Absorbing element
In mathematics, an absorbing element is a special type of element of a set with respect to a binary operation on that set. The result of combining an absorbing element with any element of the set is the absorbing element itself. In semigroup theory, the absorbing element is called a zero element[1][2] because there is no risk of confusion with other notions of zero. In this article the two notions are synonymous. An absorbing element may also be called an annihilating element.
Definition
Formally, let (S, ∘) be a set S with a closed binary operation ∘ on it (known as a magma). A zero element is an element z such that for all s in S, z∘s=s∘z=z. A refinement[2] are the notions of left zero, where one requires only that z∘s=z, and right zero, where s∘z=z.
Absorbing elements are particularly interesting for semigroups, especially the multiplicative semigroup of a semiring. In the case of a semiring with 0, the definition of an absorbing element is sometimes relaxed so that it is not required to absorb 0; otherwise, 0 would be the only absorbing element.[3]
Properties
- If a magma has both a left zero
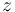 and a right zero
and a right zero 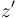 , then it has a zero, since
, then it has a zero, since 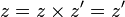 .
. - If a magma has a zero element, then the zero element is unique.
Examples
- The most well known example of an absorbing element in algebra is multiplication, where any number multiplied by zero equals zero. Zero is thus an absorbing element.
- Floating point arithmetics as defined in IEEE-754 standard contains a special value called Not-a-Number ("NaN"). It is an absorbing element for every operation; i.e., x + NaN = NaN + x = NaN, x − NaN = NaN − x = NaN etc.
- The set of binary relations over a set X, together with the composition of relations forms a monoid with zero, where the zero element is the empty relation (empty set).
- The closed interval H=[0, 1] with x∘y=min(x,y) is also a monoid with zero, and the zero element is 0.
- More examples:
| Set | Operation | Absorber |
|---|---|---|
| Real numbers | · (multiplication) | 0 |
| Integers | greatest common divisor | 1 |
| n-by-n square matrices | · (multiplication) | Matrix of all zeroes |
| Extended real numbers | minimum/infimum | −∞ |
| Extended real numbers | maximum/supremum | +∞ |
| Sets | ∩ (intersection) | { } (empty set) |
| Subsets of a set M | ∪ (union) | M |
| Boolean logic | ∧ (logical and) | ⊥ (falsity) |
| Boolean logic | ∨ (logical or) | ⊤ (truth) |
See also
Notes
References
- Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- M. Kilp, U. Knauer, A.V. Mikhalev, Monoids, Acts and Categories with Applications to Wreath Products and Graphs, De Gruyter Expositions in Mathematics vol. 29, Walter de Gruyter, 2000, ISBN 3-11-015248-7.
- Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
External links
- Absorbing element at PlanetMath