Metaxalone
 |
|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
|
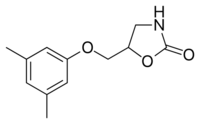
5-[(3,5-dimethylphenoxy)methyl]-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one
|
|
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Skelaxin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682010 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Legal status |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Unknown |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Biological half-life | 9.2 (± 4.8) hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 1665-48-1 |
| ATC code | none |
| PubChem | CID: 15459 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 7609 |
| DrugBank | DB00660 |
| ChemSpider | 14709 |
| UNII | 1NMA9J598Y |
| KEGG | D00773 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1079604 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C12H15NO3 |
| Molecular mass | 221.252 g/mol |
|
|
|
|
| (verify) | |
- Not to be confused with Metolazone, a diuretic.
Metaxalone (marketed by King Pharmaceuticals under the brand name Skelaxin) is a muscle relaxant used to relax muscles and relieve pain caused by strains, sprains, and other musculoskeletal conditions. Its exact mechanism of action is not known, but it may be due to general central nervous system depression. It is considered to be a moderately strong muscle relaxant, with relatively low incidence of side effects. Skelaxin is available in an 800 mg scored tablet. Possible side effects include nausea, vomiting, drowsiness and CNS side effects, such as dizziness, headache, and irritability.
Metaxalone exhibits increased bioavailability when taken with food.[1] Specifically, in one study, compared to fasted conditions, the presence of food at the time of drug administration increased Cmax by 77.5%, AUC0-t by 23.5%, and AUC0-∞ by 15.4%.[2] Thus, based on the information in the labeling, patients receiving metaxalone therapy are directed to take metaxalone with food, and are informed that taking metaxalone with food results in an increase in the oral bioavailability of metaxalone compared to taking metaxalone without food.[3][4][5]
The metabolism of metaxalone involves the liver cytochrome P450 system. Based on the information in the labeling, patients receiving metaxalone therapy and physicians prescribing metaxalone are directed to take precaution when coadministering it with other medications involving the P450 system.[6][7]
Because of potential for side effects, this drug is on the list for high risk medications in the elderly.
Assay
A literature survey reveals very few methods are reported for the determination of metaxalone to date. Nirogi et al.[2] reported a liquid chromatographic method coupled to tandem mass spectrometry for the quantification of metaxalone in human plasma. A stability-indicating HPLC method was introduced by P.K. Sahu et al.[8] Metaxalone has been used as an internal standard for few analytical methods[9][10]
References
- ↑ Skelaxin Package Insert
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
- ↑ id.
- ↑ United States Patent No. 6,407,128
- ↑ United States Patent No. 6,683,102
- ↑ United States Patent No. 7,122,566, by Jie Du, et al
- ↑ United States Patent No. 7,378,434, by Jie Du, et al
- ↑ Prafulla Kumar Sahu, M. Mathrusri Annapurna and Dillip Kumar Sahoo, Development and Validation of Stability Indicating RP-HPLC Method for the Determination of Metaxalone in Bulk and its Pharmaceutical Formulations; E-Journal of Chemistry, 2011, 8(S1), S439-S447.[1]
- ↑ Mistri H N, Jangid A G, Pudage A, Gomes N, Sanyal M and Shrivastav P, J Chromatogr B, 2007, 853(1), 320-332.
- ↑ Mistri H N, Jangid A G, Pudage A and Shrivastav P, J Chromatogr B, 2008, 864(1-2), 137-148.
External links
- Skelaxin (manufacturer's website)