Papers by Masahiro Yasutake
Journal of Nippon Medical School
Nitrous oxide (N2O) is readily available, and its abuse for recreational purposes has become a so... more Nitrous oxide (N2O) is readily available, and its abuse for recreational purposes has become a social problem. In Japan, where N2O is strictly prohibited for non-medical use, abuse is often overlooked due to a lack of experience in the field. N2O abuse causes various long-term symptoms, including vitamin B12 deficiency, myelopathy, myeloneuropathy, subacute combined degeneration, mood changes, and psychosis. The diagnosis of N2O abuse is difficult due to the compound's short half-life and rapid elimination through the lungs. This report describes a case of fever and impaired consciousness in a patient with a history of N2O abuse. (
Japanese Circulation Journal-english Edition, Mar 1, 2009
Japanese Circulation Journal-english Edition, Mar 31, 2002
Japanese Circulation Journal-english Edition, Mar 1, 2008
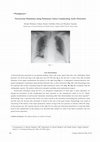
Journal of Nippon Medical School, 2016
A 54-year-old man presented to our general medicine clinic with acute upper back pain. On examina... more A 54-year-old man presented to our general medicine clinic with acute upper back pain. On examination, blood pressure was 90/46 mm Hg in the right arm and 133/100 mm Hg in the left arm. A chest X-ray film revealed dilatation of the upper mediastinum and opacity in the right lung (Fig. ). A subsequent contrast-enhanced computed tomography examination demonstrated Stanford type A aortic dissection (Fig. ) with hemorrhage from the ruptured false lumen extending along the right pulmonary artery (PA) (Fig. , Fig. ) consistent with the radiographic opacity. The patient underwent emergent ascending aorta replacement surgery. Perivascular hematoma along the PA is an infrequent complication of acute type A aortic dissection, although the prevalence of this complication has been reported, in one retrospective study, to be 9% 1 . Radiographic manifestations of perivascular hematoma mimicking other hilar abnormalities have also been reported 2-4 . Hemorrhage from a ruptured false lumen can easily extend to the adventitia surrounding the pulmonary trunk and the main PA, because this adventitia is shared at the root of the great vessels. Hemorrhage may result in narrowing of the lumina of the major pulmonary arteries owing to the low pressure of arteries within the lung 5 . In the present case, 50% luminal stenosis of the right PA was observed. Clinicians should bear in mind the likelihood of this complication in the setting of an abnormal hilar shadow on chest X-ray films in patients with suspected aortic dissection.
Japanese Circulation Journal-english Edition, Mar 1, 2003
Japanese Circulation Journal-english Edition, Mar 31, 2002
Japanese Journal of Electrocardiology, 1997

Sleep, Apr 28, 2017
Methods: Twenty-two healthy adults (M age =29.3, SD age =11.4) had one night of sleep measured by... more Methods: Twenty-two healthy adults (M age =29.3, SD age =11.4) had one night of sleep measured by polysomnography and each activity monitor simultaneously in a laboratory. Minute-by-minute data were extracted and compared. Wilcoxon signed-ranks tests assessed statistical differences between measures, and Bland-Altman analyses examined clinically meaningful differences between measures, using cut-offs of ±30 minutes for TST and ±5% for SE. Results: Compared to polysomnography, all activity monitors significantly overestimated TST and SE. Differences between polysomnography and each monitor were also clinically meaningful, as Bland-Altman upper and lower limits of agreement for TST exceeded clinical cut-offs for ACT (-64.7min-+166.1min), FB (-66.1min-+189.2min), and JB (-103.6min-+186.2min). Similarly, upper and lower limits of agreement for SE exceeded clinical cut-offs for ACT (-13.0%-+34.0%), FB (-13.1%-+38.5%), and JB (-20.7%-+37.9%). Compared to ACT, only FB significantly overestimated TST and SE. However, differences between ACT and each of FB and JB were clinically meaningful. For FB, Bland-Altman upper limits of agreement exceeded clinical cutoffs for TST (-18.7min-+40.2min) and SE (-3.8%-+8.1%). For JB, upper and lower limits of agreement exceeded clinical cut-offs for TST (-100.4min-+79.3min) and SE (-20.1%-+16.0%). Agreement between devices decreased as TST and SE decreased. All monitors demonstrated poor specificity (18.8-35.6%), but high sensitivity (94.2-99.2%). Results suggest these models of ACT, FB, and JB cannot be used interchangeably with polysomnography. When activity monitors must be used, such as in field settings, FB and JB cannot replace researchgrade ACT. Overall, users should account for each monitor's potential to overestimate or underestimate TST and SE to an unacceptable degree. Future research should examine within-subject variability over time to determine whether monitors can be used to track long-term sleep patterns. Support (If Any): N/A.
Circulation journal, 2010

Journal of Nippon Medical School, 2015
Objective: Current data indicate that the rate of trauma in children during gymnastic formation i... more Objective: Current data indicate that the rate of trauma in children during gymnastic formation is increasing, especially while creating a structure with a certain height, such as the human pyramid. The goal of the present study was to clarify the clinical characteristics of these injuries. : In this single-institution review, all children treated for a gymnastic formation-related injury at Nippon Medical School Hospital from 2013 through 2015 were identified through the institution's registry. The injury mechanism was classified, and injury severity, interventions, and outcome were examined. Results: Eight children were treated for a gymnastic formation-related injury. They were 7 boys and 1 girl aged 10 to 15 years (mean age, 13.1±1.8 years). Neurotrauma ranging from concussion to spinal cord injury without radiographic abnormality occurred in 6 patients (75%). No intracranial hemorrhagic lesions were detected. The Glasgow Coma Scale score on arrival was 15 in all 8 patients, and neurological deficits were present in 1 patient. No patient required surgical intervention. All patients made a full recovery after discharge from the hospital. No patients died. The average follow-up period was 2.1±0.9 weeks. Neurotrauma is a frequent result of gymnastic formation accidents in children. Healthcare workers and teachers should recognize this type of injury, and public education that targets parents should be introduced. (

JAPANESE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY AND THERAPEUTICS, 1988
Safety, tolerance, and pharmacokinetics of flecainide acetate , a new antiarrythmic agent, were i... more Safety, tolerance, and pharmacokinetics of flecainide acetate , a new antiarrythmic agent, were investigated by single blind study in 16 healthy Japanese volunteers. Each subject recieved a single oral dose (25 , 50, 100, 150, 200, 250 mg, or placebo) and continuous oral dose (50, 100 mg b. i. d. or placebo for 7 days). No obvious change was observed in blood pressure, pulse rate, body temperature, clinical laboratory data, and subjective symptoms except only mild, transient side effects in some subjects. Prolongation of PQ and QRS interval was noted in proportion to the plasma concentra tion of the drug. The maixmum plasma concentration (Cmax) and the area under the time-concentration curve (AUC) were almost linear to oral doses. Cmax was attained in 1.5 to 2.5 hr and the mean biological half-life in the elimination phase(t1/2β)was around 11 hr , independent of doses. The 24-hr cumulative urinary excretion of unchanged flecainide was around 30% and that of two major metabolites was detected to be around 15%. We concluded that these findings showed that oral flecainide acetate is well tolerated,

ESC Heart Failure
AimsMaintenance of euvolaemia with diuretics is critical in heart failure (HF) patients with chro... more AimsMaintenance of euvolaemia with diuretics is critical in heart failure (HF) patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD); however, it is challenging because no reliable marker of volume status exists. Fractional excretion of urea nitrogen (FEUN) is a useful index of volume status in patients with renal failure. We aimed to examine whether FEUN is a surrogate marker of volume status for risk stratification in HF patients with CKD.Methods and resultsWe examined 516 HF patients with CKD (defined as discharge estimated glomerular filtration rate < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2) whose FEUN was measured at discharge (median age, 80 years; 58% male). The patients were divided into four groups according to quartile FEUN value at discharge: low‐FEUN, FEUN ≤ 32.1; medium‐FEUN, 32.1 < FEUN ≤ 38.0; high‐FEUN, 38.0 < FEUN ≤ 43.7; and extremely‐high‐FEUN, FEUN > 43.7. FEUN was calculated by the following formula: (urinary urea × serum creatinine) × 100/(serum urea × urinary creatinine). During t...
2022 IEEE 11th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE)
Journal of Pharmacological Sciences
Japanese Circulation Journal-english Edition, 2005
Japanese Circulation Journal-english Edition, 2003
Japanese Circulation Journal-english Edition, 2002
Japanese Circulation Journal-english Edition, 2002







Uploads
Papers by Masahiro Yasutake