Covariance and contravariance (computer science)
The type system of many programming languages support subtyping. For instance, if Cat is subtype of Animal, then an expression of type Cat can be used whenever an expression of type Animal could. Variance refers to how subtyping between more complex types (list of Cats versus list of Animals, function returning Cat versus function returning Animal, ...) relates to subtyping between their components. Depending on the variance of the type constructor, the subtyping relation may be either preserved, reversed, or ignored. For example, in C#:
IEnumerable<Cat>is a subtype ofIEnumerable<Animal>. The subtyping is preserved becauseIEnumerable<T>is covariant onT.Action<Animal>is a subtype ofAction<Cat>. The subtyping is reversed becauseAction<T>is contravariant onT.- Neither
IList<Cat>norIList<Animal>is a subtype of the other, becauseIList<T>is invariant onT.
The variance of a C# interface is determined by in/out annotations on its type parameters; the above interfaces are declared as IEnumerable<out T>, Action<in T>, and IList<T>. Types with more than one type parameter may specify different variances on each type parameter. For example, the delegate type Func<in T, out TResult> represents a function with a contravariant input parameter of type T and a covariant return value of type TResult.[1]
The typing rules for interface variance ensure type safety. For example, an Action<T> represents a first-class function expecting an argument of type T, and a function that can handle any type of animal can always be used instead of one that can only handle cats.
A programming language designer will consider variance when devising typing rules for e.g. arrays, inheritance, and generic datatypes. By making type constructors covariant or contravariant instead of invariant, more programs will be accepted as well-typed. On the other hand, programmers often find contravariance unintuitive, and accurately tracking variance to avoid runtime type errors can lead to complex typing rules. In order to keep the type system simple and allow useful programs, a language may treat a type constructor as invariant even if it would be safe to consider it variant, or treat it as covariant even when that can violate type safety.
Contents
Formal definition
Within the type system of a programming language, a typing rule or a type constructor is:
- covariant if it preserves the ordering of types (≤), which orders types from more specific to more generic;
- contravariant if it reverses this ordering;
- bivariant if both of these apply (i.e., both
I<A>≤I<B>andI<B>≤I<A>at the same time); - invariant or nonvariant if neither of these applies.
The article considers how this applies to some common type constructors.
Arrays
First consider the array type constructor: from the type Animal we can make the type Animal[] ("array of animals"). Should we treat this as
- Covariant: a
Cat[]is anAnimal[] - Contravariant: an
Animal[]is aCat[] - Invariant: an
Animal[]is not aCat[]and aCat[]is not anAnimal[]?
If we wish to avoid type errors, and the array supports both reading and writing elements, then only the third choice is safe. Clearly, not every Animal[] can be treated as if it were a Cat[], since a client reading from the array will expect a Cat, but an Animal[] may contain e.g. a Dog. So the contravariant rule is not safe.
Conversely, a Cat[] cannot be treated as an Animal[]. It should always be possible to put a Dog into an Animal[]. With covariant arrays this cannot be guaranteed to be safe, since the backing store might actually be an array of cats. So the covariant rule is also not safe—the array constructor should be invariant. Note that this is only an issue for mutable arrays; the covariant rule is safe for immutable (read-only) arrays.
This illustrates a general phenomenon. Read-only data types (sources) can be covariant; write-only data types (sinks) can be contravariant. Mutable data types which act as both sources and sinks should be invariant.
Covariant arrays in Java and C#
Early versions of Java and C# did not include generics, also termed parametric polymorphism. In such a setting, making arrays invariant rules out useful polymorphic programs.
For example, consider writing a function to shuffle an array, or a function that tests two arrays for equality using the Object.equals method on the elements. The implementation does not depend on the exact type of element stored in the array, so it should be possible to write a single function that works on all types of arrays. It is easy to implement functions of type
boolean equalArrays(Object[] a1, Object[] a2);
void shuffleArray(Object[] a);
However, if array types were treated as invariant, it would only be possible to call these functions on an array of exactly the type Object[]. One could not, for example, shuffle an array of strings.
Therefore, both Java and C# treat array types covariantly. For instance, in C# string[] is a subtype of object[], and in Java String[] is a subtype of Object[].
As discussed above, covariant arrays lead to problems with writes into the array. Java and C# deal with this by marking each array object with a type when it is created. Each time a value is stored into an array, the execution environment will check that the run-time type of the value is equal to the run-time type of the array. If there is a mismatch, an ArrayStoreException (Java) or ArrayTypeMismatchException (C#) is thrown:
// a is a single-element array of String
String[] a = new String[1];
// b is an array of Object
Object[] b = a;
// Assign an Integer to b. This would be possible if b really were
// an array of Object, but since it really is an array of String,
// we will get a java.lang.ArrayStoreException.
b[0] = 1;
In the above example, one can read from the array (b) safely. It is only trying to write to the array that can lead to trouble.
One drawback to this approach is that it leaves the possibility of a run-time error that a stricter type system could have caught at compile-time. Also, it hurts performance because each write into an array requires an additional run-time check.
With the addition of generics, Java and C# now offer ways to write this kind of polymorphic functions without relying on covariance. The array comparison and shuffling functions can be given the parameterized types
<T> boolean equalArrays(T[] a1, T[] a2);
<T> void shuffleArray(T[] a);
Alternatively, to enforce that a C# method accesses a collection in a read-only way, one can use the interface IEnumerable<object> instead of passing it an array object[].
Function types
Languages with first-class functions have function types like "a function expecting a Cat and returning an Animal" (written Cat -> Animal in OCaml syntax or Func<Cat,Animal> in C# syntax).
Those languages also need to specify when one function type is a subtype of another—that is, when it is safe to use a function of one type in a context that expects a function of a different type. It is safe to substitute a function f for a function g if f accepts a more general type of arguments and returns a more specific type than g. For example, a function of type Cat->Cat can safely be used wherever a Cat->Animal was expected, and likewise a function of type Animal->Animal can be used wherever a Cat->Animal was expected. (One can compare this to the robustness principle of communication: "be liberal in what you accept and conservative in what you produce"). The general rule is
S1 → S2 ≤ T1 → T2 if T1 ≤ S1 and S2 ≤ T2.
In other words, the → type constructor is contravariant in the input type and covariant in the output type. This rule was first stated formally by John C. Reynolds,[2] and further popularized in a paper by Luca Cardelli.[3]
When dealing with functions that take functions as arguments, this rule can be applied several times. For example, by applying the rule twice, we see that (A'→B)→B ≤ (A→B)→B if A'≤A. In other words, the type (A→B)→B is covariant in the A position. For complicated types it can be confusing to mentally trace why a given type specialization is or isn't type-safe, but it is easy to calculate which positions are co- and contravariant: a position is covariant if it is on the left side of an even number of arrows applying to it.
Inheritance in object-oriented languages
When a subclass overrides a method in a superclass, the compiler must check that the overriding method has the right type. While some languages require that the type exactly matches the type in the superclass (invariance), it is also type safe to allow the overriding method to have a "better" type. By the usual subtyping rule for function types, this means that the overriding method should return a more specific type (return type covariance), and accept a more general argument (argument type contravariance). In UML notation, the possibilities are as follows:
- Variance and method overriding: overview
-
Vererbung T.svg
Subtyping of the argument/return type of the method.
-
Inheritance invariant.svg
Invariance. The signature of the overriding method is unchanged.
-
Inheritance covariant return.svg
Covariant return type. The subtyping relation is in the same direction as the relation between ClassA and ClassB.
-
Inheritance contravariant argument.svg
Contravariant argument type. The subtyping relation is in the opposite direction to the relation between ClassA and ClassB.
-
Inheritance covariant argument.svg
Covariant argument type. Not type safe.
For a concrete example, suppose we are writing a class to model an animal shelter. We assume that Cat is a subclass of Animal, and that we have a base class (using Java syntax)
class AnimalShelter {
Animal getAnimalForAdoption() {
...
}
void putAnimal(Animal animal) {
...
}
}
Now the question is: if we subclass AnimalShelter, what types are we allowed to give to getAnimalForAdoption and putAnimal?
Covariant method return type
In a language which allows covariant return types, a derived class can override the getAnimalForAdoption method to return a more specific type:
class CatShelter extends AnimalShelter {
Cat getAnimalForAdoption() {
return new Cat();
}
}
Among mainstream OO languages, Java and C++ support covariant return types, while C# does not. Adding the covariant return type was one of the first modifications of the C++ language approved by the standards committee in 1998.[4] Scala and D also support covariant return types.
Contravariant method argument type
Similarly, it is type safe to allow an overriding method to accept a more general argument than the method in the base class:
class CatShelter extends AnimalShelter {
void putAnimal(Object animal) {
...
}
}
Not many object-oriented languages actually allow this. C++ and Java would interpret this as an unrelated method with an overloaded name.
However, Sather supports both covariance and contravariance. Calling convention for overridden methods are covariant with out arguments and return values, and contravariant with normal arguments (with the mode in).
Covariant method argument type
Uniquely among mainstream languages, Eiffel allows the arguments of an overriding method to have a more specific type than the method in the superclass (argument type covariance). Thus, the Eiffel version of the following code would type check, with putAnimal overriding the method in the base class:
class CatShelter extends AnimalShelter {
void putAnimal(Cat animal) {
...
}
}
This is not type safe. By up-casting a CatShelter to an AnimalShelter, one can try to place a dog in a cat shelter. That does not meet CatShelter argument restrictions. The lack of type safety (known as the "catcall problem" in the Eiffel community) has been a long-standing issue. Over the years, various combinations of global static analysis, local static analysis, and new language features have been proposed to remedy it,[5] [6] and these have been implemented in some Eiffel compilers.
Despite the type safety problem, the Eiffel designers consider covariant argument types crucial for modeling real world requirements.[6] The cat shelter illustrates a common phenomenon: it is a kind of animal shelter but has additional restrictions, and it seems reasonable to use inheritance and restricted argument types to model this. In proposing this use of inheritance, the Eiffel designers reject the Liskov substitution principle, which states that objects of subclasses should always be less restricted than objects of their superclass.
Another example where covariant arguments seem helpful is so-called binary methods, i.e. methods where the argument is expected to be of the same type as the object the method is called on. An example is the compareTo method: a.compareTo(b) checks whether a comes before or after b in some ordering, but the way to compare, say, two rational numbers will be different from the way to compare two strings. Other common examples of binary methods include equality tests, arithmetic operations, and set operations like subset and union.
In older versions of Java, the comparison method was specified as an interface Comparable:
interface Comparable {
int compareTo(Object o);
}
The drawback of this is that the method is specified to take an argument of type Object. A typical implementation would first down-cast this argument (throwing an error if it is not of the expected type):
class RationalNumber implements Comparable {
int numerator;
int denominator;
...
public int compareTo(Object other) {
RationalNumber otherNum = (RationalNumber)other;
return Integer.compare(numerator*otherNum.denominator,
otherNum.numerator*denominator);
}
}
In a language with covariant arguments, the argument to compareTo could be directly given the desired type RationalNumber, hiding the typecast. (Of course, this would still give a runtime error if compareTo was then called on e.g. a String).
Avoiding the need for covariant argument types
Other language features can provide the apparent benefits of covariant arguments while preserving Liskov substitutability.
In a language with generics (a.k.a. parametric polymorphism) and bounded quantification, the previous examples can be written in a type-safe way .[7] Instead of defining AnimalShelter, we define a parameterized class Shelter<T>. (One drawback of this is that the implementer of the base class needs to foresee which types will need to be specialized in the subclasses).
class Shelter<T extends Animal> {
T getAnimalForAdoption() {
...
}
void putAnimal(T animal) {
...
}
}
class CatShelter extends Shelter<Cat> {
Cat getAnimalForAdoption() {
...
}
void putAnimal(Cat animal) {
...
}
}
Similarly, in recent versions of Java the Comparable interface has been parameterized, which allows the downcast to be omitted in a type-safe way:
class RationalNumber implements Comparable<RationalNumber> {
int numerator;
int denominator;
...
public int compareTo(RationalNumber otherNum) {
return Integer.compare(numerator*otherNum.denominator,
otherNum.numerator*denominator);
}
}
Another language feature that can help is multiple dispatch. One reason that binary methods are awkward to write is that in a call like a.compareTo(b), selecting the correct implementation of compareTo really depends on the runtime type of both a and b, but in a conventional OO language only the runtime type of a is taken into account. In a language with Common Lisp Object System (CLOS)-style multiple dispatch, the comparison method could be written as a generic function where both arguments are used for method selection.
Giuseppe Castagna[8] observed that in a typed language with multiple dispatch, a generic function can have some arguments which control dispatch and some "left-over" arguments which do not. Because the method selection rule chooses the most specific applicable method, if a method overrides another method, then the overriding method will have more specific types for the controlling arguments. On the other hand, to ensure type safety the language still must require the left-over arguments to be at least as general. Using the previous terminology, types used for runtime method selection are covariant while types not used for runtime method selection of the method are contravariant. Conventional single-dispatch languages like Java also obey this rule: there only one argument is used for method selection (the receiver object, passed along to a method as the hidden argument this), and indeed the type of this is more specialized inside overriding methods than in the superclass.
Castagna suggests that examples where covariant argument types are superior, particularly binary methods, should be handled using multiple dispatch which is naturally covariant. Unfortunately, most programming languages do not support multiple dispatch.
Summary of variance and inheritance
The following table summarizes the rules for overriding methods in the languages discussed above.
| Argument type | Return type | |
|---|---|---|
| C++ (since 1998), Java (since J2SE 5.0), Scala, D | Invariant | Covariant |
| C# | Invariant | Invariant |
| Sather | Contravariant | Covariant |
| Eiffel | Covariant | Covariant |
Generic types
In programming languages that support generics (a.k.a. parametric polymorphism), the programmer can extend the type system with new constructors. For example, a C# interface like IList<T> makes it possible to construct new types like IList<Animal> or IList<Cat>. The question then arises what the variance of these type constructors should be.
There are two main approaches. In languages with declaration-site variance annotations (e.g., C#), the programmer annotates the definition of a generic type with the intended variance of its type parameters. With use-site variance annotations (e.g., Java), the programmer instead annotates the places where a generic type is instantiated.
Declaration-site variance annotations
The most popular languages with declaration-site variance annotations are C# (using the keywords out and in), and Scala and OCaml (using the keywords + and -). C# only allows variance annotations for interface types, while Scala and OCaml allows them for both interface types and concrete data types.
Interfaces
In C#, each type parameter of a generic interface can be marked covariant (out), contravariant (in), or invariant (no annotation). For example, we can define an interface IEnumerator<T> of read-only iterators, and declare it to be covariant (out) in its type parameter.
interface IEnumerator<out T>
{
T Current { get; }
bool MoveNext();
}
With this declaration, IEnumerator will be treated as covariant in its type argument, e.g. IEnumerator<Cat> is a subtype of IEnumerator<Animal>.
The typechecker enforces that each method declaration in an interface only mentions the type parameters in a way consistent with the in/out annotations. That is, a parameter that was declared covariant must not occur in any contravariant positions (where a position is contravariant if it occurs under an odd number of contravariant type constructors). The precise rule[9][10] is that the return types of all methods in the interface must be valid covariantly and all the method argument types must be valid contravariantly, where valid S-ly is defined as follows:
- Non-generic types (classes, structs, enums, etc.) are valid both co- and contravariantly.
- A type argument
Tis valid covariantly if it was not markedin, and valid contravariantly if it was not markedout - An array type
A[]is valid S-ly ifAis. (This is because C# has covariant arrays). - A generic type
G<A1,A2,...,An>is valid S-ly if for each argumentAi,- Ai is valid S-ly, and the ith parameter to
Gis declared covariant, or - Ai is valid (not S)-ly, and the ith parameter to
Gis declared contravariant, or - Ai is valid both covariantly and contravariantly, and the ith parameter to
Gis declared invariant.
- Ai is valid S-ly, and the ith parameter to
As an example of how these rules apply, consider the IList<T> interface.
interface IList<T>
{
void Insert(int index, T item);
IEnumerator<T> GetEnumerator();
}
The argument type T of Insert must be valid contravariantly, i.e. the type parameter T must not be tagged out. Similarly, the result type IEnumerator<T> of GetEnumerator must be valid covariantly, i.e. (since IEnumerator is a covariant interface) the type T must be valid covariantly, i.e. the type parameter T must not be tagged in. This shows that the interface IList is not allowed to be marked either co- or contravariant.
In the common case of a generic data structure such as IList, these restrictions mean that an out parameter can only be used for methods getting data out of the structure, and an in parameter can only be used for methods putting data into the structure, hence the choice of keywords.
Data
C# allows variance annotations on the parameters of interfaces, but not the parameters of classes. Because fields in C# classes are always mutable, variantly parameterized classes in C# would not be very useful. But languages which emphasize immutable data can make good use of covariant data types. For example, both in Scala and OCaml the immutable list type is covariant: List[Cat] is a subtype of List[Animal].
Scala's rules for checking variance annotations are essentially the same as C#'s. However, there are some idioms that apply to immutable datastructures in particular. They are illustrated by the following (excerpt from the) definition of the List[A] class.
sealed abstract class List[+A] extends AbstractSeq[A] {
def head: A
def tail: List[A]
/** Adds an element at the beginning of this list. */
def ::[B >: A] (x: B): List[B] =
new scala.collection.immutable.::(x, this)
...
}
First, class members that have a variant type must be immutable. Here, head has the type A, which was declared covariant (+), and indeed head was declared as a method (def). Trying to declare it as a mutable field (var) would be rejected as type error.
Second, even if a data structure is immutable, it will often have methods where the parameter type occurs contravariantly. For example, consider the method :: which adds an element to the front of a list. (The implementation works by creating a new object of the similarly-named class ::, the class of nonempty lists). The most obvious type to give it would be
def :: (x: A): List[A]
However, this would be a type error, because the covariant parameter A appears in a contravariant position (as a function argument). But there is a trick to get around this problem. We give :: a more general type, which allows adding an element of any type B as long as B is a supertype of A. Note that this relies on List being covariant, since this has type List[A] and we treat it as having type List[B]. At first glance it may not be obvious that the generalized type is sound, but if the programmer starts out with the simpler type declaration, the type errors will point out the place that needs to be generalized.
Inferring variance
It is possible to design a type system where the compiler automatically infers the best possible variance annotations for all datatype parameters.[11] However, the analysis can get complex for several reasons. First, the analysis is nonlocal since the variance of an interface I depends the variance of all interfaces that I mentions. Second, in order to get unique best solutions the type system must allow bivariant parameters (which are simultaneously co- and contravariant). And finally, the variance of type parameters should arguably be a deliberate choice by the designer of an interface, not something that just happens.
For these reasons[12] most languages do very little variance inference. C# and Scala do not infer any variance annotations at all. OCaml can infer the variance of parameterized concrete datatypes, but the programmer must explicitly specify the variance of abstract types (interfaces).
For example, consider an OCaml datatype T which wraps a function
type ('a, 'b) t = T of ('a -> 'b)
The compiler will automatically infer that T is contravariant in the first parameter, and covariant in the second. The programmer can also provide explicit annotations, which the compiler will check are satisfied. Thus the following declaration is equivalent to the previous one:
type (-'a, +'b) t = T of ('a -> 'b)
Explicit annotations in OCaml become useful when specifying interfaces. For example, the standard library interface Map.S for association tables include an annotation saying that the map type constructor is covariant in the result type.
module type S =
sig
type key
type (+'a) t
val empty: 'a t
val mem: key -> 'a t -> bool
...
end
This ensures that e.g. cat IntMap.t is a subtype of animal IntMap.t.
Use-site variance annotations (wildcards)
One drawback of the declaration-site approach is that many interface types must be made invariant. For example, we saw above that IList needed to be invariant, because it contained both Insert and GetEnumerator. In order to expose more variance, the API designer could provide additional interfaces which provide subsets of the available methods (e.g. an "insert-only list" which only provides Insert). However this quickly becomes unwieldy.
Use-site variance annotations aim to give users of a class more opportunities for subtyping without requiring the designer of the class to define multiple interfaces with different variance. Instead, each time a class or interface is used in a type declaration, the programmer can indicate that only a subset of the methods will be used. In effect, each definition of a class also makes available interfaces for the covariant and contravariant parts of that class. Therefore the designer of the class no longer needs to take variance into account, increasing re-usability.
Java provides use-site variance annotations through wildcards, a restricted form of bounded existential types. A parameterized type can be instantiated by a wildcard ? together with an upper or lower bound, e.g. List<? extends Animal> or List<? super Animal>. (A an unbounded wildcard like List<?> is equivalent to List<? extends Object>). Such a type represents List<X> for some unknown type X which satisfies the bound. For example, if l has type List<? extends Animal>, then the typechecker will accept
Animal a = l.get(3);
because the type X is known to be a subtype of Animal, but
l.add(new Animal())
will be rejected as a type error since an Animal is not necessarily an X. In general, given some interface I<T>, a reference to a I<? extends A> forbids using methods from the interface where T occurs contravariantly in the type of the method. Conversely, if l had type List<? super Animal> one could call l.add but not l.get.
While plain generic types in Java are invariant (e.g. there is no subtyping relationship between List<Cat> and List<Animal>), wildcard types can be made more specific by specifying a tighter bound, for example List<? extends Cat> is a subtype of List<? extends Animal>. This shows that wildcard types are covariant in their upper bounds (and also contravariant in their lower bounds). In total, given a wildcard type like C<? extends T>, there are three ways to form a subtype: by specializing the class C, by specifying a tighter bound T, or by replacing the wildcard ? by a specific type (see figure).
By combining two steps of subtyping, it is therefore possible to e.g. pass an argument of type List<Cat> to a method expecting a List<? extends Animal>. This is exactly the kind of programs that covariant interface types allow. The type List<? extends Animal> acts as an interface type containing only the covariant methods of List<T>, but the implementer of List<T> did not have to define it ahead of time. This is use-site variance.
In the common case of a generic data structure IList, covariant parameters are used for methods getting data out of the structure, and contravariant parameters for methods putting data into the structure. The mnemonic for Producer Extends, Consumer Super (PECS), from the book Effective Java by Joshua Bloch gives an easy way to remember when to use covariance and contravariance.
Wildcards are flexible, but there is a drawback. While use-site variance means that API designers need not consider variance of type parameters to interfaces, they must often instead use more complicated method signatures. A common example involves the Comparable interface. Suppose we want to write a function that finds the biggest element in a collection. The elements need to implement the compareTo method, so a first try might be
<T extends Comparable<T>> T max(Collection<T> coll);
However, this type is not general enough—one can find the max of a Collection<Calendar>, but not a Collection<GregorianCalendar>. The problem is that GregorianCalendar does not implement Comparable<GregorianCalendar>, but instead the (better) interface Comparable<Calendar>. In Java, unlike in C#, Comparable<Calendar> is not considered a subtype of Comparable<GregorianCalendar>. Instead the type of max has to be modified:
<T extends Comparable<? super T>> T max(Collection<T> coll);
The bounded wildcard ? super T conveys the information that max calls only contravariant methods from the Comparable interface. This particular example is frustrating because all the methods in Comparable are contravariant, so that condition is trivially true. A declaration-site system could handle this example with less clutter by annotating only the definition of Comparable.
Comparing declaration-site and use-site annotations
Use-site variance annotations provide additional flexibility, allowing more programs to type-check. However, they have been criticized for the complexity they add to the language, leading to complicated type signatures and error messages.
One way to assess whether the extra flexibility is useful is to see if it is used in existing programs. A survey of a large set of Java libraries[11] found that 39% of wildcard annotations could have been directly replaced by a declaration-site annotations. Thus the remaining 61% is an indication on places where Java benefits from having the use-site system available.
In a declaration-site language, libraries must either expose less variance, or define more interfaces. For example, the Scala Collections library defines three separate interfaces for classes which employ covariance: a covariant base interface containing common methods, an invariant mutable version which adds side-effecting methods, and a covariant immutable version which may specialize the inherited implementations to exploit structural sharing.[13] This design works well with declaration-site annotations, but the large number of interfaces carry a complexity cost for clients of the library. And modifying the library interface may not be an option—in particular, one goal when adding generics to Java was to maintain binary backwards compatibility.
On the other hand, Java wildcards are themselves complex. In a conference presentation[14] Joshua Bloch criticized them as being too hard to understand and use, stating that when adding support for closures "we simply cannot afford another wildcards". Early versions of Scala used use-site variance annotations but programmers found them difficult to use in practice, while declaration-site annotations were found to be very helpful when designing classes.[15] Later versions of Scala added Java-style existential types and wildcards; however, according to Martin Odersky, if there were no need for interoperability with Java then these would probably not have been included.[16]
Ross Tate argues[17] that part of the complexity of Java wildcards is due to the decision to encode use-site variance using a form of existential types. The original proposals[18] [19] used special-purpose syntax for variance annotations, writing List<+Animal> instead of Java's more verbose List<? extends Animal>.
Since wildcards are a form of existential types they can be used for more things than just variance. A type like List<?> ("some type of list") lets objects be passed to methods or stored in fields without exactly specifying their type parameters. This is particularly valuable for classes such as Class where most of the methods do not mention the type parameter.
However, type inference for existential types is a difficult problem. For the compiler implementer, Java wildcards raise issues with type checker termination, type argument inference, and ambiguous programs.[20] For the programmer, it leads to complicated type error messages. Java typechecks wildcard types by replacing the wildcards with fresh type variables (so-called capture conversion). This can make error messages harder to read, because they refer to type variables that the programmer did not directly write. For example, trying to add a Cat to a List<? extends Animal> will give an error like
method List.add(capture#1) is not applicable (actual argument Cat cannot be converted to capture#1 by method invocation conversion) where capture#1 is a fresh type-variable: capture#1 extends Animal from capture of ? extends Animal
Since both declaration-site and use-site annotations can be useful, some type system provide both.[11][17]
Covariant generics in Dart
The Dart programming language does not track variance, and instead treats all parameterized types as covariant. The language specification[21] states
The type system is unsound, due to the covariance of generic types. This is a deliberate choice (and undoubtedly controversial). Experience has shown that sound type rules for generics fly in the face of programmer intuition. It is easy for tools to provide a sound type analysis if they choose, which may be useful for tasks like refactoring.
Origin of the term covariance
These terms come from the notion of covariant and contravariant functors in category theory. Consider the category 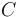 whose objects are types and whose morphisms represent the subtype relationship ≤. (This is an example of how any partially ordered set can be considered as a category). Then for example the function type constructor takes two types p and r and creates a new type p → r; so it takes objects in
whose objects are types and whose morphisms represent the subtype relationship ≤. (This is an example of how any partially ordered set can be considered as a category). Then for example the function type constructor takes two types p and r and creates a new type p → r; so it takes objects in 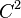 to objects in
to objects in 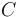 . By the subtyping rule for function types this operation reverses ≤ for the first argument and preserves it for the second, so it is a contravariant functor in the first argument and a covariant functor in the second.
. By the subtyping rule for function types this operation reverses ≤ for the first argument and preserves it for the second, so it is a contravariant functor in the first argument and a covariant functor in the second.
See also
References
- ↑ Func<T, TResult> Delegate - MSDN Documentation
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.(Longer version in Information and Computation, 76(2/3): 138-164, February 1988.)
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ Giuseppe Castagna, Covariance and contravariance: conflict without a cause, ACM Transactions on Programming Languages and Systems (TOPLAS), Volume 17, Issue 3, May 1995, pages 431-447.
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ Section II.9.7 in ECMA International Standard ECMA-335 Common Language Infrastructure (CLI) 6th edition (June 2012); available online
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
External links
- Fabulous Adventures in Coding: An article series about implementation concerns surrounding co/contravariance in C#
- Contra Vs Co Variance (note this article is not updated about C++)
- Closures for the Java 7 Programming Language (v0.5)