
- DSA - Home
- DSA - Overview
- DSA - Environment Setup
- DSA - Algorithms Basics
- DSA - Asymptotic Analysis
- Data Structures
- DSA - Data Structure Basics
- DSA - Data Structures and Types
- DSA - Array Data Structure
- DSA - Skip List Data Structure
- Linked Lists
- DSA - Linked List Data Structure
- DSA - Doubly Linked List Data Structure
- DSA - Circular Linked List Data Structure
- Stack & Queue
- DSA - Stack Data Structure
- DSA - Expression Parsing
- DSA - Queue Data Structure
- DSA - Circular Queue Data Structure
- DSA - Priority Queue Data Structure
- DSA - Deque Data Structure
- Searching Algorithms
- DSA - Searching Algorithms
- DSA - Linear Search Algorithm
- DSA - Binary Search Algorithm
- DSA - Interpolation Search
- DSA - Jump Search Algorithm
- DSA - Exponential Search
- DSA - Fibonacci Search
- DSA - Sublist Search
- DSA - Hash Table
- Sorting Algorithms
- DSA - Sorting Algorithms
- DSA - Bubble Sort Algorithm
- DSA - Insertion Sort Algorithm
- DSA - Selection Sort Algorithm
- DSA - Merge Sort Algorithm
- DSA - Shell Sort Algorithm
- DSA - Heap Sort Algorithm
- DSA - Bucket Sort Algorithm
- DSA - Counting Sort Algorithm
- DSA - Radix Sort Algorithm
- DSA - Quick Sort Algorithm
- Matrices Data Structure
- DSA - Matrices Data Structure
- DSA - Lup Decomposition In Matrices
- DSA - Lu Decomposition In Matrices
- Graph Data Structure
- DSA - Graph Data Structure
- DSA - Depth First Traversal
- DSA - Breadth First Traversal
- DSA - Spanning Tree
- DSA - Topological Sorting
- DSA - Strongly Connected Components
- DSA - Biconnected Components
- DSA - Augmenting Path
- DSA - Network Flow Problems
- DSA - Flow Networks In Data Structures
- DSA - Edmonds Blossom Algorithm
- DSA - Maxflow Mincut Theorem
- Tree Data Structure
- DSA - Tree Data Structure
- DSA - Tree Traversal
- DSA - Binary Search Tree
- DSA - AVL Tree
- DSA - Red Black Trees
- DSA - B Trees
- DSA - B+ Trees
- DSA - Splay Trees
- DSA - Range Queries
- DSA - Segment Trees
- DSA - Fenwick Tree
- DSA - Fusion Tree
- DSA - Hashed Array Tree
- DSA - K-Ary Tree
- DSA - Kd Trees
- DSA - Priority Search Tree Data Structure
- Recursion
- DSA - Recursion Algorithms
- DSA - Tower of Hanoi Using Recursion
- DSA - Fibonacci Series Using Recursion
- Divide and Conquer
- DSA - Divide and Conquer
- DSA - Max-Min Problem
- DSA - Strassen's Matrix Multiplication
- DSA - Karatsuba Algorithm
- Greedy Algorithms
- DSA - Greedy Algorithms
- DSA - Travelling Salesman Problem (Greedy Approach)
- DSA - Prim's Minimal Spanning Tree
- DSA - Kruskal's Minimal Spanning Tree
- DSA - Dijkstra's Shortest Path Algorithm
- DSA - Map Colouring Algorithm
- DSA - Fractional Knapsack Problem
- DSA - Job Sequencing with Deadline
- DSA - Optimal Merge Pattern Algorithm
- Dynamic Programming
- DSA - Dynamic Programming
- DSA - Matrix Chain Multiplication
- DSA - Floyd Warshall Algorithm
- DSA - 0-1 Knapsack Problem
- DSA - Longest Common Sub-sequence Algorithm
- DSA - Travelling Salesman Problem (Dynamic Approach)
- Hashing
- DSA - Hashing Data Structure
- DSA - Collision In Hashing
- Disjoint Set
- DSA - Disjoint Set
- DSA - Path Compression And Union By Rank
- Heap
- DSA - Heap Data Structure
- DSA - Binary Heap
- DSA - Binomial Heap
- DSA - Fibonacci Heap
- Tries Data Structure
- DSA - Tries
- DSA - Standard Tries
- DSA - Compressed Tries
- DSA - Suffix Tries
- Treaps
- DSA - Treaps Data Structure
- Bit Mask
- DSA - Bit Mask In Data Structures
- Bloom Filter
- DSA - Bloom Filter Data Structure
- Approximation Algorithms
- DSA - Approximation Algorithms
- DSA - Vertex Cover Algorithm
- DSA - Set Cover Problem
- DSA - Travelling Salesman Problem (Approximation Approach)
- Randomized Algorithms
- DSA - Randomized Algorithms
- DSA - Randomized Quick Sort Algorithm
- DSA - Karger’s Minimum Cut Algorithm
- DSA - Fisher-Yates Shuffle Algorithm
- Miscellaneous
- DSA - Infix to Postfix
- DSA - Bellmon Ford Shortest Path
- DSA - Maximum Bipartite Matching
- DSA Useful Resources
- DSA - Questions and Answers
- DSA - Selection Sort Interview Questions
- DSA - Merge Sort Interview Questions
- DSA - Insertion Sort Interview Questions
- DSA - Heap Sort Interview Questions
- DSA - Bubble Sort Interview Questions
- DSA - Bucket Sort Interview Questions
- DSA - Radix Sort Interview Questions
- DSA - Cycle Sort Interview Questions
- DSA - Quick Guide
- DSA - Useful Resources
- DSA - Discussion
Splay Trees
Splay trees are the altered versions of the Binary Search Trees, since it contains all the operations of BSTs, like insertion, deletion and searching, followed by another extended operation called splaying.
For instance, a value "A" is supposed to be inserted into the tree. If the tree is empty, add "A" to the root of the tree and exit; but if the tree is not empty, use binary search insertion operation to insert the element and then perform splaying on the new node.
Similarly, after searching an element in the splay tree, the node consisting of the element must be splayed as well.
But how do we perform splaying? Splaying, in simpler terms, is just a process to bring an operational node to the root. There are six types of rotations for it.
Zig rotation
Zag rotation
Zig-Zig rotation
Zag-Zag rotation
Zig-Zag rotation
Zag-Zig rotation
Zig rotation
The zig rotations are performed when the operational node is either the root node or the left child node of the root node. The node is rotated towards its right.

After the shift, the tree will look like −

Zag rotation
The zag rotations are also performed when the operational node is either the root node or the right child nod of the root node. The node is rotated towards its left.

The operational node becomes the root node after the shift −

Zig-Zig rotation
The zig-zig rotations are performed when the operational node has both parent and a grandparent. The node is rotated two places towards its right.

The first rotation will shift the tree to one position right −

The second right rotation will once again shift the node for one position. The final tree after the shift will look like this −

Zag-Zag rotation
The zag-zag rotations are also performed when the operational node has both parent and a grandparent. The node is rotated two places towards its left.

After the first rotation, the tree will look like −

Then the final tree after the second rotation is given as follows. However, the operational node is still not the root so the splaying is considered incomplete. Hence, other suitable rotations are again applied in this case until the node becomes the root.
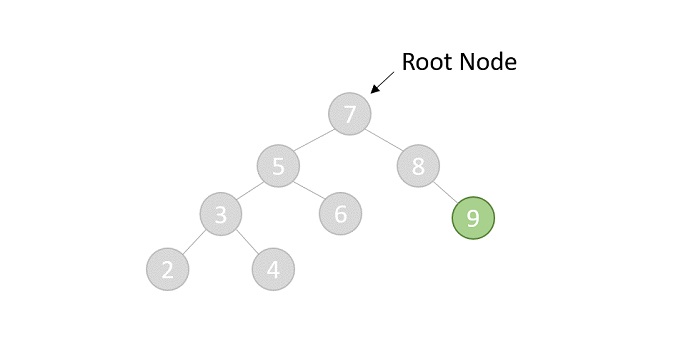
Zig-Zag rotation
The zig-zag rotations are performed when the operational node has both a parent and a grandparent. But the difference is the grandparent, parent and child are in LRL format. The node is rotated first towards its right followed by left.

After the first rotation, the tree is −

The final tree after the second rotation −

Zag-Zig rotation
The zag-zig rotations are also performed when the operational node has both parent and grandparent. But the difference is the grandparent, parent and child are in RLR format. The node is rotated first towards its left followed by right.

First rotation is performed, the tree is obtained as −

After second rotation, the final tree is given as below. However, the operational node is not the root node yet so one more rotation needs to be performed to make the said node as the root.

Basic Operations of Splay Trees
A splay contains the same basic operations that a Binary Search Tree provides with: Insertion, Deletion, and Search. However, after every operation there is an additional operation that differs them from Binary Search tree operations: Splaying. We have learned about Splaying already so let us understand the procedures of the other operations.
Insertion operation
The insertion operation in a Splay tree is performed in the exact same way insertion in a binary search tree is performed. The procedure to perform the insertion in a splay tree is given as follows −
Check whether the tree is empty; if yes, add the new node and exit

If the tree is not empty, add the new node to the existing tree using the binary search insertion.

Then, suitable splaying is chosen and applied on the newly added node.

Zag (Left) Rotation is applied on the new node

Example
Following are the implementations of this operation in various programming languages −
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild, *rightChild;
};
struct node* newNode(int data){
struct node* Node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
Node->data = data;
Node->leftChild = Node->rightChild = NULL;
return (Node);
}
struct node* rightRotate(struct node *x){
struct node *y = x->leftChild;
x->leftChild = y->rightChild;
y->rightChild = x;
return y;
}
struct node* leftRotate(struct node *x){
struct node *y = x->rightChild;
x->rightChild = y->leftChild;
y->leftChild = x;
return y;
}
struct node* splay(struct node *root, int data){
if (root == NULL || root->data == data)
return root;
if (root->data > data) {
if (root->leftChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->leftChild->data > data) {
root->leftChild->leftChild = splay(root->leftChild->leftChild, data);
root = rightRotate(root);
} else if (root->leftChild->data < data) {
root->leftChild->rightChild = splay(root->leftChild->rightChild, data);
if (root->leftChild->rightChild != NULL)
root->leftChild = leftRotate(root->leftChild);
}
return (root->leftChild == NULL)? root: rightRotate(root);
} else {
if (root->rightChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->rightChild->data > data) {
root->rightChild->leftChild = splay(root->rightChild->leftChild, data);
if (root->rightChild->leftChild != NULL)
root->rightChild = rightRotate(root->rightChild);
} else if (root->rightChild->data < data) {
root->rightChild->rightChild = splay(root->rightChild->rightChild, data);
root = leftRotate(root);
}
return (root->rightChild == NULL)? root: leftRotate(root);
}
}
struct node* insert(struct node *root, int k){
if (root == NULL) return newNode(k);
root = splay(root, k);
if (root->data == k) return root;
struct node *newnode = newNode(k);
if (root->data > k) {
newnode->rightChild = root;
newnode->leftChild = root->leftChild;
root->leftChild = NULL;
} else {
newnode->leftChild = root;
newnode->rightChild = root->rightChild;
root->rightChild = NULL;
}
return newnode;
}
void printTree(struct node *root){
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (root != NULL) {
printTree(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
printTree(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
struct node* root = newNode(34);
root->leftChild = newNode(15);
root->rightChild = newNode(40);
root->leftChild->leftChild = newNode(12);
root->leftChild->leftChild->rightChild = newNode(14);
root->rightChild->rightChild = newNode(59);
printf("The Splay tree is: \n");
printTree(root);
return 0;
}
Output
The Splay tree is: 12 14 15 34 40 59
#include <iostream>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild, *rightChild;
};
struct node* newNode(int data){
struct node* Node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
Node->data = data;
Node->leftChild = Node->rightChild = NULL;
return (Node);
}
struct node* rightRotate(struct node *x){
struct node *y = x->leftChild;
x->leftChild = y->rightChild;
y->rightChild = x;
return y;
}
struct node* leftRotate(struct node *x){
struct node *y = x->rightChild;
x->rightChild = y->leftChild;
y->leftChild = x;
return y;
}
struct node* splay(struct node *root, int data){
if (root == NULL || root->data == data)
return root;
if (root->data > data) {
if (root->leftChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->leftChild->data > data) {
root->leftChild->leftChild = splay(root->leftChild->leftChild, data);
root = rightRotate(root);
} else if (root->leftChild->data < data) {
root->leftChild->rightChild = splay(root->leftChild->rightChild, data);
if (root->leftChild->rightChild != NULL)
root->leftChild = leftRotate(root->leftChild);
}
return (root->leftChild == NULL)? root: rightRotate(root);
} else {
if (root->rightChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->rightChild->data > data) {
root->rightChild->leftChild = splay(root->rightChild->leftChild, data);
if (root->rightChild->leftChild != NULL)
root->rightChild = rightRotate(root->rightChild);
} else if (root->rightChild->data < data) {
root->rightChild->rightChild = splay(root->rightChild->rightChild, data);
root = leftRotate(root);
}
return (root->rightChild == NULL)? root: leftRotate(root);
}
}
struct node* insert(struct node *root, int k){
if (root == NULL) return newNode(k);
root = splay(root, k);
if (root->data == k) return root;
struct node *newnode = newNode(k);
if (root->data > k) {
newnode->rightChild = root;
newnode->leftChild = root->leftChild;
root->leftChild = NULL;
} else {
newnode->leftChild = root;
newnode->rightChild = root->rightChild;
root->rightChild = NULL;
}
return newnode;
}
void printTree(struct node *root){
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (root != NULL) {
printTree(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
printTree(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
struct node* root = newNode(34);
root->leftChild = newNode(15);
root->rightChild = newNode(40);
root->leftChild->leftChild = newNode(12);
root->leftChild->leftChild->rightChild = newNode(14);
root->rightChild->rightChild = newNode(59);
printf("The Splay tree is: \n");
printTree(root);
return 0;
}
Output
The Splay tree is: 12 14 15 34 40 59
import java.io.*;
public class SplayTree {
static class node {
int data;
node leftChild, rightChild;
};
static node newNode(int data) {
node Node = new node();
Node.data = data;
Node.leftChild = Node.rightChild = null;
return (Node);
}
static node rightRotate(node x) {
node y = x.leftChild;
x.leftChild = y.rightChild;
y.rightChild = x;
return y;
}
static node leftRotate(node x) {
node y = x.rightChild;
x.rightChild = y.leftChild;
y.leftChild = x;
return y;
}
static node splay(node root, int data) {
if (root == null || root.data == data)
return root;
if (root.data > data) {
if (root.leftChild == null) return root;
if (root.leftChild.data > data) {
root.leftChild.leftChild = splay(root.leftChild.leftChild, data);
root = rightRotate(root);
} else if (root.leftChild.data < data) {
root.leftChild.rightChild = splay(root.leftChild.rightChild, data);
if (root.leftChild.rightChild != null)
root.leftChild = leftRotate(root.leftChild);
}
return (root.leftChild == null)? root: rightRotate(root);
} else {
if (root.rightChild == null) return root;
if (root.rightChild.data > data) {
root.rightChild.leftChild = splay(root.rightChild.leftChild, data);
if (root.rightChild.leftChild != null)
root.rightChild = rightRotate(root.rightChild);
} else if (root.rightChild.data < data) {
root.rightChild.rightChild = splay(root.rightChild.rightChild, data);
root = leftRotate(root);
}
return (root.rightChild == null)? root: leftRotate(root);
}
}
static node insert(node root, int k) {
if (root == null) return newNode(k);
root = splay(root, k);
if (root.data == k) return root;
node newnode = newNode(k);
if (root.data > k) {
newnode.rightChild = root;
newnode.leftChild = root.leftChild;
root.leftChild = null;
} else {
newnode.leftChild = root;
newnode.rightChild = root.rightChild;
root.rightChild = null;
}
return newnode;
}
static void printTree(node root) {
if (root == null)
return;
if (root != null) {
printTree(root.leftChild);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
printTree(root.rightChild);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
node root = newNode(34);
root.leftChild = newNode(15);
root.rightChild = newNode(40);
root.leftChild.leftChild = newNode(12);
root.leftChild.leftChild.rightChild = newNode(14);
root.rightChild.rightChild = newNode(59);
System.out.println("The Splay tree is: ");
printTree(root);
}
}
Output
The Splay tree is: 12 14 15 34 40 59
#Python Code for Insertion Operation of Splay Trees
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.leftChild = None
self.rightChild = None
def newNode(data):
return Node(data)
def rightRotate(x):
y = x.leftChild
x.leftChild = y.rightChild
y.rightChild = x
return y
def leftRotate(x):
y = x.rightChild
x.rightChild = y.leftChild
y.leftChild = x
return y
def splay(root, data):
if root is None or root.data == data:
return root
if root.data > data:
if root.leftChild is None:
return root
if root.leftChild.data > data:
root.leftChild.leftChild = splay(root.leftChild.leftChild, data)
root = rightRotate(root)
elif root.leftChild.data < data:
root.leftChild.rightChild = splay(root.leftChild.rightChild, data)
if root.leftChild.rightChild is not None:
root.leftChild = leftRotate(root.leftChild)
return root if root.leftChild is None else rightRotate(root)
else:
if root.rightChild is None:
return root
if root.rightChild.data > data:
root.rightChild.leftChild = splay(root.rightChild.leftChild, data)
if root.rightChild.leftChild is not None:
root.rightChild = rightRotate(root.rightChild)
elif root.rightChild.data < data:
root.rightChild.rightChild = splay(root.rightChild.rightChild, data)
root = leftRotate(root)
return root if root.rightChild is None else leftRotate(root)
def insert(root, k):
if root is None:
return newNode(k)
root = splay(root, k)
if root.data == k:
return root
newnode = newNode(k)
if root.data > k:
newnode.rightChild = root
newnode.leftChild = root.leftChild
root.leftChild = None
else:
newnode.leftChild = root
newnode.rightChild = root.rightChild
root.rightChild = None
return newnode
def printTree(root):
if root is None:
return
if root is not None:
printTree(root.leftChild)
print(root.data, end=" ")
printTree(root.rightChild)
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = newNode(34)
root.leftChild = newNode(15)
root.rightChild = newNode(40)
root.leftChild.leftChild = newNode(12)
root.leftChild.leftChild.rightChild = newNode(14)
root.rightChild.rightChild = newNode(59)
print("The Splay tree is: ")
printTree(root)
Output
The Splay tree is: 12 14 15 34 40 59
Deletion operation
The deletion operation in a splay tree is performed as following −
Apply splaying operation on the node to be deleted.
Once, the node is made the root, delete the node.
Now, the tree is split into two trees, the left subtree and the right subtree; with their respective first nodes as the root nodes: say root_left and root_right.

If root_left is a NULL value, then the root_right will become the root of the tree. And vice versa.
But if both root_left and root_right are not NULL values, then select the maximum value from the left subtree and make it the new root by connecting the subtrees.

Example
Following are the implementations of Splay Tree deletion operation in various programming languages −
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild, *rightChild;
};
struct node* newNode(int data){
struct node* Node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
Node->data = data;
Node->leftChild = Node->rightChild = NULL;
return (Node);
}
struct node* rightRotate(struct node *x){
struct node *y = x->leftChild;
x->leftChild = y->rightChild;
y->rightChild = x;
return y;
}
struct node* leftRotate(struct node *x){
struct node *y = x->rightChild;
x->rightChild = y->leftChild;
y->leftChild = x;
return y;
}
struct node* splay(struct node *root, int data){
if (root == NULL || root->data == data)
return root;
if (root->data > data) {
if (root->leftChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->leftChild->data > data) {
root->leftChild->leftChild = splay(root->leftChild->leftChild, data);
root = rightRotate(root);
} else if (root->leftChild->data < data) {
root->leftChild->rightChild = splay(root->leftChild->rightChild, data);
if (root->leftChild->rightChild != NULL)
root->leftChild = leftRotate(root->leftChild);
}
return (root->leftChild == NULL)? root: rightRotate(root);
} else {
if (root->rightChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->rightChild->data > data) {
root->rightChild->leftChild = splay(root->rightChild->leftChild, data);
if (root->rightChild->leftChild != NULL)
root->rightChild = rightRotate(root->rightChild);
} else if (root->rightChild->data < data) {
root->rightChild->rightChild = splay(root->rightChild->rightChild, data);
root = leftRotate(root);
}
return (root->rightChild == NULL)? root: leftRotate(root);
}
}
struct node* insert(struct node *root, int k){
if (root == NULL) return newNode(k);
root = splay(root, k);
if (root->data == k) return root;
struct node *newnode = newNode(k);
if (root->data > k) {
newnode->rightChild = root;
newnode->leftChild = root->leftChild;
root->leftChild = NULL;
} else {
newnode->leftChild = root;
newnode->rightChild = root->rightChild;
root->rightChild = NULL;
}
return newnode;
}
struct node* deletenode(struct node* root, int data){
struct node* temp;
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
root = splay(root, data);
if (data != root->data)
return root;
if (!root->leftChild) {
temp = root;
root = root->rightChild;
} else {
temp = root;
root = splay(root->leftChild, data);
root->rightChild = temp->rightChild;
}
free(temp);
return root;
}
void printTree(struct node *root){
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (root != NULL) {
printTree(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
printTree(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
struct node* root = newNode(34);
root->leftChild = newNode(15);
root->rightChild = newNode(40);
printf("The Splay tree is \n");
printTree(root);
root = deletenode(root, 40);
printf("\nThe Splay tree after deletion is \n");
printTree(root);
return 0;
}
Output
The Splay tree is 15 34 40 The Splay tree after deletion is 15 34
#include <iostream>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild, *rightChild;
};
struct node* newNode(int data){
struct node* Node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
Node->data = data;
Node->leftChild = Node->rightChild = NULL;
return (Node);
}
struct node* rightRotate(struct node *x){
struct node *y = x->leftChild;
x->leftChild = y->rightChild;
y->rightChild = x;
return y;
}
struct node* leftRotate(struct node *x){
struct node *y = x->rightChild;
x->rightChild = y->leftChild;
y->leftChild = x;
return y;
}
struct node* splay(struct node *root, int data){
if (root == NULL || root->data == data)
return root;
if (root->data > data) {
if (root->leftChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->leftChild->data > data) {
root->leftChild->leftChild = splay(root->leftChild->leftChild, data);
root = rightRotate(root);
} else if (root->leftChild->data < data) {
root->leftChild->rightChild = splay(root->leftChild->rightChild, data);
if (root->leftChild->rightChild != NULL)
root->leftChild = leftRotate(root->leftChild);
}
return (root->leftChild == NULL)? root: rightRotate(root);
} else {
if (root->rightChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->rightChild->data > data) {
root->rightChild->leftChild = splay(root->rightChild->leftChild, data);
if (root->rightChild->leftChild != NULL)
root->rightChild = rightRotate(root->rightChild);
} else if (root->rightChild->data < data) {
root->rightChild->rightChild = splay(root->rightChild->rightChild, data);
root = leftRotate(root);
}
return (root->rightChild == NULL)? root: leftRotate(root);
}
}
struct node* insert(struct node *root, int k){
if (root == NULL) return newNode(k);
root = splay(root, k);
if (root->data == k) return root;
struct node *newnode = newNode(k);
if (root->data > k) {
newnode->rightChild = root;
newnode->leftChild = root->leftChild;
root->leftChild = NULL;
} else {
newnode->leftChild = root;
newnode->rightChild = root->rightChild;
root->rightChild = NULL;
}
return newnode;
}
struct node* deletenode(struct node* root, int data){
struct node* temp;
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
root = splay(root, data);
if (data != root->data)
return root;
if (!root->leftChild) {
temp = root;
root = root->rightChild;
} else {
temp = root;
root = splay(root->leftChild, data);
root->rightChild = temp->rightChild;
}
free(temp);
return root;
}
void printTree(struct node *root){
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (root != NULL) {
printTree(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
printTree(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
struct node* root = newNode(34);
root->leftChild = newNode(15);
root->rightChild = newNode(40);
printf("The Splay tree is \n");
printTree(root);
root = deletenode(root, 40);
printf("\nThe Splay tree after deletion is \n");
printTree(root);
return 0;
}
Output
The Splay tree is 15 34 40 The Splay tree after deletion is 15 34
import java.io.*;
public class SplayTree {
static class node {
int data;
node leftChild, rightChild;
};
static node newNode(int data) {
node Node = new node();
Node.data = data;
Node.leftChild = Node.rightChild = null;
return (Node);
}
static node rightRotate(node x) {
node y = x.leftChild;
x.leftChild = y.rightChild;
y.rightChild = x;
return y;
}
static node leftRotate(node x) {
node y = x.rightChild;
x.rightChild = y.leftChild;
y.leftChild = x;
return y;
}
static node splay(node root, int data) {
if (root == null || root.data == data)
return root;
if (root.data > data) {
if (root.leftChild == null) return root;
if (root.leftChild.data > data) {
root.leftChild.leftChild = splay(root.leftChild.leftChild, data);
root = rightRotate(root);
} else if (root.leftChild.data < data) {
root.leftChild.rightChild = splay(root.leftChild.rightChild, data);
if (root.leftChild.rightChild != null)
root.leftChild = leftRotate(root.leftChild);
}
return (root.leftChild == null)? root: rightRotate(root);
} else {
if (root.rightChild == null) return root;
if (root.rightChild.data > data) {
root.rightChild.leftChild = splay(root.rightChild.leftChild, data);
if (root.rightChild.leftChild != null)
root.rightChild = rightRotate(root.rightChild);
} else if (root.rightChild.data < data) {
root.rightChild.rightChild = splay(root.rightChild.rightChild, data);
root = leftRotate(root);
}
return (root.rightChild == null)? root: leftRotate(root);
}
}
static node insert(node root, int k) {
if (root == null) return newNode(k);
root = splay(root, k);
if (root.data == k) return root;
node newnode = newNode(k);
if (root.data > k) {
newnode.rightChild = root;
newnode.leftChild = root.leftChild;
root.leftChild = null;
} else {
newnode.leftChild = root;
newnode.rightChild = root.rightChild;
root.rightChild = null;
}
return newnode;
}
static node deletenode(node root, int data) {
node temp;
if (root == null)
return null;
root = splay(root, data);
if (data != root.data)
return root;
if (root.leftChild == null) {
temp = root;
root = root.rightChild;
} else {
temp = root;
root = splay(root.leftChild, data);
root.rightChild = temp.rightChild;
}
return root;
}
static void printTree(node root) {
if (root == null)
return;
if (root != null) {
printTree(root.leftChild);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
printTree(root.rightChild);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
node root = newNode(34);
root.leftChild = newNode(15);
root.rightChild = newNode(40);
System.out.println("The Splay tree is: ");
printTree(root);
root = deletenode(root, 40);
System.out.println("\nThe Splay tree after deletion is: ");
printTree(root);
}
}
Output
The Splay tree is: 15 34 40 The Splay tree after deletion is: 15 34
#Python Code for Deletion operation of Splay Trees
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.leftChild = None
self.rightChild = None
def newNode(data):
node = Node(data)
return node
def rightRotate(x):
y = x.leftChild
x.leftChild = y.rightChild
y.rightChild = x
return y
def leftRotate(x):
y = x.rightChild
x.rightChild = y.leftChild
y.leftChild = x
return y
def splay(root, data):
if root is None or root.data == data:
return root
if root.data > data:
if root.leftChild is None:
return root
if root.leftChild.data > data:
root.leftChild.leftChild = splay(root.leftChild.leftChild, data)
root = rightRotate(root)
elif root.leftChild.data < data:
root.leftChild.rightChild = splay(root.leftChild.rightChild, data)
if root.leftChild.rightChild is not None:
root.leftChild = leftRotate(root.leftChild)
return root if root.leftChild is None else rightRotate(root)
else:
if root.rightChild is None:
return root
if root.rightChild.data > data:
root.rightChild.leftChild = splay(root.rightChild.leftChild, data)
if root.rightChild.leftChild is not None:
root.rightChild = rightRotate(root.rightChild)
elif root.rightChild.data < data:
root.rightChild.rightChild = splay(root.rightChild.rightChild, data)
root = leftRotate(root)
return root if root.rightChild is None else leftRotate(root)
def insert(root, k):
if root is None:
return newNode(k)
root = splay(root, k)
if root.data == k:
return root
newnode = newNode(k)
if root.data > k:
newnode.rightChild = root
newnode.leftChild = root.leftChild
root.leftChild = None
else:
newnode.leftChild = root
newnode.rightChild = root.rightChild
root.rightChild = None
return newnode
def deletenode(root, data):
temp = None
if root is None:
return None
root = splay(root, data)
if data != root.data:
return root
if root.leftChild is None:
temp = root
root = root.rightChild
else:
temp = root
root = splay(root.leftChild, data)
root.rightChild = temp.rightChild
del temp
return root
def printTree(root):
if root is None:
return
if root is not None:
printTree(root.leftChild)
print(root.data, end=" ")
printTree(root.rightChild)
root = newNode(34)
root.leftChild = newNode(15)
root.rightChild = newNode(40)
print("The Splay tree is:")
printTree(root)
root = deletenode(root, 40)
print("\nThe Splay tree after deletion is:")
printTree(root)
Output
The Splay tree is: 15 34 40 The Splay tree after deletion is: 15 34
Search operation
The search operation in a Splay tree follows the same procedure of the Binary Search Tree operation. However, after the searching is done and the element is found, splaying is applied on the node searched. If the element is not found, then unsuccessful search is prompted.
Example
Following are the implementations of this operation in various programming languages −
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild, *rightChild;
};
struct node* newNode(int data){
struct node* Node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
Node->data = data;
Node->leftChild = Node->rightChild = NULL;
return (Node);
}
struct node* rightRotate(struct node *x){
struct node *y = x->leftChild;
x->leftChild = y->rightChild;
y->rightChild = x;
return y;
}
struct node* leftRotate(struct node *x){
struct node *y = x->rightChild;
x->rightChild = y->leftChild;
y->leftChild = x;
return y;
}
struct node* splay(struct node *root, int data){
if (root == NULL || root->data == data)
return root;
if (root->data > data) {
if (root->leftChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->leftChild->data > data) {
root->leftChild->leftChild = splay(root->leftChild->leftChild, data);
root = rightRotate(root);
} else if (root->leftChild->data < data) {
root->leftChild->rightChild = splay(root->leftChild->rightChild, data);
if (root->leftChild->rightChild != NULL)
root->leftChild = leftRotate(root->leftChild);
}
return (root->leftChild == NULL)? root: rightRotate(root);
} else {
if (root->rightChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->rightChild->data > data) {
root->rightChild->leftChild = splay(root->rightChild->leftChild, data);
if (root->rightChild->leftChild != NULL)
root->rightChild = rightRotate(root->rightChild);
} else if (root->rightChild->data < data) {
root->rightChild->rightChild = splay(root->rightChild->rightChild, data);
root = leftRotate(root);
}
return (root->rightChild == NULL)? root: leftRotate(root);
}
}
struct node* insert(struct node *root, int k){
if (root == NULL) return newNode(k);
root = splay(root, k);
if (root->data == k) return root;
struct node *newnode = newNode(k);
if (root->data > k) {
newnode->rightChild = root;
newnode->leftChild = root->leftChild;
root->leftChild = NULL;
} else {
newnode->leftChild = root;
newnode->rightChild = root->rightChild;
root->rightChild = NULL;
}
return newnode;
}
struct node* search(struct node* root, int data){
return splay(root, data);
}
void printTree(struct node *root){
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (root != NULL) {
printTree(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
printTree(root->rightChild);
}
}
void preOrder(struct node *root)
{
if (root != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", root->data);
preOrder(root->leftChild);
preOrder(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
struct node* root = newNode(34);
root->leftChild = newNode(15);
root->rightChild = newNode(40);
root->leftChild->leftChild = newNode(12);
root->leftChild->leftChild->rightChild = newNode(14);
root->rightChild->rightChild = newNode(59);
printf("The Splay tree is \n");
printTree(root);
int ele = 14;
printf("\nElement to be searched: %d", ele);
root = search(root, ele);
printf("\nModified preorder traversal if element is found: ");
preOrder(root);
}
Output
The Splay tree is 12 14 15 34 40 59 Element to be searched: 14 Modified preorder traversal if element is found: 14 12 15 34 40 59
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class node{
public:
int data;
node *leftChild, *rightChild;
};
node* newNode(int data){
node* Node = new node();
Node->data = data;
Node->leftChild = Node->rightChild = NULL;
return (Node);
}
node *rightRotate(node *x){
node *y = x->leftChild;
x->leftChild = y->rightChild;
y->rightChild = x;
return y;
}
node *leftRotate(node *x){
node *y = x->rightChild;
x->rightChild = y->leftChild;
y->leftChild = x;
return y;
}
node *splay(node *root, int data){
if (root == NULL || root->data == data)
return root;
if (root->data > data) {
if (root->leftChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->leftChild->data > data) {
root->leftChild->leftChild = splay(root->leftChild->leftChild, data);
root = rightRotate(root);
} else if (root->leftChild->data < data) {
root->leftChild->rightChild = splay(root->leftChild->rightChild, data);
if (root->leftChild->rightChild != NULL)
root->leftChild = leftRotate(root->leftChild);
}
return (root->leftChild == NULL)? root: rightRotate(root);
} else {
if (root->rightChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->rightChild->data > data) {
root->rightChild->leftChild = splay(root->rightChild->leftChild, data);
if (root->rightChild->leftChild != NULL)
root->rightChild = rightRotate(root->rightChild);
} else if (root->rightChild->data < data) {
root->rightChild->rightChild = splay(root->rightChild->rightChild, data);
root = leftRotate(root);
}
return (root->rightChild == NULL)? root: leftRotate(root);
}
}
node* insert(node *root, int k)
{
if (root == NULL) return newNode(k);
root = splay(root, k);
if (root->data == k) return root;
node *newnode = newNode(k);
if (root->data > k) {
newnode->rightChild = root;
newnode->leftChild = root->leftChild;
root->leftChild = NULL;
} else {
newnode->leftChild = root;
newnode->rightChild = root->rightChild;
root->rightChild = NULL;
}
return newnode;
}
node* search(struct node* root, int data){
return splay(root, data);
}
void printTree(node *root){
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (root != NULL) {
printTree(root->leftChild);
cout << root->data << " ";
printTree(root->rightChild);
}
}
void preOrder(struct node *root)
{
if (root != NULL)
{
cout << root->data << " ";
preOrder(root->leftChild);
preOrder(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
node* root = newNode(34);
root->leftChild = newNode(15);
root->rightChild = newNode(40);
root->leftChild->leftChild = newNode(12);
root->leftChild->leftChild->rightChild = newNode(14);
root->rightChild->rightChild = newNode(59);
cout << "The Splay tree is \n";
printTree(root);
int ele = 40;
cout << "\nThe element to be searched: " << ele;
root = search(root, ele);
cout << "\nModified preorder traversal if element is found: ";
preOrder(root);
}
Output
The Splay tree is 12 14 15 34 40 59 The element to be searched: 40 Modified preorder traversal if element is found: 40 34 15 12 14 59
import java.io.*;
public class SplayTree {
static class node {
int data;
node leftChild, rightChild;
};
static node newNode(int data) {
node Node = new node();
Node.data = data;
Node.leftChild = Node.rightChild = null;
return (Node);
}
static node rightRotate(node x) {
node y = x.leftChild;
x.leftChild = y.rightChild;
y.rightChild = x;
return y;
}
static node leftRotate(node x) {
node y = x.rightChild;
x.rightChild = y.leftChild;
y.leftChild = x;
return y;
}
static node splay(node root, int data) {
if (root == null || root.data == data)
return root;
if (root.data > data) {
if (root.leftChild == null) return root;
if (root.leftChild.data > data) {
root.leftChild.leftChild = splay(root.leftChild.leftChild, data);
root = rightRotate(root);
} else if (root.leftChild.data < data) {
root.leftChild.rightChild = splay(root.leftChild.rightChild, data);
if (root.leftChild.rightChild != null)
root.leftChild = leftRotate(root.leftChild);
}
return (root.leftChild == null)? root: rightRotate(root);
} else {
if (root.rightChild == null) return root;
if (root.rightChild.data > data) {
root.rightChild.leftChild = splay(root.rightChild.leftChild, data);
if (root.rightChild.leftChild != null)
root.rightChild = rightRotate(root.rightChild);
} else if (root.rightChild.data < data) {
root.rightChild.rightChild = splay(root.rightChild.rightChild, data);
root = leftRotate(root);
}
return (root.rightChild == null)? root: leftRotate(root);
}
}
static node insert(node root, int k) {
if (root == null) return newNode(k);
root = splay(root, k);
if (root.data == k) return root;
node newnode = newNode(k);
if (root.data > k) {
newnode.rightChild = root;
newnode.leftChild = root.leftChild;
root.leftChild = null;
} else {
newnode.leftChild = root;
newnode.rightChild = root.rightChild;
root.rightChild = null;
}
return newnode;
}
static node search(node root, int key){
return splay(root, key);
}
static void printTree(node root) {
if (root == null)
return;
if (root != null) {
printTree(root.leftChild);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
printTree(root.rightChild);
}
}
static void preOrder(node root) {
if (root != null) {
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
preOrder(root.leftChild);
preOrder(root.rightChild);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
node root = newNode(34);
root.leftChild = newNode(15);
root.rightChild = newNode(40);
root.leftChild.leftChild = newNode(12);
root.leftChild.leftChild.rightChild = newNode(14);
root.rightChild.rightChild = newNode(59);
System.out.println("The Splay tree is: ");
printTree(root);
int ele = 34;
System.out.print("\nElement to be searched: " + ele);
root = search(root, ele);
System.out.print("\nModified preorder traversal if element is found: ");
preOrder(root);
}
}
Output
The Splay tree is: 12 14 15 34 40 59 Element to be searched: 34 Modified preorder traversal if element is found: 34 15 12 14 40 59
#Python Code for Search Operation of splay Trees
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.leftChild = None
self.rightChild = None
def newNode(data):
newNode = Node(data)
newNode.leftChild = newNode.rightChild = None
return newNode
def rightRotate(x):
y = x.leftChild
x.leftChild = y.rightChild
y.rightChild = x
return y
def leftRotate(x):
y = x.rightChild
x.rightChild = y.leftChild
y.leftChild = x
return y
def splay(root, data):
if root is None or root.data == data:
return root
if root.data > data:
if root.leftChild is None:
return root
if root.leftChild.data > data:
root.leftChild.leftChild = splay(root.leftChild.leftChild, data)
root = rightRotate(root)
elif root.leftChild.data < data:
root.leftChild.rightChild = splay(root.leftChild.rightChild, data)
if root.leftChild.rightChild is not None:
root.leftChild = leftRotate(root.leftChild)
return root if root.leftChild is None else rightRotate(root)
else:
if root.rightChild is None:
return root
if root.rightChild.data > data:
root.rightChild.leftChild = splay(root.rightChild.leftChild, data)
if root.rightChild.leftChild is not None:
root.rightChild = rightRotate(root.rightChild)
elif root.rightChild.data < data:
root.rightChild.rightChild = splay(root.rightChild.rightChild, data)
root = leftRotate(root)
return root if root.rightChild is None else leftRotate(root)
def insert(root, k):
if root is None:
return newNode(k)
root = splay(root, k)
if root.data == k:
return root
newnode = newNode(k)
if root.data > k:
newnode.rightChild = root
newnode.leftChild = root.leftChild
root.leftChild = None
else:
newnode.leftChild = root
newnode.rightChild = root.rightChild
root.rightChild = None
return newnode
def search(root, data):
return splay(root, data)
def printTree(root):
if root is None:
return
if root is not None:
printTree(root.leftChild)
print(root.data, end=" ")
printTree(root.rightChild)
def preOrder(root):
if root != None:
print(root.data, end = " ")
preOrder(root.leftChild)
preOrder(root.rightChild)
root = newNode(34)
root.leftChild = newNode(15)
root.rightChild = newNode(40)
root.leftChild.leftChild = newNode(12)
root.leftChild.leftChild.rightChild = newNode(14)
root.rightChild.rightChild = newNode(59)
print("The Splay tree is")
printTree(root)
ele = 59
print("\nElement to be searched ",ele)
root = search(root, ele)
print("Modified preorder traversal if element is found: ")
preOrder(root)
Output
The Splay tree is 12 14 15 34 40 59 Element to be searched 59 Modified preorder traversal if element is found: 59 40 34 15 12 14