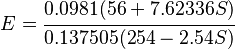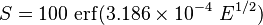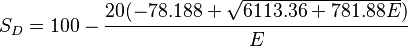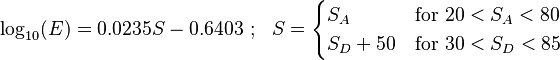Shore durometer

Durometer is one of several measures of the hardness of a material.
Hardness may be defined as a material's resistance to permanent indentation. The durometer scale was defined by Albert Ferdinand Shore, who developed a device to measure Shore hardness in the 1920s. The term durometer is often used to refer to the measurement as well as the instrument itself. Durometer is typically used as a measure of hardness in polymers, elastomers, and rubbers.[1]
Shore's device was not the first hardness tester nor the first to be called a durometer (ISV duro- and -meter; attested since the 19th century), but today that name usually refers to Shore hardness (other devices are simply called hardness testers).
Contents
Durometer scales
There are several scales of durometer, used for materials with different properties. The two most common scales, using slightly different measurement systems, are the ASTM D2240 type A and type D scales. The A scale is for softer plastics, while the D scale is for harder ones. However, the ASTM D2240-00 testing standard calls for a total of 12 scales, depending on the intended use; types A, B, C, D, DO, E, M, O, OO, OOO, OOO-S, and R. Each scale results in a value between 0 and 100, with higher values indicating a harder material.[2]
Method of measurement
Durometer, like many other hardness tests, measures the depth of an indentation in the material created by a given force on a standardized presser foot. This depth is dependent on the hardness of the material, its viscoelastic properties, the shape of the presser foot, and the duration of the test. ASTM D2240 durometers allows for a measurement of the initial hardness, or the indentation hardness after a given period of time. The basic test requires applying the force in a consistent manner, without shock, and measuring the hardness (depth of the indentation). If a timed hardness is desired, force is applied for the required time and then read. The material under test should be a minimum of 6.4 mm (0.25 inches) thick.[3]
| Durometer | Indenting foot | Applied mass (kg) | Resulting force (N) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type A | Hardened steel rod 1.1 mm – 1.4 mm diameter, with a truncated 35° cone, 0.79 mm diameter | 0.822 | 8.064 |
| Type D | Hardened steel rod 1.1 mm – 1.4 mm diameter, with a 30° conical point, 0.1 mm radius tip | 4.550 | 44.64 |
The ASTM D2240 standard recognizes twelve different durometer scales using combinations of specific spring forces and indentor configurations. These scales are properly referred to as durometer types; i.e., a durometer type is specifically designed to determine a specific scale, and the scale does not exist separately from the durometer. The table below provides details for each of these types, with the exception of Type R.[4]
| Durometer Type | Configuration | Diameter | Extension | Spring force |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 35° truncated cone (frustum) | 1.40 mm (0.055 in) | 2.54 mm (0.100 in) | 822 gf (8.06 N) |
| C | 35° truncated cone (frustum) | 1.40 mm (0.055 in) | 2.54 mm (0.100 in) | 4,536 gf (44.48 N) |
| D | 30° cone | 1.40 mm (0.055 in) | 2.54 mm (0.100 in) | 4,536 gf (44.48 N) |
| B | 30° cone | 1.40 mm (0.055 in) | 2.54 mm (0.100 in) | 822 gf (8.06 N) |
| M | 30° cone | 0.79 mm (0.031 in) | 1.25 mm (0.049 in) | 78 gf (0.76 N) |
| E | 2.5 mm (0.098 in) spherical radius | 4.50 mm (0.177 in) | 2.54 mm (0.100 in) | 822 gf (8.06 N) |
| O | 1.20 mm (0.047 in) spherical radius | 2.40 mm (0.094 in) | 2.54 mm (0.100 in) | 822 gf (8.06 N) |
| OO | 1.20 mm (0.047 in) spherical radius | 2.40 mm (0.094 in) | 2.54 mm (0.100 in) | 113 gf (1.11 N) |
| DO | 1.20 mm (0.047 in) spherical radius | 2.40 mm (0.094 in) | 2.54 mm (0.100 in) | 4,536 gf (44.48 N) |
| OOO | 6.35 mm (0.250 in) spherical radius | 10.7–11.6 mm (0.42–0.46 in) | 2.54 mm (0.100 in) | 113 gf (1.11 N) |
| OOO-S | 10.7 mm (0.42 in) radius disk | 11.9 mm (0.47 in) | 5.0 mm (0.20 in) | 197 gf (1.93 N) |
Note: "Type R is a designation, rather than a true "type". The R designation specifies a presser foot diameter (hence the R, for radius; obviously D could not be used) of 18 ± 0.5 mm (0.71 ± 0.02 in) in diameter, while the spring forces and indenter configurations remain unchanged. The R designation is applicable to any D2240 Type, with the exception of Type M; the R designation is expressed as Type xR, where x is the D2240 type, e.g., aR, dR, etc.; the R designation also mandates the employment of an operating stand".[4]
The final value of the hardness depends on the depth of the indenter after it has been applied for 15 seconds on the material. If the indenter penetrates 2.54 mm (0.100 inch) or more into the material, the durometer is 0 for that scale. If it does not penetrate at all, then the durometer is 100 for that scale. It is for this reason that multiple scales exist. Durometer is a dimensionless quantity, and there is no simple relationship between a material's durometer in one scale, and its durometer in any other scale, or by any other hardness test.[1]
| Material | Durometer | Scale |
|---|---|---|
| Bicycle gel seat | 15–30 | OO |
| Chewing gum | 20 | OO |
| Sorbothane | 30–70 | OO |
| Rubber band | 25 | A |
| Door seal | 55 | A |
| Automotive tire tread | 70 | A |
| Soft wheels of roller skates and skateboard | 78 | A |
| Hydraulic O-ring | 70-90 | A |
| Hard wheels of roller skates and skateboard | 98 | A |
| Ebonite rubber | 100 | A |
| Solid truck tires | 50 | D |
| Hard hat (typically HDPE) | 75 | D |
Relation between ASTM D2240 hardness and elastic modulus
Using linear elastic indentation hardness, a relation between the ASTM D2240 hardness and the Young's modulus for elastomers has been derived by Gent[5]and by Mix and Giacomin. [6] Gent's relation has the form
where 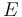 is the Young's modulus in MPa and
is the Young's modulus in MPa and 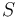 is the ASTM D2240 type A hardness. This relation gives a value of
is the ASTM D2240 type A hardness. This relation gives a value of 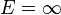 at
at 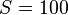 but departs from experimental data for
but departs from experimental data for 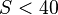 . Mix and Giacomin derive comparable equations for all 12 scales that are standardized by ASTM D2240.
. Mix and Giacomin derive comparable equations for all 12 scales that are standardized by ASTM D2240.
Another relation that fits the experimental data slightly better is[7]
where 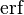 is the error function and
is the error function and 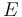 is in units of Pa.
is in units of Pa.
A first order estimate of the relation between ASTM D2240 type D hardness and the elastic modulus for a conical indenter with a 15 degree cone is [8]
where 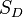 is the ASTM D2240 type D hardness and
is the ASTM D2240 type D hardness and 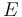 is in MPa.
is in MPa.
Another linear relation between the ASTM D2240 and elastic modulus has the form:
where 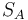 is the ASTM D2240 type A hardness,
is the ASTM D2240 type A hardness, 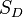 is the ASTM D2240 type D hardness, and
is the ASTM D2240 type D hardness, and 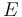 is the Young's modulus in MPa.
is the Young's modulus in MPa.
Patents
- US patent 1770045, A.F. Shore, "Apparatus for Measuring the Hardness of Materials", issued 1930-07-08
- US patent 2421449, J.G. Zuber, "Hardness Measuring Instrument", issued 1947-06-03
See also
- Brinell hardness test
- Bloom (test)
- Knoop hardness test
- Leeb Rebound Hardness Test
- Rockwell hardness test
- Vickers hardness test
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ A.N. Gent (1958), On the relation between indentation hardness and Young's modulus, Institution of Rubber Industry -- Transactions, 34, pp. 46–57.
- ↑ A. W. Mix and A. J. Giacomin (2011), Standardized Polymer Durometry, Journal of Testing and Evaluation, 39(4), pp. 1–10.
- ↑ British Standard 903 (1950, 1957), Methods of testing vulcanised rubber Part 19 (1950) and Part A7 (1957).
- ↑ Qi, HJ and Joyce, K. and Boyce, MC (2003), Durometer hardness and the stress-strain behavior of elastomeric materials, Rubber Chemistry and Technology, 76(2), pp. 419–435.