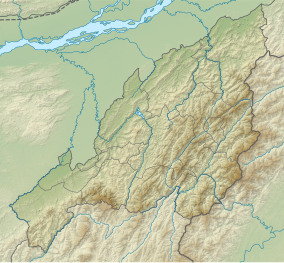
Fakim Wildlife Sanctuary
| Fakim Wildlife Sanctuary | |
|---|---|
| Location | Nagaland, India |
| Coordinates | 25°49′32″N 94°57′16″E / 25.825528°N 94.954389°E |
Fakim Wildlife Sanctuary is a protected area in Nagaland, India.[1] It is situated close to the India-Myanmar border in Pungro circle of Kiphire district, and covers an area of 642 ha (1,590 acres).[2] Fakim village is the gateway to the sanctuary.[3] It was established in 1983.[4]
Flora, fauna and terrain
[edit]The sanctuary has rich biodiversity.[5] The terrain consists of hills, high ridges, green meadows, deep gorges and narrow valleys.[2] The forest is thick with oak, Khasi pine, hollock, nahor, kachnar, cane and bamboo.[6] The sanctuary is home to slender loris, panthers, Himalayan bears, jungle cats, barking deers and hoolock gibbons.[2][7] Bird species in the sanctuary include great hornbills, butterflies, tragopans, junglefowls and doves.[2][8][9]
Conservation efforts
[edit]Nagaland government has encouraged conservation initiatives including hunting bans.[10][11][12] Campaigns by NGOs and activists are also key to the fledgling conservation efforts.[12][13][14]
References
[edit]- ^ "Wildlife conservation and management in Nagaland". The Morung Express. Retrieved 21 August 2024.
- ^ a b c d "Fakim Wild Life Sanctuary | District Kiphire | India". Retrieved 21 August 2024.
- ^ "'A Photographic Guide to Birds of Fakim' by Leyamong L released". MorungExpress. Retrieved 21 August 2024.
- ^ Negi, Sharad Singh (1991). Handbook of National Parks, Sanctuaries, and Biosphere Reserves in India. Indus Publishing Company. ISBN 978-81-85182-59-9.
- ^ District Human Development Report, 2013: Kiphire. Department of Planning and Coordination, Government of Nagaland. 2014.
- ^ Capila, Pranav (22 December 2018). "The Naga hunter who gave up hunting. And made sure his village did too". The Hindu. ISSN 0971-751X. Retrieved 21 August 2024.
- ^ Kohli, M. S. (2005). Incredible Himalayas: Environment, Culture, Tourism, and Adventure. Indus Publishing. ISBN 978-81-7387-179-5.
- ^ Aradhya. 600+ Current Affairs MCQs for UPSC Prelims 2020: General Studies Paper-1. GRASP IAS.
- ^ "Wildlife buffs spot rare butterfly 17 times - Group was on an excursion to Fakim sanctuary in Nagaland's Kiphire district bordering Myanmar". Telegraph India.
- ^ "Nagaland hunts for a way out of its bloody tradition, shows some success". The Indian Express. 27 April 2018. Retrieved 21 August 2024.
- ^ Page, Nagaland (26 January 2021). "Governor's Award Honours Community Conservation And Social Activism - Nagaland Page". nagalandpage.com. Retrieved 21 August 2024.
- ^ a b "Protection & conservation of wildlife 'burning need of the hour': Nagaland CM". MorungExpress. Retrieved 21 August 2024.
- ^ PTI (8 October 2022). "Kiphire: PCCF & HoFF visits Penkim and Fakim villages". Nagaland Tribune. Retrieved 21 August 2024.
- ^ NEWS, NE NOW (1 March 2018). "Wildlife body extends financial aid to Nagaland's hunter turned conservationist". NORTHEAST NOW. Retrieved 21 August 2024.