File:PBP catalysis.svg

Summary
Diagram depicting formation of cross-links in the bacterial cell wall by a penicillin binding protein (PBP, an enzyme).
1. The bacterial cell wall consists of strands of repeating N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) subunits. The NAM subunits have short peptide chains attached to them. (The exact composition of these can vary. The proximal alanine is usually L-ala and the distal two are usually D-ala.) These chains, in turn, are bound to chains of 5 glycine residues that will be used in cross-linking.
2. The PBP forms a bond with the peptide side chain at the second most distal alanine residue. This displaces the most distal alanine residue.
3. Another strand of bacterial cell wall arrives. The free end of one of the pentaglycine chains displaces the PBP and forms a bond with the terminal alanine on the other strand.
4. After being displaced, the PBP diffuses away.
5. The formation of one cross-link is complete.
Licensing
Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 04:46, 14 January 2017 | 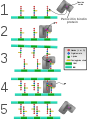 | 1,142 × 1,567 (1.44 MB) | 127.0.0.1 (talk) | Diagram depicting formation of cross-links in the bacterial cell wall by a penicillin binding protein (PBP, an enzyme). <p>1. The bacterial cell wall consists of strands of repeating N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) subunits. The NAM subunits have short peptide chains attached to them. (The exact composition of these can vary. The proximal alanine is usually L-ala and the distal two are usually D-ala.) These chains, in turn, are bound to chains of 5 glycine residues that will be used in cross-linking. </p> <p>2. The PBP forms a bond with the peptide side chain at the second most distal alanine residue. This displaces the most distal alanine residue. </p> <p>3. Another strand of bacterial cell wall arrives. The free end of one of the pentaglycine chains displaces the PBP and forms a bond with the terminal alanine on the other strand. </p> <p>4. After being displaced, the PBP diffuses away. </p> 5. The formation of one cross-link is complete. |
- You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page links to this file: