1,3-dipole
From Infogalactic: the planetary knowledge core
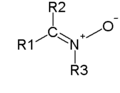 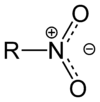 |
| From top to bottom, azides, nitrones, and nitro compounds are examples of 1,3-dipoles. |
In organic chemistry, a 1,3-dipolar compound or 1,3-dipole is a dipolar compound with delocalized electrons and a separation of charge over three atoms. They are reactants in 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions.[1] [2]
Known 1,3-dipoles are:
- Azides (RN3)
- Ozone (O3)
- Nitro compounds (RNO2)
- Diazo compounds (R2CN2)
- Some oxides
- Azoxide compounds (RN(O)NR)
- Carbonyl oxides (Criegee zwitterions)[3][4]
- Nitrile oxides (RCN-O)
- Nitrous oxide (N2O)
- Nitrones (R2CN(R)O)
- Some imines:
- Azomethine imine
- Nitrilimines (RCN-NR, analogous to nitrile oxide)
- Carbonyl imines
- Some ylides
- Azomethine ylide
- Nitrile ylide (RCNCR'2)
- Carbonyl ylide
- Thiosulfines (R2CSS)
References
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ IUPAC Gold Book dipolar compounds
- ↑ http://www.organic-chemistry.org/namedreactions/ozonolysis-criegee-mechanism.shtm Ozonolysis mechanism on Organic Chemistry Portal site
- ↑ Li, Jie Jack: Criegee mechanism of ozonolysis Book: Name Reactions. 2006, 173-174, doi:10.1007/3-540-30031-7_77
