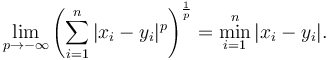Minkowski distance
The Minkowski distance is a metric in a normed vector space which can be considered as a generalization of both the Euclidean distance and the Manhattan distance.
Definition
The Minkowski distance of order p between two points
- Failed to parse (Missing <code>texvc</code> executable. Please see math/README to configure.): X=(x_1,x_2,\ldots,x_n)\text{ and }Y=(y_1,y_2,\ldots,y_n) \in \mathbb{R}^n
is defined as:
For 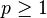 , the Minkowski distance is a metric as a result of the Minkowski inequality. When
, the Minkowski distance is a metric as a result of the Minkowski inequality. When 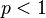 , the distance between (0,0) and (1,1) is
, the distance between (0,0) and (1,1) is  , but the point (0,1) is at a distance 1 from both of these points. Since this violates the triangle inequality, for
, but the point (0,1) is at a distance 1 from both of these points. Since this violates the triangle inequality, for 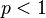 it is not a metric.
it is not a metric.
Minkowski distance is typically used with p being 1 or 2. The latter is the Euclidean distance, while the former is sometimes known as the Manhattan distance. In the limiting case of p reaching infinity, we obtain the Chebyshev distance:
Similarly, for p reaching negative infinity, we have:
The Minkowski distance can also be viewed as a multiple of the power mean of the component-wise differences between P and Q.
The following figure shows unit circles with various values of p: