Esophageal stricture
| Esophageal stricture | |
|---|---|
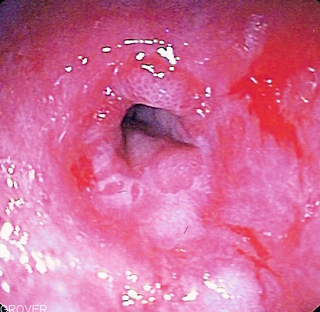
Endoscopic image of a benign peptic stricture
|
|
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Lua error in Module:Wikidata at line 446: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| ICD-10 | K22.2 |
| ICD-9-CM | 530.3 |
| DiseasesDB | 31502 |
| MedlinePlus | 000207 |
| eMedicine | article/175098 |
| Patient UK | Esophageal stricture |
| MeSH | D004940 |
A benign esophageal stricture is a narrowing or tightening of the esophagus that causes swallowing difficulties.
Contents
Causes
It can be caused by or associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease, esophagitis, a dysfunctional lower esophageal sphincter, disordered motility, lye ingestion, or a hiatal hernia. Strictures can form after esophageal surgery and other treatments such as laser therapy or photodynamic therapy. While the area heals, a scar forms, causing the tissue to pull and tighten, leading to difficulty in swallowing.[1]
Diagnosis
It can be diagnosed with an X-ray while the patient swallows barium (called a barium study of the esophagus), by a computerized tomography scan, a biopsy,[2] or by an endoscopy.
Incidence/prevalence
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) affects approximately 40% of adults. Strictures occur in 7 to 23% of patients with GERD who are untreated.[3]
Symptoms
Symptoms of esophageal strictures include heartburn, bitter or acid taste in the mouth, choking, coughing, shortness of breath, frequent burping or hiccups, pain or trouble swallowing, throwing up blood, or weight loss.[4]
Treatment
If it is caused by esophagitis, in turn caused by an underlying infection, it is commonly treated by treating the infection (typically with antibiotics). In order to open the stricture, a surgeon can insert a bougie – a weighted tube used to dilate the constricted areas in the esophagus.[1] It can sometimes be treated with other medications. For example, an H2 antagonist (e.g. ranitidine) or a proton-pump inhibitor (e.g. omeprazole) can treat underlying acid reflux disease.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Ginex, Pamela K., Manjit S. Bains, Jacqueline Hanson, and Bart L. Frazzitta. 100 Questions & Answers About Esophageal Cancer (100 Questions & Answers). New York: Jones and Bartlett, Inc., 2005. Print.
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ Esophageal Stricture at eMedicine
- ↑ PDRhealth – Esophageal Stricture: (http://www.pdrhealth.com/disease/disease-mono.aspx?contentFileName=ND7417G.xml&contentName=Esophageal+Stricture&contentId=506&TypeId=2)