3-Methoxytyramine
From Infogalactic: the planetary knowledge core
(Redirected from 3-methoxytyramine)
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
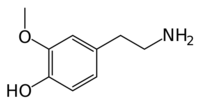
| IUPAC name
4-(2-aminoethyl)-2-methoxyphenol
|
|
| Other names
3-O-methyldopamine
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| 554-52-9 |
|
| ChemSpider | 1606 |
| 6642 | |
| Jmol 3D model | Interactive image |
| MeSH | 3-methoxytyramine |
| PubChem | 1669 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C9H13NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 167.21 g/mol |
| Vapor pressure | {{{value}}} |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
3-Methoxytyramine (3-MT), also known as 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenethylamine, is a metabolite of the neurotransmitter dopamine formed by the introduction of a methyl group to dopamine by the enzyme catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT). 3-MT can be further metabolized by the enzyme monoamine oxidase (MAO) to form homovanillic acid (HVA), which is then typically excreted in the urine.
Originally thought to be physiologically inactive, 3-MT has recently been shown to act as an agonist of human TAAR1.[1]
Occurrence
3-Methoxytyramine occurs naturally in the prickly pear cactus (genus Opuntia),[2] and is in general widespread throughout the Cactaceae.[3] It has also been found in crown gall tumors on Nicotiana sp.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found. Retrieved on June 12, 2009 through Google Book Search.
- ↑ T. A. Smith (1977). "Phenethylamine and related compounds in plants." Phytochem. 16 9-18.
- ↑ S. D. Mitchell, J. L. Firmin and D. O. Gray (1984). "Enhanced 3-methoxytyramine levels in crown gall tumours and other undifferentiated plant tissues." Biochem J. 221 891-5.