Ferricyanide
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
iron(3+) hexacyanide
|
|
| Systematic IUPAC name
hexacyanidoferrate(III)
|
|
| Other names
ferric hexacyanide; hexacyanidoferrate(3-); hexacyanoferrate(III)
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| Jmol 3D model | Interactive image |
| PubChem | 439210 |
|
|
| Properties | |
| C6N6Fe | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Ferricyanide is the anion [Fe(CN)6]3−. It is also called hexacyanoferrate(III) and in rare, but systematic nomenclature, hexacyanidoferrate(III). The most common salt of this anion is potassium ferricyanide, a red crystalline material that is used as an oxidant in organic chemistry.[1]
Contents
Properties
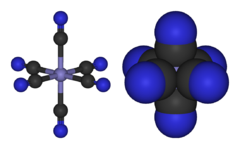
[Fe(CN)6]3− consists of a Fe3+ center bound in octahedral geometry to six cyanide ligands. The complex has Oh symmetry. The iron is low spin and easily reduced to the related ferrocyanide ion [Fe(CN)6]4−, which is a ferrous (Fe2+) derivative. This redox couple is reversible and entails no making or breaking of Fe-C bonds:
- [Fe(CN)6]3− + e− → [Fe(CN)6]4−
This redox couple is a standard in electrochemistry.
Compared to normal cyanides like potassium cyanide, ferricyanides are much less toxic because of the tight hold of the CN− to the Fe3+. They do react with mineral acids, however, to release highly toxic hydrogen cyanide gas.
Uses
Treatment of ferricyanide with ferrous salts affords the brilliant, long-lasting pigment Prussian blue, the traditional color of blueprints.
References
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
See also
- Chemical articles without CAS Registry Number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Pages using collapsible list with both background and text-align in titlestyle
- Chemical articles using a fixed chemical formula
- Anions
- Coordination compounds
- Cyanides