Template:/box-header
|
Error: Image is invalid or non-existent.
|
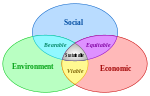
Scheme of sustainable development:
at the confluence of three preoccupations. Clickable. |
Sustainable development has been defined as balancing the fulfillment of human needs with the protection of the natural environment so that these needs can be met not only in the present, but in the indefinite future. The term was used by the Brundtland Commission which coined what has become the most often-quoted definition of sustainable development as development that "meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs."
The field of sustainable development can be conceptually divided into four general dimensions: social, economic, environmental and institutional. The first three dimensions address key principles of sustainability, while the final dimension addresses key institutional policy and capacity issues.
Template:/box-footer
Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Box-header/colours' not found.
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a comparative measure of life expectancy, literacy, education, and standard of living for countries worldwide. It is a standard means of measuring well-being, especially child welfare. It is used to determine and indicate whether a country is a developed, developing, or underdeveloped country and also to measure the impact of economic policies on quality of life. The index was developed in 1990 by Indian Nobel prize winner Amartya Sen, Pakistani economist Mahbub ul Haq, with help from Gustav Ranis of Yale University and Lord Meghnad Desai of the London School of Economics and has been used since then by the United Nations Development Programme in its annual Human Development Report.
The HDI measures the average achievements in a country in three basic dimensions of human development: a long and healthy life, as measured by life expectancy at birth; knowledge, as measured by the adult literacy rate (with two-thirds weight) and the combined primary, secondary, and tertiary gross enrollment ratio (with one-third weight); and a decent standard of living, as measured by the log of gross domestic product (GDP) per capita at purchasing power parity (PPP) in USD.
Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Box-header/colours' not found.
Agritourism is a style of vacation in which hospitality is offered on farms.
Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Box-header/colours' not found.
The Foundation for International Community Assistance (FINCA International) is a non-profit, microfinance organization, founded by John Hatch in 1984. Sometimes referred to as the "World Bank for the Poor" and a "poverty vaccine for the planet," FINCA is the innovator of the village banking methodology in microcredit and is widely regarded as one of the pioneers of modern day microfinance. With its headquarters in Washington, DC, FINCA has 21 affiliated host-country institutions (affiliates), in Latin America, the Caribbean, Africa, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus and Central Asia. Along with Grameen Bank and Accion International, FINCA is considered to be one of the most influential microfinance organizations in the world.
Pioneered by FINCA, village banking is arguably the world’s most widely-imitated microfinance methodology. A village bank is an informal self-help support group of 20-30 members, predominantly female heads-of-household. Among US-based non-profit agencies alone there are at least 31 microfinance institutions (MFIs) that have collectively created over 400 village banking programs in at least 90 countries. And in many of these countries there are host-country MFIs—sometimes dozens—that are village banking practitioners as well.
Template:/box-header
Template:/box-footer
Template:/box-header 
Template:/box-footer
Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Box-header/colours' not found.
| After years of work in Orangi I realised that I was then a solitary old man, but there was another blessing which I wrote about. A kind fate has not yet taken away from me, even in my dotage, the improvising ability of Robinson Crusoe and the benevolent fantasy of Don Quixote.
|
Template:/box-header
|
Sustainable development
Development: Development studies • Economic development • Energy development • Fair trade • Human Development Index • Informal economy • Information and communication technologies for development • International development • Least developed countries • Make Poverty History • Microfinance • Multilateral development banks • Poverty • World Bank Group
|
|
Sustainability: Anaerobic digestion • Appropriate technology • Biodegradable plastic • Carbon negative fuel • Ecological economics • Ecological modernization • Economics of biodiversity • Ecovillage • Energy conservation • Environmental design • Energy development • Environmental technology • Environmental law • Low-carbon economy • Permaculture • Population • Recycling • Renewable energy • Social sustainability • Sustainable agriculture • Sustainable city • Sustainable design • Sustainable tourism • Sustainable transport • Waste management • Water
|
|
Human/World Population: Human overpopulation • Optimum population • Overshoot (ecology) • Population ageing • Population density • Population pyramid • Tragedy of the commons
|
|
List of countries by population: List of countries by population growth rate • List of countries by population density • List of sovereign states and dependent territories by birth rate
|
|

|
|
|
|
Template:/box-footer
Template:/box-header
|
Sustainable development
|
| Development: Country classifications (Least Developed Countries) • Development charities • Development specialists • Development studies • Economic development (Informal economy, Microfinance, Poverty) • Energy development • Fair trade • Foreign aid by country • Human Development Index • International development • Make Poverty History • Multilateral development banks • Rural community development • Supranational banks (World Bank) • Water supply and sanitation by country |
 |
|
Sustainability: Advocates • Alternative energy • Anaerobic digestion • Appropriate technology • Biodegradable plastics • Biofuels • Carbon diet • Economics of sustainability • Ecovillages • Energy conservation • Environmental design • Low-carbon economy • Permaculture • Recycling • Renewable energy • Sustainable agriculture • Sustainable technologies • Waste management • WaterTemplate:/box-footer
Template:/box-header
Template:/box-footer
Template:/box-header
 |
- Attention: Environment pages, PRiSM
- Cleanup: Bioeconomics, Biofuel, Development aid, Appropedia
- Expand: Zero carbon city, International development, Zero-emissions vehicle, Solar-powered_aircraft
- Expert attention: Biodegradable plastic, International development
- Merge: Aid ← Development aid
- Neutrality: Energy economics, World Bank Group, Sustainability
- Requests: Aerobic digestion, Development charities (redirects),
- Sources: Appropriate technology, Biodegradable plastic, Energy development, Green politics, Recycling, Socially responsible investing, Sustainable agriculture, World Bank Group
- Spam cleanup: Sustainability, Sustainable development
- Stubs: Community-led total sanitation, Migration studies, Rural community development, More... Biotechnology, Environment, Environmental organizations, International development, Renewable energy, Sustainability, Waste, Water supply
- Wikify: Socially responsible investing
- Worldwide view: Recycling
|
Template:/box-footer
Template:/box-header
Template:/box-footer
Template:/box-header
Template:/box-footer |
|
|