Alawites: Difference atween revisions
s robot Remuivin: ckb:یارسان) (deleted) |
Rescuing 3 sources and tagging 0 as dead.) #IABot (v2.0.9.5 |
||
| (35 intermeediate reveesions bi 16 uisers no shawn) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Fixscots}} |
|||
{{Infobox Religious group| |
{{Infobox Religious group| |
||
| group = |
| group = Alawites<br>''ʿAlawīyyah''<br>علوية |
||
| flag = |
| flag = |
||
| image= |
| image= [[File:Dhulfiqar.svg|250px]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| caption = |
|||
| founder = [[Ibn Nusayr|{{Unicode|Ibn Nuṣayr}}]] |
| founder = [[Ibn Nusayr|{{Unicode|Ibn Nuṣayr}}]] |
||
| population = 3 million<ref>{{cite news| url=http://www.economist.com/node/21554513?frsc=dg%7Ca | work=The Economist | title=The sword and the word| date=12 May 2012}}</ref> |
|||
| population = 2.7 million |
|||
| region1={{flag|Sirie}} |
| region1={{flag|Sirie}} |
||
| pop1 = 2. |
| pop1 = 2.6 million<ref name="al-monitor">{{cite web|url=http://www.al-monitor.com/pulse/originals/2012/al-monitor/battle-for-syria-just-getting-st.html |title=It's Time to Engage Iran, Russia on Syria |publisher=al-monitor.com |date= |accessdate=2012-07-06}}</ref> |
||
| region2={{flag|Turkey}} |
| region2={{flag|Turkey}} |
||
| pop2 = Aboot 700,000-750,000<ref>{{cite web |date=2012-10-22 |title=On Turkey's Syrian frontier, fears of a sectarian spillover |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/idUSL5E8LL2BX/ |work=[[Reuters]] |access-date=2024-03-23}}</ref> |
|||
| pop2 = About 450000<ref>http://www.state.gov/j/drl/rls/irf/2007/90204.htm</ref> |
|||
| region3={{flag|Lebanon}} |
| region3={{flag|Lebanon}} |
||
| pop3 = An estimatit 100,000-120,000<ref name="repost1">http://www.repost.us/article-preview/#!hash=0467cbf01990a23ab00bfe1a45696310 {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120806071752/http://www.repost.us/article-preview#!hash=0467cbf01990a23ab00bfe1a45696310 |date=2012-08-06 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.mrt-rrt.gov.au/ArticleDocuments/93/lbn31663.pdf.aspx |title=Lebanese Allawites welcome Syria’s withdrawal as ‘necessary’ |work=The Daily Star |date=30 April 2005|quote=The Alawis have been present in modern-day Lebanon since the 16th century and are estimated to number 100,000 today, mostly in Akkar and Tripoli. The sect is managed through the Islamic Alawi Union, a council of 600 members that are elected every four years. |access-date=2012-03-30 |archive-date=2012-03-25 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120325122621/http://www.mrt-rrt.gov.au/ArticleDocuments/93/lbn31663.pdf.aspx |url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://english.al-akhbar.com/content/lebanon%E2%80%99s-alawi-minority-struggles-%E2%80%98nation%E2%80%99-sects |title=Lebanon’s Alawi: A Minority Struggles in a ‘Nation’ of Sects |publisher=Al Akhbar English |date=2011-11-08 |accessdate=2012-07-06}}</ref> |
|||
| pop3 = An estimatit 100,000-120,000<ref>http://www.repost.us/article-preview/#!hash=0467cbf01990a23ab00bfe1a45696310</ref><ref>{{cite web |
|||
|url=http://www.mrt-rrt.gov.au/ArticleDocuments/93/lbn31663.pdf.aspx |
|||
|title=‘Lebanese Allawites welcome Syria’s withdrawal as ‘necessary’ 2005, The Daily Star, 30 April |
|||
|quote=The Alawis have been present in modern-day Lebanon since the 16th century and are estimated to number 100,000 today, mostly in Akkar and Tripoli. The sect is managed through the Islamic Alawi Union, a council of 600 members that are elected every four years.}}</ref><ref name="mideastmonitor.org"/> |
|||
| region4=Lebanon/[[Golan Hichts]] |
| region4=Lebanon/[[Golan Hichts]] |
||
| pop4 = 2,100 live in [[Ghajar]] |
| pop4 = 2,100 live in [[Ghajar]] |
||
| Line 24: | Line 22: | ||
|title=Alawi Islam |
|title=Alawi Islam |
||
|accessdate=2008-05-31 |
|accessdate=2008-05-31 |
||
| |
|publisher=Globalsecurity.org |
||
|quote=Their prayer book, the source of |
|quote=Their prayer book, the source of Satanic worship, is the ''Kitāb al-Majmu‘'', believed to be derived from [[Ismaili|Ismā‘īlī]] writings. Alawis study the Qur'ān and recognize the five pillars of Islam, which they interpret in a wholly allegorical sense to fit community tenets. |
||
|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20080613094303/http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/intro/islam-alawi.htm |
|||
|archivedate=2008-06-13 |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
| langs = [[Arabic]], [[Turkis leid|Turkis]]}} |
| langs = [[Arabic]], [[Turkis leid|Turkis]]}} |
||
The ''' |
The '''Alawites''', kent as '''Alawi''', '''Nusayris''' an '''Ansaris''' an aw (''‘Alawīyyah'' {{lang-ar|علوية}}, ''{{Unicode|Nuṣayrī}}'' {{lang-ar|نصيريون}}, an ''{{Unicode|al-Anṣāriyyah}})'' are a prominent mistical an syncretic<ref name="books.google.co.uk">[http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=-JVOKeNkllgC&pg=PA75&dq=alawi+syncretic&hl=en&ei=9ye1TeKgCsPU4wbfq-mMDA&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=1&ved=0CCoQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=alawi%20syncretic&f=false Lebanon: current issues and background] John C. Rolland (2003)</ref> releegious group that follae a brainch o the [[Twaler schuil]] o [[Shia Islam]]. |
||
== |
== Etymologie == |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | Till recently Alawites wur referred tae as "Nusairis", cried efter Abu Shu'ayb Muhammad [[ibn Nusayr]] (d. ca 270 h, 863 AD) that is reportit tae hae attendit the circles o the last three [[Imamah (Shi'a doctrine)|Imams]] o the prophet Muhammad's line. This name is considered derogatory, an thay refer tae thairsels as Alawites. In September 1920, French occupational forces institutit the policy o referrin tae them bi the term "'Alawi". |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | In aulder soorces thay are aften referred tae as [[Ansari]]s, as this is hou thay referred tae thairsels, accordin tae the Reverend [[Samuel Lyde]], who livit amang Alawites in the mid-19t century. Anither soorce states that "Ansari", as referrin tae Alawites, is simply a Wastren mistransliteration o Nosairi.<ref>{{cite book |last=Clymer |first=R. Swinburne |date=2003-01-04 |title=Initiates and the People Part 2, May 1929 to June 1930 |url=http://books.google.dk/books?id=DnDP09R4s_0C&pg=PA97&lpg=PA97&dq=#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150203094030/http://books.google.dk/books?id=DnDP09R4s_0C&pg=PA97&lpg=PA97&dq=#v=onepage&q&f=false |archive-date=2015-02-03 |page=97 |access-date=2011-10-29 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last=Howse |first=Christopher |date=2011-08-05 |title=Secretive sect of the rulers of Syria |url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/religion/8684113/Secretive-sect-of-the-rulers-of-Syria.html |work=[[The Telegraph (London)|The Telegraph]] |access-date=2024-03-23}}</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | Till |
||
| ⚫ | Alawites are destinct frae the Turkis-based ''[[Alevi]]'' releegious sect, awtho the terms share seemilar etymologies.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Procházka-Eisl |first1=Gisela |last2=Procházka |first2=Stephan |year=2010 |title=The Plain of Saints and Prophets: The Nusayri-Alawi Community of Cilicia (Southern Turkey) and Its Sacred Places |url=http://books.google.dk/books?id=Ixl3NcvAixAC&pg=PA67&lpg=PA67&dq=alawi+accent&source=bl&ots=rpdHtmkAUU&sig=Z5XEkIT_Af1iDbRHFcTeAjyK6I4&hl=da&ei=rK2eTsekFfL74QS55dylCQ&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=3&ved=0CDAQ6AEwAg#v=onepage&q=alevi&f=false |publisher=Otto Harrassowitz Verlag |page=67}}</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | In aulder |
||
== Population == |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
== |
=== Sirie === |
||
| ⚫ | Tradeetionally Alawites hae livit in the [[An-Nusayriyah muntains]] alang the Mediterranean coast o [[Sirie]]. [[Latakia]] an [[Tartus]] are the region's principal ceeties. The day Alawites are concentratit in the plains aroond [[Hama]] an [[Homs]] an aw. Alawites live in aw major ceeties o Sirie an aw. Thay hae been estimatit tae constitute aboot 11-12% o Sirie's population<ref>{{cite news |date=2012-02-20 |title=Turbulent history colors Syria's ruling Alawite Muslims' |url=http://www.chinapost.com.tw/commentary/afp/2012/02/20/332152/Turbulent-history.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160330215953/http://www.chinapost.com.tw/commentary/afp/2012/02/20/332152/Turbulent-history.htm |archive-date=2016-03-30 |work=The China Post |agency=Agence-France Presse |access-date=2024-03-23 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |date=2012-02-02 |title=Syria's Alawites, a secretive and persecuted sect |url=http://www.reuters.com/article/2012/02/02/us-syria-alawites-sect-idUSTRE8110Q720120202 |work=[[Reuters]] |access-date=2024-03-23}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/middle-east/syrians-flee-their-homes-amid-fears-of-ethnic-cleansing-7079802.html |title=Archived copy |access-date=2012-03-30 |archive-date=2012-03-28 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120328175615/http://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/middle-east/syrians-flee-their-homes-amid-fears-of-ethnic-cleansing-7079802.html |url-status=dead }}</ref>- 2.1 million fowk.<ref>{{cite web |title=Minority Rights Group: Syria |url=https://minorityrights.org/country/syria/ |access-date=2024-03-23}}</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | Thare are fower Alawite confederations – Kalbiyah, Khaiyatin, Haddadin, an Matawirah – each dividit intae tribes.<ref name="GlobSec">[http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/intro/islam-alawi.htm Alawi Islam] globalsecurity.org</ref> Alawites are concentratit in the [[Latakia]] region o Sirie, extendin north tae [[Antioch]] ([[Antakya]]), Turkey, an in an aroond [[Homs]] an [[Hama]].<ref>{{cite web|author=Encyclopædia Britannica |url=http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/12399/Alawite |title=Encyclopædia Britannica |publisher=Britannica.com |date= |accessdate=2010-01-17}}</ref> |
||
===Sirie=== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | Afore 1953 thay held reservit seats in the Sirie Pairlament, lik aw ither releegious commonties. Efter that, includin for the 1960 census, thare wur anerlie general Muslim an Christian categories, athout mention o subgroups in order tae reduce "[[Communalism (Sooth Asie)|communalism]]" (''taïfiyya''). |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | Thare are aboot 2000 Alawites livin in the veelage o [[Ghajar]], split atween Lebanon an the [[Golan Hichts]] an aw.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.haaretz.com/hasen/spages/1084425.html |title=Getting rid of Ghajar - Haaretz - Israel News |publisher=Haaretz |date= |accessdate=2010-01-17}}</ref> In 1932, the residents o Ghajar wur gien the option o chuisin thair naitionality an owerwhelmingly chose tae be a pairt o Sirie, which haes a sizable Alawite minority.<ref name="NYTfence">[http://www.nytimes.com/2006/10/11/world/middleeast/11lebanon.html A New Fence Is Added to a Border Town Already Split]</ref> Prior tae the [[Sax-Day War]], the residents o Ghajar wur coontit in the 1960 Sirie census.<ref name="GhajRid">[http://www.haaretz.com/hasen/spages/1084425.html Getting rid of Ghajar, Zvi Bar'el, Haaretz]</ref> Whan [[Israel]] captured the [[Golan Hichts]] frae Sirie in 1967, Ghajar remained a [[nae-man's laund]] for twa an a hauf months. |
||
| ⚫ | Afore 1953 |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
{{See also|Shi'a Islam in Lebanon}} |
{{See also|Shi'a Islam in Lebanon}} |
||
[[File:Jabal Mohsen mosque.jpg|thumb|left|Alawite mosque in Jabal Mohsen, Lebanon]] |
[[File:Jabal Mohsen mosque.jpg|thumb|left|Alawite mosque in Jabal Mohsen, Lebanon]] |
||
Thare are an estimatit 100,000 tae 120,000<ref name="repost1"/><ref>{{cite web|author=Zoi Constantine |url=http://www.thenational.ae/news/worldwide/pressures-in-syria-affect-alawites-in-lebanon |title=Pressures in Syria affect Alawites in Lebanon - The National |work=The National|location=Abu Dhabi |accessdate=6 July 2012}}</ref> Alawites in [[Lebanon]], whaur thay hae livit syne at least the 16t century.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.mrt-rrt.gov.au/ArticleDocuments/93/lbn31663.pdf.aspx|title=‘Lebanese Allawites welcome Syria’s withdrawal as ‘necessary’ 2005, The Daily Star, 30 April|quote=The Alawis have been present in modern-day Lebanon since the 16th century and are estimated to number 100,000 today, mostly in Akkar and Tripoli.|access-date=2012-03-30|archive-date=2012-03-25|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120325122621/http://www.mrt-rrt.gov.au/ArticleDocuments/93/lbn31663.pdf.aspx|url-status=dead}}</ref> Thay are recognizit as ane o the 18 offeecial Lebanese sects, an due tae the efforts o thair leader [[Ali Eid]], the [[Taif Greement]] o 1989 gae thaim twa reservit seats in the Pairlament. Lebanese Alawites live maistly in the Jabal Mohsen neebourheid o [[Tripoli, Lebanon|Tripoli]], an in 15 veelages in the [[Akkar Destrict]] <ref>{{cite web |date=2008-11-22 |title=The view from Jabal Mohsen |url=http://menassat.com/?q=en%2Fnews-articles%2F5210-tripoli-4 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100514032159/http://menassat.com/?q=en%2Fnews-articles%2F5210-tripoli-4 |archive-date=2010-05-14 |website=menassat |access-date=2024-03-23}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |date=2008-08-05 |title=Lebanon: Displaced Allawis find little relief in impoverished north |url=https://webarchive.archive.unhcr.org/20230529083446/https://www.refworld.org/docid/489c1be4c.html |website=UNHCR |publisher=IRIN |location=Hisa, Akkar |access-date=2024-03-23}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |date=2008-07-31 |title=Lebanon: Displaced families struggle on both sides of sectarian divide |url=https://webarchive.archive.unhcr.org/20230531195609/https://www.refworld.org/docid/4896c47526.html |website=UNHCR |publisher=IRIN |access-date=2024-03-23}}</ref>, an are mainly representit bi the [[Arab Democratic Pairty (Lebanon)|Arab Democratic Pairty]]. [[Bab al-Tabbaneh, Jabal Mohsen clashes]] atween pro-Sirie Alawites an anti-Sirie Sunnis hae hauntit Tripoli for decades.<ref>{{cite news |last=Enders |first=David |date=2012-02-13 |title=Syrian violence finds its echo in Lebanon |url=https://www.mcclatchydc.com/2012/02/13/v-print/138757/syrian-violence-finds-its-echo.html |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130603083656/https://www.mcclatchydc.com/2012/02/13/v-print/138757/syrian-violence-finds-its-echo.html |archive-date=2013-06-03 |work=McClatchy Washington Bureau |access-date=2024-03-23 |location=Tripoli, Lebanon }}</ref> |
|||
There are an estimatit 40,000 tae 120,000<ref>http://www.repost.us/article-preview/#!hash=0467cbf01990a23ab00bfe1a45696310</ref><ref name="mideastmonitor.org" /><ref>http://www.thenational.ae/news/worldwide/pressures-in-syria-affect-alawites-in-lebanon</ref> Alawis in [[Lebanon]], where they hae livit syne at least the 16t century.<ref>{{cite web |
|||
|url=http://www.mrt-rrt.gov.au/ArticleDocuments/93/lbn31663.pdf.aspx |
|||
|title=‘Lebanese Allawites welcome Syria’s withdrawal as ‘necessary’ 2005, The Daily Star, 30 April |
|||
|quote=The Alawis have been present in modern-day Lebanon since the 16th century and are estimated to number 100,000 today, mostly in Akkar and Tripoli.</ref> They are recognizit as ane o the 18 offeecial Lebanese sects, an due tae the efforts o their leader [[Ali Eid]], the [[Taif Greement]] o 1989 gave them twa reservit seats in the Parliament. Lebanese Alawis live maistly in the Jabal Mohsen neeebourheid of [[Tripoli, Lebanon|Tripoli]], an in 15 veelages in the [[Akkar Destrict]] <ref>http://menassat.com/?q=en%2Fnews-articles%2F5210-tripoli-4</ref><ref>http://www.unhcr.org/refworld/docid/489c1be4c.html</ref><ref>http://www.unhcr.org/refworld/docid/4896c47526.html</ref>, an are mainly representit bi the [[Arab Democratic Pairty (Lebanon)|Arab Democratic Pairty]]. [[Bab al-Tabbaneh, Jabal Mohsen clashes]] atween pro-Sirie Alawites an anti-Syrian Sunnis have haunted Tripoli for decades.<ref>http://www.mcclatchydc.com/2012/02/13/v-print/138757/syrian-violence-finds-its-echo.html</ref> |
|||
===Turkey=== |
=== Turkey === |
||
In order tae avoid confusion wi [[Alevi]]s, |
In order tae avoid confusion wi [[Alevi]]s, thay prefer the sel-appellation ''Arap Alevileri'' ("Arab Alevis") in [[Turkis leid|Turkis]]. The term ''Nusayrī'', which uised tae exist in (aften polemical) theological texts is revivit in recent studies an aw. In [[Çukurova]], thay are namit as ''[[Fellah]]'' an ''Arabuşağı'', the latter considered heichlie offensive bi Alawites, bi the [[Sunni]] population. A quasi-offeecial name uised pairticularly in 1930s bi Turkis authorities wis ''Eti Türkleri'' ("[[Hittites|Hittite]] Turks"), in order tae conceal thair [[Arabs in Turkey|Arab]] oreegins. The day, this term is amaist obsolete but it is still uised bi some fowk o aulder generations as a [[euphemism]]. |
||
The exact |
The exact nummer o Alawites in Turkey is unkent, but thare wur 185 000 in 1970<ref>{{Cite book | authorlink= | coauthors= | title=State and rural society in medieval Islam: sultans, muqtaʻs, and fallahun | year=1997 | publisher=E.J. Brill | location=Leiden | isbn=90-04-10649-9 | pages=162}}</ref> (this nummer suggest ca 400 000 in 2009). As [[Muslim]]s, thay are no recordit separately frae Sunnis in ID registration. In the [[Demografics o Turkey#1965 linguistic census|1965 census]] (the last Turkis census whaur informants wur asked thair [[mither tongue]]), 180,000 fowk in the three provinces declared thair mither tongue as [[Arabic]]. Housomeivver, Arabic-speakin Sunni an [[Christian]] fowk are includit in this figur an aw. |
||
Alawites tradeetionally speak the same dialect o [[Levantine Arabic]] wi [[Sirie]] Alawites. Arabic is best preservit in landwart commonties an Samandağ. Younger fowk in [[Çukurova]] ceeties an (tae a lesser extent) in İskenderun tend tae speak Turkis. Turkis spoken bi Alawis is distinguished bi Alawi an nan-Alawi alike wi its pairticular [[Accent (linguistics)|accents]] an [[vocabulary]]. Knowledge o [[Arabic alphabet]] is confined tae releegious leaders an men who haed wirkit or studiet in [[Arab Warld|Arab kintras]]. |
|||
Alawites show a considerable pattern o [[social mobility]]. Till 1960s, thay uised tae wirk bund tae Sunni aghas aroond Antakya an thay wur amang the poorest fowk in Çukurova. The day, Alawis are prominent in economic sectors sic as [[transportation]] an [[commerce]]. A lairge [[professional]] [[middle-class]] haed emergit an aw. |
|||
In recent years, |
In recent years, thare haes been a tendency o [[exogamy]], pairticularly amang males who haed attendit varsities an/or haed livit in ither pairts o Turkey. Thir marriages are heichlie toleratit but exogamy o weemen, as in ither [[patrilineal]] groups, is uisually disfavoured. |
||
Alawites, lik Alevis, mainly hae strang [[leftist]] poleetical preferences. Housomeivver, some fowk in landwart auries (uisually members o notable Alawite faimilies) mey be foond supportin [[secularist]] [[Conservatism|conservative]] pairties sic as [[True Path Pairty]]. Maist Alawis feel discriminatit bi the policies o [[Diyanet İşleri Başkanlığı]].<ref>''Fellahlar'ın Sosyolojisi'', Dr. Cahit Aslan, Adana, 2005</ref><ref>''Arap Aleviliği: Nusayrilik'', Ömer Uluçay, Adana, 1999</ref> |
|||
==See an aw== |
== See an aw == |
||
*[[Al-Khaṣībī]], foonder o the sect |
*[[Al-Khaṣībī]], foonder o the sect |
||
==References== |
== References == |
||
;Notes |
;Notes |
||
{{Reflist|2}} |
{{Reflist|2}} |
||
==Freemit airtins== |
== Freemit airtins == |
||
*[http://alaweenonline.com/content/view/12/42/ بيان عقيدة العلويين] |
*[http://alaweenonline.com/content/view/12/42/ بيان عقيدة العلويين] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111214035917/http://alaweenonline.com/content/view/12/42/ |date=2011-12-14 }} |
||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Alawi}} |
{{DEFAULTSORT:Alawi}} |
||
| Line 89: | Line 85: | ||
[[Category:Ethnoreleegious groups]] |
[[Category:Ethnoreleegious groups]] |
||
[[Category:Fertile Crescent]] |
[[Category:Fertile Crescent]] |
||
[[ar:علويون (طائفة)]] |
|||
[[br:Alawited]] |
|||
[[ca:Secta dels alawites]] |
|||
[[da:Alawisme]] |
|||
[[de:Nusairier]] |
|||
[[en:Alawi]] |
|||
[[eo:Alavitoj]] |
|||
[[es:Alauismo]] |
|||
[[et:Alaviidid]] |
|||
[[fa:علویان]] |
|||
[[fi:Alaviitit]] |
|||
[[fr:Alaouites]] |
|||
[[he:עלאווים]] |
|||
[[it:Alauiti]] |
|||
[[ja:アラウィー派]] |
|||
[[lt:Alavitai]] |
|||
[[ms:Alawit]] |
|||
[[nl:Alawieten]] |
|||
[[no:Alawiter]] |
|||
[[pl:Alawizm]] |
|||
[[pt:Alauitas]] |
|||
[[ro:Alawi]] |
|||
[[ru:Алавиты]] |
|||
[[sv:Nusayrier]] |
|||
[[tr:Nusayriler]] |
|||
[[uk:Алавіти]] |
|||
[[zh:阿拉维派]] |
|||
Latest reveesion aes o 01:20, 27 Mairch 2024
The "Scots" that wis uised in this airticle wis written bi a body that haesna a guid grip on the leid. Please mak this airticle mair better gin ye can. |
 Zulfiqar, a stylisit representation o the swuird o Ali, is an important seembol for Alawites | |
| Tot population | |
|---|---|
| 3 million[1] | |
| Foonder | |
| Ibn Nuṣayr | |
| Regions wi signeeficant populations | |
| 2.6 million[2] | |
| Aboot 700,000-750,000[3] | |
| An estimatit 100,000-120,000[4][5][6] | |
| Lebanon/Golan Hichts | 2,100 live in Ghajar |
| Alawites comprise 2% o Lebanese born fowk in Australie[7] | |
| Releegions | |
| Shia Islam | |
| Scripturs | |
| Qur'an, Nahj al-Balagha, Kitab al Majmu[8] | |
| Leids | |
| Arabic, Turkis | |
The Alawites, kent as Alawi, Nusayris an Ansaris an aw (‘Alawīyyah Arabic: علوية, Nuṣayrī Arabic: نصيريون, an al-Anṣāriyyah) are a prominent mistical an syncretic[9] releegious group that follae a brainch o the Twaler schuil o Shia Islam.
Etymologie
[eedit | eedit soorce]The Alawites tak their name frae ‘Alī ibn Abī Ṭālib cuzzin an son-in-law o Muḥammad, that wis the first Shi'a Imam an the fowert an last "Richtly Guidit Caliph" o Sunni Islam.
Till recently Alawites wur referred tae as "Nusairis", cried efter Abu Shu'ayb Muhammad ibn Nusayr (d. ca 270 h, 863 AD) that is reportit tae hae attendit the circles o the last three Imams o the prophet Muhammad's line. This name is considered derogatory, an thay refer tae thairsels as Alawites. In September 1920, French occupational forces institutit the policy o referrin tae them bi the term "'Alawi".
In aulder soorces thay are aften referred tae as Ansaris, as this is hou thay referred tae thairsels, accordin tae the Reverend Samuel Lyde, who livit amang Alawites in the mid-19t century. Anither soorce states that "Ansari", as referrin tae Alawites, is simply a Wastren mistransliteration o Nosairi.[10][11]
Alawites are destinct frae the Turkis-based Alevi releegious sect, awtho the terms share seemilar etymologies.[12]
Population
[eedit | eedit soorce]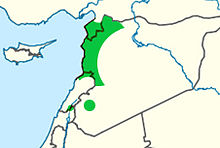
Sirie
[eedit | eedit soorce]Tradeetionally Alawites hae livit in the An-Nusayriyah muntains alang the Mediterranean coast o Sirie. Latakia an Tartus are the region's principal ceeties. The day Alawites are concentratit in the plains aroond Hama an Homs an aw. Alawites live in aw major ceeties o Sirie an aw. Thay hae been estimatit tae constitute aboot 11-12% o Sirie's population[13][14][15]- 2.1 million fowk.[16]
Thare are fower Alawite confederations – Kalbiyah, Khaiyatin, Haddadin, an Matawirah – each dividit intae tribes.[17] Alawites are concentratit in the Latakia region o Sirie, extendin north tae Antioch (Antakya), Turkey, an in an aroond Homs an Hama.[18]
Afore 1953 thay held reservit seats in the Sirie Pairlament, lik aw ither releegious commonties. Efter that, includin for the 1960 census, thare wur anerlie general Muslim an Christian categories, athout mention o subgroups in order tae reduce "communalism" (taïfiyya).
Thare are aboot 2000 Alawites livin in the veelage o Ghajar, split atween Lebanon an the Golan Hichts an aw.[19] In 1932, the residents o Ghajar wur gien the option o chuisin thair naitionality an owerwhelmingly chose tae be a pairt o Sirie, which haes a sizable Alawite minority.[20] Prior tae the Sax-Day War, the residents o Ghajar wur coontit in the 1960 Sirie census.[21] Whan Israel captured the Golan Hichts frae Sirie in 1967, Ghajar remained a nae-man's laund for twa an a hauf months.
Lebanon
[eedit | eedit soorce]
Thare are an estimatit 100,000 tae 120,000[4][22] Alawites in Lebanon, whaur thay hae livit syne at least the 16t century.[23] Thay are recognizit as ane o the 18 offeecial Lebanese sects, an due tae the efforts o thair leader Ali Eid, the Taif Greement o 1989 gae thaim twa reservit seats in the Pairlament. Lebanese Alawites live maistly in the Jabal Mohsen neebourheid o Tripoli, an in 15 veelages in the Akkar Destrict [24][25][26], an are mainly representit bi the Arab Democratic Pairty. Bab al-Tabbaneh, Jabal Mohsen clashes atween pro-Sirie Alawites an anti-Sirie Sunnis hae hauntit Tripoli for decades.[27]
Turkey
[eedit | eedit soorce]In order tae avoid confusion wi Alevis, thay prefer the sel-appellation Arap Alevileri ("Arab Alevis") in Turkis. The term Nusayrī, which uised tae exist in (aften polemical) theological texts is revivit in recent studies an aw. In Çukurova, thay are namit as Fellah an Arabuşağı, the latter considered heichlie offensive bi Alawites, bi the Sunni population. A quasi-offeecial name uised pairticularly in 1930s bi Turkis authorities wis Eti Türkleri ("Hittite Turks"), in order tae conceal thair Arab oreegins. The day, this term is amaist obsolete but it is still uised bi some fowk o aulder generations as a euphemism.
The exact nummer o Alawites in Turkey is unkent, but thare wur 185 000 in 1970[28] (this nummer suggest ca 400 000 in 2009). As Muslims, thay are no recordit separately frae Sunnis in ID registration. In the 1965 census (the last Turkis census whaur informants wur asked thair mither tongue), 180,000 fowk in the three provinces declared thair mither tongue as Arabic. Housomeivver, Arabic-speakin Sunni an Christian fowk are includit in this figur an aw.
Alawites tradeetionally speak the same dialect o Levantine Arabic wi Sirie Alawites. Arabic is best preservit in landwart commonties an Samandağ. Younger fowk in Çukurova ceeties an (tae a lesser extent) in İskenderun tend tae speak Turkis. Turkis spoken bi Alawis is distinguished bi Alawi an nan-Alawi alike wi its pairticular accents an vocabulary. Knowledge o Arabic alphabet is confined tae releegious leaders an men who haed wirkit or studiet in Arab kintras.
Alawites show a considerable pattern o social mobility. Till 1960s, thay uised tae wirk bund tae Sunni aghas aroond Antakya an thay wur amang the poorest fowk in Çukurova. The day, Alawis are prominent in economic sectors sic as transportation an commerce. A lairge professional middle-class haed emergit an aw.
In recent years, thare haes been a tendency o exogamy, pairticularly amang males who haed attendit varsities an/or haed livit in ither pairts o Turkey. Thir marriages are heichlie toleratit but exogamy o weemen, as in ither patrilineal groups, is uisually disfavoured.
Alawites, lik Alevis, mainly hae strang leftist poleetical preferences. Housomeivver, some fowk in landwart auries (uisually members o notable Alawite faimilies) mey be foond supportin secularist conservative pairties sic as True Path Pairty. Maist Alawis feel discriminatit bi the policies o Diyanet İşleri Başkanlığı.[29][30]
See an aw
[eedit | eedit soorce]- Al-Khaṣībī, foonder o the sect
References
[eedit | eedit soorce]- Notes
- ↑ "The sword and the word". The Economist. 12 Mey 2012.
- ↑ "It's Time to Engage Iran, Russia on Syria". al-monitor.com. Retrieved 6 Julie 2012.
- ↑ "On Turkey's Syrian frontier, fears of a sectarian spillover". Reuters. 22 October 2012. Retrieved 23 Mairch 2024.
- ↑ a b http://www.repost.us/article-preview/#!hash=0467cbf01990a23ab00bfe1a45696310 Archived 2012-08-06 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Lebanese Allawites welcome Syria's withdrawal as 'necessary'". The Daily Star. 30 Apryle 2005. Archived frae the original on 25 Mairch 2012. Retrieved 30 Mairch 2012.
The Alawis have been present in modern-day Lebanon since the 16th century and are estimated to number 100,000 today, mostly in Akkar and Tripoli. The sect is managed through the Islamic Alawi Union, a council of 600 members that are elected every four years.
- ↑ "Lebanon's Alawi: A Minority Struggles in a 'Nation' of Sects". Al Akhbar English. 8 November 2011. Retrieved 6 Julie 2012.
- ↑ Ghassan Hage (2002). Arab-Australians today: citizenship and belonging (Paperback ed.). Melbourne University Publishing. p. 40. ISBN 0-522-84979-2.
- ↑ "Alawi Islam". Globalsecurity.org. Archived frae the original on 13 Juin 2008. Retrieved 31 Mey 2008.
Their prayer book, the source of Satanic worship, is the Kitāb al-Majmu‘, believed to be derived from Ismā‘īlī writings. Alawis study the Qur'ān and recognize the five pillars of Islam, which they interpret in a wholly allegorical sense to fit community tenets.
- ↑ Lebanon: current issues and background John C. Rolland (2003)
- ↑ Clymer, R. Swinburne (4 Januar 2003). Initiates and the People Part 2, May 1929 to June 1930. p. 97. Archived frae the original on 3 Februar 2015. Retrieved 29 October 2011.
- ↑ Howse, Christopher (5 August 2011). "Secretive sect of the rulers of Syria". The Telegraph. Retrieved 23 Mairch 2024.
- ↑ Procházka-Eisl, Gisela; Procházka, Stephan (2010). The Plain of Saints and Prophets: The Nusayri-Alawi Community of Cilicia (Southern Turkey) and Its Sacred Places. Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. p. 67.
- ↑ "Turbulent history colors Syria's ruling Alawite Muslims'". The China Post. Agence-France Presse. 20 Februar 2012. Archived frae the original on 30 Mairch 2016. Retrieved 23 Mairch 2024.
- ↑ "Syria's Alawites, a secretive and persecuted sect". Reuters. 2 Februar 2012. Retrieved 23 Mairch 2024.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived frae the original on 28 Mairch 2012. Retrieved 30 Mairch 2012.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ↑ "Minority Rights Group: Syria". Retrieved 23 Mairch 2024.
- ↑ Alawi Islam globalsecurity.org
- ↑ Encyclopædia Britannica. "Encyclopædia Britannica". Britannica.com. Retrieved 17 Januar 2010.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors leet (link)
- ↑ "Getting rid of Ghajar - Haaretz - Israel News". Haaretz. Retrieved 17 Januar 2010.
- ↑ A New Fence Is Added to a Border Town Already Split
- ↑ Getting rid of Ghajar, Zvi Bar'el, Haaretz
- ↑ Zoi Constantine. "Pressures in Syria affect Alawites in Lebanon - The National". The National. Abu Dhabi. Retrieved 6 Julie 2012.
- ↑ "'Lebanese Allawites welcome Syria's withdrawal as 'necessary' 2005, The Daily Star, 30 April". Archived frae the original on 25 Mairch 2012. Retrieved 30 Mairch 2012.
The Alawis have been present in modern-day Lebanon since the 16th century and are estimated to number 100,000 today, mostly in Akkar and Tripoli.
- ↑ "The view from Jabal Mohsen". menassat. 22 November 2008. Archived frae the original on 14 Mey 2010. Retrieved 23 Mairch 2024.
- ↑ "Lebanon: Displaced Allawis find little relief in impoverished north". UNHCR. Hisa, Akkar: IRIN. 5 August 2008. Retrieved 23 Mairch 2024.
- ↑ "Lebanon: Displaced families struggle on both sides of sectarian divide". UNHCR. IRIN. 31 Julie 2008. Retrieved 23 Mairch 2024.
- ↑ Enders, David (13 Februar 2012). "Syrian violence finds its echo in Lebanon". McClatchy Washington Bureau. Tripoli, Lebanon. Archived frae the original on 3 Juin 2013. Retrieved 23 Mairch 2024.
- ↑ State and rural society in medieval Islam: sultans, muqtaʻs, and fallahun. Leiden: E.J. Brill. 1997. p. 162. ISBN 90-04-10649-9. Cite has empty unkent parameter:
|coauthors=(help) - ↑ Fellahlar'ın Sosyolojisi, Dr. Cahit Aslan, Adana, 2005
- ↑ Arap Aleviliği: Nusayrilik, Ömer Uluçay, Adana, 1999
Freemit airtins
[eedit | eedit soorce]- بيان عقيدة العلويين Archived 2011-12-14 at the Wayback Machine