
- Java - Home
- Java - Overview
- Java - History
- Java - Features
- Java Vs. C++
- JVM - Java Virtual Machine
- Java - JDK vs JRE vs JVM
- Java - Environment Setup
- Java - Hello World Program
- Java - Comments
- Java - Basic Syntax
- Java - Variables
- Java - Data Types
- Java - Type Casting
- Java - Unicode System
- Java - User Input
- Java - Date & Time
Java Operators
- Java - Operators
- Java - Arithmetic Operators
- Java - Assignment Operators
- Java - Relational Operators
- Java - Logical Operators
- Java - Bitwise Operators
- Java Operator Precedence & Associativity
Java Control Statements
- Java - Decision Making
- Java - If Else Statement
- Java - Switch Statement
- Java - Loop Control
- Java - For Loop
- Java - For-Each Loop
- Java - While Loop
- Java - Do While Loop
- Java - Break Statement
- Java - Continue Statement
Object Oriented Programming
- Java - OOPs Concepts
- Java - Object & Classes
- Java - Class Attributes
- Java - Class Methods
- Java - Methods
- Java - Variables Scope
- Java - Constructors
- Java - Access Modifiers
- Java - Inheritance
- Java - Aggregation
- Java - Polymorphism
- Java - Overriding
- Java - Method Overloading
- Java - Dynamic Binding
- Java - Static Binding
- Java - Instance Initializer Block
- Java - Abstraction
- Java - Encapsulation
- Java - Interfaces
- Java - Packages
- Java - Inner Classes
- Java - Static Class
- Java - Anonymous Class
- Java - Singleton Class
- Java - Wrapper Classes
- Java - Enums
- Java - Enum Constructor
- Java - Enum Strings
Java Built-in Classes
Java File Handling
- Java - Files
- Java - Create a File
- Java - Write to File
- Java - Read Files
- Java - Delete Files
- Java - Directories
- Java - I/O Streams
Java Error & Exceptions
- Java - Exceptions
- Java - try-catch Block
- Java - try-with-resources
- Java - Multi-catch Block
- Java - Nested try Block
- Java - Finally Block
- Java - throw Exception
- Java - Exception Propagation
- Java - Built-in Exceptions
- Java - Custom Exception
Java Multithreading
- Java - Multithreading
- Java - Thread Life Cycle
- Java - Creating a Thread
- Java - Starting a Thread
- Java - Joining Threads
- Java - Naming Thread
- Java - Thread Scheduler
- Java - Thread Pools
- Java - Main Thread
- Java - Thread Priority
- Java - Daemon Threads
- Java - Thread Group
- Java - Shutdown Hook
Java Synchronization
- Java - Synchronization
- Java - Block Synchronization
- Java - Static Synchronization
- Java - Inter-thread Communication
- Java - Thread Deadlock
- Java - Interrupting a Thread
- Java - Thread Control
- Java - Reentrant Monitor
Java Networking
- Java - Networking
- Java - Socket Programming
- Java - URL Processing
- Java - URL Class
- Java - URLConnection Class
- Java - HttpURLConnection Class
- Java - Socket Class
- Java - Generics
Java Collections
Java Interfaces
- Java - List Interface
- Java - Queue Interface
- Java - Map Interface
- Java - SortedMap Interface
- Java - Set Interface
- Java - SortedSet Interface
Java Data Structures
Java Collections Algorithms
Advanced Java
- Java - Command-Line Arguments
- Java - Lambda Expressions
- Java - Sending Email
- Java - Applet Basics
- Java - Javadoc Comments
- Java - Autoboxing and Unboxing
- Java - File Mismatch Method
- Java - REPL (JShell)
- Java - Multi-Release Jar Files
- Java - Private Interface Methods
- Java - Inner Class Diamond Operator
- Java - Multiresolution Image API
- Java - Collection Factory Methods
- Java - Module System
- Java - Nashorn JavaScript
- Java - Optional Class
- Java - Method References
- Java - Functional Interfaces
- Java - Default Methods
- Java - Base64 Encode Decode
- Java - Switch Expressions
- Java - Teeing Collectors
- Java - Microbenchmark
- Java - Text Blocks
- Java - Dynamic CDS archive
- Java - Z Garbage Collector (ZGC)
- Java - Null Pointer Exception
- Java - Packaging Tools
- Java - Sealed Classes
- Java - Record Classes
- Java - Hidden Classes
- Java - Pattern Matching
- Java - Compact Number Formatting
- Java - Garbage Collection
- Java - JIT Compiler
Java Miscellaneous
- Java - Recursion
- Java - Regular Expressions
- Java - Serialization
- Java - Strings
- Java - Process API Improvements
- Java - Stream API Improvements
- Java - Enhanced @Deprecated Annotation
- Java - CompletableFuture API Improvements
- Java - Streams
- Java - Datetime Api
- Java 8 - New Features
- Java 9 - New Features
- Java 10 - New Features
- Java 11 - New Features
- Java 12 - New Features
- Java 13 - New Features
- Java 14 - New Features
- Java 15 - New Features
- Java 16 - New Features
Java APIs & Frameworks
Java Class References
- Java - Scanner
- Java - Arrays
- Java - Strings
- Java - Date
- Java - ArrayList
- Java - Vector
- Java - Stack
- Java - PriorityQueue
- Java - LinkedList
- Java - ArrayDeque
- Java - HashMap
- Java - LinkedHashMap
- Java - WeakHashMap
- Java - EnumMap
- Java - TreeMap
- Java - IdentityHashMap
- Java - HashSet
- Java - EnumSet
- Java - LinkedHashSet
- Java - TreeSet
- Java - BitSet
- Java - Dictionary
- Java - Hashtable
- Java - Properties
- Java - Collection
- Java - Array
Java Useful Resources
Java vs C++
Java is a general-purpose, high-level programming language. Java programming language was originally developed by Sun Microsystems which was initiated by James Gosling and released in 1995 as core component of Sun Microsystems' Java platform (Java 1.0 [J2SE]).
C++ is a middle-level, case-sensitive, object-oriented programming language. Bjarne Stroustrupcreated C++ at Bell Labs. C++ is a platform-independent programming language that works on Windows, Mac OS, and Linux.
Read through this chapter to get an overview of C++ and Java and the features that differentiate these two popular programming languages.
What is Java?
The latest release of the Java Standard Edition is Java SE 23. With the advancement of Java and its widespread popularity, multiple configurations were built to suit various types of platforms. For example: J2EE for Enterprise Applications, J2ME for Mobile Applications.
The new J2 versions were renamed as Java SE, Java EE, and Java ME respectively. Java is guaranteed to be Write Once, Run Anywhere.
Features of Java
The most important features of Java are listed below −
- Object Oriented − In Java, everything is an Object. Java can be easily extended since it is based on the Object model.
- Platform Independent − Unlike many other programming languages including C and C++, when Java is compiled, it is not compiled into platform specific machine, rather into platform independent byte code. This byte code is distributed over the web and interpreted by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) on whichever platform it is being run on.
- Secure − The Java is highly secure as it does not allow anyone to interact with memory. It has bytecode verification and security APIs.
- Portable − The Java is architecture-neutral and having no implementation dependent aspects of the specification makes Java portable.
- Robust − Java makes an effort to eliminate error prone situations by emphasizing mainly on compile time error checking and runtime checking.
- Multithreaded − With Java's multithreaded feature it is possible to write programs that can perform many tasks simultaneously. This design feature allows the developers to construct interactive applications that can run smoothly.
- Interpreted − Java byte code is translated on the fly to native machine instructions and is not stored anywhere. The development process is more rapid and analytical since the linking is an incremental and light-weight process.

Example
Take a look at the following simple Java program −
package com.tutorialspoint;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class JavaTester {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String a, b;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter The value for variable a");
a = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("Enter The value for variable b");
b = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("The value you have entered for a is " + a);
System.out.println("The value you have entered for b is " + b);
scanner.close();
}
}
In our example, we have taken two variables "a" and "b" and assigning some value to those variables. Note that in Java, we need to declare datatype for variables explicitly, as Java is strictly typed language. As Java is an object oriented language, we use objects to perform any action. We have used the Scanner class object to read user input from console which is represented by System.in object. System.out object method println() is used to print the values received.
On execution, this Java code will produce the following output −
Enter The value for variable a 10 Enter The value for variable b 20 The value you have entered for a is 10 The value you have entered for b is 20
What is C++?
C++ is a statically typed, compiled, multi-paradigm, general-purpose programming language with a steep learning curve. Video games, desktop apps, and embedded systems use it extensively. C++ is so compatible with C that it can build practically all C source code without any changes. Object-oriented programming makes C++ a better-structured.
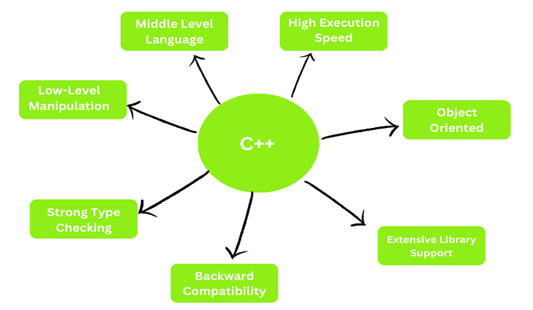
Features of C++
Let's see some features of C++ and the reason of its popularity.
- Middle-level language − It's a middle-level language since it can be used for both systems development and large-scale consumer applications like Media Players, Photoshop, Game Engines, etc.
- Execution Speed − C++ code runs quickly. Because it's compiled and uses procedures extensively. Garbage collection, dynamic typing, and other modern features impede program execution.
- Object-oriented language − Object-oriented programming is flexible and manageable. Large apps are possible. Growing code makes procedural code harder to handle. C++'s key advantage over C.
- Extensive Library Support − C++ has a vast library. Third-party libraries are supported for fast development.
Example
Let's understand the syntax of C++ through an example −
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a, b;
cout << "Enter The value for variable a \n";
cin >> a;
cout << "Enter The value for variable b";
cin >> b;
cout << "The value of a is "<< a << "and" << b;
return 0;
}
In our example, we are taking input for two variables "a" and "b" from the user through the keyboard and displaying the data on the console.
On execution, it will produce the following output −
Enter The value for variable a 10 Enter The value for variable b 20 The value of a is 10 and 20
Difference between Java and C++
The following table compares and contrasts the important features of C++ and Java −
| Java | C++ |
|---|---|
| The Java bytecode works on any operating System. Bytecode is targeted for JVM. The JVM then interprets the byte code and runs the underlying machine specific code. Thus, Java code needs not to be changed to run on different machines. |
It doesn't work on every operating system since libraries are different on different systems. |
| It can run on any OS. Java code is platform independent. No platform specific code is required. Size of int, long remains same on all platforms. | C++ programs are compiled differently on each platform, so the compiled file canât run on all operating systems without recompilation |
| It is portable. Being platform independent, a java code can be transferred as it is on any machine without any plaform specific modification. A Java code written in Windows machine can run in Unix machine in same fashion without any modification. | It is portable to a limited extend. |
| It is an interpreted language. | It is a compiled language. |
| It supports single inheritance only. Multiple inheritance can be achieved using interfaces (partial only). A class can extend only a single class, however an interface can extend multiple inheritance. Multiple inheritance can lead to ambigous results. As virtual keyword is not supported in Java, multiple inhertance is not supported. |
It supports single and multiple Inheritance. Using the virtual keyword, ambigous reference can be resolved. |
| Java provides limited support to pointers. Pointers being a complex functionality, Java refrains from using them. Java provides concept of reference to point to objects or precisely their addresses. | C++ supports pointer operations. Developers can perform complex operations, can write optimized memory based code using pointers. But it is quite complex and requires strong programming skills to master them. |
| Java supports thread operations. Java has by default support for multithreading. It allows concurrent programming to improve efficiency and to reduce time taken | It doesn't support threads by design. It can be done by using third party threading libraries. |
| Java doesn't support global scope. Java is a strict object oriented language and global scope is not available. Using packages, it supports across package scope though. | C++ supports global scope as well as namespace scope. |
| Java doesn't have the goto keyword. But same functionality is achivable using label. A break/continue statement can jump to a labelled statement location. | It supports the goto keyword. Using the goto keyword, we can jump to any labelled location. |
| It performs object management automatically using garbage collector. Garbage Collector service automatically detects and frees up the space. | It performs object management manually with the help of "new" and "delete". Developers have to take measures to ensure memory is properly allocated/deallocated to prevent memory leaks. |
Conclusion
Java is independent of the operating system, which allows it to operate on any OS through the JVM. Additionally, it offers automatic memory management and built-in multithreading for safety and ease of use. It does not include complex features like pointers, which increases the security and maintainability of the code.
On the other hand, the C++ provides greater flexibility with the use of pointers and manual memory management. This, in turn, increases the level of complexity. For this and other reasons, Java is the most suitable option when it comes to companies that want to develop secure, dependable, and portable software.