libxutils is a cross-platform C library that provides safer implementations of various functionality to make routine tasks easier for programs written in C and it's compatible languages like C++, Rust, and Objective C. The library offers a range of features including containers, data structures, network tools, cryptography algorithms, string manipulations, system utilities, HTTP/S & WS/WSS client/server, JSON parser/serializer, JWT tokens, and etc. A list of key features can be found below.
libxutils is available for Linux, Unix and Windows operating systems and is released under the MIT License. To check the version of the library you have, you can refer to the file src/xver.h. Please note that the list of features provided in the README is incomplete. For more information about the full range of features, you can refer to the individual header files linked below or browse the source code.
- Dynamically allocated array with sort and search features
- Dynamically allocated byte and data buffers
- Dynamically allocated key-value pair map
- Dynamically allocated hash map
- Dynamically allocated C string
- Implementation of linked list
- Event based client/server API for HTTP/S, WS/WSS and UNIX/TCP connections
- Cross-platform socket library with RAW, UNIX, TCP, UDP and SSL support
- Cross-platform event library based on poll(), epoll() and WSAPoll()
- Web Socket client/server library
- HTTP client/server library
- MDTP client/server library
- RTP packet parser library
- Implementation of various encrypt/decrypt algorithms
- Base64 and Base64Url encrypt/decrypt functions
- AES based on FIPS-197 implementation by Christophe Devine
- Implementation of HMAC algorithm with SHA256 and MD5
- RSA implementation based on OpenSSL library
- Implementation of SHA256 calculations
- Implementation of SHA1 calculations
- Implementation of CRC32 calculations
- Implementation of MD5 calculations
- Cross-platform file and directory operations
- Cross-platform CPU affinity manipulation
- Implementation of advanced file search
- System time manipulation library
- Performance monitoring library
- Simple and fast memory pool
- Advanced logging library
- JSON parser and writer library with lint and minify support
- Implementation of JSON Web Tokens with HS256 and RS256
- Cross-platform synchronization library
- Cross-platform multithreading library
- Command-Line interface operations
- C String manipulation library
There are several ways to build and install the project.
A relatively simple way to build and install the libary and tools is to use the included build script:
git clone https://github.com/kala13x/libxutils.git && ./libxutils/build.sh --installList options that build script supports:
--prefix=<path>Install destination prefix for the library and header files.--tool=<tool>SpecifyMakefilegeneration tool or use includedMakefile.--ssl=yes/noManually enable or disable SSL support (default: yes).--installInstall library and the tools after the build.--cleanupCleanup object files after build/installation.--examplesInclude examples in the build.--toolsInclude tools in the build.
You can either choose cmake, smake or make as the tool argument, but cmake is recommended on platforms other than the Linux.
If the tool will not be specified the script will use make (included Makefile) as default.
If you have a CMake tool installed in your operating system, here is how project can be built and installed using cmake:
git clone https://github.com/kala13x/libxutils.git
cd libxutils
cmake . && make
sudo make installSMake is a simple Makefile generator tool for the Linux/Unix operating systems:
git clone https://github.com/kala13x/libxutils.git
cd libxutils
smake && make
sudo make installThe project can also be built with a pre-generated Makefile for the Linux.
git clone https://github.com/kala13x/libxutils.git
cd libxutils
make
sudo make installIf you want to use particular files and functions, you can configure the library and select only that functionality for the build. In this way, it is possible not to increase the size of the program and to avoid the linkage of unused code.
The libxutils project has a config file that contains a list of modules that will be included in the build. This file is used by the build.sh script, which resolves dependencies for each enabled module and generates a CMakeList.txt file.
Open xutils.conf file with a text editor and mark only the functionality you want to include in the build. Use a low-case y symbol to enable and any other symbol to disable modules. Removing a related line from the list will also disable the module.
Example:
...
USE_ARRAY=n
USE_CRYPT=n
USE_XTIME=n
USE_EVENT=y
USE_LIST=n
USE_XBUF=n
USE_HASH=n
USE_SOCK=n
USE_XLOG=y
USE_XSTR=n
...
After updating the configuration, use the build.sh script to generate the Makefile and build the project.
./build.sh --tool=cmakeYou may notice that when you select only one module, several other modules may be also included in the build. Because some files depend on other files in the project, the build.sh script will automatically resolve these dependencies and include required files in the build as well.
For example, if you only mark HTTP library for a build, the socket library will be automatically enabled because HTTP uses some functionality from sockets.
The only dependency that the library uses is the openssl-devel package for the SSL and RSA implementations.
You can either install the openssl-devel package or disable the SSL support in the library.
Red-Hat family: sudo dnf install openssl-devel
Debian family: sudo apt-get install libssl-dev
If you use the build.sh script for building the project, you do not need to disable anything manually,
the script will automatically disable SSL support if the OpenSSL library is not installed in the system.
If you use raw Makefile to build the project, all you need to adjust CFLAGS and LIBS in Makefile.
- Remove
-D_XUTILS_USE_SSLentry from theCFLAGS. - Remove
-lssland-lcryptoentries from theLIBS.
Use build script to force disable SSL even if it is installed in the system:
./build.sh --ssl=noJust include the required <xutils/*.h> header files in your source code and use -lxutils
linker flag while compiling your project. See the example directory for more information.
Use the included script to build or install CLI apps from the tools directory.
The script can be used to build the sources from the examples directory as well.
./libxutils/build.sh --tools --examplesThese sources can also be built by using the CMake tool or Makefile from that directory.
You may need to export the SSL flag accordingly if you are doing a build without the script:
cd examples
export XUTILS_USE_SSL=y
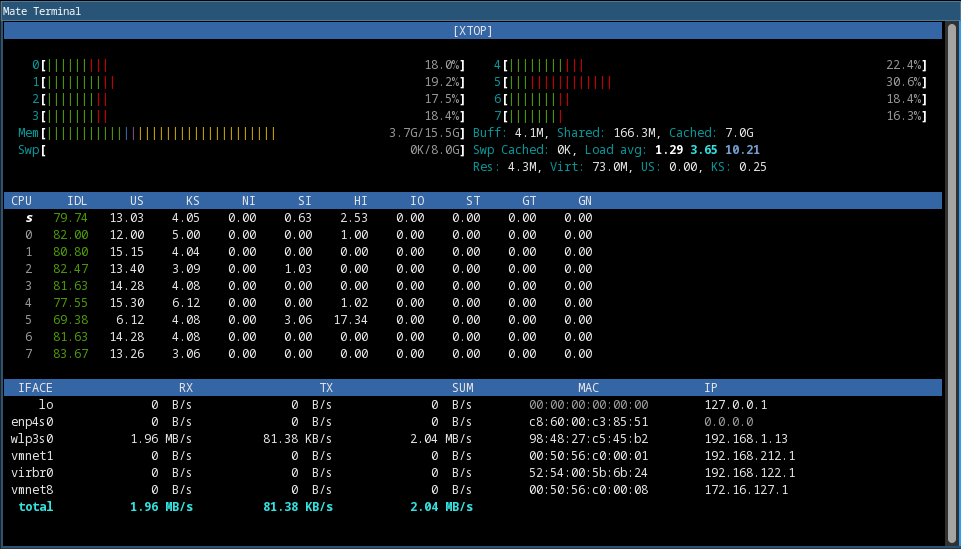
cmake . && makeXTOP is HTOP like performance monitor that supports to monitor CPU, memory, and network traffic into a single window. In addition, it has powerful REST API client/server mode and much more.
After building the sources in tools directory, run sudo make install command to install following apps in the system:
xcrypt- File and text encrypt/decrypt tool for CLIxpass- Secure password manager tool for CLIxjson- JSON linter and minifier tool for CLIxhttp- Powerful HTTP client tool for CLIxtop- Advanced resource monithor for CLIxsrc- Advanced file search tool for CLI
Run each of this tool with -h argument to check out the usage and version information.