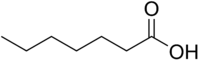
Heptanoic acid
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Heptanoic acid
|
|
| Other names
Enanthic acid; Oenanthic acid; n-Heptylic acid; n-Heptoic acid
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| 111-14-8 |
|
| ChEBI | CHEBI:45571 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL320358 |
| ChemSpider | 7803 |
| DrugBank | DB02938 |
| Jmol 3D model | Interactive image |
| KEGG | C17714 |
| PubChem | 8094 |
| UNII | THE3YNP39D |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C7H14O2 | |
| Molar mass | 130.19 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Oily liquid |
| Density | 0.9181 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | −7.5 °C (18.5 °F; 265.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 223 °C (433 °F; 496 K) |
| 0.2419 g/100 mL (15 °C) | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Heptanoic acid, also called enanthic acid, is an organic compound composed of a seven-carbon chain terminating in a carboxylic acid. It is an oily liquid with an unpleasant, rancid odor.[1] It contributes to the odor of some rancid oils. It is slightly soluble in water, but very soluble in ethanol and ether.
Production and uses
The methyl ester of ricinoleic acid, obtained from castor bean oil is the main commercial precursor to heptanoic acid. It is pyrolyzed to the methyl ester of undecenoic acid and heptanal, which is then air oxidized to the carboxylic acid. Approximately 20,000 tons were consumed in Europe and US in 1980.[2]
-
 Ricinoleic acid is the main precursor to heptanoic acid.
Ricinoleic acid is the main precursor to heptanoic acid.
Heptanoic acid is used in the preparation of esters, such as ethyl heptanoate, which are used in fragrances and as artificial flavors.
Heptanoic acid is used to esterify steroids in the preparation of drugs such as testosterone enanthate, trenbolone enanthate, drostanolone enanthate and methenolone enanthate (Primobolan). It is also one of many additives in cigarettes.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Merck Index, 11th Edition, 4581
- ↑ David J. Anneken, Sabine Both, Ralf Christoph, Georg Fieg, Udo Steinberner, Alfred Westfechtel "Fatty Acids" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2006, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a10_245.pub2