Granular cell tumor
| Granular cell tumor | |
|---|---|
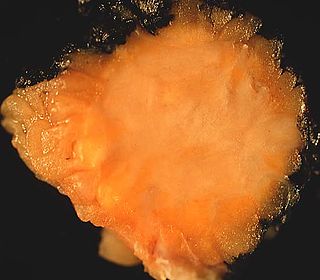
2-cm tumor presented as an abdominal wall mass in a middle-aged woman
|
|
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Lua error in Module:Wikidata at line 446: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| ICD-10 | D36.1 (ILDS D36.170) |
| ICD-O | M9582/0 |
| DiseasesDB | 31674 |
| Patient UK | Granular cell tumor |
Granular cell tumor is a tumor that can develop on any skin or mucosal surface, but occurs on the tongue 40% of the time.
It is also known as Abrikossoff's tumor,[1] Granular cell myoblastoma,[1] Granular cell nerve sheath tumor,[1] and Granular cell schwannoma.[1])
Pathology
Granular cell tumors show similarity to neural tissue, as can be demonstrated by immunohistochemistry and ultrastructural evidence using electron microscopy.
Multiple granular cell tumors may seen in the context of LEOPARD syndrome, due to a mutation in the PTPN11 gene.[2]
Epidemiology
Granular cell tumors can affect all parts of the body; however, the head and neck areas are affected 45% to 65% of the time. Of the head and neck cases 70% of lesions are located intraorally (tongue, oral mucosa, hard palate). The next most common location that lesions are found in the head and neck area is the larynx (10%).[3] Granular cell tumors are also found in the internal organs, particularly in the upper aerodigestive tract.
The usual presentation is of slow growing behavior, forming a polygonal accumulation of secondary lysosomes in the cytoplasm. Granular cell tumors are typically solitary and are rarely larger than three centimeters. This type of tumor has been found to be both benign and malignant, although malignancy is rare and comprises only 2% of all granular cell tumors.[4]
Treatment
The primary method for treatment is surgical, not medical. Radiation and chemotherapy are not needed for benign lesions and are not effective for malignant lesions.
Benign granular cell tumors have a recurrence rate of 2% to 8% when resection margins are deemed clear of tumor infiltration. When the resection margins of a benign granular cell tumor are positive for tumor infiltration the recurrence rate is increased to 20%. Malignant lesions are aggressive and difficult to eradicate with surgery and have a recurrence rate of 32%.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ Kahn, Michael A. Basic Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. Volume 1. 2001.
- ↑ Fanburg-Smith JC, Meis-Kindblom JM, et al. Malignant granular cell tumor of soft tissue: diagnostic criteria and clinicopathologic correlation. Am J Surg Pathol. Jul 1998;22(7):779-94.
