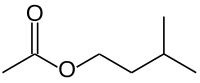
Isoamyl acetate
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-methylbut-1-yl ethanoate
|
|
| Other names
isopentyl acetate
banana oil isopentyl ethanoate pear essence 3-methylbutyl acetate 3-methylbutyl ethanoate |
|
| Identifiers | |
| 123-92-2 |
|
| ChEBI | CHEBI:31725 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL42013 |
| ChemSpider | 29016 |
| Jmol 3D model | Interactive image |
| KEGG | C12296 |
| UNII | Z135787824 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C7H14O2 | |
| Molar mass | 130.19 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Odor | banana-like[1] |
| Density | 0.876 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −78 °C (−108 °F; 195 K) |
| Boiling point | 142 °C (288 °F; 415 K) |
| 0.3% (20 °C)[1] | |
| Vapor pressure | 4 mmHg (20 °C)[1] |
| Vapor pressure | {{{value}}} |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Isoamyl acetate, also known as isopentyl acetate, is an organic compound that is the ester formed from isoamyl alcohol and acetic acid. It is a colorless liquid that is only slightly soluble in water, but very soluble in most organic solvents. Isoamyl acetate has a strong odor which is also described as similar to both banana and pear.[2] Banana oil is a term that is applied either to pure isoamyl acetate or to flavorings that are mixtures of isoamyl acetate, amyl acetate, and other flavors.[3]
Production
Isoamyl acetate is prepared by the acid catalyzed reaction (Fischer esterification) between isoamyl alcohol and glacial acetic acid as shown in the reaction equation below. Typically, sulfuric acid is used as the catalyst. Alternately, an acidic ion exchange resin can be used as the catalyst.
Applications
Isoamyl acetate is used to confer banana flavor in foods. Pear oil commonly refers to a solution of isoamyl acetate in ethanol that is used as an artificial flavor.
It is also used as a solvent for some varnishes and nitrocellulose lacquers, as well as being a honey bee pheromone and can be used to attract large groups of honeybees to a small area. As a solvent and carrier for materials such as nitrocellulose, it was extensively used in the aircraft industry for stiffening and wind-proofing fabric flying surfaces, where it and its derivatives were generally known as 'aircraft dope'. Now that most aircraft are all-metal, such use is now limited to model aircraft, where it is still popularly used for strengthening tissue coverings and balsa wood.
Because of its intense, pleasant odor and its low toxicity, isoamyl acetate is used to test the effectiveness of respirators or gas masks.
Occurrence in nature
Banana oil is made naturally by the banana plant;[4] it is also produced synthetically.[5]
Isoamyl acetate is released by a honey bee's sting apparatus where it serves as a pheromone beacon to attract other bees and provoke them to sting.[6]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedPGCH - ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ Karl-Georg Fahlbusch, Franz-Josef Hammerschmidt, Johannes Panten, Wilhelm Pickenhagen, Dietmar Schatkowski, Kurt Bauer, Dorothea Garbe, Horst Surburg "Flavors and Fragrances" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2002. doi:10.1002/14356007.a11_141.
- ↑ McGee, Harold. On Food and Cooking. 2003, Scribner, New York.
- ↑ Isoamyl Acetate, Occupational Safety and Health Administration
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
