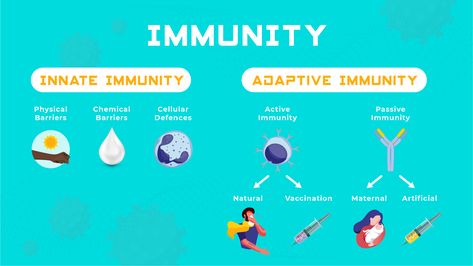
Immunity: Two Intrinsic Defense Systems Innate (nonspecific) system responds quickly and consists of: First line of defense – intact skin and mucosae prevent entry of microorganisms Second line of defense – antimicrobial proteins, phagocytes, and other cells Inhibit spread of invaders throughout the body Inflammation is its hallmark and most important mechanism Chapter 21, Immune System
1