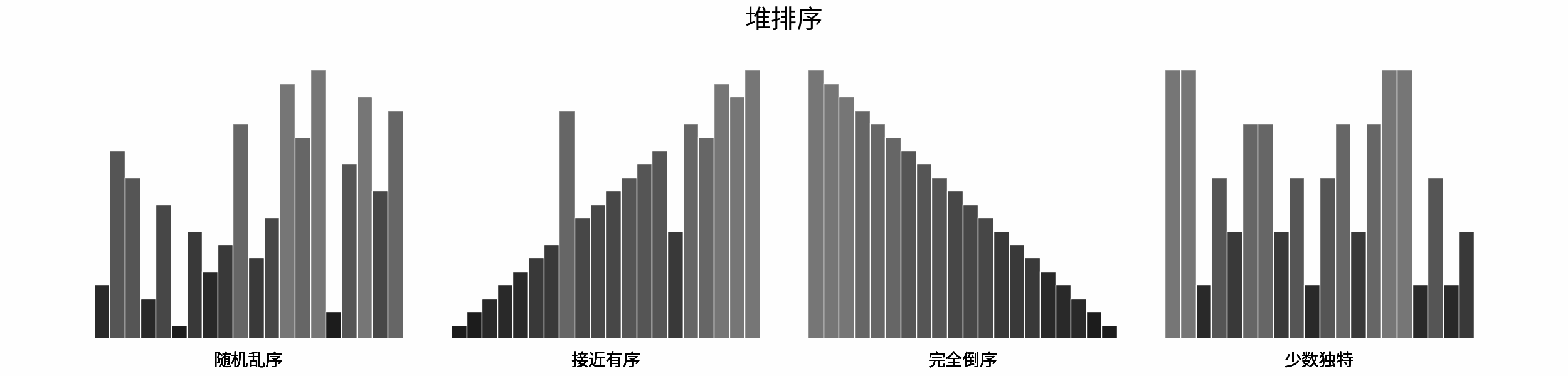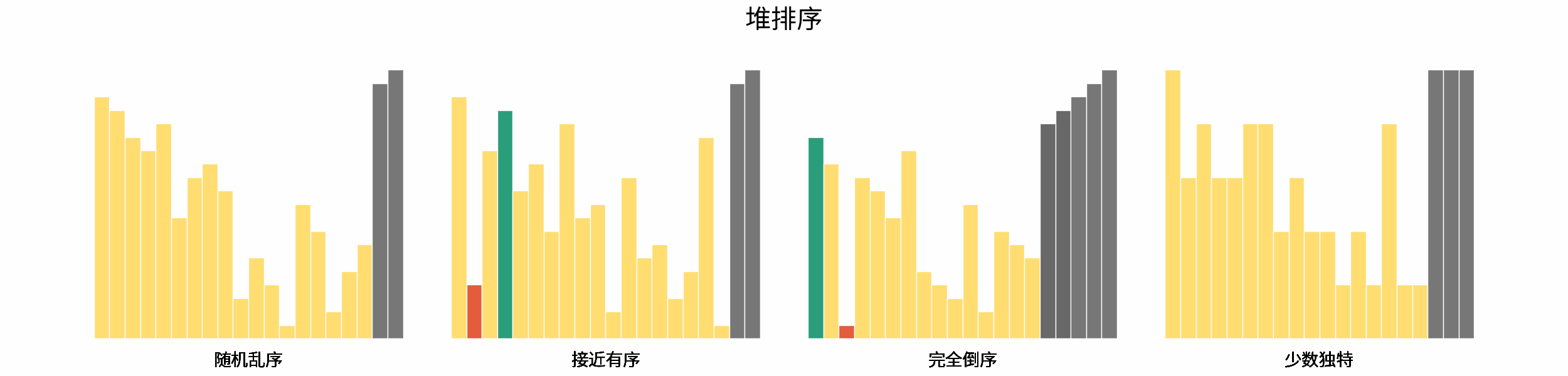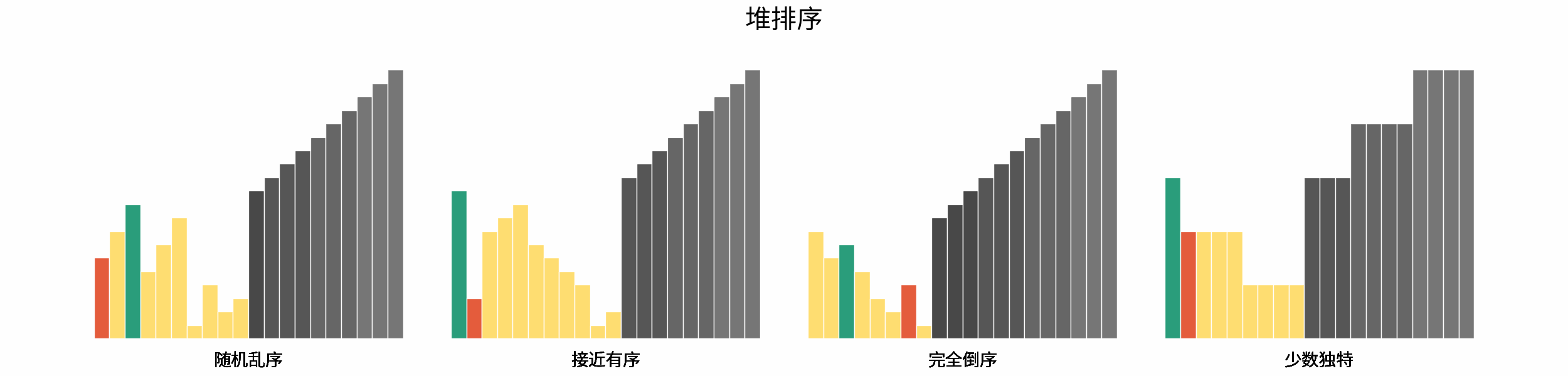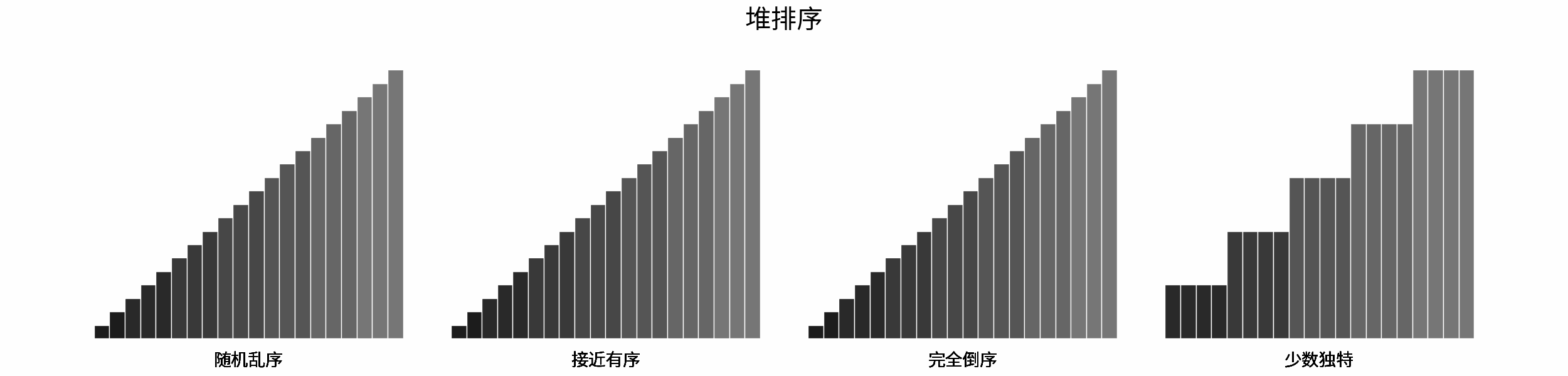
+
+---
+
+## 分类方法
+
+排序算法主要可根据 **稳定性** 、**就地性** 、**自适应性** 分类。理想的排序算法具有以下特性:
+
+- 具有稳定性,即相等元素的相对位置不变化;
+- 具有就地性,即不使用额外的辅助空间;
+- 具有自适应性,即时间复杂度受元素分布影响;
+
+特别地,任意排序算法都 **不同时具有以上所有特性** 。因此,排序算法的选型使用取决于具体的列表类型、元素数量、元素分布情况等应用场景特点。
+
+### 稳定性:
+
+根据 **相等元素** 在数组中的 **相对顺序** 是否被改变,排序算法可分为「稳定排序」和「非稳定排序」两类。
+
+- 「稳定排序」在完成排序后,**不改变** 相等元素在数组中的相对顺序。例如:冒泡排序、插入排序、归并排序、基数排序、桶排序。
+- 「非稳定排序」在完成排序后,相等素在数组中的相对位置 **可能被改变**。例如:选择排序、快速排序、堆排序。
+
+> **何时需考虑排序算法的稳定性?**
+>
+> 数组排序中,由于元素皆为数字,因此稳定和非稳定排序皆可输出相同结果,此时无需考虑排序算法的稳定性。
+>
+> 非稳定排序会改变相等元素的相对次序,这在实际应用场景中可能是不能接受的。如以下代码所示,非稳定排序破坏了输入列表 `people` 按姓名排序的性质。
+>
+> ```Python
+> # 人 = (姓名, 年龄) ,按姓名排序
+> people = [
+> ('A', 19),
+> ('B', 18),
+> ('C', 21),
+> ('D', 19),
+> ('E', 23)
+> ]
+>
+> # 非稳定排序(按年龄)
+> sort_by_age(people)
+>
+> # 人 = (姓名, 年龄) ,按年龄排序
+> people = [
+> ('B', 18),
+> ('D', 19), # ('D', 19) 和 ('A', 19) 的相对位置改变,输入时按姓名排序的性质丢失
+> ('A', 19),
+> ('C', 21),
+> ('E', 23)
+> ]
+> ```
+
+### 就地性:
+
+根据排序过程中 **是否使用额外内存(辅助数组)**,排序算法可分为「原地排序」和「异地排序」两类。一般地,由于不使用外部内存,原地排序相比非原地排序的执行效率更高。
+
+- 「原地排序」不使用额外辅助数组,例如:冒泡排序、插入排序、选择排序、快速排序、堆排序。
+- 「非原地排序」使用额外辅助数组,例如:归并排序、基数排序、桶排序。
+
+### 自适应性:
+
+根据算法 **时间复杂度** 是否 **受待排序数组的元素分布影响** ,排序算法可分为「自适应排序」和「非自适应排序」两类。
+
+- 「自适应排序」的时间复杂度受元素分布影响;例如:冒泡排序、插入排序、快速排序、桶排序。
+- 「非自适应排序」的时间复杂度恒定;例如:选择排序、归并排序、堆排序、基数排序。
+
+### 是否基于比较:
+
+比较类排序基于元素之间的 **比较算子**(小于、相等、大于)来决定元素的相对顺序;相对的,非比较排序则不基于比较算子实现。
+
+- 「基于比较排序」基于元素之间的比较完成排序,例如:冒泡排序、插入排序、选择排序、快速排序、归并排序、堆排序。
+- 「非基于比较排序」不基于元素之间的比较完成排序,例如:基数排序、桶排序。
+
+> 基于比较的排序算法的平均时间复杂度最优为 $O(N \log N)$ ,而非比较排序算法可以达到线性级别的时间复杂度。
+
+---
+
+## 时空复杂度
+
+总体上看,排序算法追求时间与空间复杂度最低。而即使某些排序算法的时间复杂度相等,但实际性能还受 **输入列表性质、元素数量、元素分布等** 等因素影响。
+
+> 设输入列表元素数量为 $N$ ,常见排序算法的「时间复杂度」和「空间复杂度」如下图所示。
+
+| 算法 | 最佳时间 | 平均时间 | 最差时间 | 最差空间 |
+| :------: | :-----------------: | :----------------: | :-----------: | :---------: |
+| 冒泡排序 | $\Omega(N)$ | $\Theta(N^2)$ | $O(N^2)$ | $O(1)$ |
+| 插入排序 | $\Omega(N)$ | $\Theta(N^2)$ | $O(N^2)$ | $O(1)$ |
+| 选择排序 | $\Omega(N^2)$ | $\Theta(N^2)$ | $O(N^2)$ | $O(1)$ |
+| 快速排序 | $\Omega(N \log N )$ | $\Theta(N \log N)$ | $O(N^2)$ | $O(\log N)$ |
+| 归并排序 | $\Omega(N \log N)$ | $\Theta(N \log N)$ | $O(N \log N)$ | $O(N)$ |
+| 堆排序 | $\Omega(N \log N)$ | $\Theta(N \log N)$ | $O(N \log N)$ | $O(1)$ |
+| 基数排序 | $\Omega(Nk)$ | $\Theta(Nk)$ | $O(Nk)$ | $O(N + k)$ |
+| 桶排序 | $\Omega(N + k)$ | $\Theta(N + k)$ | $O(N^2)$ | $O(N)$ |
+
+对于上表,需要特别注意:
+
+- 「基数排序」适用于正整数、字符串、特定格式的浮点数排序,$k$ 为最大数字的位数;「桶排序」中 $k$ 为桶的数量。
+- 普通「冒泡排序」的最佳时间复杂度为 $O(N^2)$ ,通过增加标志位实现 **提前返回** ,可以将最佳时间复杂度降低至 $O(N)$ 。
+- 在输入列表完全倒序下,普通「快速排序」的空间复杂度劣化至 $O(N)$ ,通过代码优化 **尾递归优化** 保持算法递归较短子数组,可以将最差递归深度降低至 $\log N$ 。
+- 普通「快速排序」总以最左或最右元素为基准数,因此在输入列表有序或倒序下,时间复杂度劣化至 $O(N^2)$ ;通过 **随机选择基准数** ,可极大减少此类最差情况发生,尽可能地保持 $O(N \log N)$ 的时间复杂度。
+- 若输入列表是数组,则归并排序的空间复杂度为 $O(N)$ ;而若排序 **链表** ,则「归并排序」不需要借助额外辅助空间,空间复杂度可以降低至 $O(1)$ 。
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 7.2 \345\206\222\346\263\241\346\216\222\345\272\217.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 7.2 \345\206\222\346\263\241\346\216\222\345\272\217.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..98e9fe1
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 7.2 \345\206\222\346\263\241\346\216\222\345\272\217.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,125 @@
+# 冒泡排序
+
+冒泡排序是最基础的排序算法,由于其直观性,经常作为首个介绍的排序算法。其原理为:
+
+- **内循环:** 使用相邻双指针 `j` , `j + 1` 从左至右遍历,依次比较相邻元素大小,若左元素大于右元素则将它们交换;遍历完成时,**最大元素会被交换至数组最右边** 。
+- **外循环:** 不断重复「内循环」,每轮将当前最大元素交换至 **剩余未排序数组最右边** ,直至所有元素都被交换至正确位置时结束。
+
+如下图所示,首轮「内循环」后,数组最大元素已被交换至数组最右边;接下来,只需要完成数组剩余 $N - 1$ 个元素的排序即可(设数组元素数量为 $N$ )。同理,对剩余 $N - 1$ 个元素执行「内循环」,可将第二大元素交换至剩余数组最右端,以此类推……
+
+
+
+如下图所示,冒泡排序的「外循环」共 $N - 1$ 轮,每轮「内循环」都将当前最大元素交换至数组最右边,从而完成对整个数组的排序。
+
+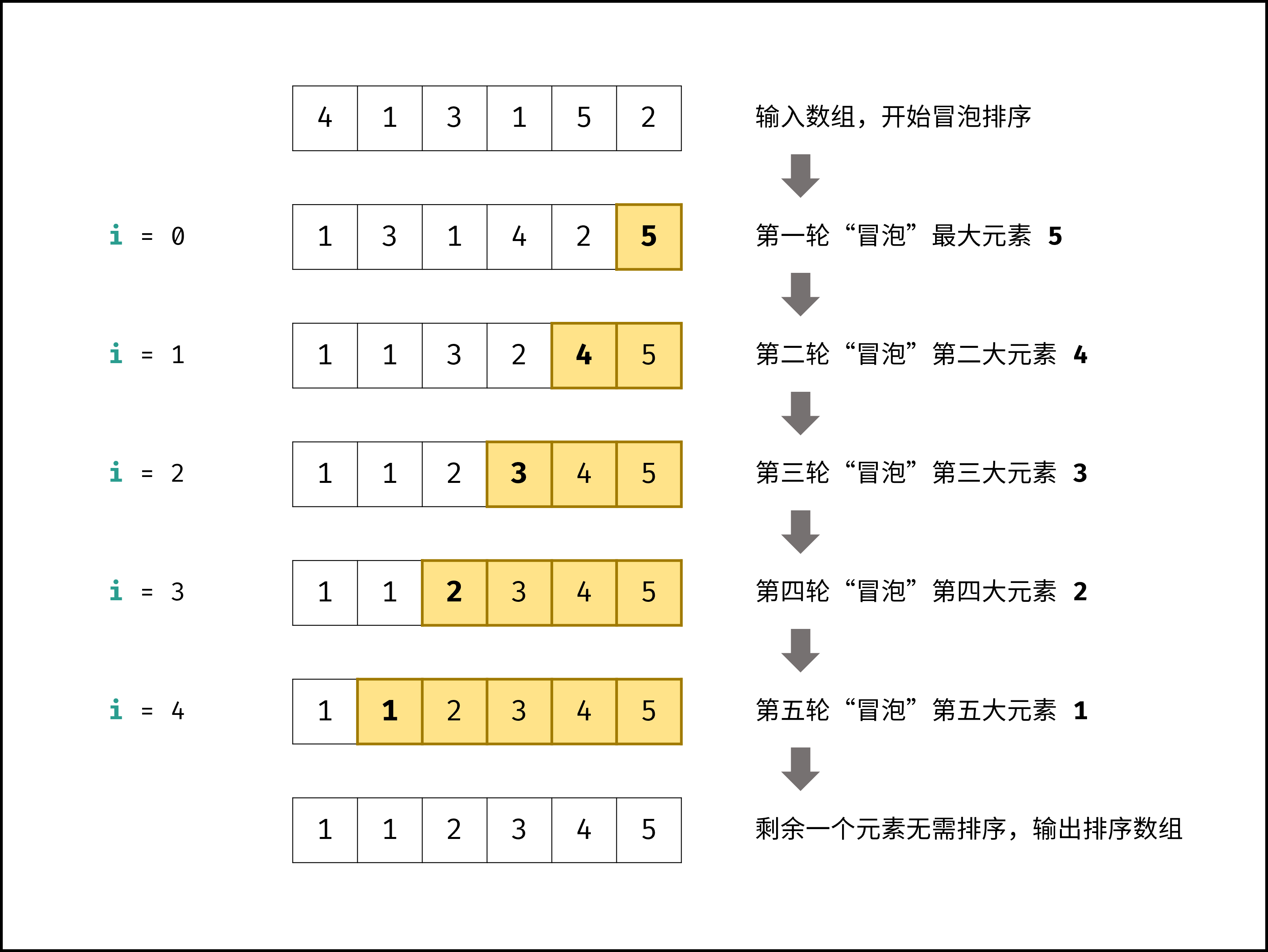{:width=550}
+
+如下图所示,为示例数组 `nums = [4, 1, 3, 1, 5, 2]` 的冒泡排序算法运行过程。
+
+
+
+## 代码
+
+```Python []
+def bubble_sort(nums):
+ N = len(nums)
+ for i in range(N - 1): # 外循环
+ for j in range(N - i - 1): # 内循环
+ if nums[j] > nums[j + 1]:
+ # 交换 nums[j], nums[j + 1]
+ nums[j], nums[j + 1] = nums[j + 1], nums[j]
+```
+
+```Java []
+void bubbleSort(int[] nums) {
+ int N = nums.length;
+ for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) { // 外循环
+ for (int j = 0; j < N - i - 1; j++) { // 内循环
+ if (nums[j] > nums[j + 1]) {
+ // 交换 nums[j], nums[j + 1]
+ int tmp = nums[j];
+ nums[j] = nums[j + 1];
+ nums[j + 1] = tmp;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+void bubbleSort(vector &nums) {
+ int N = nums.size();
+ for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) { // 外循环
+ for (int j = 0; j < N - i - 1; j++) { // 内循环
+ if (nums[j] > nums[j + 1]) {
+ // 交换 nums[j], nums[j + 1]
+ swap(nums[j], nums[j + 1]);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+## 算法特性
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(N^2)$ :**
+ - **最佳 $\Omega(N)$ :** 普通冒泡排序的时间复杂度恒为 $O(N^2)$ ,对于近似排序数组,通过加入标志位可实现提前返回(详情请见下文)。
+ - **平均与最差 $O(N^2)$ :**「外循环」共 $N - 1$ 轮,使用 $O(N)$ 时间;每轮「内循环」分别遍历 $N - 1$ , $N - 2$ , $\cdots$ , $2$ , $1$ 次,平均 $\frac{N}{2}$ 次,使用 $O(\frac{N}{2}) = O(N)$ 时间;因此,总体时间复杂度为 $O(N^2)$ 。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(1)$ :** 只需原地交换元素,使用常数大小的额外空间。
+- 冒泡排序是通过不断 **交换元素** 实现排序(交换 2 个元素需要 3 次赋值操作),因此速度较慢;
+- **原地:** 指针变量仅使用常数大小额外空间,空间复杂度为 $O(1)$ ;
+- **稳定:** 元素值相同时不交换,因此不会改变相同元素的相对位置;
+- **自适应:** 通过增加一个标志位 `flag` ,若某轮内循环未执行任何交换操作时,说明已经完成排序,因此直接返回。此优化使冒泡排序的最优时间复杂度达到 $O(N)$(当输入数组已排序时);
+
+## 标志位优化
+
+> 普通冒泡排序的时间复杂度恒为 $O(N^2)$ ,与输入数组的元素分布无关。
+
+通过增加一个标志位 `flag` ,若在某轮「内循环」中未执行任何交换操作,则说明数组已经完成排序,直接返回结果即可。
+
+优化后的冒泡排序的最差和平均时间复杂度仍为 $O(N^2)$ ;在输入数组 **已排序** 时,达到 **最佳时间复杂度** $\Omega(N)$ 。
+
+```Python []
+def bubble_sort(nums):
+ N = len(nums)
+ for i in range(N - 1):
+ flag = False # 初始化标志位
+ for j in range(N - i - 1):
+ if nums[j] > nums[j + 1]:
+ nums[j], nums[j + 1] = nums[j + 1], nums[j]
+ flag = True # 记录交换元素
+ if not flag: break # 内循环未交换任何元素,则跳出
+```
+
+```Java []
+void bubbleSort(int[] nums) {
+ int N = nums.length;
+ for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
+ boolean flag = false; // 初始化标志位
+ for (int j = 0; j < N - i - 1; j++) {
+ if (nums[j] > nums[j + 1]) {
+ int tmp = nums[j];
+ nums[j] = nums[j + 1];
+ nums[j + 1] = tmp;
+ flag = true; // 记录交换元素
+ }
+ }
+ if (!flag) break; // 内循环未交换任何元素,则跳出
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+void bubbleSort(vector &nums) {
+ int N = nums.size();
+ for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
+ bool flag = false; // 初始化标志位
+ for (int j = 0; j < N - i - 1; j++) {
+ if (nums[j] > nums[j + 1]) {
+ swap(nums[j], nums[j + 1]);
+ flag = true; // 记录交换元素
+ }
+ }
+ if (!flag) break; // 内循环未交换任何元素,则跳出
+ }
+}
+```
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 7.3 \345\277\253\351\200\237\346\216\222\345\272\217.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 7.3 \345\277\253\351\200\237\346\216\222\345\272\217.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..fad9abb
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 7.3 \345\277\253\351\200\237\346\216\222\345\272\217.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,244 @@
+# 快速排序
+
+快速排序算法有两个核心点,分别为 **哨兵划分** 和 **递归** 。
+
+**哨兵划分**:以数组某个元素(一般选取首元素)为 **基准数** ,将所有小于基准数的元素移动至其左边,大于基准数的元素移动至其右边。
+
+> 下图展示了哨兵划分操作流程。经过一轮 **哨兵划分** ,可将数组排序问题拆分为 **两个较短数组的排序问题** (本文称之为左(右)子数组)。
+
+
+
+**递归**:对 **左子数组** 和 **右子数组** 分别递归执行 **哨兵划分**,直至子数组长度为 1 时终止递归,即可完成对整个数组的排序。
+
+> 下图展示了数组 `[2,4,1,0,3,5]` 的快速排序流程。观察发现,快速排序和 **二分法** 的原理类似,都是以 $\log$ 时间复杂度实现搜索区间缩小。
+
+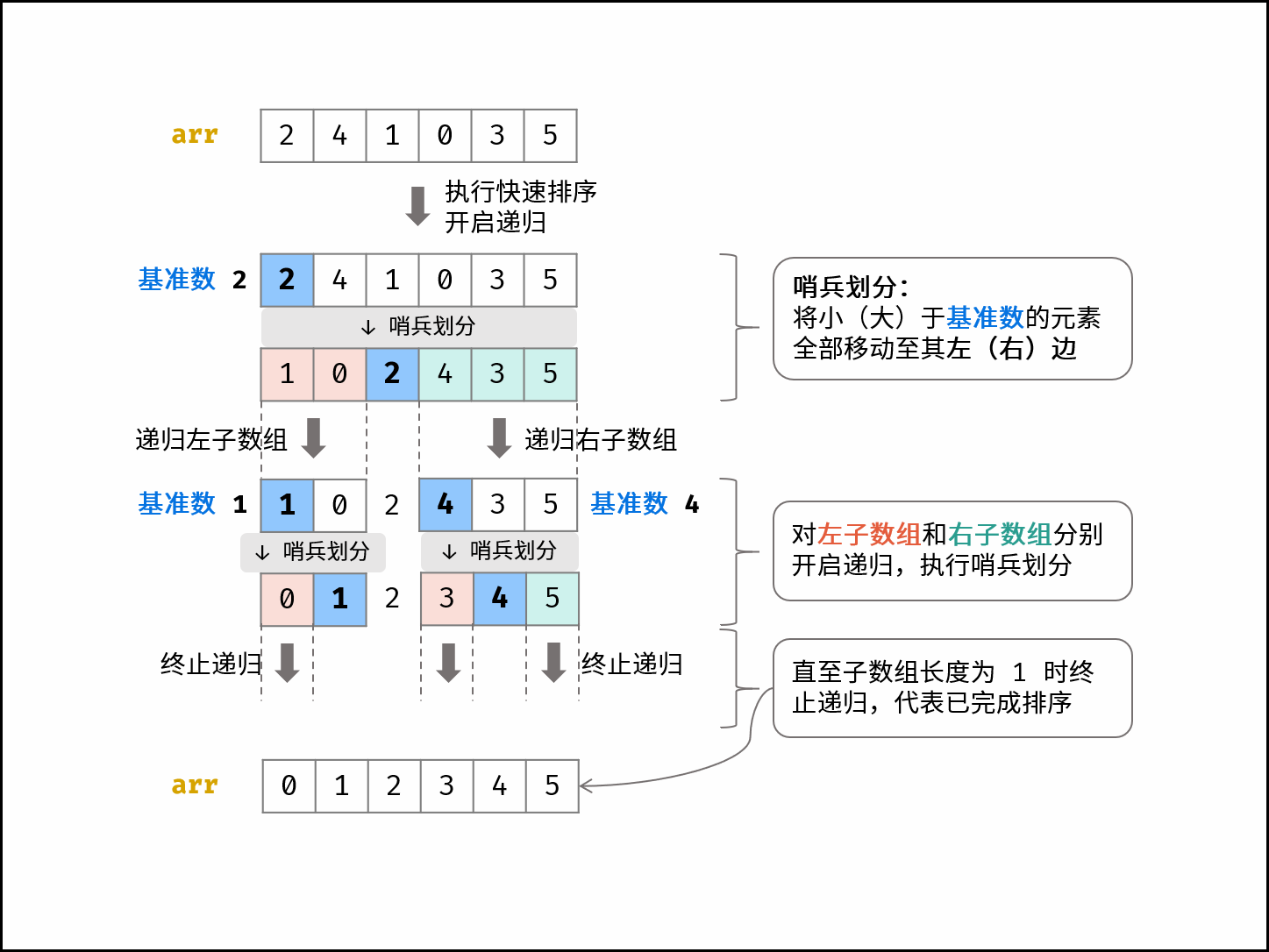{:width=550}
+
+## 代码
+
+```Python []
+def quick_sort(nums, l, r):
+ # 子数组长度为 1 时终止递归
+ if l >= r: return
+ # 哨兵划分操作
+ i = partition(nums, l, r)
+ # 递归左(右)子数组执行哨兵划分
+ quick_sort(nums, l, i - 1)
+ quick_sort(nums, i + 1, r)
+
+def partition(nums, l, r):
+ # 以 nums[l] 作为基准数
+ i, j = l, r
+ while i < j:
+ while i < j and nums[j] >= nums[l]: j -= 1
+ while i < j and nums[i] <= nums[l]: i += 1
+ nums[i], nums[j] = nums[j], nums[i]
+ nums[l], nums[i] = nums[i], nums[l]
+ return i
+
+# 调用
+nums = [3, 4, 1, 5, 2]
+quick_sort(nums, 0, len(nums) - 1)
+```
+
+```Java []
+void quickSort(int[] nums, int l, int r) {
+ // 子数组长度为 1 时终止递归
+ if (l >= r) return;
+ // 哨兵划分操作
+ int i = partition(nums, l, r);
+ // 递归左(右)子数组执行哨兵划分
+ quickSort(nums, l, i - 1);
+ quickSort(nums, i + 1, r);
+}
+
+int partition(int[] nums, int l, int r) {
+ // 以 nums[l] 作为基准数
+ int i = l, j = r;
+ while (i < j) {
+ while (i < j && nums[j] >= nums[l]) j--;
+ while (i < j && nums[i] <= nums[l]) i++;
+ swap(nums, i, j);
+ }
+ swap(nums, i, l);
+ return i;
+}
+
+void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
+ // 交换 nums[i] 和 nums[j]
+ int tmp = nums[i];
+ nums[i] = nums[j];
+ nums[j] = tmp;
+}
+
+// 调用
+int[] nums = { 4, 1, 3, 2, 5 };
+quickSort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int partition(vector& nums, int l, int r) {
+ // 以 nums[l] 作为基准数
+ int i = l, j = r;
+ while (i < j) {
+ while (i < j && nums[j] >= nums[l]) j--;
+ while (i < j && nums[i] <= nums[l]) i++;
+ swap(nums[i], nums[j]);
+ }
+ swap(nums[i], nums[l]);
+ return i;
+}
+
+void quickSort(vector& nums, int l, int r) {
+ // 子数组长度为 1 时终止递归
+ if (l >= r) return;
+ // 哨兵划分操作
+ int i = partition(nums, l, r);
+ // 递归左(右)子数组执行哨兵划分
+ quickSort(nums, l, i - 1);
+ quickSort(nums, i + 1, r);
+}
+
+// 调用
+vector nums = { 4, 1, 3, 2, 5, 1 };
+quickSort(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1);
+```
+
+## 算法特性
+
+- **时间复杂度:**
+ - **最佳 $\Omega(N \log N )$ :** 最佳情况下, 每轮哨兵划分操作将数组划分为等长度的两个子数组;哨兵划分操作为线性时间复杂度 $O(N)$ ;递归轮数共 $O(\log N)$ 。
+ - **平均 $\Theta(N \log N)$ :** 对于随机输入数组,哨兵划分操作的递归轮数也为 $O(\log N)$ 。
+ - **最差 $O(N^2)$ :** 对于某些特殊输入数组,每轮哨兵划分操作都将长度为 $N$ 的数组划分为长度为 $1$ 和 $N - 1$ 的两个子数组,此时递归轮数达到 $N$ 。
+ > 通过 「随机选择基准数」优化,可尽可能避免出现最差情况,详情请见下文。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(N)$ :** 快速排序的递归深度最好与平均皆为 $\log N$ ;输入数组完全倒序下,达到最差递归深度 $N$ 。
+ > 通过「尾递归」优化,可将最差空间复杂度降低至 $O(\log N)$ ,详情请见下文。
+- 虽然平均时间复杂度与「归并排序」和「堆排序」一致,但在实际使用中快速排序 **效率更高** ,这是因为:
+ - **最差情况稀疏性:** 虽然快速排序的最差时间复杂度为 $O(N^2)$ ,差于归并排序和堆排序,但统计意义上看,这种情况出现的机率很低。大部分情况下,快速排序以 $O(N \log N)$ 复杂度运行。
+ - **缓存使用效率高:** 哨兵划分操作时,将整个子数组加载入缓存中,访问元素效率很高;堆排序需要跳跃式访问元素,因此不具有此特性。
+ - **常数系数低:** 在提及的三种算法中,快速排序的 **比较**、**赋值**、**交换** 三种操作的综合耗时最低(类似于插入排序快于冒泡排序的原理)。
+- **原地:** 不用借助辅助数组的额外空间,递归仅使用 $O(\log N)$ 大小的栈帧空间。
+- **非稳定:** 哨兵划分操作可能改变相等元素的相对顺序。
+- **自适应:** 对于极少输入数据,每轮哨兵划分操作都将长度为 $N$ 的数组划分为长度 $1$ 和 $N - 1$ 两个子数组,此时时间复杂度劣化至 $O(N^2)$ 。
+
+## 算法优化
+
+快速排序的常见优化手段有「尾递归」和「随机基准数」两种。
+
+### 尾递归:
+
+由于普通快速排序每轮选取「子数组最左元素」作为「基准数」,因此在输入数组 **完全倒序** 时, `partition()` 的递归深度会达到 $N$ ,即 **最差空间复杂度** 为 $O(N)$ 。
+
+每轮递归时,仅对 **较短的子数组** 执行哨兵划分 `partition()` ,就可将最差的递归深度控制在 $O(\log N)$ (每轮递归的子数组长度都 $\leq$ 当前数组长度 $/ 2$ ),即实现最差空间复杂度 $O(\log N)$ 。
+
+> 代码仅需修改 `quick_sort()` 方法,其余方法不变,在此省略。
+
+```Python []
+def quick_sort(nums, l, r):
+ # 子数组长度为 1 时终止递归
+ while l < r:
+ # 哨兵划分操作
+ i = partition(nums, l, r)
+ # 仅递归至较短子数组,控制递归深度
+ if i - l < r - i:
+ quick_sort(nums, l, i - 1)
+ l = i + 1
+ else:
+ quick_sort(nums, i + 1, r)
+ r = i - 1
+```
+
+```Java []
+void quickSort(int[] nums, int l, int r) {
+ // 子数组长度为 1 时终止递归
+ while (l < r) {
+ // 哨兵划分操作
+ int i = partition(nums, l, r);
+ // 仅递归至较短子数组,控制递归深度
+ if (i - l < r - i) {
+ quickSort(nums, l, i - 1);
+ l = i + 1;
+ } else {
+ quickSort(nums, i + 1, r);
+ r = i - 1;
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+void quickSort(vector& nums, int l, int r) {
+ // 子数组长度为 1 时终止递归
+ while (l < r) {
+ // 哨兵划分操作
+ int i = partition(nums, l, r);
+ // 仅递归至较短子数组,控制递归深度
+ if (i - l < r - i) {
+ quickSort(nums, l, i - 1);
+ l = i + 1;
+ } else {
+ quickSort(nums, i + 1, r);
+ r = i - 1;
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### 随机基准数:
+
+同样地,由于快速排序每轮选取「子数组最左元素」作为「基准数」,因此在输入数组 **完全有序** 或 **完全倒序** 时, `partition()` 每轮只划分一个元素,达到最差时间复杂度 $O(N^2)$ 。
+
+因此,可使用 **随机函数** ,每轮在子数组中随机选择一个元素作为基准数,这样就可以极大概率避免以上劣化情况。
+
+值得注意的是,由于仍然可能出现最差情况,因此快速排序的最差时间复杂度仍为 $O(N^2)$ 。
+
+> 代码仅需修改 `partition()` 方法,其余方法不变,在此省略。
+
+```Python []
+def partition(nums, l, r):
+ # 在闭区间 [l, r] 随机选取任意索引,并与 nums[l] 交换
+ ra = random.randrange(l, r + 1)
+ nums[l], nums[ra] = nums[ra], nums[l]
+ # 以 nums[l] 作为基准数
+ i, j = l, r
+ while i < j:
+ while i < j and nums[j] >= nums[l]: j -= 1
+ while i < j and nums[i] <= nums[l]: i += 1
+ nums[i], nums[j] = nums[j], nums[i]
+ nums[l], nums[i] = nums[i], nums[l]
+ return i
+```
+
+```Java []
+int partition(int[] nums, int l, int r) {
+ // 在闭区间 [l, r] 随机选取任意索引,并与 nums[l] 交换
+ int ra = (int)(l + Math.random() * (r - l + 1));
+ swap(nums, l, ra);
+ // 以 nums[l] 作为基准数
+ int i = l, j = r;
+ while (i < j) {
+ while (i < j && nums[j] >= nums[l]) j--;
+ while (i < j && nums[i] <= nums[l]) i++;
+ swap(nums, i, j);
+ }
+ swap(nums, i, l);
+ return i;
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int partition(vector& nums, int l, int r) {
+ // 在闭区间 [l, r] 随机选取任意索引,并与 nums[l] 交换
+ int ra = l + rand() % (r - l + 1);
+ swap(nums[l], nums[ra]);
+ // 以 nums[l] 作为基准数
+ int i = l, j = r;
+ while (i < j) {
+ while (i < j && nums[j] >= nums[l]) j--;
+ while (i < j && nums[i] <= nums[l]) i++;
+ swap(nums[i], nums[j]);
+ }
+ swap(nums[i], nums[l]);
+ return i;
+}
+```
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 7.4 \345\275\222\345\271\266\346\216\222\345\272\217.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 7.4 \345\275\222\345\271\266\346\216\222\345\272\217.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..5c0ceaf
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/# 7.4 \345\275\222\345\271\266\346\216\222\345\272\217.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
+# 归并排序
+
+归并排序体现了 “分而治之” 的算法思想,具体为:
+
+- **「分」:** 不断将数组从 **中点位置** 划分开,将原数组的排序问题转化为子数组的排序问题;
+- **「治」:** 划分到子数组长度为 1 时,开始向上合并,不断将 **左右两个较短排序数组** 合并为 **一个较长排序数组**,直至合并至原数组时完成排序;
+
+> 如下图所示,为数组 `[7,3,2,6,0,1,5,4]` 的归并排序过程。
+
+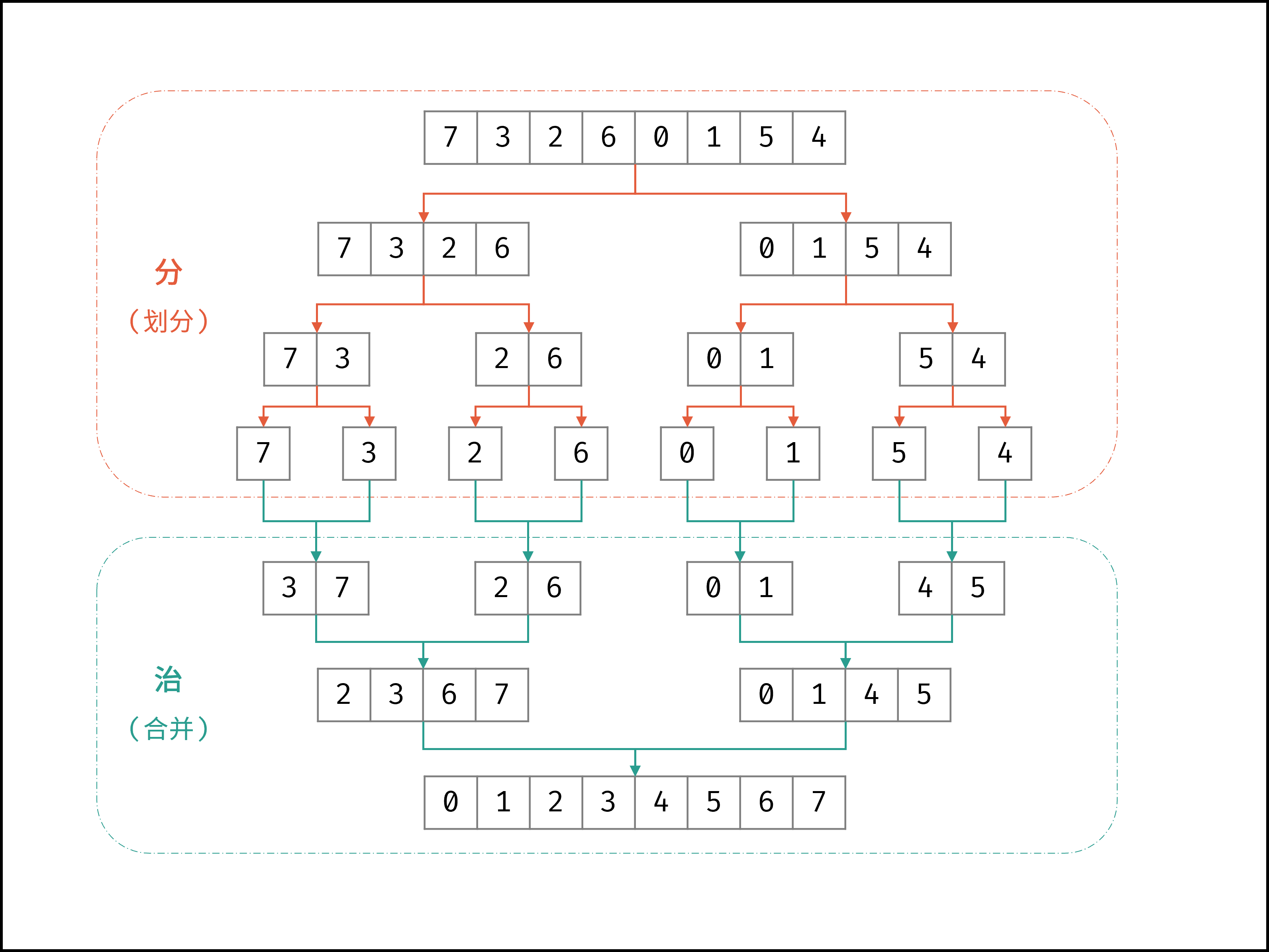{:width=500}
+
+## 算法流程
+
+1. **递归划分:**
+ 1. 计算数组中点 $m$ ,递归划分左子数组 `merge_sort(l, m)` 和右子数组 `merge_sort(m + 1, r)` ;
+ 2. 当 $l \geq r$ 时,代表子数组长度为 1 或 0 ,此时 **终止划分** ,开始合并;
+
+2. **合并子数组:**
+ 1. 暂存数组 $nums$ 闭区间 $[l, r]$ 内的元素至辅助数组 $tmp$ ;
+ 2. **循环合并:** 设置双指针 $i$ , $j$ 分别指向 $tmp$ 的左 / 右子数组的首元素;
+ > **注意:** $nums$ 子数组的左边界、中点、右边界分别为 $l$ , $m$ , $r$ ,而辅助数组 $tmp$ 中的对应索引为 $0$ , $m - l$ , $r - l$ ;
+ - **当 $i == m - l + 1$ 时:** 代表左子数组已合并完,因此添加右子数组元素 $tmp[j]$ ,并执行 $j = j + 1$ ;
+ - **否则,当 $j == r - l + 1$ 时:** 代表右子数组已合并完,因此添加左子数组元素 $tmp[i]$ ,并执行 $i = i + 1$ ;
+ - **否则,当 $tmp[i] \leq tmp[j]$ 时:** 添加左子数组元素 $tmp[i]$ ,并执行 $i = i + 1$ ;
+ - **否则(即当 $tmp[i] > tmp[j]$ 时):** 添加右子数组元素 $tmp[j]$ ,并执行 $j = j + 1$ ;
+
+> 如下动图所示,为数组 `[7,3,2,6]` 的归并排序过程。
+
+
+
+## 代码
+
+为简化代码,「当 $j = r + 1$ 时」 与 「当 $tmp[i] \leq tmp[j]$ 时」 两判断项可合并。
+
+```Python []
+def merge_sort(nums, l, r):
+ # 终止条件
+ if l >= r: return
+ # 递归划分数组
+ m = (l + r) // 2
+ merge_sort(nums, l, m)
+ merge_sort(nums, m + 1, r)
+ # 合并子数组
+ tmp = nums[l:r + 1] # 暂存需合并区间元素
+ i, j = 0, m - l + 1 # 两指针分别指向左/右子数组的首个元素
+ for k in range(l, r + 1): # 遍历合并左/右子数组
+ if i == m - l + 1:
+ nums[k] = tmp[j]
+ j += 1
+ elif j == r - l + 1 or tmp[i] <= tmp[j]:
+ nums[k] = tmp[i]
+ i += 1
+ else:
+ nums[k] = tmp[j]
+ j += 1
+
+# 调用
+nums = [3, 4, 1, 5, 2, 1]
+merge_sort(0, len(nums) - 1)
+```
+
+```Java []
+void mergeSort(int[] nums, int l, int r) {
+ // 终止条件
+ if (l >= r) return;
+ // 递归划分
+ int m = (l + r) / 2;
+ mergeSort(nums, l, m);
+ mergeSort(nums, m + 1, r);
+ // 合并子数组
+ int[] tmp = new int[r - l + 1]; // 暂存需合并区间元素
+ for (int k = l; k <= r; k++)
+ tmp[k - l] = nums[k];
+ int i = 0, j = m - l + 1; // 两指针分别指向左/右子数组的首个元素
+ for (int k = l; k <= r; k++) { // 遍历合并左/右子数组
+ if (i == m - l + 1)
+ nums[k] = tmp[j++];
+ else if (j == r - l + 1 || tmp[i] <= tmp[j])
+ nums[k] = tmp[i++];
+ else {
+ nums[k] = tmp[j++];
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// 调用
+int[] nums = { 3, 4, 1, 5, 2, 1 };
+mergeSort(nums, 0, len(nums) - 1);
+```
+
+```C++ []
+void mergeSort(vector& nums, int l, int r) {
+ // 终止条件
+ if (l >= r) return;
+ // 递归划分
+ int m = (l + r) / 2;
+ mergeSort(nums, l, m);
+ mergeSort(nums, m + 1, r);
+ // 合并阶段
+ int tmp[r - l + 1]; // 暂存需合并区间元素
+ for (int k = l; k <= r; k++)
+ tmp[k - l] = nums[k];
+ int i = 0, j = m - l + 1; // 两指针分别指向左/右子数组的首个元素
+ for (int k = l; k <= r; k++) { // 遍历合并左/右子数组
+ if (i == m - l + 1)
+ nums[k] = tmp[j++];
+ else if (j == r - l + 1 || tmp[i] <= tmp[j])
+ nums[k] = tmp[i++];
+ else {
+ nums[k] = tmp[j++];
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// 调用
+vector nums = { 4, 1, 3, 2, 5, 1 };
+mergeSort(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1);
+```
+
+## 算法特性
+
+- **时间复杂度:** 最佳 $\Omega(N \log N )$ ,平均 $\Theta(N \log N)$ ,最差 $O(N \log N)$ 。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(N)$ :** 合并过程中需要借助辅助数组 $tmp$ ,使用 $O(N)$ 大小的额外空间;划分的递归深度为 $\log N$ ,使用 $O(\log N)$ 大小的栈帧空间。
+- 若输入数据是 **链表** ,则归并排序的空间复杂度可被优化至 $O(1)$ ,这是因为:
+ - 通过应用「双指针法」,可在 $O(1)$ 空间下完成两个排序链表的合并,省去辅助数组 $tmp$ 使用的额外空间;
+ - 通过使用「迭代」代替「递归划分」,可省去递归使用的栈帧空间;
+ > 详情请参考:[148. 排序链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-list/solution/sort-list-gui-bing-pai-xu-lian-biao-by-jyd/)
+- **非原地:** 辅助数组 $tmp$ 需要使用额外空间。
+- **稳定:** 归并排序不改变相等元素的相对顺序。
+- **非自适应:** 对于任意输入数据,归并排序的时间复杂度皆相同。
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 120. \345\257\273\346\211\276\346\226\207\344\273\266\345\211\257\346\234\254.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 120. \345\257\273\346\211\276\346\226\207\344\273\266\345\211\257\346\234\254.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..646d56a
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 120. \345\257\273\346\211\276\346\226\207\344\273\266\345\211\257\346\234\254.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,140 @@
+## 方法一:哈希表
+
+利用数据结构特点,容易想到使用哈希表(Set)记录数组的各个数字,当查找到重复数字则直接返回。
+
+### 算法流程:
+
+1. 初始化: 新建 HashSet ,记为 $hmap$ ;
+2. 遍历数组 $documents$ 中的每个数字 $doc$ :
+ 1. 当 $doc$ 在 $hmap$ 中,说明重复,直接返回 $doc$ ;
+ 2. 将 $doc$ 添加至 $hmap$ 中;
+3. 返回 $-1$ 。本题中一定有重复数字,因此这里返回多少都可以。
+
+> 下图中的 `nums` 对应本题的 `documents` 。
+
+
+
+### 代码:
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def findRepeatDocument(self, documents: List[int]) -> int:
+ hmap = set()
+ for doc in documents:
+ if doc in hmap: return doc
+ hmap.add(doc)
+ return -1
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public int findRepeatDocument(int[] documents) {
+ Set hmap = new HashSet<>();
+ for(int doc : documents) {
+ if(hmap.contains(doc)) return doc;
+ hmap.add(doc);
+ }
+ return -1;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int findRepeatDocument(vector& documents) {
+ unordered_map map;
+ for(int doc : documents) {
+ if(map[doc]) return doc;
+ map[doc] = true;
+ }
+ return -1;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(N)$ :** 遍历数组使用 $O(N)$ ,HashSet 添加与查找元素皆为 $O(1)$ 。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(N)$ :** HashSet 占用 $O(N)$ 大小的额外空间。
+
+## 方法二:原地交换
+
+题目说明尚未被充分使用,即 `在一个长度为 n 的数组 documents 里的所有数字都在 0 ~ n-1 的范围内` 。 此说明含义:数组元素的 **索引** 和 **值** 是 **一对多** 的关系。
+因此,可遍历数组并通过交换操作,使元素的 **索引** 与 **值** 一一对应(即 $documents[i] = i$ )。因而,就能通过索引映射对应的值,起到与字典等价的作用。
+
+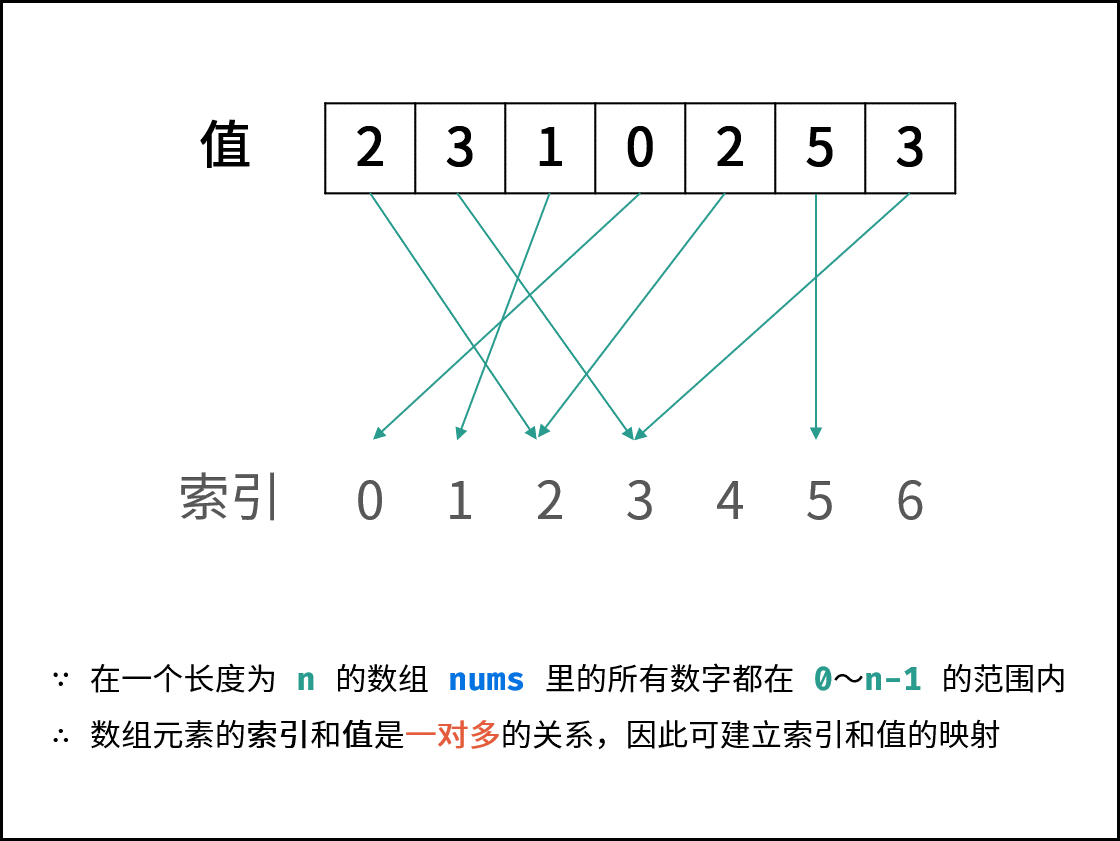{:align=center width=500}
+
+遍历中,第一次遇到数字 $x$ 时,将其交换至索引 $x$ 处;而当第二次遇到数字 $x$ 时,一定有 $documents[x] = x$ ,此时即可得到一组重复数字。
+
+### 算法流程:
+
+1. 遍历数组 $documents$ ,设索引初始值为 $i = 0$ :
+ 1. **若 $documents[i] = i$ :** 说明此数字已在对应索引位置,无需交换,因此跳过;
+ 2. **若 $documents[documents[i]] = documents[i]$ :** 代表索引 $documents[i]$ 处和索引 $i$ 处的元素值都为 $documents[i]$ ,即找到一组重复值,返回此值 $documents[i]$ ;
+ 3. **否则:** 交换索引为 $i$ 和 $documents[i]$ 的元素值,将此数字交换至对应索引位置。
+
+2. 若遍历完毕尚未返回,则返回 $-1$ 。
+
+
+
+### 代码:
+
+Python 中,$a, b = c, d$ 操作的原理是先暂存元组 $(c, d)$ ,然后 “按左右顺序” 赋值给 a 和 b 。
+因此,若写为 $documents[i], documents[documents[i]] = documents[documents[i]], documents[i]$ ,则 $documents[i]$ 会先被赋值,之后 $documents[documents[i]]$ 指向的元素则会出错。
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def findRepeatDocument(self, documents: List[int]) -> int:
+ i = 0
+ while i < len(documents):
+ if documents[i] == i:
+ i += 1
+ continue
+ if documents[documents[i]] == documents[i]: return documents[i]
+ documents[documents[i]], documents[i] = documents[i], documents[documents[i]]
+ return -1
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public int findRepeatDocument(int[] documents) {
+ int i = 0;
+ while(i < documents.length) {
+ if(documents[i] == i) {
+ i++;
+ continue;
+ }
+ if(documents[documents[i]] == documents[i]) return documents[i];
+ int tmp = documents[i];
+ documents[i] = documents[tmp];
+ documents[tmp] = tmp;
+ }
+ return -1;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int findRepeatDocument(vector& documents) {
+ int i = 0;
+ while(i < documents.size()) {
+ if(documents[i] == i) {
+ i++;
+ continue;
+ }
+ if(documents[documents[i]] == documents[i])
+ return documents[i];
+ swap(documents[i],documents[documents[i]]);
+ }
+ return -1;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(N)$ :** 遍历数组使用 $O(N)$ ,每轮遍历的判断和交换操作使用 $O(1)$ 。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(1)$ :** 使用常数复杂度的额外空间。
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 121. \345\257\273\346\211\276\347\233\256\346\240\207\345\200\274 - \344\272\214\347\273\264\346\225\260\347\273\204.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 121. \345\257\273\346\211\276\347\233\256\346\240\207\345\200\274 - \344\272\214\347\273\264\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..17898e7
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 121. \345\257\273\346\211\276\347\233\256\346\240\207\345\200\274 - \344\272\214\347\273\264\346\225\260\347\273\204.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+## 解题思路:
+
+> 若使用暴力法遍历矩阵 `plants` ,则时间复杂度为 $O(NM)$ 。暴力法未利用矩阵 **“从上到下递增、从左到右递增”** 的特点,显然不是最优解法。
+
+如下图所示,我们将矩阵逆时针旋转 45° ,并将其转化为图形式,发现其类似于 **二叉搜索树** ,即对于每个元素,其左分支元素更小、右分支元素更大。
+
+因此,考虑从 “根节点” 开始搜索,遇到比 `target` 大的元素就向左,反之向右,即可找到目标值 `target` 。
+
+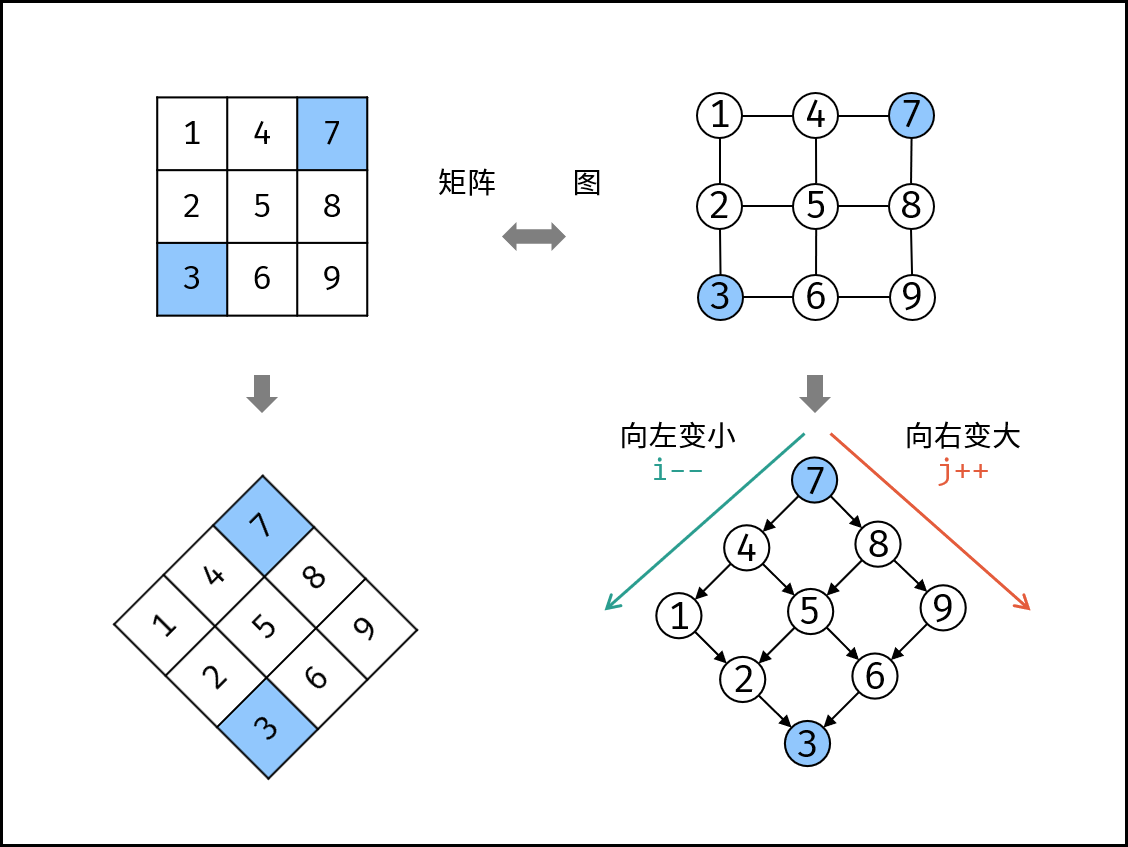{:align=center width=450}
+
+### 算法流程:
+
+“根节点” 对应的是矩阵的 “左下角” 和 “右上角” 元素。以 `plants` 中的 **左下角元素** 为起始点,则有:
+
+1. 从矩阵 `plants` 左下角元素(索引设为 `(i, j)` )开始遍历,并与目标值对比:
+ - 当 `plants[i][j] > target` 时,执行 `i--` ,即消去第 `i` 行元素;
+ - 当 `plants[i][j] < target` 时,执行 `j++` ,即消去第 `j` 列元素;
+ - 当 `plants[i][j] = target` 时,返回 $\text{true}$ ,代表找到目标值。
+2. 若行索引或列索引越界,则代表矩阵中无目标值,返回 $\text{false}$ 。
+
+> 每轮 `i` 或 `j` 移动后,相当于生成了“消去一行(列)的新矩阵”, 索引`(i,j)` 指向新矩阵的左下角元素,因此可重复使用以上性质消去行(列)。
+
+
+
+## 代码:
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def findTargetIn2DPlants(self, plants: List[List[int]], target: int) -> bool:
+ i, j = len(plants) - 1, 0
+ while i >= 0 and j < len(plants[0]):
+ if plants[i][j] > target: i -= 1
+ elif plants[i][j] < target: j += 1
+ else: return True
+ return False
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public boolean findTargetIn2DPlants(int[][] plants, int target) {
+ int i = plants.length - 1, j = 0;
+ while(i >= 0 && j < plants[0].length)
+ {
+ if(plants[i][j] > target) i--;
+ else if(plants[i][j] < target) j++;
+ else return true;
+ }
+ return false;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ bool findTargetIn2DPlants(vector>& plants, int target) {
+ int i = plants.size() - 1, j = 0;
+ while(i >= 0 && j < plants[0].size())
+ {
+ if(plants[i][j] > target) i--;
+ else if(plants[i][j] < target) j++;
+ else return true;
+ }
+ return false;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+- 时间复杂度 $O(M+N)$ :其中,$N$ 和 $M$ 分别为矩阵行数和列数,此算法最多循环 $M+N$ 次。
+- 空间复杂度 $O(1)$ : `i`, `j` 指针使用常数大小额外空间。
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 122. \350\267\257\345\276\204\345\212\240\345\257\206.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 122. \350\267\257\345\276\204\345\212\240\345\257\206.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..fcf1f3d
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 122. \350\267\257\345\276\204\345\212\240\345\257\206.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+## 方法一:遍历添加
+
+在 Python 和 Java 等语言中,字符串都被设计成「不可变」的类型,即无法直接修改字符串的某一位字符,需要新建一个字符串实现。
+
+### 算法流程:
+
+1. 初始化一个 `list` (Python) 或 `StringBuilder` (Java) ,记为 `res` ;
+2. 遍历列表 `path` 中的每个字符 `c` :
+ - 当 `c` 为空格时:向 `res` 后添加空格 " " ;
+ - 当 `c` 不为空格时:向 `res` 后添加字符 `c` ;
+3. 将列表 `res` 转化为字符串并返回。
+
+> 下图中的 `s` 对应本题的 `path` 。
+
+
+
+## 代码:
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def pathEncryption(self, path: str) -> str:
+ res = []
+ for c in path:
+ if c == '.': res.append(' ')
+ else: res.append(c)
+ return "".join(res)
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public String pathEncryption(String path) {
+ StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
+ for(Character c : path.toCharArray())
+ {
+ if(c == '.') res.append(' ');
+ else res.append(c);
+ }
+ return res.toString();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(N)$ :** 遍历使用 $O(N)$ ,每轮添加(修改)字符操作使用 $O(1)$ ;
+- **空间复杂度 $O(N)$ :** Python 新建的 list 和 Java 新建的 StringBuilder 都使用了线性大小的额外空间。
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 123. \345\233\276\344\271\246\346\225\264\347\220\206 I.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 123. \345\233\276\344\271\246\346\225\264\347\220\206 I.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..197f59e
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 123. \345\233\276\344\271\246\346\225\264\347\220\206 I.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
+## 方法一:递归
+
+利用递归,先递推至链表末端;回溯时,依次将节点值加入列表,即可实现链表值的倒序输出。
+
+1. **终止条件:** 当 `head == None` 时,代表越过了链表尾节点,则返回空列表;
+2. **递推工作:** 访问下一节点 `head.next` ;
+3. **回溯阶段:**
+ - **Python:** 返回 `当前 list + 当前节点值 [head.val]` ;
+ - **Java / C++:** 将当前节点值 `head.val` 加入列表 `tmp` ;
+
+
+
+### 代码:
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def reverseBookList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> List[int]:
+ return self.reverseBookList(head.next) + [head.val] if head else []
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ ArrayList tmp = new ArrayList();
+ public int[] reverseBookList(ListNode head) {
+ recur(head);
+ int[] res = new int[tmp.size()];
+ for(int i = 0; i < res.length; i++)
+ res[i] = tmp.get(i);
+ return res;
+ }
+ void recur(ListNode head) {
+ if(head == null) return;
+ recur(head.next);
+ tmp.add(head.val);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ vector reverseBookList(ListNode* head) {
+ recur(head);
+ return res;
+ }
+private:
+ vector res;
+ void recur(ListNode* head) {
+ if(head == nullptr) return;
+ recur(head->next);
+ res.push_back(head->val);
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(N)$:** 遍历链表,递归 $N$ 次。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(N)$:** 系统递归需要使用 $O(N)$ 的栈空间。
+
+## 方法二:辅助栈法
+
+链表只能 **从前至后** 访问每个节点,而题目要求 **倒序输出** 各节点值,这种 **先入后出** 的需求可以借助 **栈** 来实现。
+
+### 算法流程:
+
+1. **入栈:** 遍历链表,将各节点值 `push` 入栈。
+2. **出栈:** 将各节点值 `pop` 出栈,存储于数组并返回。
+
+> 图解以 Java 代码为例,Python 无需将 `stack` 转移至 `res`,而是直接返回倒序数组。
+
+
+
+### 代码:
+
+Java 数组长度不可变,因此使用 List 先存储,再转为数组并返回。
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def reverseBookList(self, head: ListNode) -> List[int]:
+ stack = []
+ while head:
+ stack.append(head.val)
+ head = head.next
+ return stack[::-1]
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public int[] reverseBookList(ListNode head) {
+ LinkedList stack = new LinkedList();
+ while(head != null) {
+ stack.addLast(head.val);
+ head = head.next;
+ }
+ int[] res = new int[stack.size()];
+ for(int i = 0; i < res.length; i++)
+ res[i] = stack.removeLast();
+ return res;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ vector reverseBookList(ListNode* head) {
+ stack stk;
+ while(head != nullptr) {
+ stk.push(head->val);
+ head = head->next;
+ }
+ vector res;
+ while(!stk.empty()) {
+ res.push_back(stk.top());
+ stk.pop();
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(N)$:** 入栈和出栈共使用 $O(N)$ 时间。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(N)$:** 辅助栈 `stack` 和数组 `res` 共使用 $O(N)$ 的额外空间。
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 124. \346\216\250\347\220\206\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 124. \346\216\250\347\220\206\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..d91cbf9
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 124. \346\216\250\347\220\206\344\272\214\345\217\211\346\240\221.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,117 @@
+## 解题思路:
+
+前序遍历性质: 节点按照 `[ 根节点 | 左子树 | 右子树 ]` 排序。
+中序遍历性质: 节点按照 `[ 左子树 | 根节点 | 右子树 ]` 排序。
+
+> 以题目示例为例:
+>
+> - 前序遍历划分 `[ 3 | 9 | 20 15 7 ]`
+> - 中序遍历划分 `[ 9 | 3 | 15 20 7 ]`
+
+根据以上性质,可得出以下推论:
+
+1. 前序遍历的首元素 为 树的根节点 `node` 的值。
+2. 在中序遍历中搜索根节点 `node` 的索引 ,可将 中序遍历 划分为 `[ 左子树 | 根节点 | 右子树 ]` 。
+3. 根据中序遍历中的左(右)子树的节点数量,可将 前序遍历 划分为 `[ 根节点 | 左子树 | 右子树 ] ` 。
+
+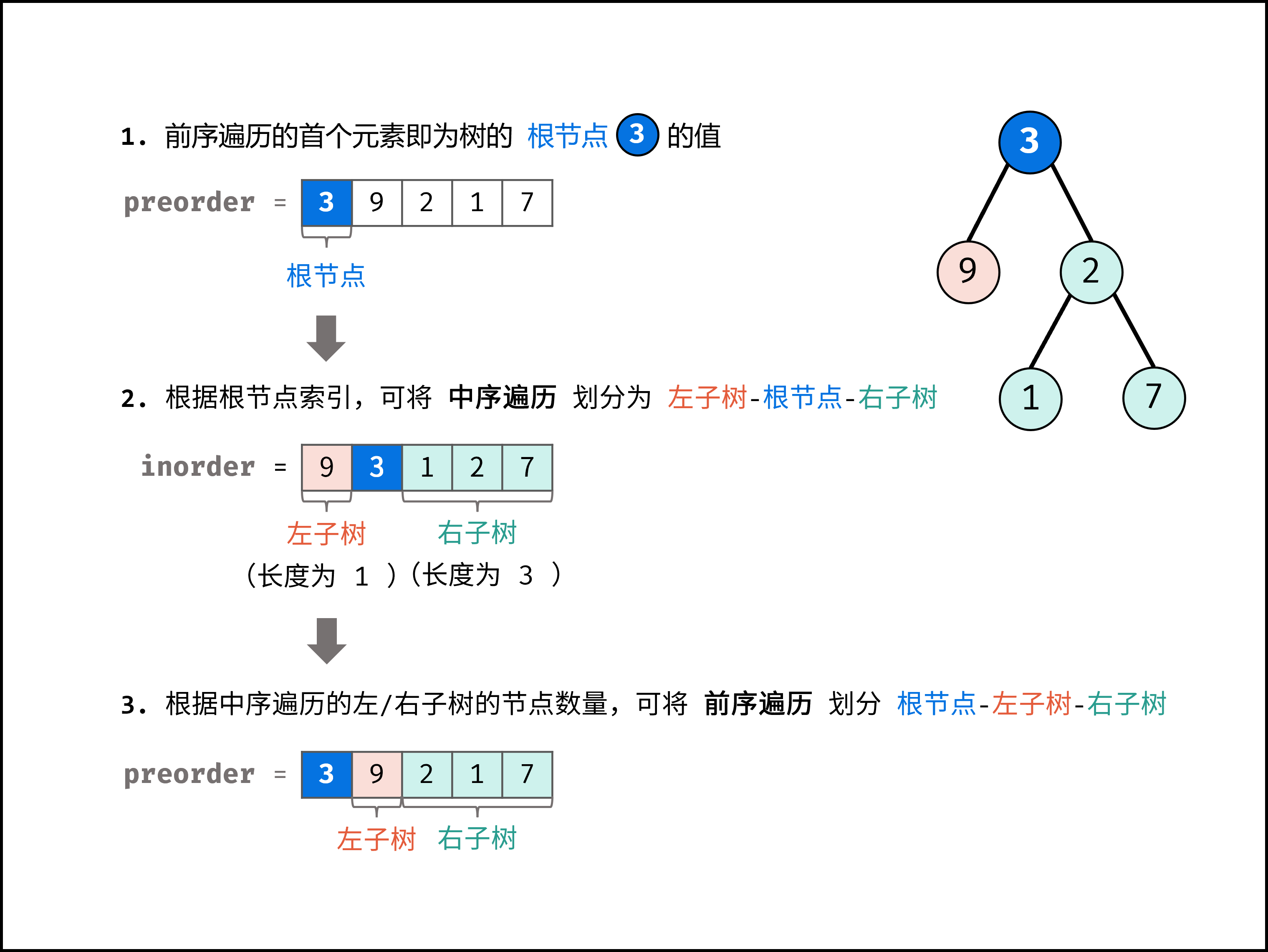{:align=center width=550}
+
+通过以上三步,可确定 **三个节点** :1.树的根节点、2.左子树根节点、3.右子树根节点。
+
+根据「分治算法」思想,对于树的左、右子树,仍可复用以上方法划分子树的左右子树。
+
+### 分治解析:
+
+**递推参数:** 根节点在前序遍历的索引 `root` 、子树在中序遍历的左边界 `left` 、子树在中序遍历的右边界 `right` ;
+
+**终止条件:** 当 `left > right` ,代表已经越过叶节点,此时返回 $\text{null}$ ;
+
+**递推工作:**
+
+1. **建立根节点 `node` :** 节点值为 `preorder[root]` ;
+2. **划分左右子树:** 查找根节点在中序遍历 `inorder` 中的索引 `i` ;
+
+> 为了提升效率,本文使用哈希表 `hmap` 存储中序遍历的值与索引的映射,查找操作的时间复杂度为 $O(1)$ ;
+
+3. **构建左右子树:** 开启左右子树递归;
+
+| | 根节点索引 | 中序遍历左边界 | 中序遍历右边界 |
+| ---------- | --------------------- | -------------- | -------------- |
+| **左子树** | `root + 1` | `left` | `i - 1` |
+| **右子树** | `i - left + root + 1` | `i + 1` | `right` |
+
+> **TIPS:** `i - left + root + 1`含义为 `根节点索引 + 左子树长度 + 1`
+
+**返回值:** 回溯返回 `node` ,作为上一层递归中根节点的左 / 右子节点;
+
+
+
+## 代码:
+
+> 注意:本文方法只适用于 “无重复节点值” 的二叉树。
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def deduceTree(self, preorder: List[int], inorder: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
+ def recur(root, left, right):
+ if left > right: return # 递归终止
+ node = TreeNode(preorder[root]) # 建立根节点
+ i = hmap[preorder[root]] # 划分根节点、左子树、右子树
+ node.left = recur(root + 1, left, i - 1) # 开启左子树递归
+ node.right = recur(i - left + root + 1, i + 1, right) # 开启右子树递归
+ return node # 回溯返回根节点
+
+ hmap, preorder = {}, preorder
+ for i in range(len(inorder)):
+ hmap[inorder[i]] = i
+ return recur(0, 0, len(inorder) - 1)
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ int[] preorder;
+ HashMap hmap = new HashMap<>();
+ public TreeNode deduceTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
+ this.preorder = preorder;
+ for(int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++)
+ hmap.put(inorder[i], i);
+ return recur(0, 0, inorder.length - 1);
+ }
+ TreeNode recur(int root, int left, int right) {
+ if(left > right) return null; // 递归终止
+ TreeNode node = new TreeNode(preorder[root]); // 建立根节点
+ int i = hmap.get(preorder[root]); // 划分根节点、左子树、右子树
+ node.left = recur(root + 1, left, i - 1); // 开启左子树递归
+ node.right = recur(root + i - left + 1, i + 1, right); // 开启右子树递归
+ return node; // 回溯返回根节点
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ TreeNode* deduceTree(vector& preorder, vector& inorder) {
+ this->preorder = preorder;
+ for(int i = 0; i < inorder.size(); i++)
+ hmap[inorder[i]] = i;
+ return recur(0, 0, inorder.size() - 1);
+ }
+private:
+ vector preorder;
+ unordered_map hmap;
+ TreeNode* recur(int root, int left, int right) {
+ if(left > right) return nullptr; // 递归终止
+ TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(preorder[root]); // 建立根节点
+ int i = hmap[preorder[root]]; // 划分根节点、左子树、右子树
+ node->left = recur(root + 1, left, i - 1); // 开启左子树递归
+ node->right = recur(root + i - left + 1, i + 1, right); // 开启右子树递归
+ return node; // 回溯返回根节点
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(N)$ :** 其中 $N$ 为树的节点数量。初始化 HashMap 需遍历 `inorder` ,占用 $O(N)$ 。递归共建立 $N$ 个节点,每层递归中的节点建立、搜索操作占用 $O(1)$ ,因此使用 $O(N)$ 时间。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(N)$ :** HashMap 使用 $O(N)$ 额外空间;最差情况下(输入二叉树为链表时),递归深度达到 $N$ ,占用 $O(N)$ 的栈帧空间;因此总共使用 $O(N)$ 空间。
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 125. \345\233\276\344\271\246\346\225\264\347\220\206 II.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 125. \345\233\276\344\271\246\346\225\264\347\220\206 II.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..0d35601
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 125. \345\233\276\344\271\246\346\225\264\347\220\206 II.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
+## 解题思路:
+
+> 我们可将两个书车看作两个“栈”,本题可被转化为“用两个栈实现一个队列”。
+
+栈实现队列的出队操作效率低下:栈底元素(对应队首元素)无法直接删除,需要将上方所有元素出栈。
+
+列表倒序操作可使用双栈实现:设有含三个元素的栈 `A = [1,2,3]` 和空栈 `B = []` 。若循环执行 `A` 元素出栈并添加入栈 `B` ,直到栈 `A` 为空,则 `A = []` , `B = [3,2,1]` ,即栈 `B` 元素为栈 `A` 元素倒序。
+
+利用栈 `B` 删除队首元素:倒序后,`B` 执行出栈则相当于删除了 `A` 的栈底元素,即对应队首元素。
+
+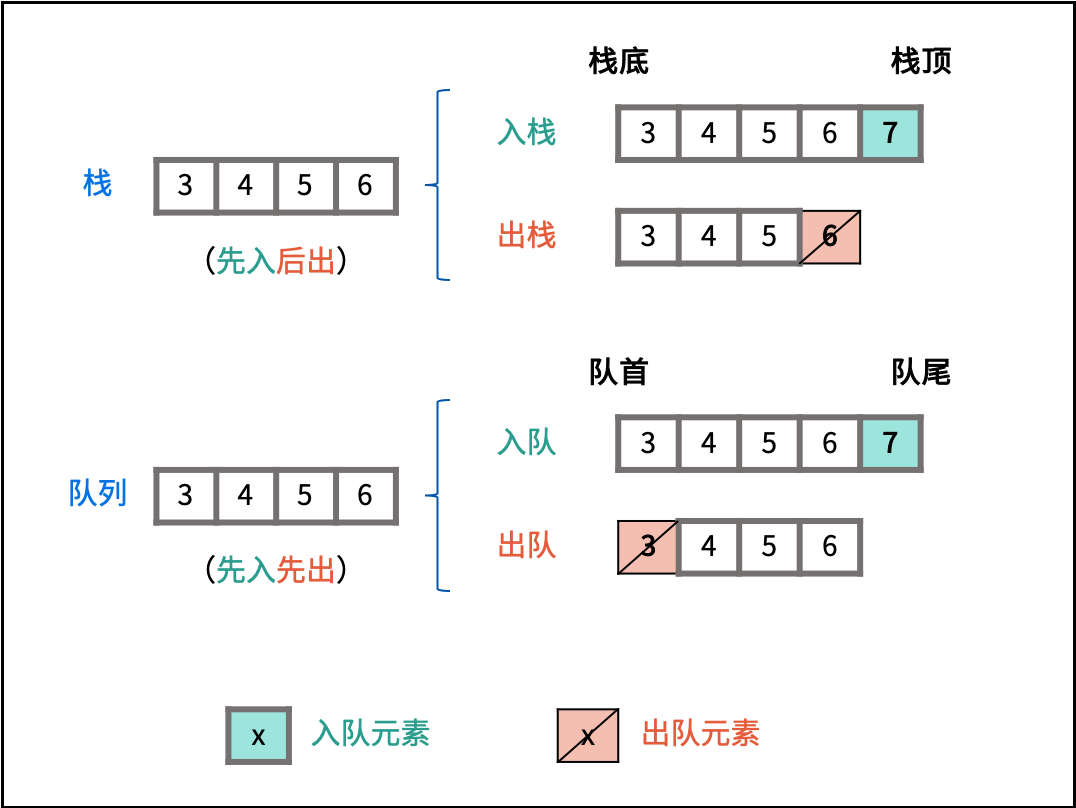{:align=center width=500}
+
+题目要求实现 **加入队尾**`appendTail()` 和 **删除队首**`deleteHead()` 两个函数的正常工作。因此,可以设计栈 `A` 用于加入队尾操作,栈 `B` 用于将元素倒序,从而实现删除队首元素。
+
+### 函数设计:
+
+1. **加入队尾 `appendTail()` :** 将数字 `val` 加入栈 `A` 即可。
+2. **删除队首`deleteHead()` :** 有以下三种情况。
+ 1. **当栈 `B` 不为空:** `B`中仍有已完成倒序的元素,因此直接返回 `B` 的栈顶元素。
+ 2. **否则,当 `A` 为空:** 即两个栈都为空,无元素,因此返回 -1 。
+ 3. **否则:** 将栈 `A` 元素全部转移至栈 `B` 中,实现元素倒序,并返回栈 `B` 的栈顶元素。
+
+
+
+## 代码:
+
+Python 和 Java 的栈的 `pop()` 函数返回栈顶元素,而 C++ 不返回;因此对于 C++ ,需要先使用 `top()` 方法暂存栈顶元素,再执行 `pop()` 出栈操作。
+
+```Python []
+class CQueue:
+ def __init__(self):
+ self.A, self.B = [], []
+
+ def appendTail(self, value: int) -> None:
+ self.A.append(value)
+
+ def deleteHead(self) -> int:
+ if self.B: return self.B.pop()
+ if not self.A: return -1
+ while self.A:
+ self.B.append(self.A.pop())
+ return self.B.pop()
+```
+
+```Java []
+class CQueue {
+ LinkedList A, B;
+ public CQueue() {
+ A = new LinkedList();
+ B = new LinkedList();
+ }
+ public void appendTail(int value) {
+ A.addLast(value);
+ }
+ public int deleteHead() {
+ if(!B.isEmpty()) return B.removeLast();
+ if(A.isEmpty()) return -1;
+ while(!A.isEmpty())
+ B.addLast(A.removeLast());
+ return B.removeLast();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class CQueue {
+public:
+ stack A, B;
+ CQueue() {}
+ void appendTail(int value) {
+ A.push(value);
+ }
+ int deleteHead() {
+ if(!B.empty()) {
+ int tmp = B.top();
+ B.pop();
+ return tmp;
+ }
+ if(A.empty()) return -1;
+ while(!A.empty()) {
+ int tmp = A.top();
+ A.pop();
+ B.push(tmp);
+ }
+ int tmp = B.top();
+ B.pop();
+ return tmp;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+> 以下分析仅满足添加 $N$ 个元素并删除 $N$ 个元素,即栈初始和结束状态下都为空的情况。
+
+- **时间复杂度:** `appendTail()`函数为 $O(1)$ ;`deleteHead()` 函数在 $N$ 次队首元素删除操作中总共需完成 $N$ 个元素的倒序。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(N)$ :** 最差情况下,栈 `A` 和 `B` 共保存 $N$ 个元素。
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 126. \346\226\220\346\263\242\351\202\243\345\245\221\346\225\260.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 126. \346\226\220\346\263\242\351\202\243\345\245\221\346\225\260.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..c4e4a05
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 126. \346\226\220\346\263\242\351\202\243\345\245\221\346\225\260.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
+## 解题思路:
+
+斐波那契数列的定义是 $f(n + 1) = f(n) + f(n - 1)$ ,生成第 $n$ 项的做法有以下几种:
+
+1. **递归:**
+ - **原理:** 把 $f(n)$ 问题的计算拆分成 $f(n-1)$ 和 $f(n-2)$ 两个子问题的计算,并递归,以 $f(0)$ 和 $f(1)$ 为终止条件。
+ - **缺点:** 大量重复的递归计算,例如 $f(n)$ 和 $f(n - 1)$ 两者向下递归需要 **各自计算** $f(n - 2)$ 的值。
+2. **记忆化递归:**
+ - **原理:** 在递归的基础上,新建一个长度为 $n$ 的数组,用于在递归时存储 $f(0)$ 至 $f(n)$ 的数字值,重复遇到某数字则直接从数组取用,避免了重复的递归计算。
+ - **缺点:** 记忆化存储需要使用 $O(N)$ 的额外空间。
+3. **动态规划:**
+ - **原理:** 以斐波那契数列性质 $f(n + 1) = f(n) + f(n - 1)$ 为转移方程。
+ - 从计算效率、空间复杂度上看,动态规划是本题的最佳解法。
+
+> 下图帮助理解递归的 “重复计算” 概念。
+
+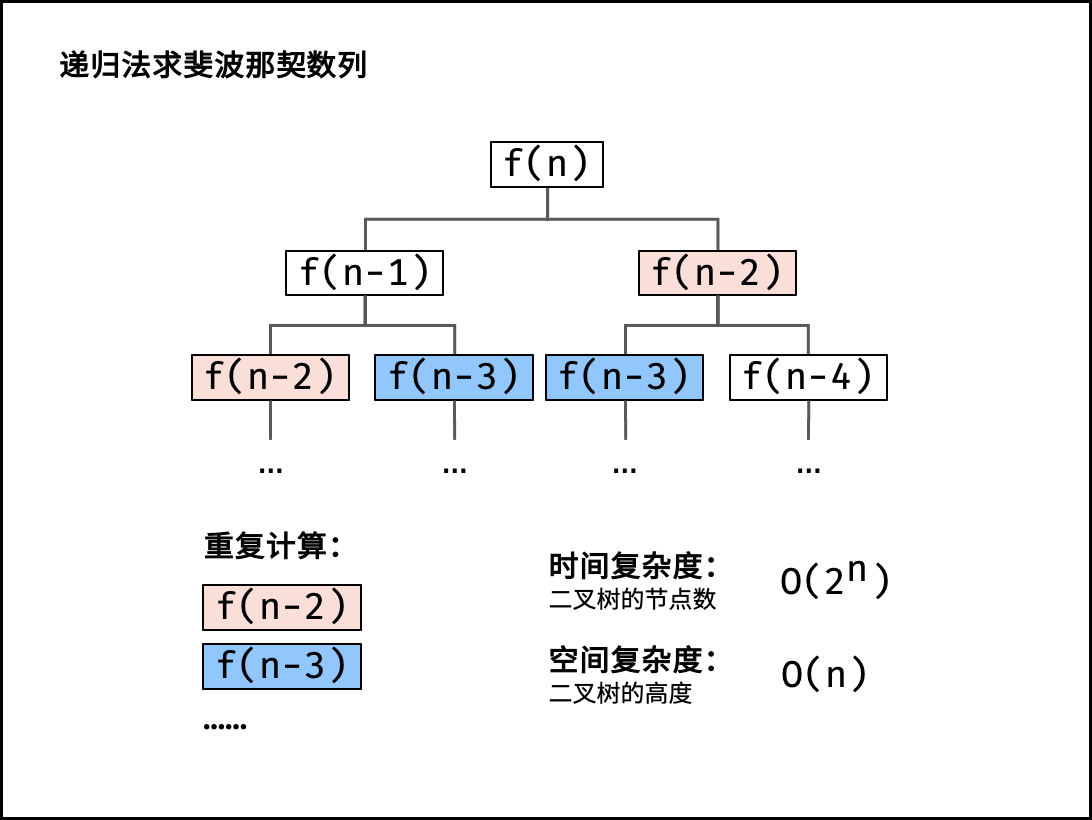{:align=center width=500}
+
+### 动态规划解析:
+
+- **状态定义:** 设 $dp$ 为一维数组,其中 $dp[i]$ 的值代表 斐波那契数列第 $i$ 个数字 。
+- **转移方程:** $dp[i + 1] = dp[i] + dp[i - 1]$ ,即对应数列定义 $f(n + 1) = f(n) + f(n - 1)$ ;
+- **初始状态:** $dp[0] = 0$, $dp[1] = 1$ ,即初始化前两个数字;
+- **返回值:** $dp[n]$ ,即斐波那契数列的第 $n$ 个数字。
+
+### 空间优化:
+
+> 若新建长度为 $n$ 的 $dp$ 列表,则空间复杂度为 $O(N)$ 。
+
+- 由于 $dp$ 列表第 $i$ 项只与第 $i-1$ 和第 $i-2$ 项有关,因此只需要初始化三个整形变量 `sum`, `a`, `b` ,利用辅助变量 $sum$ 使 $a, b$ 两数字交替前进即可 *(具体实现见代码)* 。
+- 节省了 $dp$ 列表空间,因此空间复杂度降至 $O(1)$ 。
+
+### 循环求余法:
+
+> **大数越界:** 随着 $n$ 增大, $f(n)$ 会超过 `Int32` 甚至 `Int64` 的取值范围,导致最终的返回值错误。
+
+- **求余运算规则:** 设正整数 $x, y, p$ ,求余符号为 $\odot$ ,则有 $(x + y) \odot p = (x \odot p + y \odot p) \odot p$ 。
+- **解析:** 根据以上规则,可推出 $f(n) \odot p = [f(n-1) \odot p + f(n-2) \odot p] \odot p$ ,从而可以在循环过程中每次计算 $sum = (a + b) \odot 1000000007$ ,此操作与最终返回前取余等价。
+
+
+
+## 代码:
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def fib(self, n: int) -> int:
+ a, b = 0, 1
+ for _ in range(n):
+ a, b = b, (a + b) % 1000000007
+ return a
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public int fib(int n) {
+ int a = 0, b = 1, sum;
+ for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
+ sum = (a + b) % 1000000007;
+ a = b;
+ b = sum;
+ }
+ return a;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int fib(int n) {
+ int a = 0, b = 1, sum;
+ for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
+ sum = (a + b) % 1000000007;
+ a = b;
+ b = sum;
+ }
+ return a;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+由于 Python 中整形数字的大小限制取决计算机的内存(可理解为无限大),因此也可不考虑大数越界问题;但当数字很大时,加法运算的效率也会降低,因此不推荐此方法。
+
+```Python []
+# 不考虑大数越界问题
+class Solution:
+ def fib(self, n: int) -> int:
+ a, b = 0, 1
+ for _ in range(n):
+ a, b = b, a + b
+ return a % 1000000007
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(n)$ :** 计算 $f(n)$ 需循环 $n$ 次,每轮循环内计算操作使用 $O(1)$ 。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(1)$ :** 几个标志变量使用常数大小的额外空间。
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 127. \350\267\263\350\267\203\350\256\255\347\273\203.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 127. \350\267\263\350\267\203\350\256\255\347\273\203.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..adff689
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 127. \350\267\263\350\267\203\350\256\255\347\273\203.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
+## 解题思路:
+
+设跳上 $n$ 级平台有 $f(n)$ 种跳法。在所有跳法中,青蛙的最后一步只有两种情况: **跳上 $1$ 级或 $2$ 级平台**。
+
+1. **当为 $1$ 级平台:** 剩 $n-1$ 个平台,此情况共有 $f(n-1)$ 种跳法;
+2. **当为 $2$ 级平台:** 剩 $n-2$ 个平台,此情况共有 $f(n-2)$ 种跳法。
+
+即 $f(n)$ 为以上两种情况之和,即 $f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2)$ ,以上递推性质为斐波那契数列。因此,本题可转化为 **求斐波那契数列第 $n$ 项的值** ,唯一的不同在于起始数字不同。
+
+- 跳跃训练问题: $f(0)=1$ , $f(1)=1$ , $f(2)=2$ ;
+- 斐波那契数列问题: $f(0)=0$ , $f(1)=1$ , $f(2)=1$ 。
+
+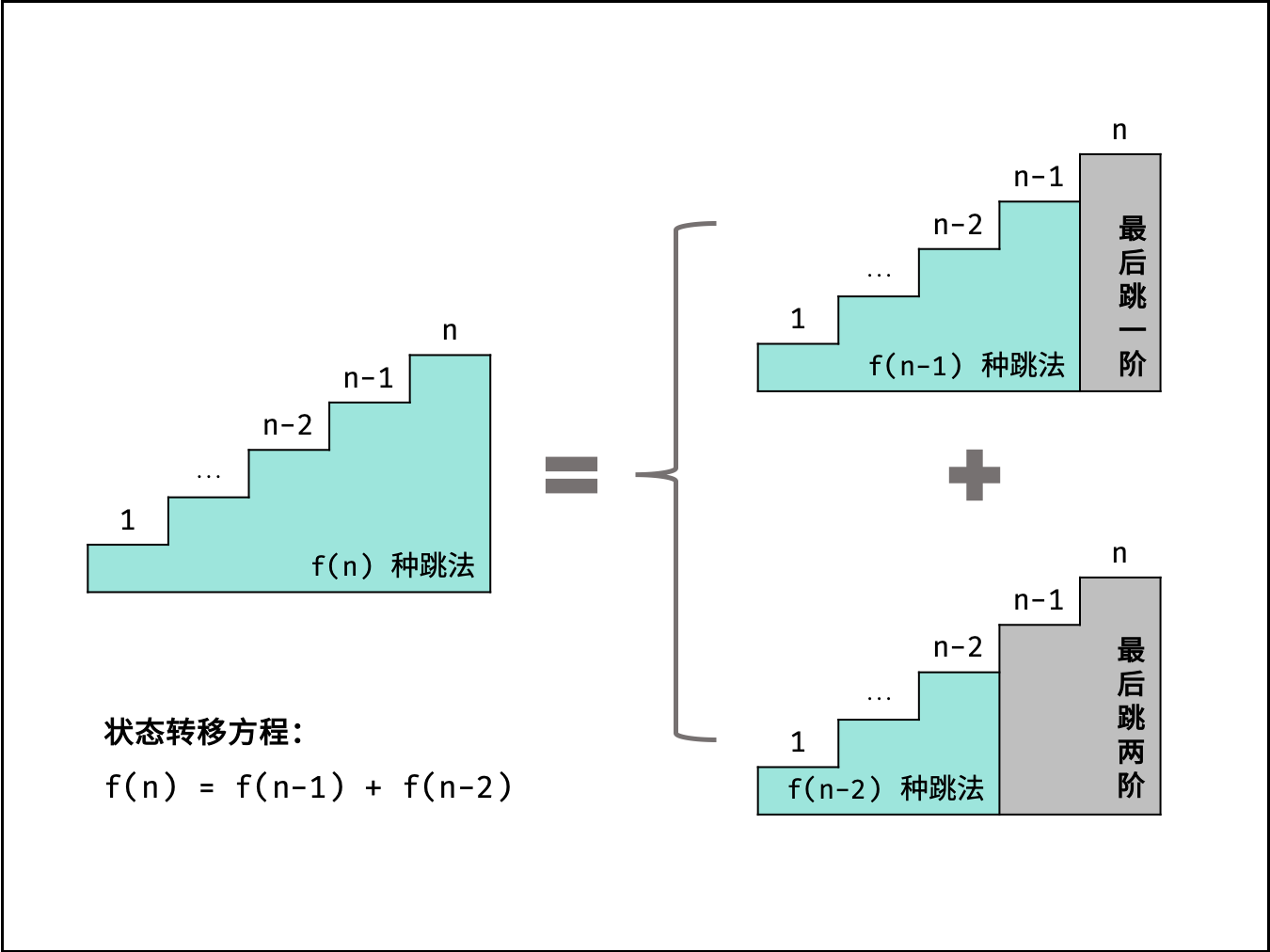{:align=center width=500}
+
+### 动态规划解析:
+
+- **状态定义:** 设 $dp$ 为一维数组,其中 $dp[i]$ 的值代表斐波那契数列的第 $i$ 个数字。
+- **转移方程:** $dp[i + 1] = dp[i] + dp[i - 1]$ ,即对应数列定义 $f(n + 1) = f(n) + f(n - 1)$ ;
+- **初始状态:** $dp[0] = 1$, $dp[1] = 1$ ,即初始化前两个数字;
+- **返回值:** $dp[n]$ ,即斐波那契数列的第 $n$ 个数字。
+
+### 空间优化:
+
+> 若新建长度为 $n$ 的 $dp$ 列表,则空间复杂度为 $O(N)$ 。
+
+- 由于 $dp$ 列表第 $i$ 项只与第 $i-1$ 和第 $i-2$ 项有关,因此只需要初始化三个整形变量 `sum`, `a`, `b` ,利用辅助变量 $sum$ 使 $a, b$ 两数字交替前进即可 *(具体实现见代码)* 。
+- 因为节省了 $dp$ 列表空间,因此空间复杂度降至 $O(1)$ 。
+
+### 循环求余法:
+
+> **大数越界:** 随着 $n$ 增大, $f(n)$ 会超过 `Int32` 甚至 `Int64` 的取值范围,导致最终的返回值错误。
+
+- **求余运算规则:** 设正整数 $x, y, p$ ,求余符号为 $\odot$ ,则有 $(x + y) \odot p = (x \odot p + y \odot p) \odot p$ 。
+- **解析:** 根据以上规则,可推出 $f(n) \odot p = [f(n-1) \odot p + f(n-2) \odot p] \odot p$ ,从而可以在循环过程中每次计算 $sum = a + b \odot 1000000007$ ,此操作与最终返回前取余等价。
+
+
+
+## 代码:
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def trainWays(self, num: int) -> int:
+ a, b = 1, 1
+ for _ in range(num):
+ a, b = b, (a + b) % 1000000007
+ return a
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public int trainWays(int num) {
+ int a = 1, b = 1, sum;
+ for(int i = 0; i < num; i++){
+ sum = (a + b) % 1000000007;
+ a = b;
+ b = sum;
+ }
+ return a;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int trainWays(int num) {
+ int a = 1, b = 1, sum;
+ for(int i = 0; i < num; i++){
+ sum = (a + b) % 1000000007;
+ a = b;
+ b = sum;
+ }
+ return a;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+由于 Python 中整形数字的大小限制取决计算机的内存(可理解为无限大),因此也可不考虑大数越界问题;但当数字很大时,加法运算的效率也会降低,因此不推荐此方法。
+
+```Python []
+# 不考虑大数越界问题
+class Solution:
+ def trainWays(self, num: int) -> int:
+ a, b = 1, 1
+ for _ in range(num):
+ a, b = b, a + b
+ return a % 1000000007
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(n)$ :** 计算 $f(n)$ 需循环 $n$ 次,每轮循环内计算操作使用 $O(1)$ 。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(1)$ :** 几个标志变量使用常数大小的额外空间。
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 128. \345\272\223\345\255\230\347\256\241\347\220\206 I.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 128. \345\272\223\345\255\230\347\256\241\347\220\206 I.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..e4c2887
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 128. \345\272\223\345\255\230\347\256\241\347\220\206 I.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,161 @@
+## 解题思路:
+
+如下图所示,寻找旋转数组的最小元素即为寻找 **右排序数组** 的首个元素 $stock[x]$ ,称 $x$ 为 **旋转点** 。
+
+> 下图中的 `numbers` 对应本题的 `stock` 。
+
+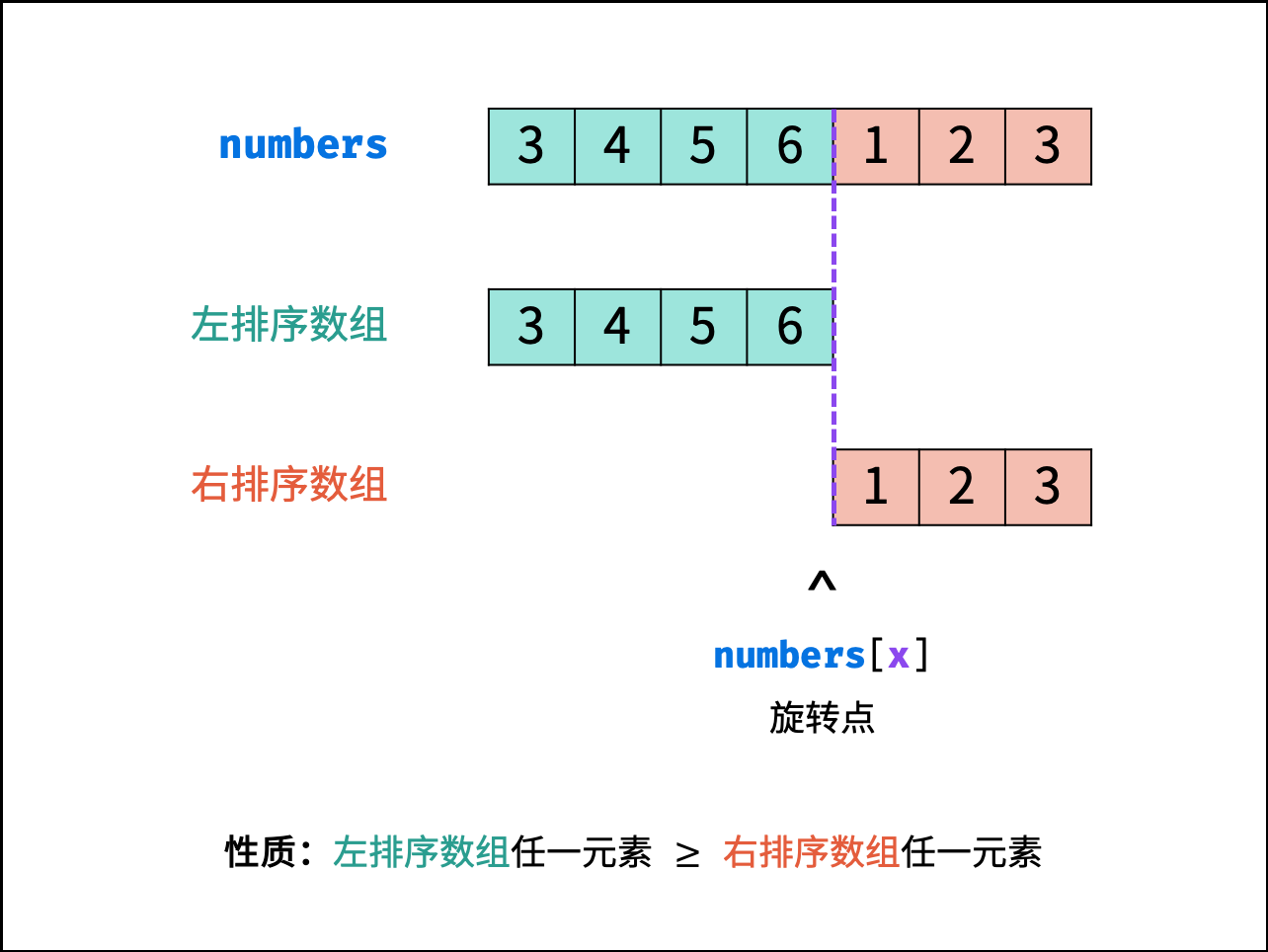{:align=center width=450}
+
+排序数组的查找问题首先考虑使用 **二分法** 解决,其可将 **遍历法** 的 **线性级别** 时间复杂度降低至 **对数级别** 。
+
+### 算法流程:
+
+1. **初始化:** 声明 $i$, $j$ 双指针分别指向 $stock$ 数组左右两端;
+2. **循环二分:** 设 $m = (i + j) / 2$ 为每次二分的中点( "`/`" 代表向下取整除法,因此恒有 $i \leq m < j$ ),可分为以下三种情况:
+ 1. **当 $stock[m] > stock[j]$ 时:** $m$ 一定在 左排序数组 中,即旋转点 $x$ 一定在 $[m + 1, j]$ 闭区间内,因此执行 $i = m + 1$;
+ 2. **当 $stock[m] < stock[j]$ 时:** $m$ 一定在 右排序数组 中,即旋转点 $x$ 一定在$[i, m]$ 闭区间内,因此执行 $j = m$;
+ 3. **当 $stock[m] = stock[j]$ 时:** 无法判断 $m$ 在哪个排序数组中,即无法判断旋转点 $x$ 在 $[i, m]$ 还是 $[m + 1, j]$ 区间中。**解决方案:** 执行 $j = j - 1$ 缩小判断范围,分析见下文。
+3. **返回值:** 当 $i = j$ 时跳出二分循环,并返回 **旋转点的值** $stock[i]$ 即可。
+
+### 正确性证明:
+
+当 $stock[m] = stock[j]$ 时,无法判定 $m$ 在左(右)排序数组,自然也无法通过二分法安全地缩小区间,因为其会导致旋转点 $x$ 不在区间 $[i, j]$ 内。举例如下:
+
+> 设以下两个旋转点值为 $0$ 的示例数组,则当 $i = 0$, $j = 4$ 时 $m = 2$ ,两示例结果不同。
+> 示例一 $[1, 0, 1, 1, 1]$ :旋转点 $x = 1$ ,因此 $m = 2$ 在 **右排序数组** 中。
+> 示例二 $[1, 1, 1, 0, 1]$ :旋转点 $x = 3$ ,因此 $m = 2$ 在 **左排序数组** 中。
+
+而证明 $j = j - 1$ 正确(缩小区间安全性),需分为两种情况:
+
+1. **当 $x < j$ 时:** 易得执行 $j = j - 1$ 后,旋转点 $x$ 仍在区间 $[i, j]$ 内。
+2. **当 $x = j$ 时:** 执行 $j = j - 1$ 后越过(丢失)了旋转点 $x$ ,但最终返回的元素值 $stock[i]$ 仍等于旋转点值 $stock[x]$ 。
+
+ 1. 由于 $x = j$ ,因此 $stock[x] = stock[j] = stock[m] \leq number[i]$ ;
+ 2. 又由于 $i \leq m 综上所述,此方法可以保证返回值 $stock[i]$ 等于旋转点值 $stock[x]$ ,但在少数特例下 $i \ne x$ ;而本题目只要求返回 “旋转点的值” ,因此本方法正确。
+
+**补充思考:** 为什么本题二分法不用 $stock[m]$ 和 $stock[i]$ 作比较?
+
+二分目的是判断 $m$ 在哪个排序数组中,从而缩小区间。而在 $stock[m] > stock[i]$情况下,无法判断 $m$ 在哪个排序数组中。本质上是由于 $j$ 初始值肯定在右排序数组中;$i$ 初始值无法确定在哪个排序数组中。举例如下:
+
+> 对于以下两示例,当 $i = 0, j = 4, m = 2$ 时,有 `stock[m] > stock[i]` ,而结果不同。
+> $[1, 2, 3, 4 ,5]$ 旋转点 $x = 0$ : $m$ 在右排序数组(此示例只有右排序数组);
+> $[3, 4, 5, 1 ,2]$ 旋转点 $x = 3$ : $m$ 在左排序数组。
+
+
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(\log N)$ :** 在特例情况下(例如 $[1, 1, 1, 1]$),会退化到 $O(N)$。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(1)$ :** $i$ , $j$ , $m$ 变量使用常数大小的额外空间。
+
+## 代码:
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def stockManagement(self, stock: List[int]) -> int:
+ i, j = 0, len(stock) - 1
+ while i < j:
+ m = (i + j) // 2
+ if stock[m] > stock[j]: i = m + 1
+ elif stock[m] < stock[j]: j = m
+ else: j -= 1
+ return stock[i]
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public int stockManagement(int[] stock) {
+ int i = 0, j = stock.length - 1;
+ while (i < j) {
+ int m = (i + j) / 2;
+ if (stock[m] > stock[j]) i = m + 1;
+ else if (stock[m] < stock[j]) j = m;
+ else j--;
+ }
+ return stock[i];
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int stockManagement(vector& stock) {
+ int i = 0, j = stock.size() - 1;
+ while (i < j) {
+ int m = (i + j) / 2;
+ if (stock[m] > stock[j]) i = m + 1;
+ else if (stock[m] < stock[j]) j = m;
+ else j--;
+ }
+ return stock[i];
+ }
+};
+```
+
+实际上,当出现 $stock[m] = stock[j]$ 时,一定有区间 $[i, m]$ 内所有元素相等 或 区间 $[m, j]$ 内所有元素相等(或两者皆满足)。对于寻找此类数组的最小值问题,可直接放弃二分查找,而使用线性查找替代。
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def stockManagement(self, stock: List[int]) -> int:
+ i, j = 0, len(stock) - 1
+ while i < j:
+ m = (i + j) // 2
+ if stock[m] > stock[j]: i = m + 1
+ elif stock[m] < stock[j]: j = m
+ else: return min(stock[i:j])
+ return stock[i]
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public int stockManagement(int[] stock) {
+ int i = 0, j = stock.length - 1;
+ while (i < j) {
+ int m = (i + j) / 2;
+ if (stock[m] > stock[j]) i = m + 1;
+ else if (stock[m] < stock[j]) j = m;
+ else {
+ int x = i;
+ for(int k = i + 1; k < j; k++) {
+ if(stock[k] < stock[x]) x = k;
+ }
+ return stock[x];
+ }
+ }
+ return stock[i];
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int stockManagement(vector& stock) {
+ int i = 0, j = stock.size() - 1;
+ while (i < j) {
+ int m = (i + j) / 2;
+ if (stock[m] > stock[j]) i = m + 1;
+ else if (stock[m] < stock[j]) j = m;
+ else {
+ int x = i;
+ for(int k = i + 1; k < j; k++) {
+ if(stock[k] < stock[x]) x = k;
+ }
+ return stock[x];
+ }
+ }
+ return stock[i];
+ }
+};
+```
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 129. \345\255\227\346\257\215\350\277\267\345\256\253.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 129. \345\255\227\346\257\215\350\277\267\345\256\253.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..7d26483
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 129. \345\255\227\346\257\215\350\277\267\345\256\253.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
+## 解题思路:
+
+本问题是典型的回溯问题,可使用 **深度优先搜索(DFS)+ 剪枝** 解决。
+
+- **深度优先搜索:** 可以理解为暴力法遍历矩阵中所有字符串可能性。DFS 通过递归,先朝一个方向搜到底,再回溯至上个节点,沿另一个方向搜索,以此类推。
+- **剪枝:** 在搜索中,遇到 `这条路不可能和目标字符串匹配成功` 的情况(*例如:此矩阵元素和目标字符不同、此元素已被访问)*,则应立即返回,称之为 `可行性剪枝` 。
+
+> 下图中的 `word` 对应本题的 `target` 。
+
+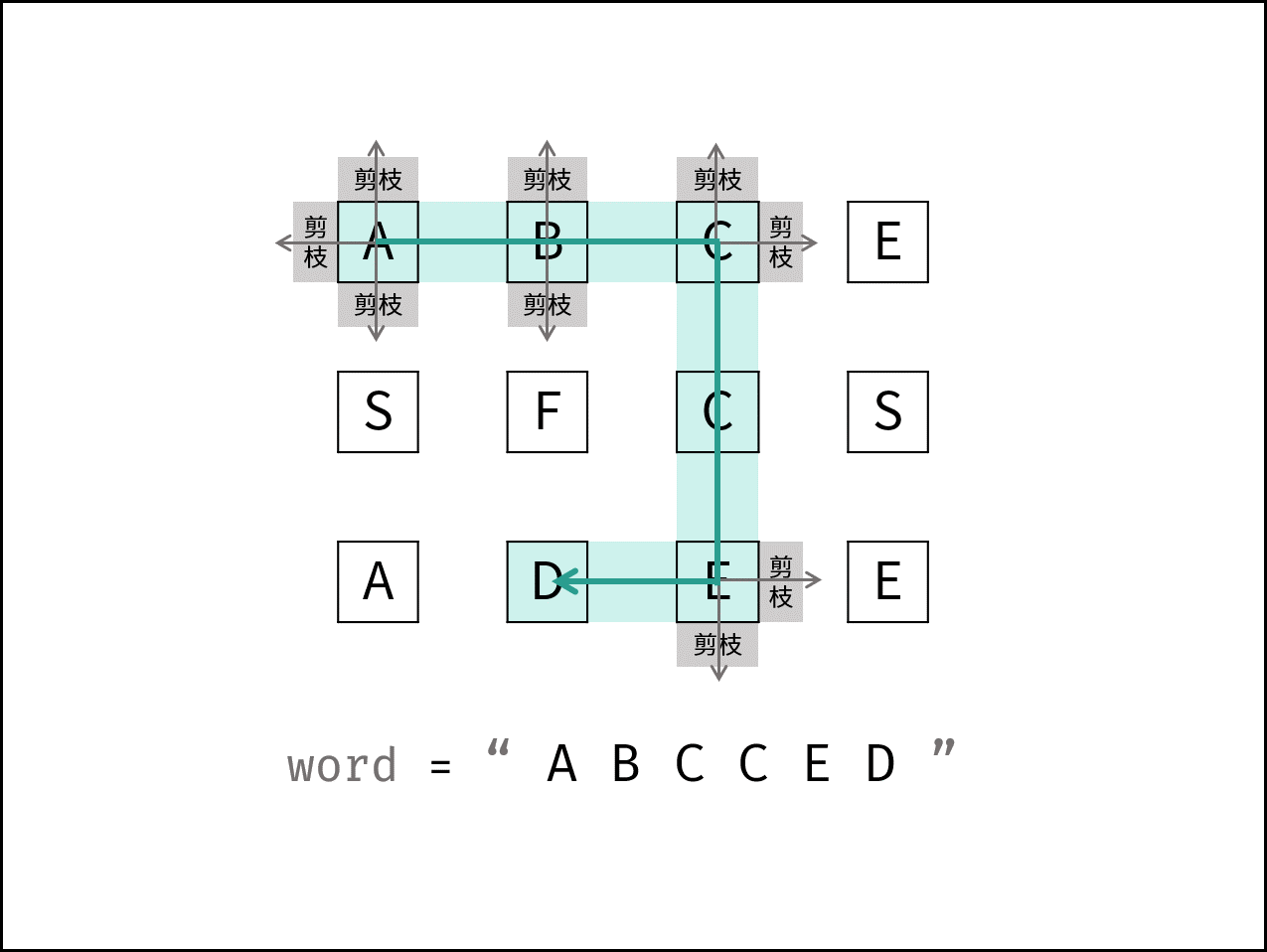{:align=center width=500}
+
+### DFS 解析:
+
+- **递归参数:** 当前元素在矩阵 `grid` 中的行列索引 `i` 和 `j` ,当前目标字符在 `target` 中的索引 `k` 。
+- **终止条件:**
+ 1. 返回 $\text{false}$ : (1) 行或列索引越界 **或** (2) 当前矩阵元素与目标字符不同 **或** (3) 当前矩阵元素已访问过 ( (3) 可合并至 (2) ) 。
+ 2. 返回 $\text{true}$ : `k = len(target) - 1` ,即字符串 `target` 已全部匹配。
+- **递推工作:**
+ 1. 标记当前矩阵元素: 将 `grid[i][j]` 修改为 **空字符** `''` ,代表此元素已访问过,防止之后搜索时重复访问。
+ 2. 搜索下一单元格: 朝当前元素的 **上、下、左、右** 四个方向开启下层递归,使用 `或` 连接 (代表只需找到一条可行路径就直接返回,不再做后续 DFS ),并记录结果至 `res` 。
+ 3. 还原当前矩阵元素: 将 `grid[i][j]` 元素还原至初始值,即 `target[k]` 。
+- **返回值:** 返回布尔量 `res` ,代表是否搜索到目标字符串。
+
+> 使用空字符(Python: `''` , Java/C++: `'\0'` )做标记是为了防止标记字符与矩阵原有字符重复。当存在重复时,此算法会将矩阵原有字符认作标记字符,从而出现错误。
+
+
+
+## 代码:
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def wordPuzzle(self, grid: List[List[str]], target: str) -> bool:
+ def dfs(i, j, k):
+ if not 0 <= i < len(grid) or not 0 <= j < len(grid[0]) or grid[i][j] != target[k]: return False
+ if k == len(target) - 1: return True
+ grid[i][j] = ''
+ res = dfs(i + 1, j, k + 1) or dfs(i - 1, j, k + 1) or dfs(i, j + 1, k + 1) or dfs(i, j - 1, k + 1)
+ grid[i][j] = target[k]
+ return res
+
+ for i in range(len(grid)):
+ for j in range(len(grid[0])):
+ if dfs(i, j, 0): return True
+ return False
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public boolean wordPuzzle(char[][] grid, String target) {
+ char[] words = target.toCharArray();
+ for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
+ for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
+ if(dfs(grid, words, i, j, 0)) return true;
+ }
+ }
+ return false;
+ }
+ boolean dfs(char[][] grid, char[] target, int i, int j, int k) {
+ if(i >= grid.length || i < 0 || j >= grid[0].length || j < 0 || grid[i][j] != target[k]) return false;
+ if(k == target.length - 1) return true;
+ grid[i][j] = '\0';
+ boolean res = dfs(grid, target, i + 1, j, k + 1) || dfs(grid, target, i - 1, j, k + 1) ||
+ dfs(grid, target, i, j + 1, k + 1) || dfs(grid, target, i , j - 1, k + 1);
+ grid[i][j] = target[k];
+ return res;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ bool wordPuzzle(vector>& grid, string target) {
+ rows = grid.size();
+ cols = grid[0].size();
+ for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
+ for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
+ if(dfs(grid, target, i, j, 0)) return true;
+ }
+ }
+ return false;
+ }
+private:
+ int rows, cols;
+ bool dfs(vector>& grid, string target, int i, int j, int k) {
+ if(i >= rows || i < 0 || j >= cols || j < 0 || grid[i][j] != target[k]) return false;
+ if(k == target.size() - 1) return true;
+ grid[i][j] = '\0';
+ bool res = dfs(grid, target, i + 1, j, k + 1) || dfs(grid, target, i - 1, j, k + 1) ||
+ dfs(grid, target, i, j + 1, k + 1) || dfs(grid, target, i , j - 1, k + 1);
+ grid[i][j] = target[k];
+ return res;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+> $M, N$ 分别为矩阵行列大小,$K$ 为字符串 `target` 长度。
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(3^KMN)$ :** 最差情况下,需要遍历矩阵中长度为 $K$ 字符串的所有方案,时间复杂度为 $O(3^K)$;矩阵中共有 $MN$ 个起点,时间复杂度为 $O(MN)$ 。
+ - **方案数计算:** 设字符串长度为 $K$ ,搜索中每个字符有上、下、左、右四个方向可以选择,舍弃回头(上个字符)的方向,剩下 $3$ 种选择,因此方案数的复杂度为 $O(3^K)$ 。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(K)$ :** 搜索过程中的递归深度不超过 $K$ ,因此系统因函数调用累计使用的栈空间占用 $O(K)$ (因为函数返回后,系统调用的[栈空间会释放](https://leetcode-cn.com/explore/orignial/card/recursion-i/259/complexity-analysis/1223/))。最坏情况下 $K = MN$ ,递归深度为 $MN$ ,此时系统栈使用 $O(MN)$ 的额外空间。
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 130. \350\241\243\346\251\261\346\225\264\347\220\206.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 130. \350\241\243\346\251\261\346\225\264\347\220\206.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..7d1e2b5
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 130. \350\241\243\346\251\261\346\225\264\347\220\206.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,242 @@
+## 解题思路:
+
+为提升回溯的计算效率,首先讲述两项前置工作: **数位之和计算** 、 **可达解分析** 。
+
+### 数位之和计算:
+
+设一数字 $x$ ,向下取整除法符号 $//$ ,求余符号 $\odot$ ,则有:
+
+- $x \odot 10$ :得到 $x$ 的个位数字;
+- $x // 10$ : 令 $x$ 的十进制数向右移动一位,即删除个位数字。
+
+因此,可通过循环求得数位和 $s$ ,数位和计算的封装函数如下所示:
+
+```Python []
+def sums(x):
+ s = 0
+ while x != 0:
+ s += x % 10
+ x = x // 10
+ return s
+```
+
+```Java []
+int sums(int x)
+ int s = 0;
+ while(x != 0) {
+ s += x % 10;
+ x = x / 10;
+ }
+ return s;
+```
+
+```C++ []
+int sums(int x)
+ int s = 0;
+ while(x != 0) {
+ s += x % 10;
+ x = x / 10;
+ }
+ return s;
+```
+
+由于机器人每次只能移动一格(即只能从 $x$ 运动至 $x \pm 1$),因此每次只需计算 $x$ 到 $x \pm 1$ 的**数位和增量**。本题说明 $1 \leq n,m \leq 100$ ,以下公式仅在此范围适用。
+
+**数位和增量公式:** 设 $x$ 的数位和为 $s_x$ ,$x+1$ 的数位和为 $s_{x+1}$ ;
+
+1. **当 $(x + 1) \odot 10 = 0$ 时:** $s_{x+1} = s_x - 8$ ,例如 $19, 20$ 的数位和分别为 $10, 2$ ;
+2. **当 $(x + 1) \odot 10 \neq 0$ 时:** $s_{x+1} = s_x + 1$ ,例如 $1, 2$ 的数位和分别为 $1, 2$ 。
+
+> 以下代码为增量公式的三元表达式写法,将整合入最终代码中。
+
+```Python []
+s_x + 1 if (x + 1) % 10 else s_x - 8
+```
+
+```Java []
+(x + 1) % 10 != 0 ? s_x + 1 : s_x - 8;
+```
+
+```C++ []
+(x + 1) % 10 != 0 ? s_x + 1 : s_x - 8;
+```
+
+### 可达解分析:
+
+根据数位和增量公式得知,数位和每逢 **进位** 突变一次。根据此特点,矩阵中 **满足数位和的解** 构成的几何形状形如多个 **等腰直角三角形** ,每个三角形的直角顶点位于 $0, 10, 20, ...$ 等数位和突变的矩阵索引处 。
+
+三角形内的解虽然都满足数位和要求,但由于机器人每步只能走一个单元格,而三角形间不一定是连通的,因此机器人不一定能到达,称之为 **不可达解** ;同理,可到达的解称为 **可达解** *(本题求此解)* 。
+
+> 下图展示了 $n,m = 20$ ,$cnt \in [6, 19]$ 的可达解、不可达解、非解,以及连通性的变化。其中 $k$ 对应本题的 $cnt$ 。
+
+
+
+根据可达解的结构和连通性,易推出机器人可 **仅通过向右和向下移动,访问所有可达解** 。
+
+- **三角形内部:** 全部连通,易证;
+- **两三角形连通处:** 若某三角形内的解为可达解,则必与其左边或上边的三角形连通(即相交),即机器人必可从左边或上边走进此三角形。
+
+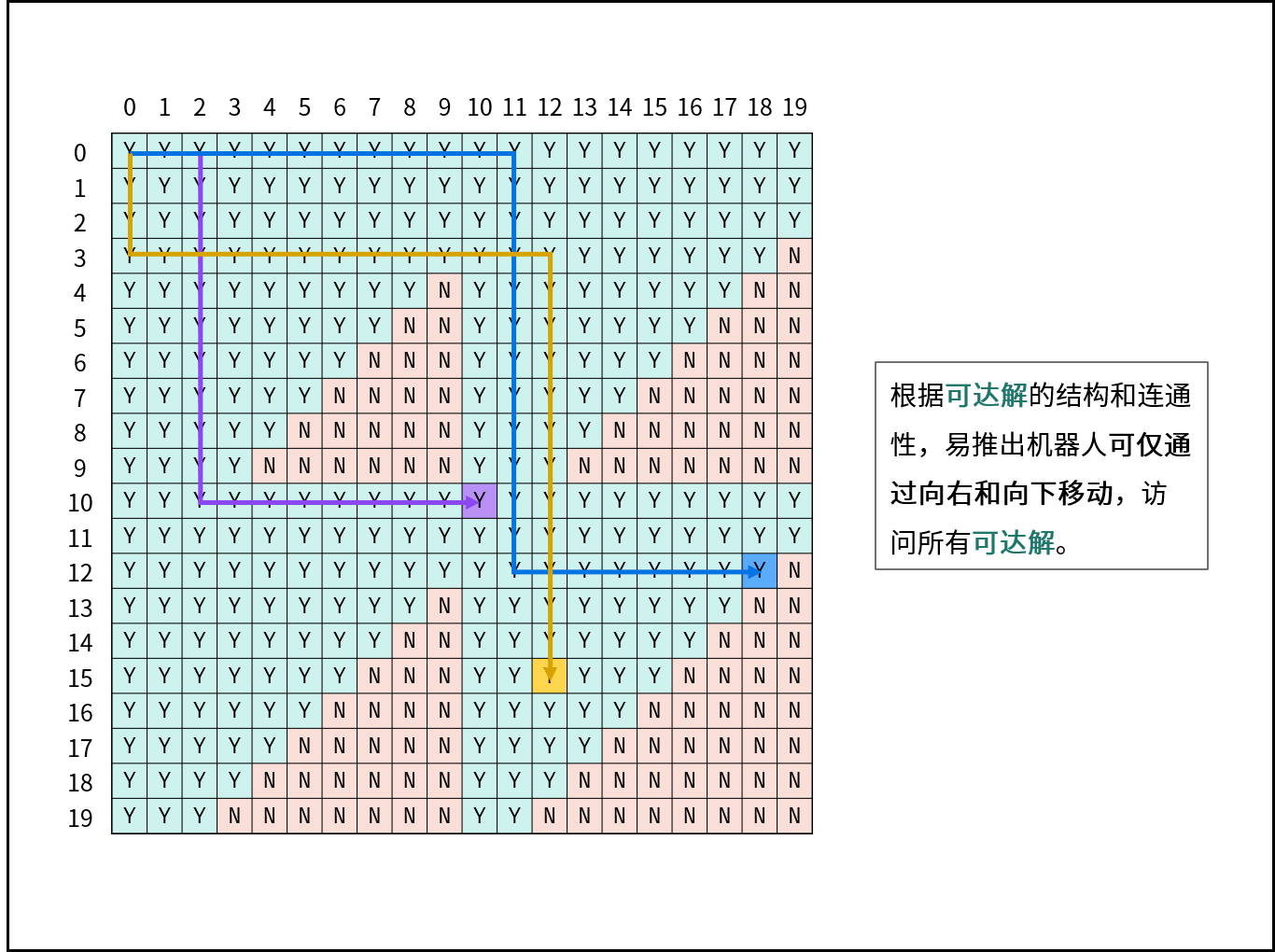{:align=center width=500}
+
+## 方法一:深度优先遍历(DFS)
+
+**深度优先搜索:** 可以理解为暴力法模拟机器人在矩阵中的所有路径。DFS 通过递归,先朝一个方向搜到底,再回溯至上个节点,沿另一个方向搜索,以此类推。
+
+**剪枝:** 在搜索中,遇到数位和超出目标值、此元素已访问,则应立即返回,称之为 `可行性剪枝` 。
+
+### 算法解析:
+
+- **递归参数:** 当前元素在矩阵中的行列索引 `i` 和 `j` ,两者的数位和 `si`, `sj` 。
+- **终止条件:** 当 (1) 行列索引越界 **或** (2) 数位和超出目标值 `cnt` **或** (3) 当前元素已访问过 时,返回 $0$ ,代表不计入可达解。
+- **递推工作:**
+ 1. **标记当前单元格** :将索引 `(i, j)` 存入 Set `visited` 中,代表此单元格已被访问过。
+ 2. **搜索下一单元格:** 计算当前元素的 **下、右** 两个方向元素的数位和,并开启下层递归 。
+- **回溯返回值:** 返回 `1 + 右方搜索的可达解总数 + 下方搜索的可达解总数`,代表从本单元格递归搜索的可达解总数。
+
+
+
+### 代码:
+
+> Java/C++ 代码中 `visited` 为辅助矩阵,Python 中为 Set 。
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def wardrobeFinishing(self, m: int, n: int, cnt: int) -> int:
+ def dfs(i, j, si, sj):
+ if i >= m or j >= n or cnt < si + sj or (i, j) in visited: return 0
+ visited.add((i,j))
+ return 1 + dfs(i + 1, j, si + 1 if (i + 1) % 10 else si - 8, sj) + dfs(i, j + 1, si, sj + 1 if (j + 1) % 10 else sj - 8)
+
+ visited = set()
+ return dfs(0, 0, 0, 0)
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ int m, n, cnt;
+ boolean[][] visited;
+ public int wardrobeFinishing(int m, int n, int cnt) {
+ this.m = m; this.n = n; this.cnt = cnt;
+ this.visited = new boolean[m][n];
+ return dfs(0, 0, 0, 0);
+ }
+ public int dfs(int i, int j, int si, int sj) {
+ if(i >= m || j >= n || cnt < si + sj || visited[i][j]) return 0;
+ visited[i][j] = true;
+ return 1 + dfs(i + 1, j, (i + 1) % 10 != 0 ? si + 1 : si - 8, sj) + dfs(i, j + 1, si, (j + 1) % 10 != 0 ? sj + 1 : sj - 8);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int wardrobeFinishing(int m, int n, int cnt) {
+ vector> visited(m, vector(n, 0));
+ return dfs(0, 0, 0, 0, visited, m, n, cnt);
+ }
+private:
+ int dfs(int i, int j, int si, int sj, vector> &visited, int m, int n, int cnt) {
+ if(i >= m || j >= n || cnt < si + sj || visited[i][j]) return 0;
+ visited[i][j] = true;
+ return 1 + dfs(i + 1, j, (i + 1) % 10 != 0 ? si + 1 : si - 8, sj, visited, m, n, cnt) +
+ dfs(i, j + 1, si, (j + 1) % 10 != 0 ? sj + 1 : sj - 8, visited, m, n, cnt);
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+> 设矩阵行列数分别为 $M, N$ 。
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(MN)$ :** 最差情况下,机器人遍历矩阵所有单元格,此时时间复杂度为 $O(MN)$ 。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(MN)$ :** 最差情况下,Set `visited` 内存储矩阵所有单元格的索引,使用 $O(MN)$ 的额外空间。
+
+## 方法二:广度优先遍历(BFS)
+
+BFS 和 DFS 的目标都是遍历整个矩阵,不同点在于搜索顺序不同。DFS 是朝一个方向走到底,再回退,以此类推;BFS 则是按照“平推”的方式向前搜索。
+
+**BFS 实现:** 通常利用队列实现广度优先遍历。
+
+### 算法解析:
+
+- **初始化:** 将机器人初始点 $(0, 0)$ 加入队列 `queue` ;
+- **迭代终止条件:** `queue` 为空。代表已遍历完所有可达解。
+- **迭代工作:**
+ 1. **单元格出队:** 将队首单元格的 索引、数位和 弹出,作为当前搜索单元格。
+ 2. **判断是否跳过:** 若 (1) 行列索引越界 **或** (2) 数位和超出目标值 `cnt` **或** (3) 当前元素已访问过 时,执行 `continue` 。
+ 3. **标记当前单元格** :将单元格索引 `(i, j)` 存入 Set `visited` 中,代表此单元格 **已被访问过** 。
+ 4. **单元格入队:** 将当前元素的 **下方、右方** 单元格的 **索引、数位和** 加入 `queue` 。
+- **返回值:** Set `visited` 的长度 `len(visited)` ,即可达解的数量。
+
+> Java/C++ 使用了辅助变量 `res` 统计可达解数量; Python 直接返回 Set 的元素数 `len(visited)` 即可。
+
+
+
+### 代码:
+
+> Java/C++ 代码中 `visited` 为辅助矩阵,Python 中为 Set 。
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def wardrobeFinishing(self, m: int, n: int, cnt: int) -> int:
+ queue, visited = [(0, 0, 0, 0)], set()
+ while queue:
+ i, j, si, sj = queue.pop(0)
+ if i >= m or j >= n or cnt < si + sj or (i, j) in visited: continue
+ visited.add((i,j))
+ queue.append((i + 1, j, si + 1 if (i + 1) % 10 else si - 8, sj))
+ queue.append((i, j + 1, si, sj + 1 if (j + 1) % 10 else sj - 8))
+ return len(visited)
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public int wardrobeFinishing(int m, int n, int cnt) {
+ boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];
+ int res = 0;
+ Queue queue= new LinkedList();
+ queue.add(new int[] { 0, 0, 0, 0 });
+ while(queue.size() > 0) {
+ int[] x = queue.poll();
+ int i = x[0], j = x[1], si = x[2], sj = x[3];
+ if(i >= m || j >= n || cnt < si + sj || visited[i][j]) continue;
+ visited[i][j] = true;
+ res ++;
+ queue.add(new int[] { i + 1, j, (i + 1) % 10 != 0 ? si + 1 : si - 8, sj });
+ queue.add(new int[] { i, j + 1, si, (j + 1) % 10 != 0 ? sj + 1 : sj - 8 });
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int wardrobeFinishing(int m, int n, int cnt) {
+ vector> visited(m, vector(n, 0));
+ int res = 0;
+ queue> que;
+ que.push({ 0, 0, 0, 0 });
+ while(que.size() > 0) {
+ vector x = que.front();
+ que.pop();
+ int i = x[0], j = x[1], si = x[2], sj = x[3];
+ if(i >= m || j >= n || cnt < si + sj || visited[i][j]) continue;
+ visited[i][j] = true;
+ res++;
+ que.push({ i + 1, j, (i + 1) % 10 != 0 ? si + 1 : si - 8, sj });
+ que.push({ i, j + 1, si, (j + 1) % 10 != 0 ? sj + 1 : sj - 8 });
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+> 设矩阵行列数分别为 $M, N$ 。
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(MN)$ :** 最差情况下,机器人遍历矩阵所有单元格,此时时间复杂度为 $O(MN)$ 。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(MN)$ :** 最差情况下,Set `visited` 内存储矩阵所有单元格的索引,使用 $O(MN)$ 的额外空间。
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 131. \347\240\215\347\253\271\345\255\220 I.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 131. \347\240\215\347\253\271\345\255\220 I.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..e00337c
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 131. \347\240\215\347\253\271\345\255\220 I.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,164 @@
+## 解题思路:
+
+设将长度为 $n$ 的竹子切为 $a$ 段:
+
+$$
+n = n_1 + n_2 + ... + n_a
+$$
+
+本题等价于求解:
+
+$$
+\max(n_1 \times n_2 \times ... \times n_a)
+$$
+
+> 以下数学推导总体分为两步:(1) 当所有绳段长度相等时,乘积最大。(2) 最优的绳段长度为 $3$ 。
+
+### 数学推导:
+
+以下公式为“算术几何均值不等式” ,等号当且仅当 $n_1 = n_2 = ... = n_a$ 时成立。
+
+$$
+\frac{n_1 + n_2 + ... + n_a}{a} \geq \sqrt[a]{n_1 n_2 ... n_a}
+$$
+
+> **推论一:** 将竹子 **以相等的长度等分为多段** ,得到的乘积最大。
+
+设将竹子按照 $x$ 长度等分为 $a$ 段,即 $n = ax$ ,则乘积为 $x^a$ 。观察以下公式,由于 $n$ 为常数,因此当 $x^{\frac{1}{x}}$ 取最大值时, 乘积达到最大值。
+
+$$
+x^a = x^{\frac{n}{x}} = (x^{\frac{1}{x}})^n
+$$
+
+根据分析,可将问题转化为求 $y = x^{\frac{1}{x}}$ 的极大值,因此对 $x$ 求导数。
+
+$$
+\begin{aligned}
+ \ln y & = \frac{1}{x} \ln x & \text{取对数} \\
+ \frac{1}{y} \dot {y} & = \frac{1}{x^2} - \frac{1}{x^2} \ln x & \text{对 $x$ 求导} \\
+ & = \frac{1 - \ln x}{x^2} \\
+ \dot {y} & = \frac{1 - \ln x}{x^2} x^{\frac{1}{x}} & \text{整理得}
+\end{aligned}
+$$
+
+令 $\dot {y} = 0$ ,则 $1 - \ln x = 0$ ,易得驻点为 $x_0 = e \approx 2.7$ ;根据以下公式,可知 $x_0$ 为极大值点。
+
+$$
+\dot {y}
+\begin{cases}
+ > 0 & , x \in [- \infty, e) \\
+ < 0 & , x \in (e, \infty] \\
+\end{cases}
+$$
+
+由于切分长度 $x$ 必须为整数,最接近 $e$ 的整数为 $2$ 或 $3$ 。如下式所示,代入 $x = 2$ 和 $x = 3$ ,得出 $x = 3$ 时,乘积达到最大。
+
+$$
+y(3) = 3^{1/3} \approx 1.44 \\
+y(2) = 2^{1/2} \approx 1.41
+$$
+
+口算对比方法:给两数字同时取 $6$ 次方,再对比。
+
+$$
+y(3)^6 = (3^{1/3})^6 = 9 \\
+y(2)^6 = (2^{1/2})^6 = 8
+$$
+
+> **推论二:** 尽可能将竹子以长度 $3$ 等分为多段时,乘积最大。
+
+### 切分规则:
+
+1. **最优:** $3$ 。把竹子尽可能切为多个长度为 $3$ 的片段,留下的最后一段竹子的长度可能为 $0,1,2$ 三种情况。
+2. **次优:** $2$ 。若最后一段竹子长度为 $2$ ;则保留,不再拆为 $1+1$ 。
+3. **最差:** $1$ 。若最后一段竹子长度为 $1$ ;则应把一份 $3 + 1$ 替换为 $2 + 2$,因为 $2 \times 2 > 3 \times 1$。
+
+### 算法流程:
+
+1. 当 $n \leq 3$ 时,按照规则应不切分,但由于题目要求必须剪成 $m>1$ 段,因此必须剪出一段长度为 $1$ 的竹子,即返回 $n - 1$ 。
+2. 当 $n>3$ 时,求 $n$ 除以 $3$ 的 整数部分 $a$ 和 余数部分 $b$ (即 $n = 3a + b$ ),并分为以下三种情况:
+ - 当 $b = 0$ 时,直接返回 $3^a$;
+ - 当 $b = 1$ 时,要将一个 $1 + 3$ 转换为 $2+2$,因此返回 $3^{a-1} \times 4$;
+ - 当 $b = 2$ 时,返回 $3^a \times 2$。
+
+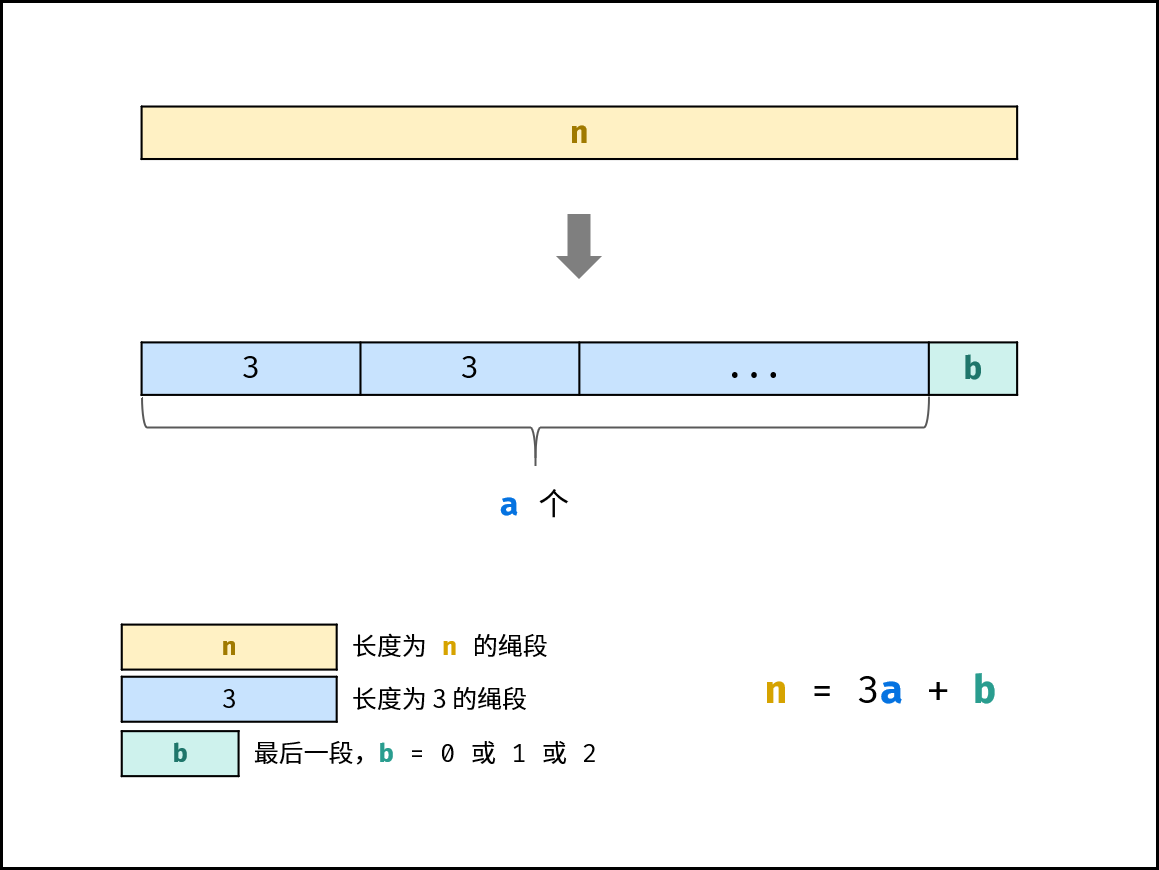{:align=center width=600}
+
+## 代码:
+
+> Python 中常见有三种幂计算函数: **`*`** 和 **`pow()`** 的时间复杂度均为 $O(\log a)$ ;而 **`math.pow()`** 始终调用 C 库的 `pow()` 函数,其执行浮点取幂,时间复杂度为 $O(1)$ 。
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def cuttingBamboo(self, bamboo_len: int) -> int:
+ if bamboo_len <= 3: return bamboo_len - 1
+ a, b = bamboo_len // 3, bamboo_len % 3
+ if b == 0: return int(math.pow(3, a))
+ if b == 1: return int(math.pow(3, a - 1) * 4)
+ return int(math.pow(3, a) * 2)
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public int cuttingBamboo(int bamboo_len) {
+ if(bamboo_len <= 3) return bamboo_len - 1;
+ int a = bamboo_len / 3, b = bamboo_len % 3;
+ if(b == 0) return (int)Math.pow(3, a);
+ if(b == 1) return (int)Math.pow(3, a - 1) * 4;
+ return (int)Math.pow(3, a) * 2;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int cuttingBamboo(int bamboo_len) {
+ if(bamboo_len <= 3) return bamboo_len - 1;
+ int a = bamboo_len / 3, b = bamboo_len % 3;
+ if(b == 0) return pow(3, a);
+ if(b == 1) return pow(3, a - 1) * 4;
+ return pow(3, a) * 2;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(1)$ :** 仅有求整、求余、次方运算。
+ - [求整和求余运算](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/35189851/time-complexity-of-modulo-operator-in-python):资料提到不超过机器数的整数可以看作是 $O(1)$ ;
+ - [幂运算](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/32418731/java-math-powa-b-time-complexity):查阅资料,提到浮点取幂为 $O(1)$ 。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(1)$ :** 变量 `a` 和 `b` 使用常数大小额外空间。
+
+## 贪心思路:
+
+数学推导需要一定的知识基础,贪心算法的思路更加适合快速解题。
+
+> 设一竹子长度为 $n$ ( $n>1$ ),则其必可被切分为两段 $n=n_1+n_2$ 。
+> 根据经验推测,切分的两数字乘积往往原数字更大,即往往有 $n_1 \times n_2 > n_1 + n_2 = n$ 。
+>
+> - **例如竹子长度为 $6$ :** $6 = 3 + 3 < 3 \times 3 = 9$ ;
+> - **也有少数反例,例如 $2$ :** $2 = 1 + 1 > 1 \times 1 = 1$ 。
+
+- **推论一:** 合理的切分方案可以带来更大的乘积。
+
+> 设一竹子长度为 $n$ ( $n>1$ ),**切分为两段** $n=n_1+n_2$ ,**切分为三段** $n=n_1+n_2+n_3$ 。
+> 根据经验推测,**三段** 的乘积往往更大,即往往有 $n_1 n_2 n_3 > n_1 n_2$ 。
+>
+> - **例如竹子长度为 $9$ :** 两段 $9=4+5$ 和 三段 $9=3+3+3$,则有 $4 \times 5 < 3 \times 3 \times 3$ 。
+> - **也有少数反例,例如 $6$ :** 两段 $6=3+3$ 和 三段 $6=2+2+2$,则有 $3 \times 3 > 2 \times 2 \times 2$ 。
+
+- **推论二:** 若切分方案合理,竹子段切分的越多,乘积越大。
+
+> 总体上看,貌似长竹子切分为越多段乘积越大,但其实到某个长度分界点后,乘积到达最大值,就不应再切分了。
+> **问题转化:** 是否有**优先级最高的长度** $x$ 存在?若有,则应该尽可能把竹子以 $x$ 长度切为多段,以获取最大乘积。
+
+- **推论三:** 为使乘积最大,只有长度为 $2$ 和 $3$ 的竹子不应再切分,且 $3$ 比 $2$ 更优 *(详情见下表)* 。
+
+| 竹子切分方案 | 乘积 | 结论 |
+| ------------- | ------------------------------------------ | ----------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| $2 = 1 + 1$ | $1 \times 1 = 1$ | $2$ 不应切分 |
+| $3=1+2$ | $1 \times 2 = 2$ | $3$ 不应切分 |
+| $4=2+2=1+3$ | $2 \times 2 = 4 > 1 \times 3 = 3$ | $4$ 和 $2$ 等价,且 $2+2$ 比 $1+3$ 更优 |
+| $5=2+3=1+4$ | $2 \times 3 = 6 > 1 \times 4 = 4$ | $5$ 应切分为 $2+3$ |
+| $6=3+3=2+2+2$ | $3 \times 3 = 9 > 2 \times 2 \times 2 = 8$ | $6$ 应切分为 $3+3$ ,进而**推出 $3$ 比 $2$ 更优** |
+| $>7$ | ... | **长绳**(长度>7)可转化为多个**短绳**(长度1~6),因此肯定应切分 |
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 132. \347\240\215\347\253\271\345\255\220 II.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 132. \347\240\215\347\253\271\345\255\220 II.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..e31e4b0
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 132. \347\240\215\347\253\271\345\255\220 II.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,166 @@
+## 解题思路:
+
+> 切分规则的推导流程请见上一题「砍竹子 I」。
+
+### 切分规则:
+
+1. **最优:** $3$ 。把竹子尽可能切为多个长度为 $3$ 的片段,留下的最后一段竹子的长度可能为 $0,1,2$ 三种情况。
+2. **次优:** $2$ 。若最后一段竹子长度为 $2$ ;则保留,不再拆为 $1+1$ 。
+3. **最差:** $1$ 。若最后一段竹子长度为 $1$ ;则应把一份 $3 + 1$ 替换为 $2 + 2$,因为 $2 \times 2 > 3 \times 1$。
+
+### 算法流程:
+
+1. 当 $n \leq 3$ 时,按照规则应不切分,但由于题目要求必须剪成 $m>1$ 段,因此必须剪出一段长度为 $1$ 的竹子,即返回 $n - 1$ 。
+2. 当 $n>3$ 时,求 $n$ 除以 $3$ 的 整数部分 $a$ 和 余数部分 $b$ (即 $n = 3a + b$ ),并分为以下三种情况(设求余操作符号为 "$\odot$" ):
+ - 当 $b = 0$ 时,直接返回 $3^a \odot 1000000007$;
+ - 当 $b = 1$ 时,要将一个 $1 + 3$ 转换为 $2+2$,因此返回 $(3^{a-1} \times 4)\odot 1000000007$;
+ - 当 $b = 2$ 时,返回 $(3^a \times 2) \odot 1000000007$。
+
+{:align=center width=600}
+
+### 大数求余解法:
+
+**大数越界:** 当 $a$ 增大时,最后返回的 $3^a$ 大小以指数级别增长,可能超出 `int32` 甚至 `int64` 的取值范围,导致返回值错误。
+**大数求余问题:** 在仅使用 `int32` 类型存储的前提下,正确计算 $x^a$ 对 $p$ 求余(即 $x^a \odot p$ )的值。
+**解决方案:** *循环求余* 、 *快速幂求余* ,其中后者的时间复杂度更低,两种方法均基于以下求余运算规则推出:
+
+$$
+(xy) \odot p = [(x \odot p)(y \odot p)] \odot p
+$$
+
+### 1. 循环求余:
+
+根据求余运算性质推出(∵ 本题中 $x 0:
+ if a % 2: rem = (rem * x) % p
+ x = x ** 2 % p
+ a //= 2
+ return rem
+```
+
+**帮助理解:** 根据下表, 初始状态 $rem=1$, $x=3$, $a=19$, $p=1000000007$ ,最后会将 $rem \times (x^a \odot p)$ 化为 $rem \times (x^0 \odot p) = rem \times 1$ 的形式,即 $rem$ 为余数答案。
+
+| $n$ | $rem \times (x^a \odot p)$ | $rem_n=rem_{n-1} \times x_{n-1} \odot p$ | $x_n=x_{n-1}^2 \odot p$ | $a_n=a_{n-1}//2$ |
+| --- | -----------------------------------------: | ---------------------------------------: | -----------------------------: | :--------------: |
+| $1$ | $1 \times (3^{19} \odot p)$ | $1$ | $3$ | $19$ |
+| $2$ | $3 \times (9^{9} \odot p)$ | $3=1\times3\odot p$ | $9=3^2 \odot p$ | $9=19//2$ |
+| $3$ | $27 \times (81^{4} \odot p)$ | $27 = 3 \times 9 \odot p$ | $81=9^2\odot p$ | $4=9//2$ |
+| $4$ | $27 \times (6561^{2} \odot p)$ | $27$ | $6561=81^2 \odot p$ | $2=4//2$ |
+| $5$ | $27 \times (43046721^{1} \odot p)$ | $27$ | $43046721=6561^2 \odot p$ | $1=2//2$ |
+| $6$ | $162261460 \times (175880701^{0} \odot p)$ | $162261460=27 \times 43046721 \odot p$ | $175880701=43046721^2 \odot p$ | $0=1//2$ |
+
+## 代码:
+
+**Python 代码:** 由于语言特性,理论上 Python 中的变量取值范围由系统内存大小决定(无限大),因此在 Python 中其实不用考虑大数越界问题。
+**Java/C++ 代码:** 根据二分法计算原理,至少要保证变量 `x` 和 `rem` 可以正确存储 $1000000007^2$ ,而 $2^{64} > 1000000007^2 > 2^{32}$ ,因此我们选取 `long` 类型。
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def cuttingBamboo(self, bamboo_len: int) -> int:
+ if bamboo_len <= 3: return bamboo_len - 1
+ a, b, p, x, rem = bamboo_len // 3 - 1, bamboo_len % 3, 1000000007, 3 , 1
+ while a > 0:
+ if a % 2: rem = (rem * x) % p
+ x = x ** 2 % p
+ a //= 2
+ if b == 0: return (rem * 3) % p # = 3^(a+1) % p
+ if b == 1: return (rem * 4) % p # = 3^a * 4 % p
+ return (rem * 6) % p # = 3^(a+1) * 2 % p
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public int cuttingBamboo(int bamboo_len) {
+ if(bamboo_len <= 3) return bamboo_len - 1;
+ int b = bamboo_len % 3, p = 1000000007;
+ long rem = 1, x = 3;
+ for(int a = bamboo_len / 3 - 1; a > 0; a /= 2) {
+ if(a % 2 == 1) rem = (rem * x) % p;
+ x = (x * x) % p;
+ }
+ if(b == 0) return (int)(rem * 3 % p);
+ if(b == 1) return (int)(rem * 4 % p);
+ return (int)(rem * 6 % p);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int cuttingBamboo(int bamboo_len) {
+ if(bamboo_len <= 3) return bamboo_len - 1;
+ int b = bamboo_len % 3, p = 1000000007;
+ long rem = 1, x = 3;
+ for(int a = bamboo_len / 3 - 1; a > 0; a /= 2) {
+ if(a % 2 == 1) rem = (rem * x) % p;
+ x = (x * x) % p;
+ }
+ if(b == 0) return (int)(rem * 3 % p);
+ if(b == 1) return (int)(rem * 4 % p);
+ return (int)(rem * 6 % p);
+ }
+};
+```
+
+```Python []
+# 由于语言特性,Python 可以不考虑大数越界问题
+class Solution:
+ def cuttingBamboo(self, bamboo_len: int) -> int:
+ if bamboo_len <= 3: return bamboo_len - 1
+ a, b, p = bamboo_len // 3, bamboo_len % 3, 1000000007
+ if b == 0: return 3 ** a % p
+ if b == 1: return 3 ** (a - 1) * 4 % p
+ return 3 ** a * 2 % p
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+> 以下为 **二分求余法** 的复杂度。
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(\log N)$ :** 其中 $N=a$ ,二分法为对数级别复杂度,每轮仅有求整、求余、次方运算。
+ - [求整和求余运算](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/35189851/time-complexity-of-modulo-operator-in-python):资料提到不超过机器数的整数可以看作是 $O(1)$ ;
+ - [幂运算](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/32418731/java-math-powa-b-time-complexity):查阅资料,提到浮点取幂为 $O(1)$ 。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(1)$ :** 变量 `a, b, p, x, rem` 使用常数大小额外空间。
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 133. \344\275\215 1 \347\232\204\344\270\252\346\225\260.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 133. \344\275\215 1 \347\232\204\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..9cb4025
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 133. \344\275\215 1 \347\232\204\344\270\252\346\225\260.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
+## 方法一:逐位判断
+
+根据 **与运算** 定义,设二进制数字 $n$ ,则有:
+
+- 若 $n \& 1 = 0$ ,则 $n$ 二进制 **最右一位** 为 $0$ ;
+- 若 $n \& 1 = 1$ ,则 $n$ 二进制 **最右一位** 为 $1$ 。
+
+根据以上特点,考虑以下 **循环判断** :
+
+1. 判断 $n$ 最右一位是否为 $1$ ,根据结果计数。
+2. 将 $n$ 右移一位(本题要求把数字 $n$ 看作无符号数,因此使用 **无符号右移** 操作)。
+
+### 算法流程:
+
+1. 初始化数量统计变量 $res = 0$ 。
+2. 循环逐位判断: 当 $n = 0$ 时跳出。
+ 1. **`res += n & 1` :** 若 $n \& 1 = 1$ ,则统计数 $res$ 加一。
+ 2. **`n >>= 1` :** 将二进制数字 $n$ 无符号右移一位( Java 中无符号右移为 "$>>>$" ) 。
+3. 返回统计数量 $res$ 。
+
+
+
+### 代码:
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def hammingWeight(self, n: int) -> int:
+ res = 0
+ while n:
+ res += n & 1
+ n >>= 1
+ return res
+```
+
+```Java []
+public class Solution {
+ public int hammingWeight(int n) {
+ int res = 0;
+ while(n != 0) {
+ res += n & 1;
+ n >>>= 1;
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int hammingWeight(uint32_t n) {
+ unsigned int res = 0; // c++ 使用无符号数
+ while(n != 0) {
+ res += n & 1;
+ n >>= 1;
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(\log_2 n)$ :** 此算法循环内部仅有 **移位、与、加** 等基本运算,占用 $O(1)$ ;逐位判断需循环 $log_2 n$ 次,其中 $\log_2 n$ 代表数字 $n$ 最高位 $1$ 的所在位数(例如 $\log_2 4 = 2$, $\log_2 16 = 4$)。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(1)$ :** 变量 $res$ 使用常数大小额外空间。
+
+## 方法二:巧用 $n \& (n - 1)$
+
+- **$(n - 1)$ 解析:** 二进制数字 $n$ 最右边的 $1$ 变成 $0$ ,此 $1$ 右边的 $0$ 都变成 $1$ 。
+- **$n \& (n - 1)$ 解析:** 二进制数字 $n$ 最右边的 $1$ 变成 $0$ ,其余不变。
+
+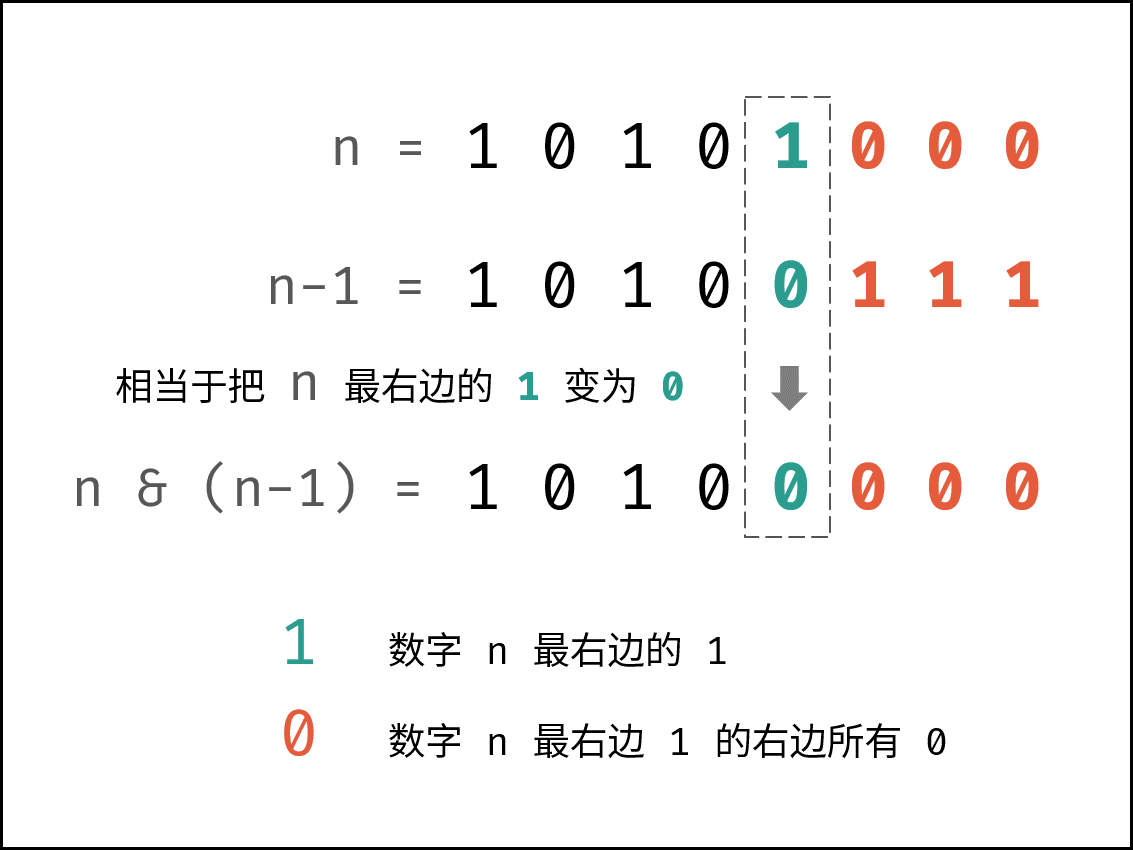{:align=center width=450}
+
+### 算法流程:
+
+1. 初始化数量统计变量 $res$ 。
+2. 循环消去最右边的 $1$ :当 $n = 0$ 时跳出。
+ 1. **`res += 1` :** 统计变量加 $1$ ;
+ 2. **`n &= n - 1` :** 消去数字 $n$ 最右边的 $1$ 。
+3. 返回统计数量 $res$ 。
+
+
+
+### 代码:
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def hammingWeight(self, n: int) -> int:
+ res = 0
+ while n:
+ res += 1
+ n &= n - 1
+ return res
+```
+
+```Java []
+public class Solution {
+ public int hammingWeight(int n) {
+ int res = 0;
+ while(n != 0) {
+ res++;
+ n &= n - 1;
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int hammingWeight(uint32_t n) {
+ int res = 0;
+ while(n != 0) {
+ res++;
+ n &= n - 1;
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(M)$ :** $n \& (n - 1)$ 操作仅有减法和与运算,占用 $O(1)$ ;设 $M$ 为二进制数字 $n$ 中 $1$ 的个数,则需循环 $M$ 次(每轮消去一个 $1$ ),占用 $O(M)$ 。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(1)$ :** 变量 $res$ 使用常数大小额外空间。
diff --git a/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 134. Pow(x, n).md b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 134. Pow(x, n).md
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..fef1472
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 134. Pow(x, n).md
@@ -0,0 +1,134 @@
+## 解题思路:
+
+求 $x^n$ 最简单的方法是通过循环将 $n$ 个 $x$ 乘起来,依次求 $x^1, x^2, ..., x^{n-1}, x^n$ ,时间复杂度为 $O(n)$ 。
+**快速幂法** 可将时间复杂度降低至 $O(\log n)$ ,以下从 「分治法」 和 「二进制」 两个角度解析快速幂法。
+
+### 快速幂解析(分治法角度):
+
+> 快速幂实际上是分治思想的一种应用。
+
+**二分推导:** $x^n = x^{n/2} \times x^{n/2} = (x^2)^{n/2}$ ,令 $n/2$ 为整数,则需要分为奇偶两种情况(设向下取整除法符号为 "$//$" ):
+
+$$
+x^n =
+\begin{cases}
+ (x^2)^{n//2} & , n 为偶数 \\
+ x(x^2)^{n//2} & , n 为奇数 \\
+\end{cases}
+$$
+
+> 观察发现,当 $n$ 为奇数时,二分后会多出一项 $x$ 。
+
+**幂结果获取:**
+
+- 根据推导,可通过循环 $x = x^2$ 操作,每次把幂从 $n$ 降至 $n//2$ ,直至将幂降为 $0$ ;
+- 设 $res=1$ ,则初始状态 $x^n = x^n \times res$ 。在循环二分时,每当 $n$ 为奇数时,将多出的一项 $x$ 乘入 $res$ ,则最终可化至 $x^n = x^0 \times res = res$ ,返回 $res$ 即可。
+
+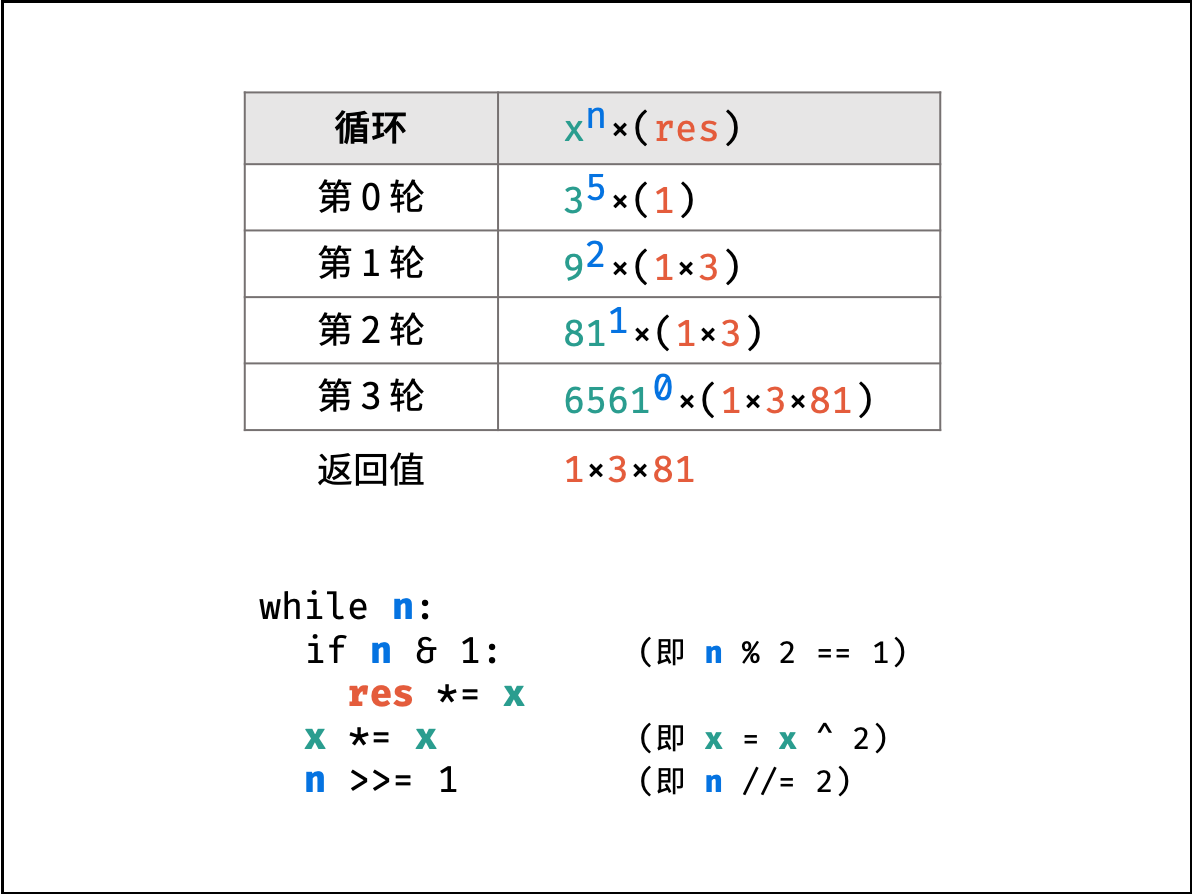{:align=center width=500}
+
+**转化为位运算:**
+
+- 向下整除 $n // 2$ **等价于** 右移一位 $n >> 1$ ;
+- 取余数 $n \mod 2$ **等价于** 判断二进制最右位 $n \& 1$ ;
+
+### 快速幂解析(二进制角度):
+
+> 利用十进制数字 $n$ 的二进制表示,可对快速幂进行数学化解释。
+
+对于任何十进制正整数 $n$ ,设其二进制为 "$b_m...b_3b_2b_1$"( $b_i$ 为二进制某位值,$i \in [1,m]$ ),则有:
+
+- **二进制转十进制:** $n = 1b_1 + 2b_2 + 4b_3 + ... + 2^{m-1}b_m$ *(即二进制转十进制公式)* ;
+- **幂的二进制展开:** $x^n = x^{1b_1 + 2b_2 + 4b_3 + ... + 2^{m-1}b_m} = x^{1b_1}x^{2b_2}x^{4b_3}...x^{2^{m-1}b_m}$ ;
+
+根据以上推导,可把计算 $x^n$ 转化为解决以下两个问题:
+
+- **计算 $x^1, x^2, x^4, ..., x^{2^{m-1}}$ 的值:** 循环赋值操作 $x = x^2$ 即可;
+- **获取二进制各位 $b_1, b_2, b_3, ..., b_m$ 的值:** 循环执行以下操作即可。
+ 1. **$n \& 1$ (与操作):** 判断 $n$ 二进制最右一位是否为 $1$ ;
+ 2. **$n>>1$ (移位操作):** $n$ 右移一位(可理解为删除最后一位)。
+
+因此,应用以上操作,可在循环中依次计算 $x^{2^{0}b_1}, x^{2^{1}b_2}, ..., x^{2^{m-1}b_m}$ 的值,并将所有 $x^{2^{i-1}b_i}$ 累计相乘即可,其中:
+
+$$
+x^{2^{i-1}b_i}=
+\begin{cases}
+ 1 & , b_i = 0 \\
+ x^{2^{i-1}} & , b_i = 1 \\
+\end{cases}
+$$
+
+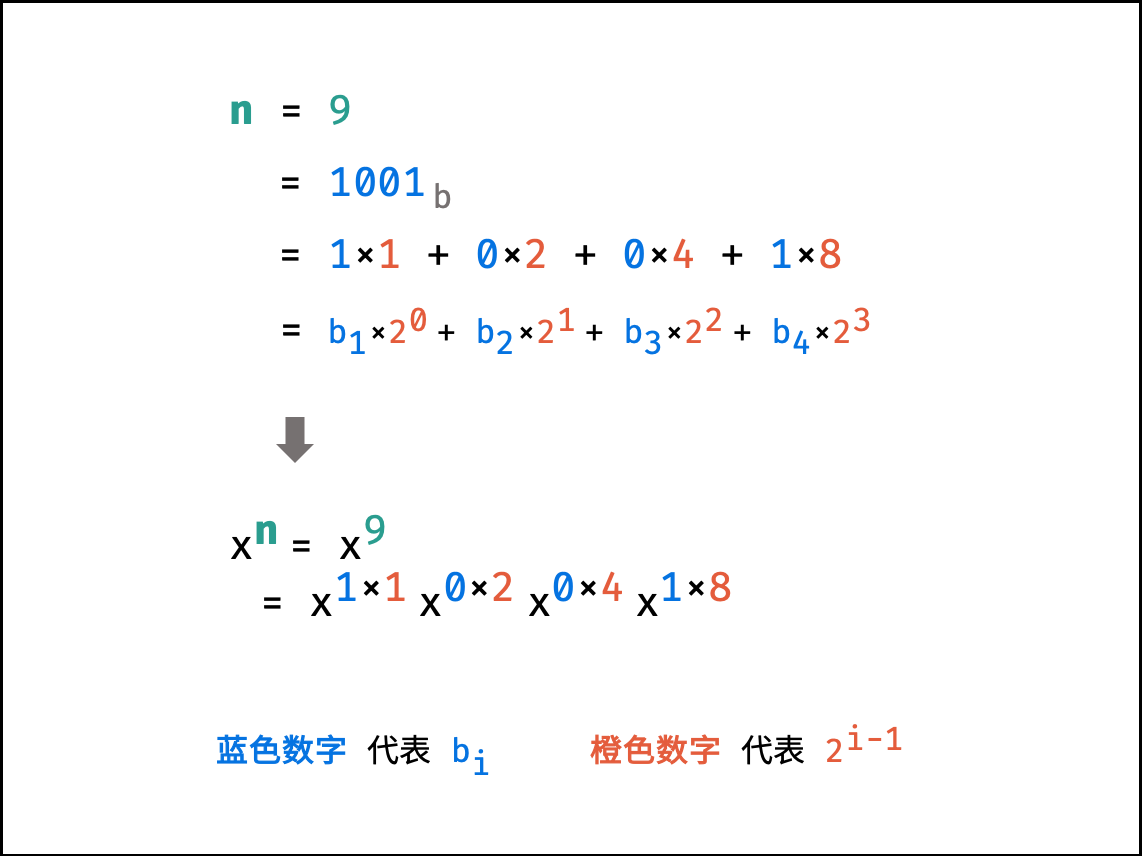{:align=center width=500}
+
+### 算法流程:
+
+1. 当 $x = 0.0$ 时:直接返回 $0.0$ ,以避免后续 $1$ 除以 $0$ 操作报错。**分析:** 数字 $0$ 的正数次幂恒为 $0$ ;$0$ 的 $0$ 次幂和负数次幂没有意义,因此直接返回 $0.0$ 即可。
+2. 初始化 $res = 1$ 。
+3. 当 $n < 0$ 时:把问题转化至 $n \geq 0$ 的范围内,即执行 $x = 1/x$ ,$n = - n$ 。
+4. 循环计算:当 $n = 0$ 时跳出。
+ 1. 当 $n \& 1 = 1$ 时:将当前 $x$ 乘入 $res$ (即 $res *= x$ )。
+ 2. 执行 $x = x^2$ (即 $x *= x$ )。
+ 3. 执行 $n$ 右移一位(即 $n >>= 1$)。
+5. 返回 $res$ 。
+
+## 代码:
+
+Java 中 int32 变量区间 $n \in [-2147483648, 2147483647]$ ,因此当 $n = -2147483648$ 时执行 $n = -n$ 会因越界而赋值出错。解决方法是先将 $n$ 存入 long 变量 $b$ ,后面用 $b$ 操作即可。
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def myPow(self, x: float, n: int) -> float:
+ if x == 0.0: return 0.0
+ res = 1
+ if n < 0: x, n = 1 / x, -n
+ while n:
+ if n & 1: res *= x
+ x *= x
+ n >>= 1
+ return res
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public double myPow(double x, int n) {
+ if(x == 0.0f) return 0.0d;
+ long b = n;
+ double res = 1.0;
+ if(b < 0) {
+ x = 1 / x;
+ b = -b;
+ }
+ while(b > 0) {
+ if((b & 1) == 1) res *= x;
+ x *= x;
+ b >>= 1;
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ double myPow(double x, int n) {
+ if(x == 0.0f) return 0.0;
+ long b = n;
+ double res = 1.0;
+ if(b < 0) {
+ x = 1 / x;
+ b = -b;
+ }
+ while(b > 0) {
+ if((b & 1) == 1) res *= x;
+ x *= x;
+ b >>= 1;
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(\log n)$ :** 二分的时间复杂度为对数级别。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(1)$ :** $res$, $b$ 等变量占用常数大小额外空间。
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 135. \346\212\245\346\225\260.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 135. \346\212\245\346\225\260.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..7ec06f2
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 135. \346\212\245\346\225\260.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,269 @@
+## 解题思路:
+
+题目要求打印 “从 $1$ 至 $cnt$ 的数字” ,因此需考虑以下两个问题:
+
+1. **最大的 $cnt$ 位数(记为 $end$ )和位数 $cnt$ 的关系:** 例如最大的 $1$ 位数是 $9$ ,最大的 $2$ 位数是 $99$ ,最大的 $3$ 位数是 $999$ 。则可推出公式:
+
+$$
+end = 10^{cnt} - 1
+$$
+
+2. **大数越界问题:** 当 $cnt$ 较大时,$end$ 会超出 $int32$ 整型的取值范围,超出取值范围的数字无法正常存储。但由于本题要求返回 int 类型数组,相当于默认所有数字都在 int32 整型取值范围内,因此不考虑大数越界问题。
+
+因此,只需定义区间 $[1, 10^{cnt} - 1]$ 和步长 $1$ ,通过 $for$ 循环生成结果列表 $res$ 并返回即可。
+
+### 代码:
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def countNumbers(self, cnt: int) -> List[int]:
+ res = []
+ for i in range(1, 10 ** cnt):
+ res.append(i)
+ return res
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public int[] countNumbers(int cnt) {
+ int end = (int)Math.pow(10, cnt) - 1;
+ int[] res = new int[end];
+ for(int i = 0; i < end; i++)
+ res[i] = i + 1;
+ return res;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+利用 Python 的语言特性,可以简化代码:先使用 `range()` 方法生成可迭代对象,再使用 `list()` 方法转化为列表并返回即可。
+
+```Python
+class Solution:
+ def countNumbers(self, cnt: int) -> List[int]:
+ return list(range(1, 10 ** cnt))
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(10^{cnt})$ :** 生成长度为 $10^{cnt}$ 的列表需使用 $O(10^{cnt})$ 时间。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(1)$ :** 建立列表需使用 $O(1)$ 大小的额外空间( 列表作为返回结果,不计入额外空间 )。
+
+## 大数打印拓展:
+
+实际上,本题的主要考点是大数越界情况下的打印。需要解决以下三个问题:
+
+**1. 表示大数的变量类型:**
+
+- 无论是 short / int / long ... 任意变量类型,数字的取值范围都是有限的。因此,大数的表示应用字符串 String 类型。
+
+**2. 生成数字的字符串集:**
+
+- 使用 int 类型时,每轮可通过 $+1$ 生成下个数字,而此方法无法应用至 String 类型。并且, String 类型的数字的进位操作效率较低,例如 `"9999"` 至 `"10000"` 需要从个位到千位循环判断,进位 4 次。
+- 观察可知,生成的列表实际上是 $cnt$ 位 $0$ - $9$ 的 **全排列** ,因此可避开进位操作,通过递归生成数字的 String 列表。
+
+**3. 递归生成全排列:**
+
+- 基于分治算法的思想,先固定高位,向低位递归,当个位已被固定时,添加数字的字符串。例如当 $cnt = 2$ 时(数字范围 $1 - 99$ ),固定十位为 $0$ - $9$ ,按顺序依次开启递归,固定个位 $0$ - $9$ ,终止递归并添加数字字符串。
+
+> 下图中的 `n` 对应本题中的 `cnt` 。
+
+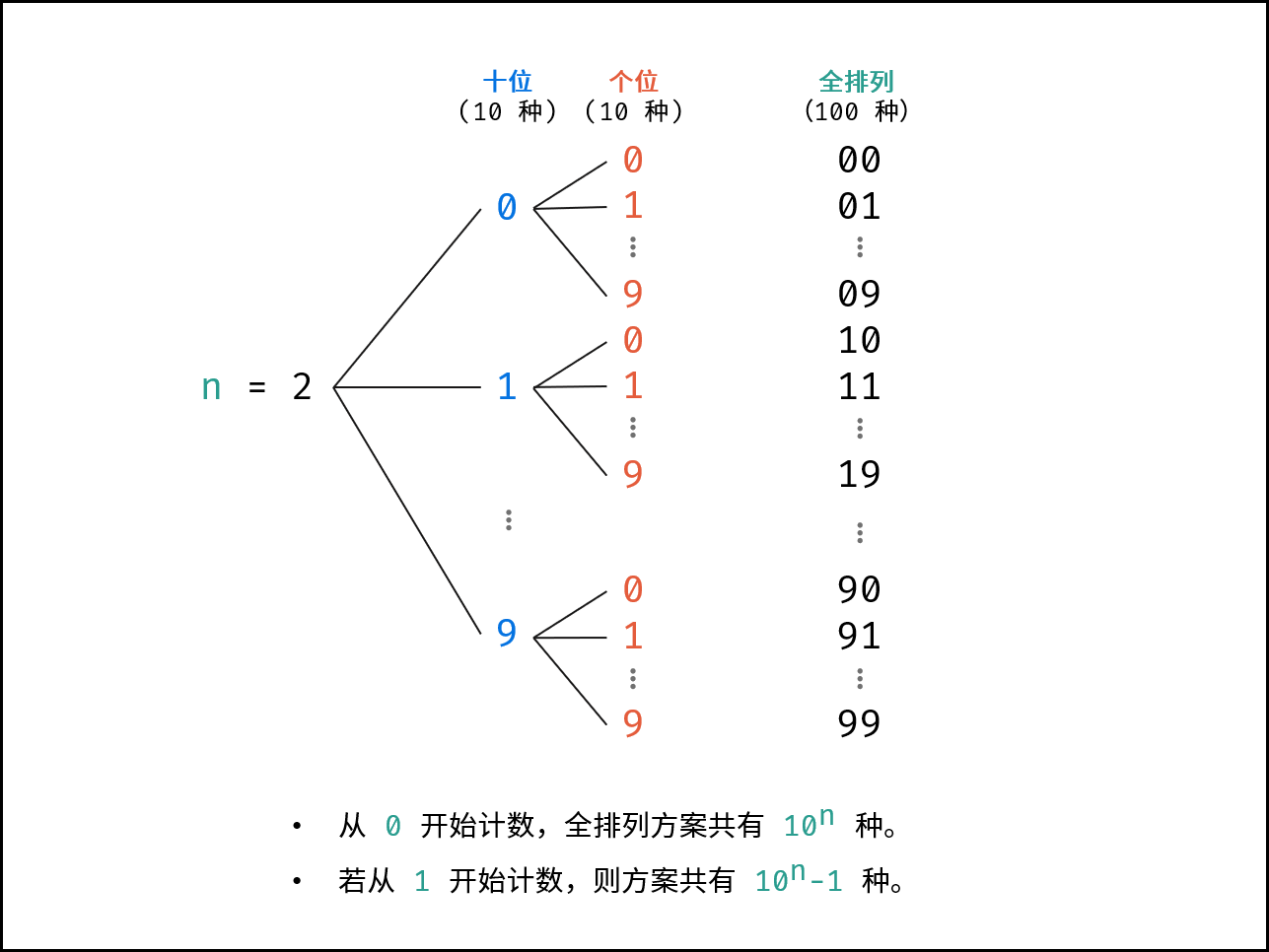{:align=center width=500}
+
+根据以上方法,可初步编写全排列代码:
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def countNumbers(self, cnt: int) -> [int]:
+ def dfs(x):
+ if x == cnt: # 终止条件:已固定完所有位
+ res.append(''.join(num)) # 拼接 num 并添加至 res 尾部
+ return
+ for i in range(10): # 遍历 0 - 9
+ num[x] = str(i) # 固定第 x 位为 i
+ dfs(x + 1) # 开启固定第 x + 1 位
+
+ num = ['0'] * cnt # 起始数字定义为 cnt 个 0 组成的字符列表
+ res = [] # 数字字符串列表
+ dfs(0) # 开启全排列递归
+ return ','.join(res) # 拼接所有数字字符串,使用逗号隔开,并返回
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ StringBuilder res;
+ int count = 0, cnt;
+ char[] num, loop = {'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9'};
+ public String countNumbers(int cnt) {
+ this.cnt = cnt;
+ res = new StringBuilder(); // 数字字符串集
+ num = new char[cnt]; // 定义长度为 cnt 的字符列表
+ dfs(0); // 开启全排列递归
+ res.deleteCharAt(res.length() - 1); // 删除最后多余的逗号
+ return res.toString(); // 转化为字符串并返回
+ }
+ void dfs(int x) {
+ if(x == cnt) { // 终止条件:已固定完所有位
+ res.append(String.valueOf(num) + ","); // 拼接 num 并添加至 res 尾部,使用逗号隔开
+ return;
+ }
+ for(char i : loop) { // 遍历 ‘0‘ - ’9‘
+ num[x] = i; // 固定第 x 位为 i
+ dfs(x + 1); // 开启固定第 x + 1 位
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+在此方法下,各数字字符串被逗号隔开,共同组成长字符串。返回的数字集字符串如下所示:
+
+```yaml
+输入:n = 1
+输出:"0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9"
+
+输入:n = 2
+输出:"00,01,02,...,10,11,12,...,97,98,99"
+
+输入:n = 3
+输出:"000,001,002,...,100,101,102,...,997,998,999"
+```
+
+观察可知,当前的生成方法仍有以下问题:
+
+1. 诸如 $00, 01, 02, \cdots$ 应显示为 $0, 1, 2, \cdots$ ,即应 **删除高位多余的 $0$** ;
+2. 此方法从 $0$ 开始生成,而题目要求 **列表从 $1$ 开始** ;
+
+以上两个问题的解决方法如下:
+
+**1. 删除高位多余的 $0$ :**
+
+- **字符串左边界定义:** 声明变量 $start$ 规定字符串的左边界,以保证添加的数字字符串 `num[start:]` 中无高位多余的 $0$ 。例如当 $cnt = 2$ 时,$1 - 9$ 时 $start = 1$ ,$10 - 99$ 时 $start = 0$ 。
+
+- **左边界 $start$ 变化规律:** 观察可知,当输出数字的所有位都是 $9$ 时,则下个数字需要向更高位进 $1$ ,此时左边界 $start$ 需要减 $1$ (即高位多余的 $0$ 减少一个)。例如当 $cnt = 3$ (数字范围 $1 - 999$ )时,左边界 $start$ 需要减 $1$ 的情况有: "009" 进位至 "010" , "099" 进位至 "100" 。设数字各位中 $9$ 的数量为 $nine$ ,所有位都为 $9$ 的判断条件可用以下公式表示:
+
+$$
+cnt - start = nine
+$$
+
+- **统计 $nine$ 的方法:** 固定第 $x$ 位时,当 $i = 9$ 则执行 $nine = nine + 1$ ,并在回溯前恢复 $nine = nine - 1$ 。
+
+**2. 列表从 $1$ 开始:**
+
+- 在以上方法的基础上,添加数字字符串前判断其是否为 `"0"` ,若为 `"0"` 则直接跳过。
+
+
+
+### 代码:
+
+为 **正确表示大数** ,以下代码的返回值为数字字符串集拼接而成的长字符串。
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def countNumbers(self, cnt: int) -> [int]:
+ def dfs(x):
+ if x == cnt:
+ s = ''.join(num[self.start:])
+ if s != '0': res.append(s)
+ if cnt - self.start == self.nine: self.start -= 1
+ return
+ for i in range(10):
+ if i == 9: self.nine += 1
+ num[x] = str(i)
+ dfs(x + 1)
+ self.nine -= 1
+
+ num, res = ['0'] * cnt, []
+ self.nine = 0
+ self.start = cnt - 1
+ dfs(0)
+ return ','.join(res)
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ StringBuilder res;
+ int nine = 0, count = 0, start, cnt;
+ char[] num, loop = {'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9'};
+ public String countNumbers(int cnt) {
+ this.cnt = cnt;
+ res = new StringBuilder();
+ num = new char[cnt];
+ start = cnt - 1;
+ dfs(0);
+ res.deleteCharAt(res.length() - 1);
+ return res.toString();
+ }
+ void dfs(int x) {
+ if(x == cnt) {
+ String s = String.valueOf(num).substring(start);
+ if(!s.equals("0")) res.append(s + ",");
+ if(cnt - start == nine) start--;
+ return;
+ }
+ for(char i : loop) {
+ if(i == '9') nine++;
+ num[x] = i;
+ dfs(x + 1);
+ }
+ nine--;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+本题要求输出 int 类型数组。为 **运行通过** ,可在添加数字字符串 $s$ 前,将其转化为 int 类型。代码如下所示:
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def countNumbers(self, cnt: int) -> [int]:
+ def dfs(x):
+ if x == cnt:
+ s = ''.join(num[self.start:])
+ if s != '0': res.append(int(s))
+ if cnt - self.start == self.nine: self.start -= 1
+ return
+ for i in range(10):
+ if i == 9: self.nine += 1
+ num[x] = str(i)
+ dfs(x + 1)
+ self.nine -= 1
+
+ num, res = ['0'] * cnt, []
+ self.nine = 0
+ self.start = cnt - 1
+ dfs(0)
+ return res
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ int[] res;
+ int nine = 0, count = 0, start, cnt;
+ char[] num, loop = {'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9'};
+ public int[] countNumbers(int cnt) {
+ this.cnt = cnt;
+ res = new int[(int)Math.pow(10, cnt) - 1];
+ num = new char[cnt];
+ start = cnt - 1;
+ dfs(0);
+ return res;
+ }
+ void dfs(int x) {
+ if(x == cnt) {
+ String s = String.valueOf(num).substring(start);
+ if(!s.equals("0")) res[count++] = Integer.parseInt(s);
+ if(cnt - start == nine) start--;
+ return;
+ }
+ for(char i : loop) {
+ if(i == '9') nine++;
+ num[x] = i;
+ dfs(x + 1);
+ }
+ nine--;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(10^{cnt})$ :** 递归的生成的排列的数量为 $10^{cnt}$ 。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(10^{cnt})$ :** 结果列表 $res$ 的长度为 $10^{cnt} - 1$ ,各数字字符串的长度区间为 $1, 2, ..., cnt$ ,因此占用 $O(10^{cnt})$ 大小的额外空间。
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 136. \345\210\240\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\350\212\202\347\202\271.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 136. \345\210\240\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..d271763
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 136. \345\210\240\351\231\244\351\223\276\350\241\250\350\212\202\347\202\271.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+## 解题思路:
+
+本题删除值为 `val` 的节点分需为两步:定位节点、修改引用。
+
+1. **定位节点:** 遍历链表,直到 `head.val == val` 时跳出,即可定位目标节点。
+2. **修改引用:** 设节点 `cur` 的前驱节点为 `pre` ,后继节点为 `cur.next` ;则执行 `pre.next = cur.next` ,即可实现删除 `cur` 节点。
+
+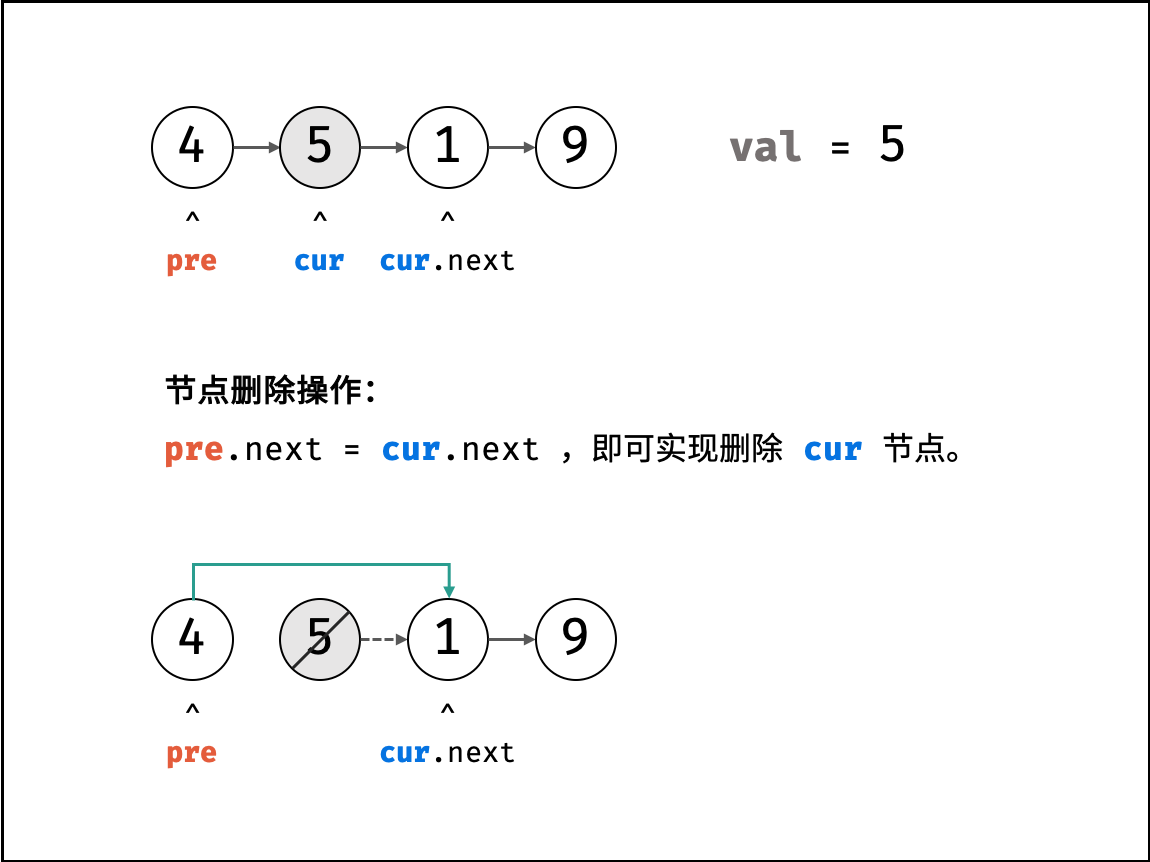{:align=center width=450}
+
+### 算法流程:
+
+1. **特例处理:** 当应删除头节点 `head` 时,直接返回 `head.next` 即可。
+2. **初始化:** `pre = head` , `cur = head.next` 。
+3. **定位节点:** 当 `cur` 为空 **或** `cur` 节点值等于 `val` 时跳出。
+ 1. 保存当前节点索引,即 `pre = cur` 。
+ 2. 遍历下一节点,即 `cur = cur.next` 。
+4. **删除节点:** 若 `cur` 指向某节点,则执行 `pre.next = cur.next` ;若 `cur` 指向 $\text{null}$ ,代表链表中不包含值为 `val` 的节点。
+5. **返回值:** 返回链表头部节点 `head` 即可。
+
+
+
+## 代码:
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def deleteNode(self, head: ListNode, val: int) -> ListNode:
+ if head.val == val: return head.next
+ pre, cur = head, head.next
+ while cur and cur.val != val:
+ pre, cur = cur, cur.next
+ if cur: pre.next = cur.next
+ return head
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) {
+ if(head.val == val) return head.next;
+ ListNode pre = head, cur = head.next;
+ while(cur != null && cur.val != val) {
+ pre = cur;
+ cur = cur.next;
+ }
+ if(cur != null) pre.next = cur.next;
+ return head;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ ListNode* deleteNode(ListNode* head, int val) {
+ if(head->val == val) return head->next;
+ ListNode *pre = head, *cur = head->next;
+ while(cur != nullptr && cur->val != val) {
+ pre = cur;
+ cur = cur->next;
+ }
+ if(cur != nullptr) pre->next = cur->next;
+ return head;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(N)$ :** $N$ 为链表长度,删除操作平均需循环 $N/2$ 次,最差 $N$ 次。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(1)$ :** `cur`, `pre` 占用常数大小额外空间。
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 137. \346\250\241\347\263\212\346\220\234\347\264\242\351\252\214\350\257\201.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 137. \346\250\241\347\263\212\346\220\234\347\264\242\351\252\214\350\257\201.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..134cad1
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 137. \346\250\241\347\263\212\346\220\234\347\264\242\351\252\214\350\257\201.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,185 @@
+## 解题思路:
+
+> 设 $s$ 的长度为 $n$ ,$p$ 的长度为 $m$ ;将 $s$ 的第 $i$ 个字符记为 $s_i$ ,$p$ 的第 $j$ 个字符记为 $p_j$ ,将 $s$ 的前 $i$ 个字符组成的子字符串记为 $s[:i]$ , 同理将 $p$ 的前 $j$ 个字符组成的子字符串记为 $p[:j]$ 。
+>
+> 因此,本题可转化为求 $s[:n]$ 是否能和 $p[:m]$ 匹配。
+
+总体思路是从 $s[:1]$ 和 $p[:1]$ 是否能匹配开始判断,每轮添加一个字符并判断是否能匹配,直至添加完整个字符串 $s$ 和 $p$ 。展开来看,假设 $s[:i]$ 与 $p[:j]$ 可以匹配,那么下一状态有两种:
+
+1. 添加一个字符 $s_{i+1}$ 后是否能匹配?
+2. 添加字符 $p_{j+1}$ 后是否能匹配?
+
+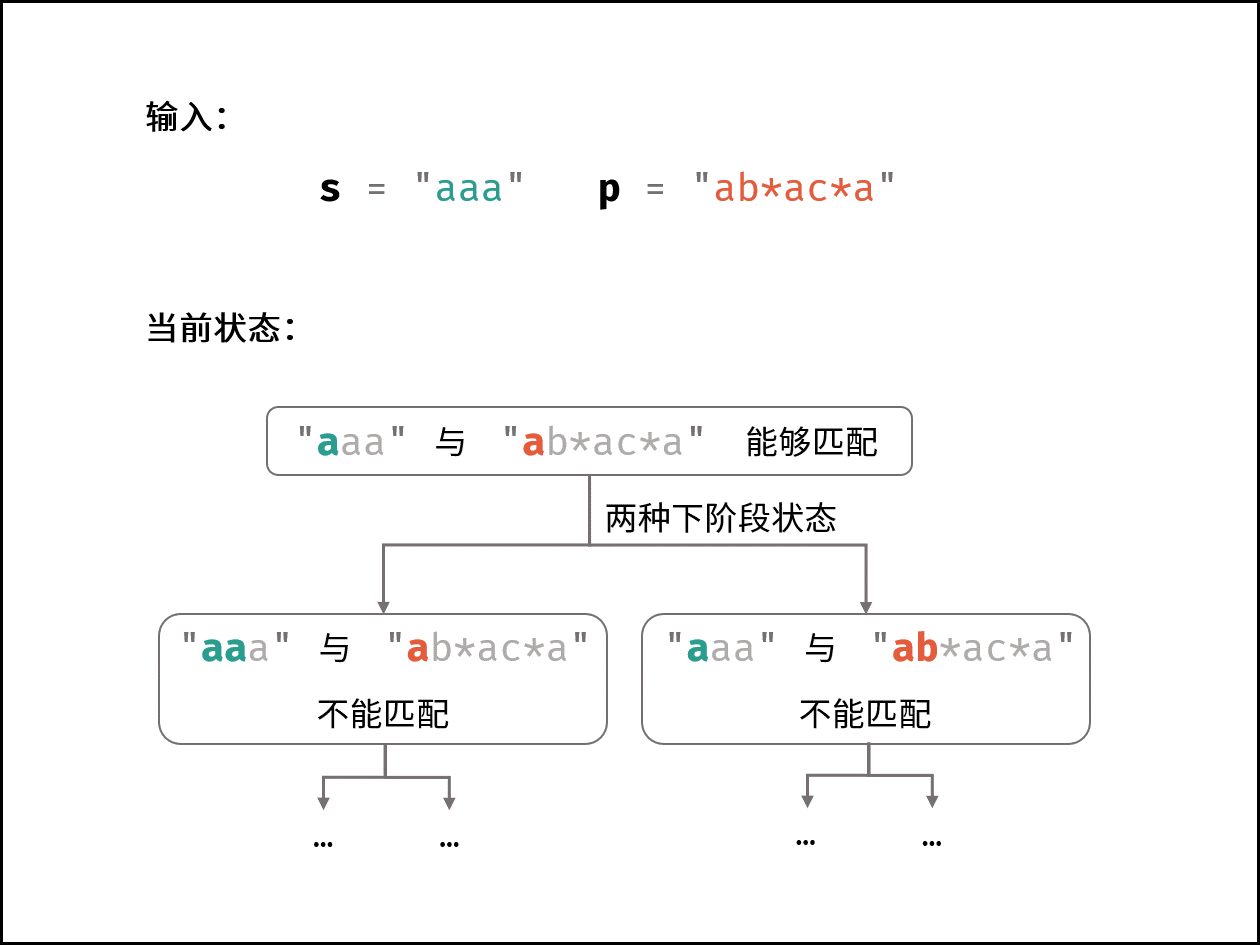{:align=center width=500}
+
+因此,本题的状态共有 $m \times n$ 种,应定义状态矩阵 $dp$ ,$dp[i][j]$ 代表 $s[:i]$ 与 $p[:j]$ 是否可以匹配。
+
+做好状态定义,接下来就是根据 「`普通字符`」 , 「`.`」 , 「`*`」三种字符的功能定义,分析出动态规划的转移方程。
+
+### 动态规划解析:
+
+**状态定义:** 设动态规划矩阵 `dp` ,`dp[i][j]` 代表字符串 `s` 的前 `i` 个字符和 `p` 的前 `j` 个字符能否匹配。
+
+**转移方程:** 需要注意,由于 `dp[0][0]` 代表的是空字符的状态, 因此 `dp[i][j]` 对应的添加字符是 `s[i - 1]` 和 `p[j - 1]` 。
+
+- 当 `p[j - 1] = '*'` 时,`dp[i][j]` 在当以下任一情况为 $\text{true}$ 时等于 $\text{true}$ :
+
+ 1. **`dp[i][j - 2]`:** 即将字符组合 `p[j - 2] *` 看作出现 0 次时,能否匹配;
+ 2. **`dp[i - 1][j]` 且 `s[i - 1] = p[j - 2]`:** 即让字符 `p[j - 2]` 多出现 1 次时,能否匹配;
+ 3. **`dp[i - 1][j]` 且 `p[j - 2] = '.'`:** 即让字符 `'.'` 多出现 1 次时,能否匹配;
+
+- 当 `p[j - 1] != '*'` 时,`dp[i][j]` 在当以下任一情况为 $\text{true}$ 时等于 $\text{true}$ :
+
+ 1. **`dp[i - 1][j - 1]` 且 `s[i - 1] = p[j - 1]`:** 即让字符 `p[j - 1]` 多出现一次时,能否匹配;
+ 2. **`dp[i - 1][j - 1]` 且 `p[j - 1] = '.'`:** 即将字符 `.` 看作字符 `s[i - 1]` 时,能否匹配;
+
+**初始化:** 需要先初始化 `dp` 矩阵首行,以避免状态转移时索引越界。
+
+- **`dp[0][0] = true`:** 代表两个空字符串能够匹配。
+- **`dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 2]` 且 `p[j - 1] = '*'`:** 首行 `s` 为空字符串,因此当 `p` 的偶数位为 `*` 时才能够匹配(即让 `p` 的奇数位出现 0 次,保持 `p` 是空字符串)。因此,循环遍历字符串 `p` ,步长为 2(即只看偶数位)。
+
+**返回值:** `dp` 矩阵右下角字符,代表字符串 `s` 和 `p` 能否匹配。
+
+
+
+## 代码:
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def articleMatch(self, s: str, p: str) -> bool:
+ m, n = len(s) + 1, len(p) + 1
+ dp = [[False] * n for _ in range(m)]
+ dp[0][0] = True
+ for j in range(2, n, 2):
+ dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 2] and p[j - 1] == '*'
+ for i in range(1, m):
+ for j in range(1, n):
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 2] or dp[i - 1][j] and (s[i - 1] == p[j - 2] or p[j - 2] == '.') \
+ if p[j - 1] == '*' else \
+ dp[i - 1][j - 1] and (p[j - 1] == '.' or s[i - 1] == p[j - 1])
+ return dp[-1][-1]
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public boolean articleMatch(String s, String p) {
+ int m = s.length() + 1, n = p.length() + 1;
+ boolean[][] dp = new boolean[m][n];
+ dp[0][0] = true;
+ for(int j = 2; j < n; j += 2)
+ dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 2] && p.charAt(j - 1) == '*';
+ for(int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
+ for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
+ dp[i][j] = p.charAt(j - 1) == '*' ?
+ dp[i][j - 2] || dp[i - 1][j] && (s.charAt(i - 1) == p.charAt(j - 2) || p.charAt(j - 2) == '.') :
+ dp[i - 1][j - 1] && (p.charAt(j - 1) == '.' || s.charAt(i - 1) == p.charAt(j - 1));
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[m - 1][n - 1];
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ bool articleMatch(string s, string p) {
+ int m = s.size() + 1, n = p.size() + 1;
+ vector> dp(m, vector(n, false));
+ dp[0][0] = true;
+ for(int j = 2; j < n; j += 2)
+ dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 2] && p[j - 1] == '*';
+ for(int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
+ for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
+ dp[i][j] = p[j - 1] == '*' ?
+ dp[i][j - 2] || dp[i - 1][j] && (s[i - 1] == p[j - 2] || p[j - 2] == '.'):
+ dp[i - 1][j - 1] && (p[j - 1] == '.' || s[i - 1] == p[j - 1]);
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[m - 1][n - 1];
+ }
+};
+```
+
+以上代码利用布尔运算实现简短长度,若阅读不畅,可先理解以下代码,与文中内容一一对应:
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def articleMatch(self, s: str, p: str) -> bool:
+ m, n = len(s) + 1, len(p) + 1
+ dp = [[False] * n for _ in range(m)]
+ dp[0][0] = True
+ # 初始化首行
+ for j in range(2, n, 2):
+ dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 2] and p[j - 1] == '*'
+ # 状态转移
+ for i in range(1, m):
+ for j in range(1, n):
+ if p[j - 1] == '*':
+ if dp[i][j - 2]: dp[i][j] = True # 1.
+ elif dp[i - 1][j] and s[i - 1] == p[j - 2]: dp[i][j] = True # 2.
+ elif dp[i - 1][j] and p[j - 2] == '.': dp[i][j] = True # 3.
+ else:
+ if dp[i - 1][j - 1] and s[i - 1] == p[j - 1]: dp[i][j] = True # 1.
+ elif dp[i - 1][j - 1] and p[j - 1] == '.': dp[i][j] = True # 2.
+ return dp[-1][-1]
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public boolean articleMatch(String s, String p) {
+ int m = s.length() + 1, n = p.length() + 1;
+ boolean[][] dp = new boolean[m][n];
+ dp[0][0] = true;
+ // 初始化首行
+ for(int j = 2; j < n; j += 2)
+ dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 2] && p.charAt(j - 1) == '*';
+ // 状态转移
+ for(int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
+ for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
+ if(p.charAt(j - 1) == '*') {
+ if(dp[i][j - 2]) dp[i][j] = true; // 1.
+ else if(dp[i - 1][j] && s.charAt(i - 1) == p.charAt(j - 2)) dp[i][j] = true; // 2.
+ else if(dp[i - 1][j] && p.charAt(j - 2) == '.') dp[i][j] = true; // 3.
+ } else {
+ if(dp[i - 1][j - 1] && s.charAt(i - 1) == p.charAt(j - 1)) dp[i][j] = true; // 1.
+ else if(dp[i - 1][j - 1] && p.charAt(j - 1) == '.') dp[i][j] = true; // 2.
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[m - 1][n - 1];
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ bool articleMatch(string s, string p) {
+ int m = s.size() + 1, n = p.size() + 1;
+ vector> dp(m, vector(n, false));
+ dp[0][0] = true;
+ // 初始化首行
+ for(int j = 2; j < n; j += 2)
+ dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 2] && p[j - 1] == '*';
+ // 状态转移
+ for(int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
+ for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
+ if(p[j - 1] == '*') {
+ if(dp[i][j - 2]) dp[i][j] = true; // 1.
+ else if(dp[i - 1][j] && s[i - 1] == p[j - 2]) dp[i][j] = true; // 2.
+ else if(dp[i - 1][j] && p[j - 2] == '.') dp[i][j] = true; // 3.
+ } else {
+ if(dp[i - 1][j - 1] && s[i - 1] == p[j - 1]) dp[i][j] = true; // 1.
+ else if(dp[i - 1][j - 1] && p[j - 1] == '.') dp[i][j] = true; // 2.
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[m - 1][n - 1];
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(MN)$ :** 其中 $M, N$ 分别为 `s` 和 `p` 的长度,状态转移需遍历整个 `dp` 矩阵。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(MN)$ :** 状态矩阵 `dp` 使用 $O(MN)$ 的额外空间。
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 138. \346\234\211\346\225\210\346\225\260\345\255\227.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 138. \346\234\211\346\225\210\346\225\260\345\255\227.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..7f68180
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 138. \346\234\211\346\225\210\346\225\260\345\255\227.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,112 @@
+## 解题思路:
+
+本题使用有限状态自动机。根据字符类型和合法数值的特点,先定义状态,再画出状态转移图,最后编写代码即可。
+
+**字符类型:**
+
+空格 「 」、数字「 $0—9$ 」 、正负号 「 $+$, $-$ 」 、小数点 「 $.$ 」 、幂符号 「 $e$, $E$ 」 。
+
+**状态定义:**
+
+按照字符串从左到右的顺序,定义以下 9 种状态。
+
+0. 开始的空格
+1. 幂符号前的正负号
+2. 小数点前的数字
+3. 小数点、小数点后的数字
+4. 当小数点前为空格时,小数点、小数点后的数字
+5. 幂符号
+6. 幂符号后的正负号
+7. 幂符号后的数字
+8. 结尾的空格
+
+**结束状态:**
+
+合法的结束状态有 2, 3, 7, 8 。
+
+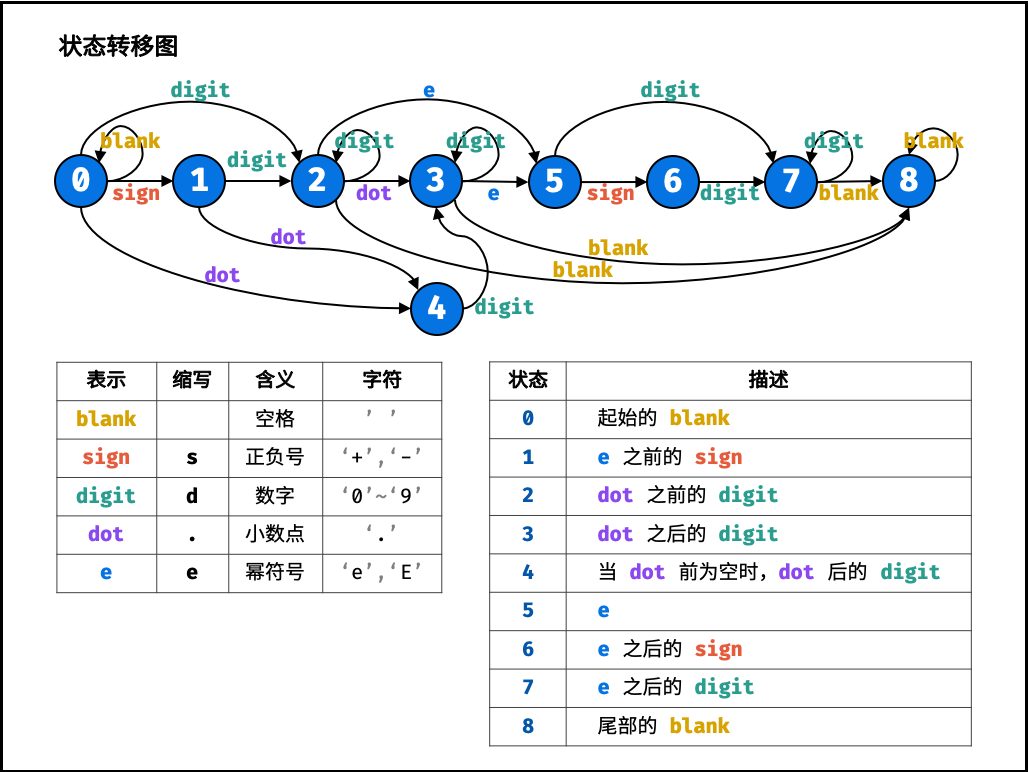{:align=center width=650}
+
+### 算法流程:
+
+1. **初始化:**
+ 1. **状态转移表 `states` :** 设 `states[i]` ,其中 `i` 为所处状态,`states[i]` 使用哈希表存储可转移至的状态。键值对 `(key, value)` 含义:输入字符 `key` ,则从状态 `i` 转移至状态 `value` 。
+ 2. **当前状态 `p` :** 起始状态初始化为 `p = 0` 。
+
+2. **状态转移循环:** 遍历字符串 `s` 的每个字符 `c` 。
+ 1. **记录字符类型 `t` :** 分为四种情况。
+ - 当 `c` 为正负号时,执行 `t = 's'` ;
+ - 当 `c` 为数字时,执行 `t = 'd'` ;
+ - 当 `c` 为 `e` 或 `E` 时,执行 `t = 'e'` ;
+ - 当 `c` 为 `.` 或 `空格` 时,执行 `t = c` (即用字符本身表示字符类型);
+ - 否则,执行 `t = '?'` ,代表为不属于判断范围的非法字符,后续直接返回 $\text{false}$ 。
+ 2. **终止条件:** 若字符类型 `t` 不在哈希表 `states[p]` 中,说明无法转移至下一状态,因此直接返回 $\text{false}$ 。
+ 3. **状态转移:** 状态 `p` 转移至 `states[p][t]` 。
+
+3. **返回值:** 跳出循环后,若状态 `p` $\in {2, 3, 7, 8}$ ,说明结尾合法,返回 $\text{true}$ ,否则返回 $\text{false}$ 。
+
+
+
+## 代码:
+
+Java 的状态转移表 `states` 使用 Map[] 数组存储。
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def validNumber(self, s: str) -> bool:
+ states = [
+ { ' ': 0, 's': 1, 'd': 2, '.': 4 }, # 0. start with 'blank'
+ { 'd': 2, '.': 4 } , # 1. 'sign' before 'e'
+ { 'd': 2, '.': 3, 'e': 5, ' ': 8 }, # 2. 'digit' before 'dot'
+ { 'd': 3, 'e': 5, ' ': 8 }, # 3. 'digit' after 'dot'
+ { 'd': 3 }, # 4. 'digit' after 'dot' (‘blank’ before 'dot')
+ { 's': 6, 'd': 7 }, # 5. 'e'
+ { 'd': 7 }, # 6. 'sign' after 'e'
+ { 'd': 7, ' ': 8 }, # 7. 'digit' after 'e'
+ { ' ': 8 } # 8. end with 'blank'
+ ]
+ p = 0 # start with state 0
+ for c in s:
+ if '0' <= c <= '9': t = 'd' # digit
+ elif c in "+-": t = 's' # sign
+ elif c in "eE": t = 'e' # e or E
+ elif c in ". ": t = c # dot, blank
+ else: t = '?' # unknown
+ if t not in states[p]: return False
+ p = states[p][t]
+ return p in (2, 3, 7, 8)
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public boolean validNumber(String s) {
+ Map[] states = {
+ new HashMap<>() {{ put(' ', 0); put('s', 1); put('d', 2); put('.', 4); }}, // 0.
+ new HashMap<>() {{ put('d', 2); put('.', 4); }}, // 1.
+ new HashMap<>() {{ put('d', 2); put('.', 3); put('e', 5); put(' ', 8); }}, // 2.
+ new HashMap<>() {{ put('d', 3); put('e', 5); put(' ', 8); }}, // 3.
+ new HashMap<>() {{ put('d', 3); }}, // 4.
+ new HashMap<>() {{ put('s', 6); put('d', 7); }}, // 5.
+ new HashMap<>() {{ put('d', 7); }}, // 6.
+ new HashMap<>() {{ put('d', 7); put(' ', 8); }}, // 7.
+ new HashMap<>() {{ put(' ', 8); }} // 8.
+ };
+ int p = 0;
+ char t;
+ for(char c : s.toCharArray()) {
+ if(c >= '0' && c <= '9') t = 'd';
+ else if(c == '+' || c == '-') t = 's';
+ else if(c == 'e' || c == 'E') t = 'e';
+ else if(c == '.' || c == ' ') t = c;
+ else t = '?';
+ if(!states[p].containsKey(t)) return false;
+ p = (int)states[p].get(t);
+ }
+ return p == 2 || p == 3 || p == 7 || p == 8;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### 复杂度分析:
+
+- **时间复杂度 $O(N)$ :** 其中 $N$ 为字符串 `s` 的长度,判断需遍历字符串,每轮状态转移的使用 $O(1)$ 时间。
+- **空间复杂度 $O(1)$ :** `states` 和 `p` 使用常数大小的额外空间。
diff --git "a/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 139. \350\256\255\347\273\203\350\256\241\345\210\222 I.md" "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 139. \350\256\255\347\273\203\350\256\241\345\210\222 I.md"
new file mode 100755
index 0000000..792ef3f
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/leetbook_ioa/docs/LCR 139. \350\256\255\347\273\203\350\256\241\345\210\222 I.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
+## 解题思路:
+
+考虑定义双指针 $i$ , $j$ 分列数组左右两端,循环执行:
+
+1. 指针 $i$ 从左向右寻找偶数;
+2. 指针 $j$ 从右向左寻找奇数;
+3. 将 偶数 $actions[i]$ 和 奇数 $actions[j]$ 交换。
+
+可始终保证: 指针 $i$ 左边都是奇数,指针 $j$ 右边都是偶数 。
+
+> 下图中的 `nums` 对应本题的 `actions` 。
+
+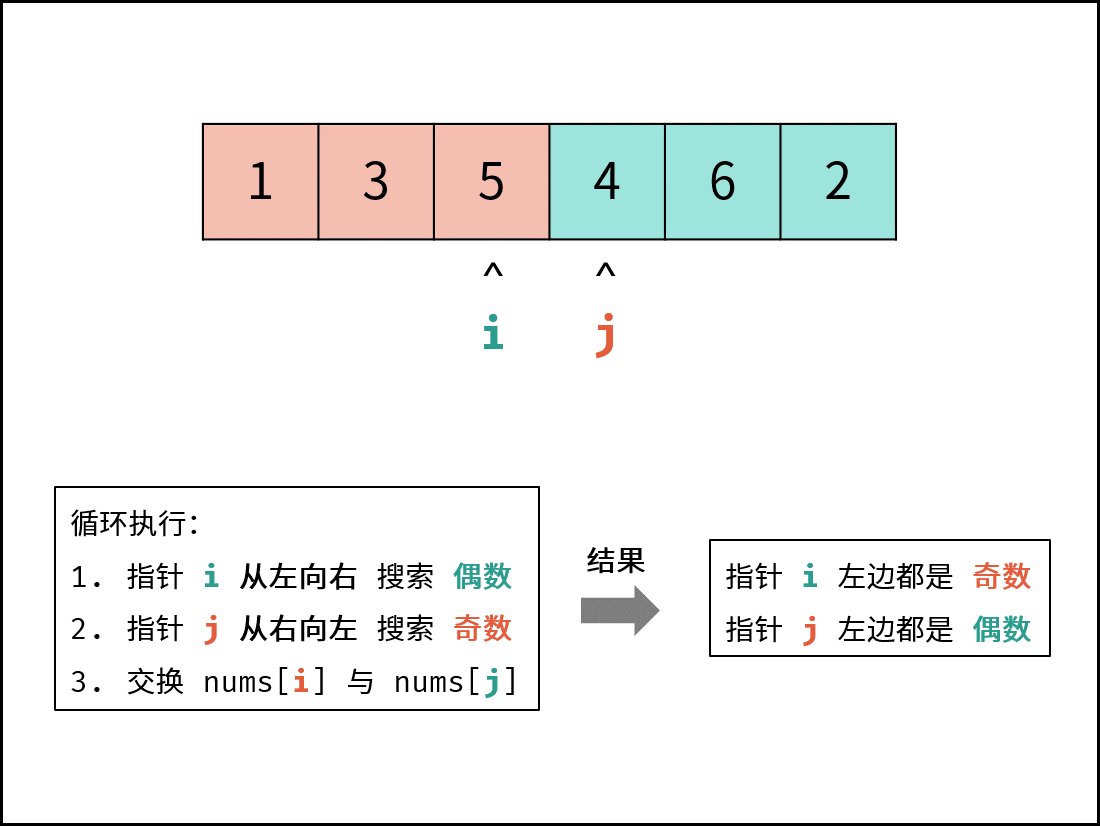{:align=center width=450}
+
+### 算法流程:
+
+1. **初始化:** $i$ , $j$ 双指针,分别指向数组 $actions$ 左右两端;
+2. **循环交换:** 当 $i = j$ 时跳出;
+ 1. 指针 $i$ 遇到奇数则执行 $i = i + 1$ 跳过,直到找到偶数;
+ 2. 指针 $j$ 遇到偶数则执行 $j = j - 1$ 跳过,直到找到奇数;
+ 3. 交换 $actions[i]$ 和 $actions[j]$ 值;
+3. **返回值:** 返回已修改的 $actions$ 数组。
+
+
+
+## 代码:
+
+$x \& 1$ 位运算 等价于 $x \mod 2$ 取余运算,即皆可用于判断数字奇偶性。
+
+```Python []
+class Solution:
+ def trainingPlan(self, actions: List[int]) -> List[int]:
+ i, j = 0, len(actions) - 1
+ while i < j:
+ while i < j and actions[i] & 1 == 1: i += 1
+ while i < j and actions[j] & 1 == 0: j -= 1
+ actions[i], actions[j] = actions[j], actions[i]
+ return actions
+```
+
+```Java []
+class Solution {
+ public int[] trainingPlan(int[] actions) {
+ int i = 0, j = actions.length - 1, tmp;
+ while(i < j) {
+ while(i < j && (actions[i] & 1) == 1) i++;
+ while(i < j && (actions[j] & 1) == 0) j--;
+ tmp = actions[i];
+ actions[i] = actions[j];
+ actions[j] = tmp;
+ }
+ return actions;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+```C++ []
+class Solution {
+public:
+ vector  +
+
+
+ +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
 ](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/detail/illustration-of-algorithm/)
+- 图文详解 75 道题目,覆盖主要算法知识点。
+- 题目活跃于各大互联网公司招聘中,可使笔面试准备事半功倍。
+- 致力于行文深入浅出、图文搭配,提供简洁的 Python, Java, C++ 解题代码。
-LeetBook《图解算法数据结构》面向算法初学者、互联网求职者设计,主要内容包括:
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> 本仓库包含“图解算法数据结构”、“Krahets 笔面试精选 88 题”和“剑指 Offer”的题解内容:
+>
+> ```python
+> LeetCode-Book
+> ├── leetbook_ioa # 《图解算法数据结构》题解和专栏文档
+> ├── selected_coding_interview # 《Krahets 笔面试精选 88 题》题解文档
+> └── sword_for_offer # 《剑指 Offer》题解文档、代码、刷题计划
+> ```
-### :green_book: 剑指 Offer 图文题解
+> 若本仓库对您有所帮助,请在页面右上角点个 **Star** :star: 支持一下,谢谢!
-- 图文详解 75 道题目,覆盖主要算法知识点,非常适合作为算法学习的 **第一份题库** 。
-- 题库活跃于各大互联网公司招聘中,可使笔面试准备事半功倍。
-- 致力于行文深入浅出、图文搭配,提供简洁的 **Python3, Java, C++** 解题代码。
-- 笔者整理了 **30 天刷题计划**、**题目分类**,让刷题有迹可循。
-
-### :blue_book: 数据结构与算法专栏
-
-- **基础知识:** 时间复杂度、空间复杂度等算法知识。
-- **数据结构:** 数组、栈、队列、字符串、链表、树、图、堆、哈希表。
-- **算法专题:** 分治算法、动态规划、搜索与回溯算法、查找算法、贪心算法、排序、位运算、双指针、模拟、数学。
-
-## :student: 适合人群
-
-- 互联网算法、软件岗位求职者。
-- 从零开始接触数据结构与算法的同学。
-- 具有一定编程基础,计划系统学习算法的同学。
-
----
-
-## :ledger: 算法专栏
-
-### 「[数据结构](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50e446/)」
-
-> 建议对数据结构不熟悉的同学,先看这篇熟悉用法。
-
-- 常用数据结构的**分类**和**基本特点**。
-- 在算法解题中,数据结构的**常用操作**。
-- 在 Python3 , Java , C++ 语言中,各数据结构的**初始化与构建方法**。
-
-### 「[算法复杂度](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/r84gmi/)」
-
-> 复杂度是算法优劣性的有力评价指标,对于理解算法起着至关重要的作用。
-
-- 什么是时间复杂度、空间复杂度?
-- 时间复杂度和空间复杂度的**概念定义**、**符号表示**、**常见种类**、**时空权衡**。
-- 时间与空间复杂度的**示例题目与解析**。
-
-### 「[动态规划](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/m5zfc1/)」
-
-> 动态规划是算法重难点,也是笔面试重要考点,需要重点理解与练习。
-
-- 动态规划问题特点,动态规划和分治算法的联系与区别;
-- 借助例题介绍**重叠子问题**和**最优子结构**分别是什么,以及动态规划是如何解决它们的;
-- 动态规划的**解题框架**总结;
-- 动态规划的**练习例题**,从易到难排序;
-
-### 「[排序算法](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/pxal47/)」
-
-> 排序是最经典的算法问题之一,由浅入深的多种算法涵盖多个算法知识点(例如暴力搜索、分治算法、堆数据结构等)。
-
-- 排序算法分类方法,包括稳定性 、就地性 、自适应性;
-- 排序算法与二分查找、双指针算法之间的关系;
-- 各主要排序算法的时间复杂度与空间复杂度;
-
----
-
-## :hourglass: 刷题计划
-
-笔者整理了《剑指 Offer 》刷题计划,核心理念为从易到难、从基础类题目到综合类题目,供希望按照知识点类型顺序刷题的小伙伴们参考。行百里者半九十,坚持一个月刷完,一起加油!
-
-| 日程 | 题目 |
-| :--------: | :------------------------------------------------ |
-| **Day 1** | **栈与队列(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 09. 用两个栈实现队列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5d3i87/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 30. 包含 min 函数的栈](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50bp33/) |
-| **Day 2** | **链表(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dt66m/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9pdjbm/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9p0yy1/) |
-| **Day 3** | **字符串(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 05. 替换空格](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50ywkd/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 58 - II. 左旋转字符串](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/589fz2/) |
-| **Day 4** | **查找算法(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 03. 数组中重复的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/59bjss/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 53 - I. 在排序数组中查找数字 I](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5874p1/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 53 - II. 0~n-1 中缺失的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58iqo5/) |
-| **Day 5** | **查找算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 04. 二维数组中的查找](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5v76yi/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 11. 旋转数组的最小数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50xofm/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 50. 第一个只出现一次的字符](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5viisg/) |
-| **Day 6** | **搜索与回溯算法(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9ackoe/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vawr3/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vnp91/) |
-| **Day 7** | **搜索与回溯算法(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 26. 树的子结构](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dshwe/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 27. 二叉树的镜像](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/59zt5i/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 28. 对称的二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5d412v/) |
-| **Day 8** | **动态规划(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 10- I. 斐波那契数列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50fxu1/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 10- II. 青蛙跳台阶问题](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57hyl5/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 63. 股票的最大利润](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58nn7r/) |
-| **Day 9** | **动态规划(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 42. 连续子数组的最大和](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/59gq9c/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 47. 礼物的最大价值](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vokvr/) |
-| **Day 10** | **动态规划(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 46. 把数字翻译成字符串](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/99wd55/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 48. 最长不含重复字符的子字符串](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dgr0c/) |
-| **Day 11** | **双指针(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/505fc7/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第 k 个节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58tl52/) |
-| **Day 12** | **双指针(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vq98s/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/oe5os3/) |
-| **Day 13** | **双指针(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 21. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5v8a6t/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 57. 和为 s 的两个数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5832fi/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 58 - I. 翻转单词顺序](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/586ecg/) |
-| **Day 14** | **搜索与回溯算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 12. 矩阵中的路径](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58wowd/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 13. 机器人的运动范围](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9h6vo2/) |
-| **Day 15** | **搜索与回溯算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dy6pt/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dbies/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 54. 二叉搜索树的第 k 大节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58df23/) |
-| **Day 16** | **排序(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 45. 把数组排成最小的数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/59ypcj/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 61. 扑克牌中的顺子](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57mpoj/) |
-| **Day 17** | **排序(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 40. 最小的 k 个数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/ohvl0d/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 41. 数据流中的中位数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vd1j2/) |
-| **Day 18** | **搜索与回溯算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 55 - I. 二叉树的深度](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9hgr5i/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 55 - II. 平衡二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9hzffg/) |
-| **Day 19** | **搜索与回溯算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 64. 求 1 + 2 + … + n](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9h44cj/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/575kd2/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 68 - II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57euni/) |
-| **Day 20** | **分治算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 07. 重建二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/99lxci/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 16. 数值的整数次方](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57rwmg/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vwxx5/) |
-| **Day 21** | **位运算(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 15. 二进制中 1 的个数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vk1l3/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 65. 不用加减乘除做加法](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vz6d1/) |
-| **Day 22** | **位运算(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 56 - I. 数组中数字出现的次数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/eubbnm/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 56 - II. 数组中数字出现的次数 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9hyq1r/) |
-| **Day 23** | **数学(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/99iy4g/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 66. 构建乘积数组](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57d8cm/) |
-| **Day 24** | **数学(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 14- I. 剪绳子](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5v1026/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 57 - II. 和为 s 的连续正数序列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/eufzm7/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 62. 圆圈中最后剩下的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/oxrkot/) |
-| **Day 25** | **模拟(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 29. 顺时针打印矩阵](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vfh9g/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 31. 栈的压入、弹出序列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5wh1hj/) |
-| **Day 26** | **字符串(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 20. 表示数值的字符串](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5d6vi6/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 67. 把字符串转换成整数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58pq8g/) |
-| **Day 27** | **栈与队列(困难)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 59 - I. 滑动窗口的最大值](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58o46i/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 59 - II. 队列的最大值](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/e2t5ug/) |
-| **Day 28** | **搜索与回溯算法(困难)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 37. 序列化二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/990pf2/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 38. 字符串的排列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dfv5h/) |
-| **Day 29** | **动态规划(困难)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 19. 正则表达式匹配](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9a1ypc/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 49. 丑数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9h3im5/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 60. n 个骰子的点数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/ozzl1r/) |
-| **Day 30** | **分治算法(困难)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 17. 打印从 1 到最大的 n 位数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/594wfg/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 51. 数组中的逆序对](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/o58jfs/) |
-| **Day 31** | **数学(困难)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 14- II. 剪绳子 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vcapc/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 43. 1~n 整数中 1 出现的次数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/572jxs/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 44. 数字序列中某一位的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57vzfh/) |
-
----
-
-若本书对您有所帮助,麻烦请您点个 Star :star: 啦,谢谢!
-
-
](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/detail/illustration-of-algorithm/)
+- 图文详解 75 道题目,覆盖主要算法知识点。
+- 题目活跃于各大互联网公司招聘中,可使笔面试准备事半功倍。
+- 致力于行文深入浅出、图文搭配,提供简洁的 Python, Java, C++ 解题代码。
-LeetBook《图解算法数据结构》面向算法初学者、互联网求职者设计,主要内容包括:
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> 本仓库包含“图解算法数据结构”、“Krahets 笔面试精选 88 题”和“剑指 Offer”的题解内容:
+>
+> ```python
+> LeetCode-Book
+> ├── leetbook_ioa # 《图解算法数据结构》题解和专栏文档
+> ├── selected_coding_interview # 《Krahets 笔面试精选 88 题》题解文档
+> └── sword_for_offer # 《剑指 Offer》题解文档、代码、刷题计划
+> ```
-### :green_book: 剑指 Offer 图文题解
+> 若本仓库对您有所帮助,请在页面右上角点个 **Star** :star: 支持一下,谢谢!
-- 图文详解 75 道题目,覆盖主要算法知识点,非常适合作为算法学习的 **第一份题库** 。
-- 题库活跃于各大互联网公司招聘中,可使笔面试准备事半功倍。
-- 致力于行文深入浅出、图文搭配,提供简洁的 **Python3, Java, C++** 解题代码。
-- 笔者整理了 **30 天刷题计划**、**题目分类**,让刷题有迹可循。
-
-### :blue_book: 数据结构与算法专栏
-
-- **基础知识:** 时间复杂度、空间复杂度等算法知识。
-- **数据结构:** 数组、栈、队列、字符串、链表、树、图、堆、哈希表。
-- **算法专题:** 分治算法、动态规划、搜索与回溯算法、查找算法、贪心算法、排序、位运算、双指针、模拟、数学。
-
-## :student: 适合人群
-
-- 互联网算法、软件岗位求职者。
-- 从零开始接触数据结构与算法的同学。
-- 具有一定编程基础,计划系统学习算法的同学。
-
----
-
-## :ledger: 算法专栏
-
-### 「[数据结构](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50e446/)」
-
-> 建议对数据结构不熟悉的同学,先看这篇熟悉用法。
-
-- 常用数据结构的**分类**和**基本特点**。
-- 在算法解题中,数据结构的**常用操作**。
-- 在 Python3 , Java , C++ 语言中,各数据结构的**初始化与构建方法**。
-
-### 「[算法复杂度](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/r84gmi/)」
-
-> 复杂度是算法优劣性的有力评价指标,对于理解算法起着至关重要的作用。
-
-- 什么是时间复杂度、空间复杂度?
-- 时间复杂度和空间复杂度的**概念定义**、**符号表示**、**常见种类**、**时空权衡**。
-- 时间与空间复杂度的**示例题目与解析**。
-
-### 「[动态规划](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/m5zfc1/)」
-
-> 动态规划是算法重难点,也是笔面试重要考点,需要重点理解与练习。
-
-- 动态规划问题特点,动态规划和分治算法的联系与区别;
-- 借助例题介绍**重叠子问题**和**最优子结构**分别是什么,以及动态规划是如何解决它们的;
-- 动态规划的**解题框架**总结;
-- 动态规划的**练习例题**,从易到难排序;
-
-### 「[排序算法](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/pxal47/)」
-
-> 排序是最经典的算法问题之一,由浅入深的多种算法涵盖多个算法知识点(例如暴力搜索、分治算法、堆数据结构等)。
-
-- 排序算法分类方法,包括稳定性 、就地性 、自适应性;
-- 排序算法与二分查找、双指针算法之间的关系;
-- 各主要排序算法的时间复杂度与空间复杂度;
-
----
-
-## :hourglass: 刷题计划
-
-笔者整理了《剑指 Offer 》刷题计划,核心理念为从易到难、从基础类题目到综合类题目,供希望按照知识点类型顺序刷题的小伙伴们参考。行百里者半九十,坚持一个月刷完,一起加油!
-
-| 日程 | 题目 |
-| :--------: | :------------------------------------------------ |
-| **Day 1** | **栈与队列(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 09. 用两个栈实现队列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5d3i87/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 30. 包含 min 函数的栈](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50bp33/) |
-| **Day 2** | **链表(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dt66m/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9pdjbm/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9p0yy1/) |
-| **Day 3** | **字符串(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 05. 替换空格](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50ywkd/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 58 - II. 左旋转字符串](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/589fz2/) |
-| **Day 4** | **查找算法(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 03. 数组中重复的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/59bjss/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 53 - I. 在排序数组中查找数字 I](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5874p1/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 53 - II. 0~n-1 中缺失的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58iqo5/) |
-| **Day 5** | **查找算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 04. 二维数组中的查找](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5v76yi/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 11. 旋转数组的最小数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50xofm/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 50. 第一个只出现一次的字符](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5viisg/) |
-| **Day 6** | **搜索与回溯算法(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9ackoe/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vawr3/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vnp91/) |
-| **Day 7** | **搜索与回溯算法(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 26. 树的子结构](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dshwe/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 27. 二叉树的镜像](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/59zt5i/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 28. 对称的二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5d412v/) |
-| **Day 8** | **动态规划(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 10- I. 斐波那契数列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/50fxu1/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 10- II. 青蛙跳台阶问题](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57hyl5/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 63. 股票的最大利润](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58nn7r/) |
-| **Day 9** | **动态规划(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 42. 连续子数组的最大和](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/59gq9c/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 47. 礼物的最大价值](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vokvr/) |
-| **Day 10** | **动态规划(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 46. 把数字翻译成字符串](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/99wd55/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 48. 最长不含重复字符的子字符串](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dgr0c/) |
-| **Day 11** | **双指针(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/505fc7/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第 k 个节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58tl52/) |
-| **Day 12** | **双指针(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vq98s/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/oe5os3/) |
-| **Day 13** | **双指针(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 21. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5v8a6t/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 57. 和为 s 的两个数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5832fi/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 58 - I. 翻转单词顺序](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/586ecg/) |
-| **Day 14** | **搜索与回溯算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 12. 矩阵中的路径](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58wowd/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 13. 机器人的运动范围](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9h6vo2/) |
-| **Day 15** | **搜索与回溯算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dy6pt/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dbies/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 54. 二叉搜索树的第 k 大节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58df23/) |
-| **Day 16** | **排序(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 45. 把数组排成最小的数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/59ypcj/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 61. 扑克牌中的顺子](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57mpoj/) |
-| **Day 17** | **排序(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 40. 最小的 k 个数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/ohvl0d/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 41. 数据流中的中位数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vd1j2/) |
-| **Day 18** | **搜索与回溯算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 55 - I. 二叉树的深度](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9hgr5i/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 55 - II. 平衡二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9hzffg/) |
-| **Day 19** | **搜索与回溯算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 64. 求 1 + 2 + … + n](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9h44cj/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/575kd2/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 68 - II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57euni/) |
-| **Day 20** | **分治算法(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 07. 重建二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/99lxci/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 16. 数值的整数次方](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57rwmg/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vwxx5/) |
-| **Day 21** | **位运算(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 15. 二进制中 1 的个数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vk1l3/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 65. 不用加减乘除做加法](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vz6d1/) |
-| **Day 22** | **位运算(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 56 - I. 数组中数字出现的次数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/eubbnm/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 56 - II. 数组中数字出现的次数 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9hyq1r/) |
-| **Day 23** | **数学(简单)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/99iy4g/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 66. 构建乘积数组](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57d8cm/) |
-| **Day 24** | **数学(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 14- I. 剪绳子](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5v1026/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 57 - II. 和为 s 的连续正数序列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/eufzm7/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 62. 圆圈中最后剩下的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/oxrkot/) |
-| **Day 25** | **模拟(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 29. 顺时针打印矩阵](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vfh9g/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 31. 栈的压入、弹出序列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5wh1hj/) |
-| **Day 26** | **字符串(中等)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 20. 表示数值的字符串](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5d6vi6/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 67. 把字符串转换成整数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58pq8g/) |
-| **Day 27** | **栈与队列(困难)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 59 - I. 滑动窗口的最大值](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/58o46i/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 59 - II. 队列的最大值](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/e2t5ug/) |
-| **Day 28** | **搜索与回溯算法(困难)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 37. 序列化二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/990pf2/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 38. 字符串的排列](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5dfv5h/) |
-| **Day 29** | **动态规划(困难)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 19. 正则表达式匹配](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9a1ypc/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 49. 丑数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9h3im5/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 60. n 个骰子的点数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/ozzl1r/) |
-| **Day 30** | **分治算法(困难)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 17. 打印从 1 到最大的 n 位数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/594wfg/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 51. 数组中的逆序对](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/o58jfs/) |
-| **Day 31** | **数学(困难)** |
-| | [剑指 Offer 14- II. 剪绳子 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/5vcapc/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 43. 1~n 整数中 1 出现的次数](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/572jxs/) |
-| | [剑指 Offer 44. 数字序列中某一位的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/57vzfh/) |
-
----
-
-若本书对您有所帮助,麻烦请您点个 Star :star: 啦,谢谢!
-
-
 +
+