Portal:Andes
Portal maintenance status: (November 2018)
|
The Andes Portal

The Andes (/ˈændiːz/ AN-deez), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (Spanish: Cordillera de los Andes; Quechua: Anti) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is 8,900 km (5,530 mi) long and 200 to 700 km (124 to 435 mi) wide (widest between 18°S and 20°S latitude) and has an average height of about 4,000 m (13,123 ft). The Andes extend from South to North through seven South American countries: Argentina, Chile, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela.
Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, El Alto, and La Paz. The Altiplano Plateau is the world's second highest after the Tibetan Plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three major divisions based on climate: the Tropical Andes, the Dry Andes, and the Wet Andes.
The Andes are the highest mountain range which is outside of Asia. The range's highest peak, Argentina's Aconcagua, rises to an elevation of about 6,961 m (22,838 ft) above sea level. The peak of Chimborazo in the Ecuadorian Andes is farther from the Earth's center than any other location on the Earth's surface, due to the equatorial bulge resulting from the Earth's rotation. The world's highest volcanoes are in the Andes, including Ojos del Salado on the Chile-Argentina border, which rises to 6,893 m (22,615 ft). (Full article...)
Selected articles
-
Image 1

The Titicaca orestias, Lake Titicaca orestias, or Lake Titicaca flat-headed fish (Orestias cuvieri), also known by its native name amanto, is a likely extinct freshwater killifish from Lake Titicaca in South America. It belongs in the pupfish genus Orestias, endemic to lakes, rivers and streams in the Andean highlands. With a total length of up to 27 cm (10.6 in), it was the largest member in that genus. In the hope that an undiscovered population remains, it is listed as Data Deficient by the IUCN. Despite its common name, it is not the only Orestias from Lake Titicaca.
Its mouth was nearly turned upwards, thereby giving the flat head a concave shape. The head took up nearly a third of the whole body length. The upperside was greenish-yellow to umber. The lower jaw was black. Its scales were oddly light coloured at their centre. The scales of the young were blotched. (Full article...) -
Image 2
Cerro Bonete is a mountain in the north of the province of La Rioja, Argentina, near the provincial border with Catamarca.
Its summit is 6,759 m above mean sea level, making it the fifth-highest separate mountain in the Americas (after Aconcagua, Ojos del Salado, Monte Pissis, and Huascaran). SRTM data disproves the frequently-made claim that its summit is 6,872 m above sea level. (Full article...) -
Image 3

The llama (/ˈlɑːmə/; Spanish pronunciation: [ˈʎama] or [ˈʝama]) (Lama glama) is a domesticated South American camelid, widely used as a meat and pack animal by Andean cultures since the pre-Columbian era.
Llamas are social animals and live with others as a herd. Their wool is soft and contains only a small amount of lanolin. Llamas can learn simple tasks after a few repetitions. When using a pack, they can carry about 25 to 30% of their body weight for 8 to 13 km (5–8 miles). The name llama (in the past also spelled "lama" or "glama") was adopted by European settlers from native Peruvians. (Full article...) -
Image 4
Siula Grande is a mountain in the Huayhuash mountain range in the Peruvian Andes. It is 6,344 metres (20,814 ft) high and has a subpeak, Siula Chico, 6,260 m (20,540 ft) high. (Full article...) -
Image 5Pico Bonpland as seen from the Pico Humboldt
Pico Bonpland is Venezuela's fourth-highest peak, at 4,883 metres above sea level. It is located in the Sierra Nevada de Merida, in the Venezuelan Andes of (Mérida State). The peak with its sister peak Pico Humboldt, and the surrounding páramos are protected by the Sierra Nevada National Park. The name of the peak is in honor of Aimé Bonpland, although he never visited the Venezuelan Andes.
The glaciers located in the Bonpland were the result from Merida glaciation in the Pleistocene. By 2011 they had all disappeared. (Full article...) -
Image 6
Sierra Nevada, also known as Sierra Nevada de Lagunas Bravas, is a major ignimbrite-lava dome complex which lies in both Chile and Argentina in one of the most remote parts of the Central Andes.
Activity in the complex started in Argentina and formed two stratovolcanoes. Later, 12 or more vents formed, some with craters up to 400 metres (1,300 ft) wide. Lava flows up to 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) long with flow ridges are also found. It covers a total area of 225 km2. Radiometric dating has yielded ages of 1.7 ± 0.4 to 0.431 ± 0.012 million years ago, a lava flow from the neighbouring Azufrera Los Cuyanos volcano that is sometimes considered part of Sierra Nevada is 140,000 years old. Together with Cerro el Condor and Peinado it forms the Culampaja line, a line of volcanoes that reaches Cerro Blanco. Strong seismic attenuation is observed beneath Sierra Nevada. Hydrothermally altered rocks in Sierra Nevada may be the source of sulfate and arsenic in the Juncalito and Negro rivers, and heat sources for regional hot springs. The snowline in the area lies at 5,800 metres (19,000 ft) altitude at Cumbre del Laudo. (Full article...) -
Image 7
Acamarachi (also known as Pili) is a 6,046-metre (19,836 ft) high volcano in northern Chile. In this part of Chile, it is the highest volcano. Its name means "black moon". It is a volcano in the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, a zone of strong volcanic activity during the last million years. Old volcanoes in the area are well-preserved, due to the dry climate.
Acamarachi itself is a cone-shaped volcano with steep upper flanks and a lava dome on its northern side. While there is no indication of historical activity and the flank lava flows are old, some lava flows around the summit crater and a lava coulee north of Acamarachi on the saddle between Acamarachi and Colachi volcano may be postglacial in age. Acamarachi is formed by andesitic and dacitic rocks. (Full article...) -
Image 8
Pico El Águila or Collado del Cóndor is the milestone that stands at the highest elevation on the Venezuelan Transandean Highway (a branch of the Pan-American Highway) in the Cordillera de Mérida of Venezuela. Nearby stands a monument, sculpted by a Colombian artist, Marcos León Mariño, depicting a condor, commemorating an event in the campaign of the Liberator, Simón Bolivar. It is located in the state of Mérida and has an altitude of 4,118 meters. (Full article...) -
Image 9
Cerro Mercedario is the highest peak of the Cordillera de la Ramada range and the eighth-highest mountain of the Andes. It is located 100 km to the north of Aconcagua, in the Argentine province of San Juan. (Full article...) -
Image 10
Llullaillaco (Spanish pronunciation: [ʎuʎajˈʎako]) is a dormant stratovolcano on the border between Argentina (Salta Province) and Chile (Antofagasta Region). It lies in the Puna de Atacama, a region of tall volcanic peaks on a high plateau close to the Atacama Desert, one of the driest places in the world. Its maximum elevation is most commonly given as 6723 m, making it the second- or third-highest volcano in the world. Despite its height, it is not clear whether the volcano has any glaciers or merely patches of perennial snow and ice. Between 3700 m and 5000 m elevation there is a sparse plant cover, while at lower altitudes the climate is too dry for plants to grow. A species of mouse on Llullaillaco is the highest-living known vertebrate species.
The volcano formed during the Pleistocene in two stages, named Llullaillaco I and Llullaillaco II. The oldest rocks are about 1.5 million years old. About 150,000 years ago, the volcano's southeastern flank collapsed, generating a debris avalanche that reached as far as 25 km from the summit. During the last stage, three conspicuous lava flows were emplaced on the summit. The youngest dated rocks are 930 ± 140 years old, but there are reports of activity from the 19th century. (Full article...) -
Image 11The double peak of The Illinizas
The Illinizas are a pair of volcanic mountains that are located in the north of Latacunga, Cotopaxi, Ecuador. They are located in the Illinizas Ecological Reserve (Spanish: Reserva Ecológica Los Illinizas). These twin mountains are separated by a saddle that is about a kilometer long. The peaks are among the highest in Ecuador, with Illiniza Sur standing slightly taller than Illiniza Norte, its northern counterpart, at 5245 metres and 5126 metres respectively.
Most guidebooks (for example, Lonely Planet Ecuador, Ecuador: A Climbing Guide) spell the mountain with only one "l" as in Iliniza. The name Illinizas is derived from the Kunza words for "masculine hill." (Full article...) -
Image 12
Nevado Ojos del Salado is a dormant complex volcano in the Andes on the Argentina–Chile border. It is the highest volcano on Earth and the highest peak in Chile. The upper reaches of Ojos del Salado consist of several overlapping lava domes, lava flows and volcanic craters, with sparse ice cover. The complex extends over an area of 70–160 square kilometres (27–62 sq mi) and its highest summit reaches an altitude of 6,893 metres (22,615 ft) above sea level. Numerous other volcanoes rise around Ojos del Salado.
Being close to the Arid Diagonal of South America, the mountain has extremely dry conditions, which prevent the formation of substantial glaciers and a permanent snow cover. Despite the arid climate, there is a permanent crater lake about 100 m (330 ft) in diameter at an elevation of 6,480 metres (21,260 ft)-6,500 metres (21,300 ft) within the summit crater and east of the main summit. This is the highest lake of any kind in the world. Owing to its altitude and the desiccated climate, the mountain lacks vegetation. (Full article...) -
Image 13
The Titicaca grebe (Rollandia microptera), also known as the Titicaca flightless grebe or short-winged grebe, is a grebe found on the altiplano of Peru and Bolivia. As its name implies, its main population occurs on Lake Titicaca. Lake Uru Uru and Poopó, the Rio Desaguadero, and small lakes that connect to Lake Titicaca in wet years, serve as "spillovers" territory. In the past, the population was larger and several of these lakes – such as Lakes Umayo and Arapa – apparently had and may still have permanent large colonies (BirdLife International 2006). It is sometimes placed in Podiceps or a monotypic genus Centropelma. Its local name is zampullín del Titicaca. (Full article...) -
Image 14
Rasac (possibly Quechua for toad) is a mountain in the Huayhuash mountain range in west central Peru, part of the Andes. It has a summit elevation of 6,017 metres (19,741 ft), although other sources cite a height of 6,040 metres (19,816 ft). Rasac is a long, relatively squat mountain on the western edge of the Huayhuash range, across the glacier from the tallest peak in the range, Yerupajá. Although it is a 6,000 metre mountain, Rasac's broad profile is dwarfed by Yerupajá. (Full article...) -
Image 15
Cerro del Nacimiento is an Andean volcano of the Cordillera de la Ramada range, in the Catamarca Province of Argentina. Its summit is 6,436 metres (21,115 ft) above sea level. (Full article...) -
Image 16
Reventador is an active stratovolcano which lies in the eastern Andes of Ecuador. It lies in a remote area of the national park of the same name, which is Spanish for "exploder". Since 1541, it has erupted over 25 times, although its isolated location means that many of its eruptions have gone unreported.
The largest historical eruption occurred in 2002. During that eruption, the plume from the volcano reached a height of 17 kilometres (11 mi) and pyroclastic flows proceeded to 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) from the cone. On March 30, 2007, the mountain ejected ash to a height of about 3.2 kilometres (2.0 mi). No injuries or damage were reported. Its most recent eruption began on 27 July 2008, and it has remained in continuing eruption status (intermittent eruptive events without a break of 3 months or more) as of 15 October 2021. (Full article...) -
Image 17Image from Expedition 9 shows the snow-capped peak Cabaray volcano in the Bolivian Andes (north is to the upper right).
Cabaraya is a stratovolcano in Bolivia. It lies between the volcanoes Isluga and Tata Sabaya, immediately east of the border with Chile. (Full article...) -
Image 18Patilla Pata is located NW of Nevado Sajama (this latter is in the lower center of this NASA image, with north to the top right corner).
Patilla Pata is a stratovolcano in the Oruro Department in Bolivia. It is situated in the Sajama Province, in the west of the Curahuara de Carangas Municipality, at the border with Chile. Patilla Pata lies south-west of the mountain Jisk'a Kunturiri, north-east of the lake Q'asiri Quta (Khasiri Kkota) and the mountain Qullqi Warani, west of the little lake Sura Pata, south-east of the mountains Laram Q'awa, Kunturiri and Milluni and south of the little lake named Ch'iyar Quta.
The river Junt'uma K'uchu (Aymara junt'u warm, hot, uma water, k'uchu corner, "warm water corner", Junthuma Khuchu) originates south of Patilla Pata. It flows to the south-east as a right affluent of the Sajama River. (Full article...) -
Image 19The volcano Parinacota rises over Chungará
Chungará is a lake situated in the extreme north of Chile at an elevation of 4,517 metres (14,820 ft), in the Altiplano of Arica y Parinacota Region in the Lauca National Park. It has a surface area of about 21.5–22.5 square kilometres (8.3–8.7 sq mi) and has a maximum depth of about 26–40 metres (85–131 ft). It receives inflow through the Río Chungara with some minor additional inflows, and loses most of its water to evaporation; seepage into the Laguna Quta Qutani plays a minor role.
The lake formed between 8,000 and 17,000 years ago when the volcano Parinacota collapsed and the debris from the collapse dammed the Lauca River. Since then the lake has progressively grown owing to decreasing seepage. The lake is part of the Lauca National Park; a planned diversion of the lake's waters into the Azapa Valley being abandoned after a decision by the Chilean Supreme Court. (Full article...) -
Image 20Illimani is a mountain in the Khari Khari mountain range of the Bolivian Andes, about 5,030 m (16,503 ft) high. It is situated south-east of Potosí in the Potosí Department, Tomás Frías Province, Potosí Municipality. Illimani lies south-west of the mountain Uma Jalanta, north-east of Challwiri Lake and north of Illimani Lake. (Full article...)
-
Image 21Falso Azufre volcanic complex and Laguna Verde.
Falso Azufre is a complex volcano at the border of Argentina and Chile.
Falso Azufre is elongated in east–west direction and contains craters and lava domes; most craters have diameters of 300–600 metres (980–1,970 ft) with the exception of the main crater, which is 1 by 1.3 kilometres (0.62 mi × 0.81 mi) wide. The highest summit Cerro Falso Azufre lies at the western end in Chile, which has mostly generated pyroclastic material from craters. The probably youngest segment of the volcano is the eastern section in Argentina, where two lava domes and two cones are located; these form the Dos Conos volcano. Some lava flows linked to Dos Conos are up to 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) long. The oldest is known as the Kunstmann edifice on the northwestern side of Falso Azufre; Kunstmann volcano features a 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) wide scar formed by a sector collapse. Falso Azufre with a base surface of 387 square kilometres (149 sq mi) is one of the biggest volcanoes in the area. The presence of two oppositely curved vent alignments gives the complex an arc-like shape which reaches heights of about 5,900 metres (19,400 ft) above sea level. (Full article...) -
Image 22
El Altar or Capac Urcu (possibly from Kichwa kapak principal, great, important / magnificence, urku mountain) is an extinct volcano on the western side of Sangay National Park in Ecuador, 170 km (110 mi) south of Quito, with a highest point of 5,319 m (17,451 ft). Spaniards named it so because it resembled two nuns and four friars listening to a bishop around a church altar. In older English sources it is also called The Altar. (Full article...) -
Image 23
Salcantay, Salkantay or Sallqantay (in Quechua) is the highest peak in the Vilcabamba mountain range, part of the Peruvian Andes. It is located in the Cusco Region, about 60 km (40 mi) west-northwest of the city of Cusco. It is the 38th-highest peak in the Andes and the twelfth-highest in Peru. However, as a range highpoint in deeply incised terrain, it is the second most topographically prominent peak in the country, after Huascarán.
Salcantay's proximity to Machu Picchu makes trekking around it an alternative to the oversubscribed Inca Trail; this is known as the Salkantay trek. (Full article...) -
Image 24Cotopaxi seen from the high plain (at least 3,700 m (12,139 ft)) of Cotopaxi National Park
Cotopaxi (Spanish pronunciation: [kotoˈpaksi]) is an active stratovolcano in the Andes Mountains, located near Latacunga city of Cotopaxi Province, about 50 km (31 mi) south of Quito, and 31 km (19 mi) northeast of the city of Latacunga, Ecuador. It is the second highest summit in Ecuador (after Chimborazo), reaching a height of 5,897 m (19,347 ft). Cotopaxi is among the highest active volcanoes in the world.
Cotopaxi is known to have erupted 87 times, resulting in the creation of numerous valleys formed by lahars (mudflows) around the volcano. An ongoing eruption began on 21 October 2022. (Full article...) -
Image 25View of Cardenal Antonio Samoré Pass during winter, latitude 41°S
The Wet Andes (Spanish: Andes húmedos) is a climatic and glaciological subregion of the Andes. Together with the Dry Andes it is one of the two subregions of the Argentine and Chilean Andes. The Wet Andes runs from a latitude of 35°S to Cape Horn at 56°S. According to Luis Lliboutry the Wet Andes can be classified after the absence of penitentes. In Argentina well developed penitentes are found as south as on Lanín Volcano (40°S). Another difference is that the Wet Andes is largely devoid of rock glaciers. The glaciers of the Wet Andes have a far more stable line of equilibrium than those of the Dry Andes due to summer precipitations, low thermal oscillations and an overall high moisture. (Full article...)
Did you know...
- ... that the 1930s Polish Andean expeditions have been credited with several first ascents and the tracing of a new route to the summit of Aconcagua, the Andes' highest peak?
Need help?
Do you have a question about Andes that you can't find the answer to?
Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk.
General images
-
Image 2A male Andean cock-of-the-rock, a species found in humid Andean forests and the national bird of Peru (from Andes)
-
Image 5Aerial view of Valle Carbajal in the Tierra del Fuego. The Andes range is about 200 km (124 mi) wide throughout its length, except in the Bolivian flexure where it is about 640 kilometres (398 mi) wide. (from Andes)
-
Image 6Pacha Mama Ceremony (from Andean agriculture)
-
Image 11Central Andes (from Andes)
-
Image 14Huayna Potosí, Bolivia (from Andes)
-
Image 17Peruvian farmers sowing maize and beans (from Andes)
-
Image 18Bolivian Andes (from Andes)
-
Image 19Ulluco: Common crop of the Andean region (from Andean agriculture)
-
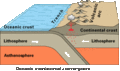
Image 20Simplified sketch of the present-situation along most of the Andes (from Andean orogeny)
-
Image 21Pico Humboldt at sunset (from Andes)
-
Image 22Mashua tubers (from Andean agriculture)
-
Image 24Irrigating land in the Peruvian Andes (from Andes)
-
Image 25Paleogeography of the Late Cretaceous South America. Areas subject to the Andean orogeny are shown in light grey while the stable cratons are shown as grey squares. The sedimentary formations of Los Alamitos and La Colonia that formed in the Late Cretaceous are indicated. (from Andean orogeny)
-
Image 26The seaward tilting of the sedimentary strata of Salto del Fraile Formation in Peru was caused by the Andean orogeny. (from Andean orogeny)
-
Image 28Topographic map of the Andes by the NASA. The southern and northern ends of the Andes are not shown. The Bolivian Orocline is visible as a bend in the coastline and the Andes lower half of the map. (from Andean orogeny)
-
Image 29Syncline next to Nordenskjöld Lake in Torres del Paine National Park. The syncline formed during the Andean orogeny. (from Andean orogeny)
-
Image 31Map of a north-south sea-parallel pattern of rock ages in western Colombia. This pattern is a result of the Andean orogeny. (from Andean orogeny)
Subcategories
Related portals
Subtopics
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus